Index tuning persists the recommendations that it produces in a set of tables located under the intelligentperformance schema in the azure_sys database.
However, none of those two methods reveal the text of the queries for which the recommendations were produced. This behavior is intentional, because the texts of the queries might contain sensitive information. Seeing the text of those statements should only be allowed to subjects with authorization to access the database. But it shouldn't be allowed to subjects who are only granted access to the instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server, as an Azure resource.
Hence, if you need to read the text of the queries, you need to be granted permissions to connect to the database engine, so that you can execute queries to retrieve that information from two views available inside the intelligent performance of the azure_sys database.
Using the Azure portal:
Select your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
In the resource menu, under Intelligent Performance, select Index tuning.
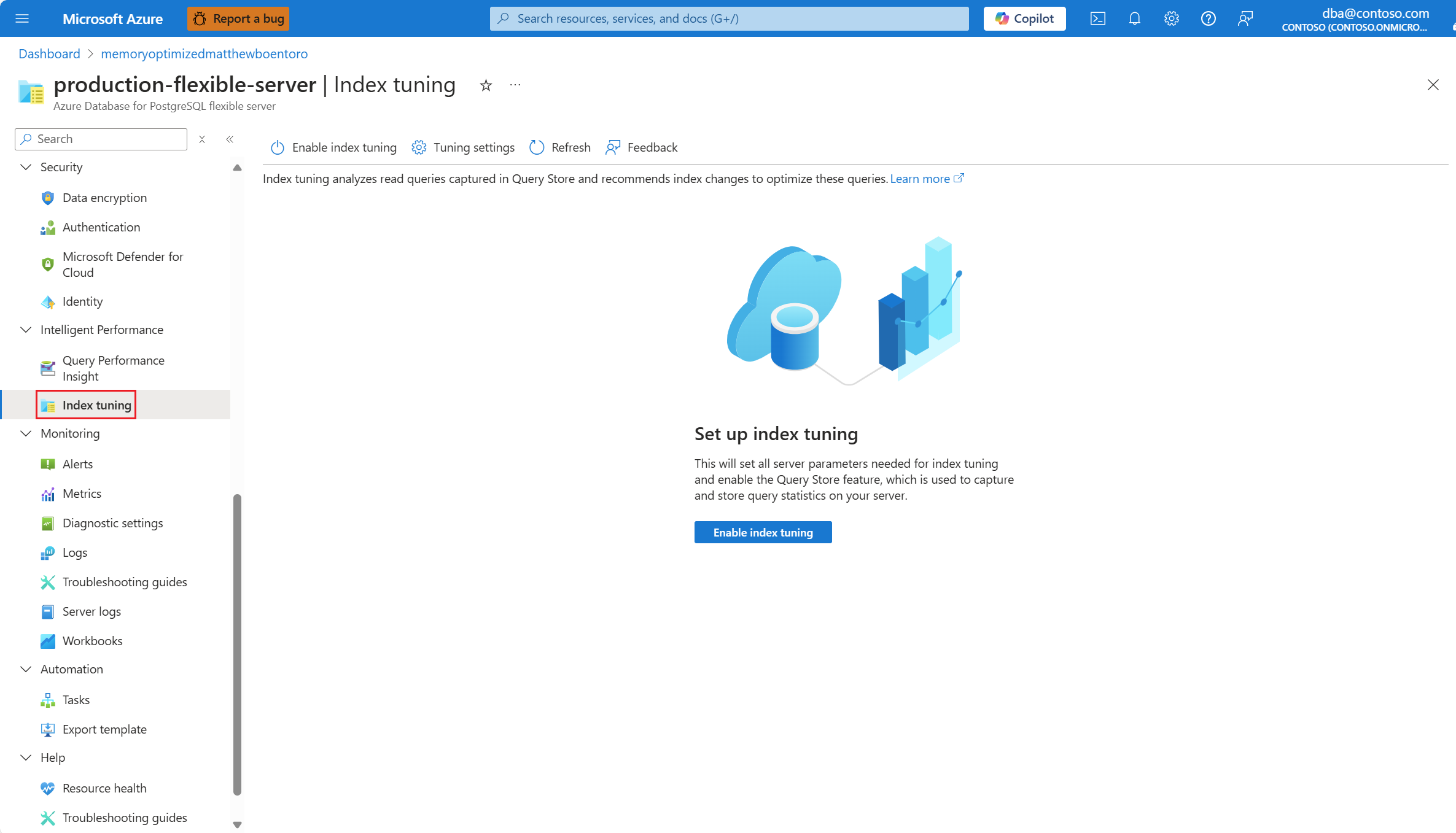
If the feature is enabled but no recommendations are produced yet, the screen looks like this:
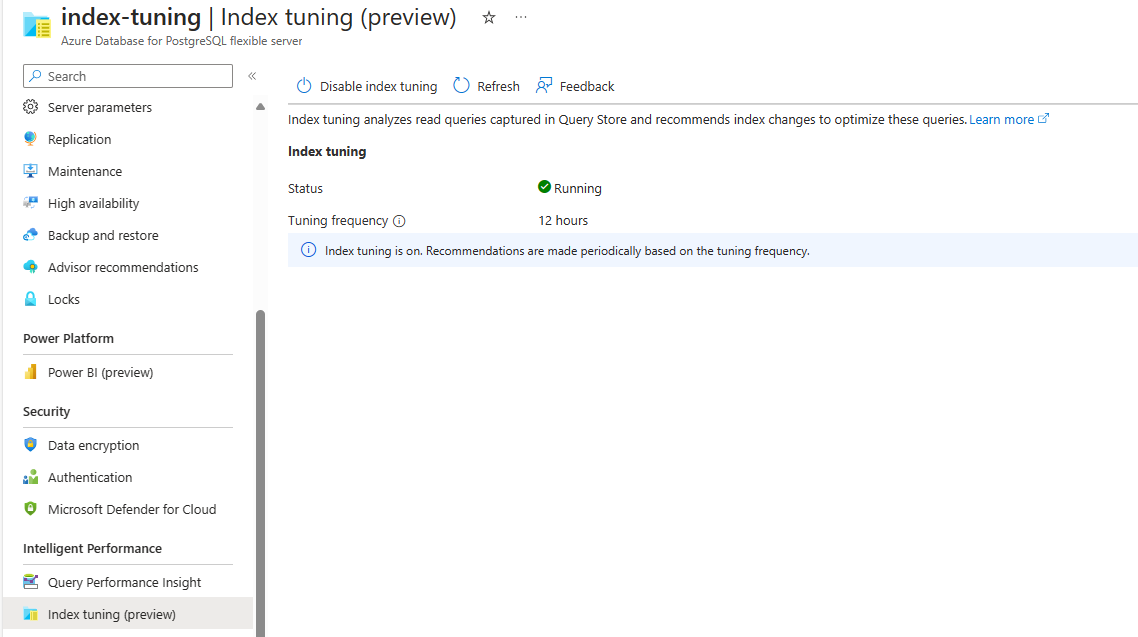
If the feature is disabled and it never produced recommendations in the past, the screen looks like this:
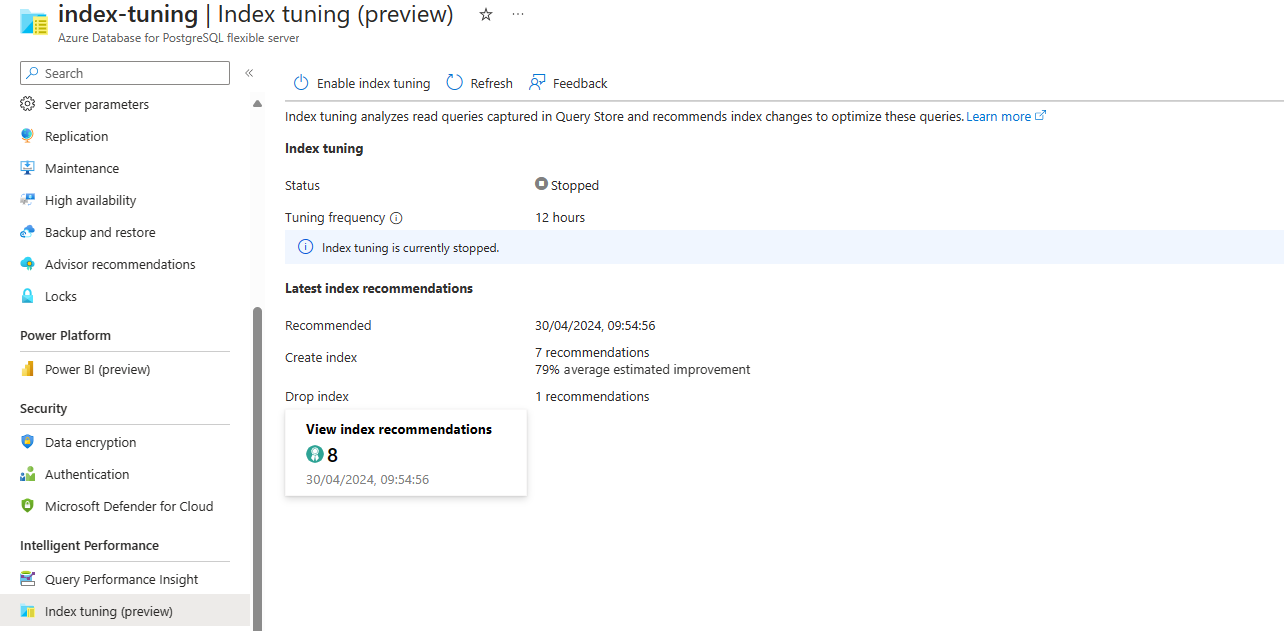
If the feature is disabled but it was enabled before and produced recommendations, the screen looks like this:
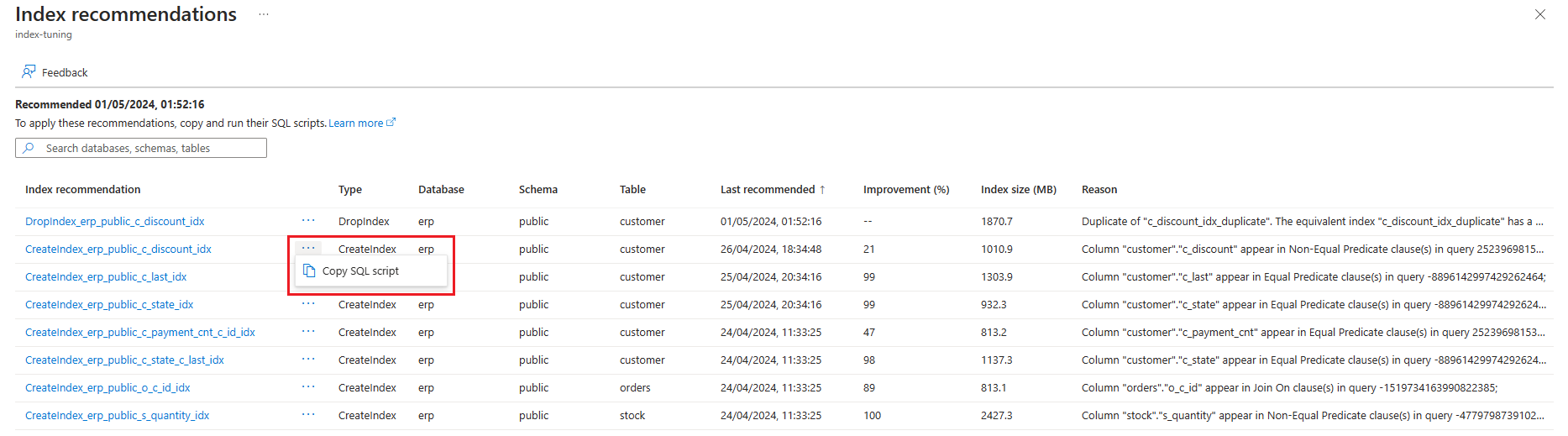
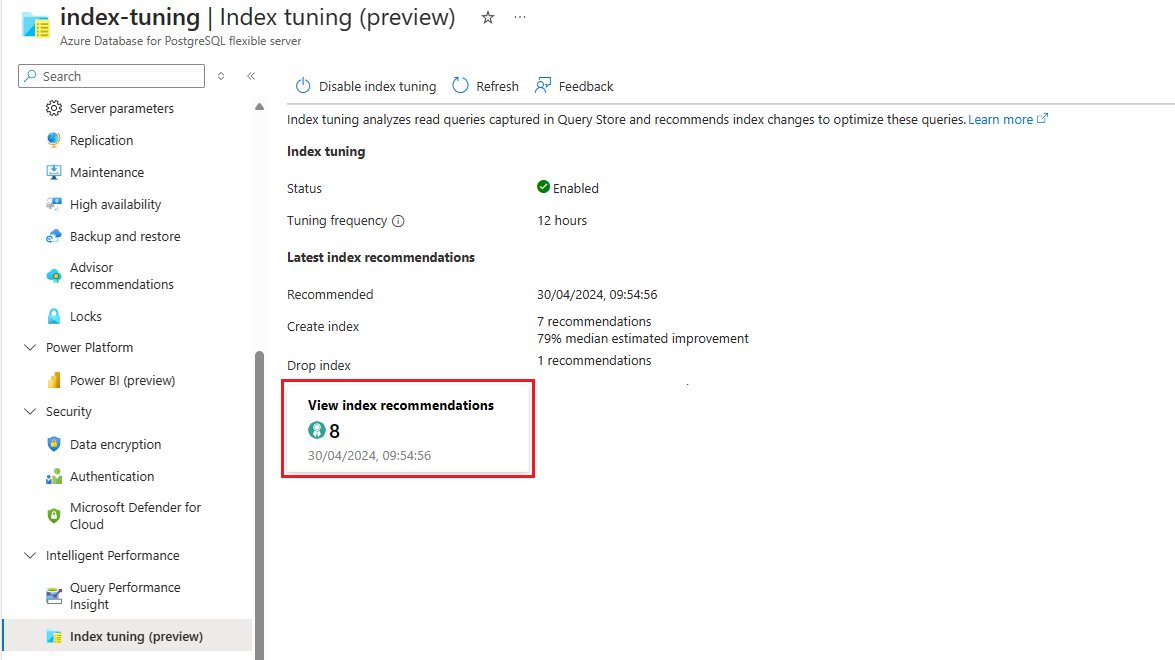
If there are recommendations available, select on the View index recommendations summarization to access to the full list:
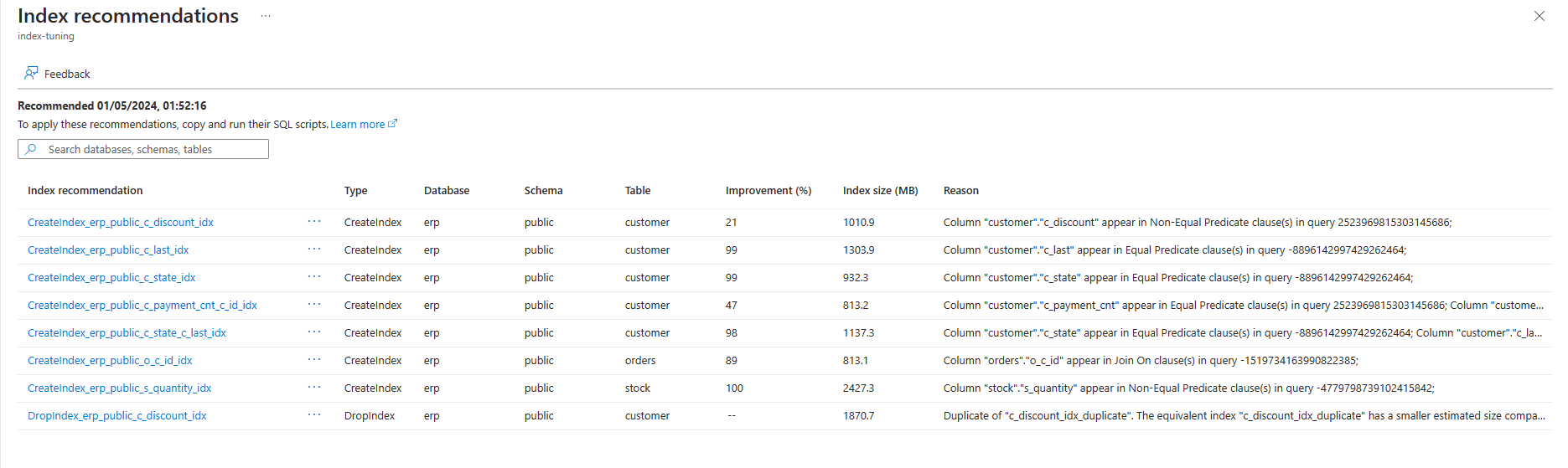
The list shows all available recommendations with some details for each of them. By default, the list is sorted by Last recommended in descending order, showing the most recent recommendations at the top. However, you can sort by any other column, and can use the filtering box to reduce the list of items shown. Filtered items are those whose database, schema, or table names contain the text provided:
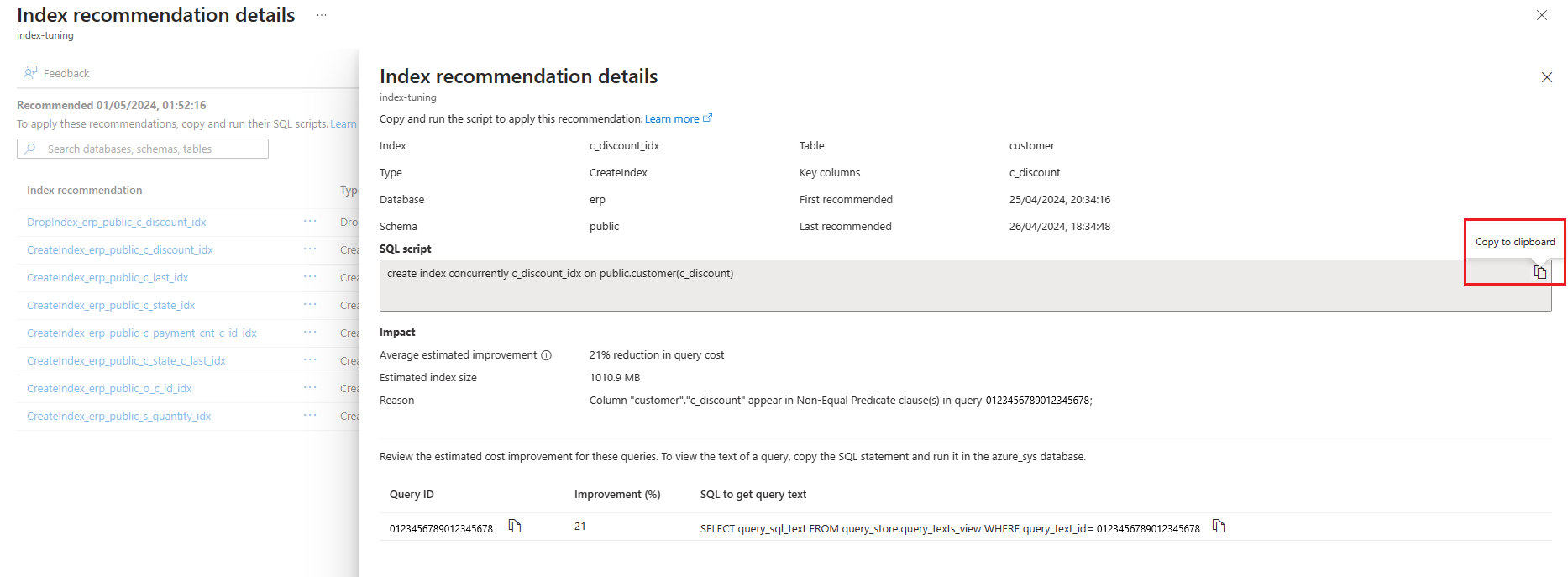
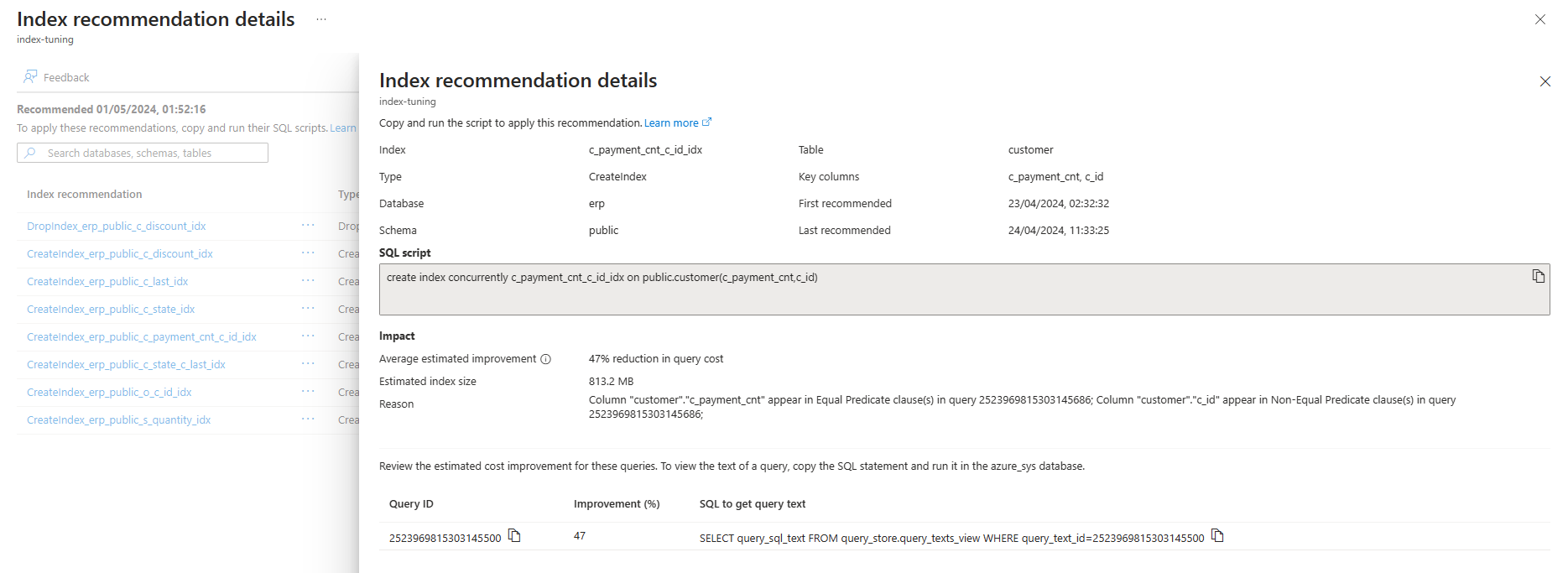
To see further information about any specific recommendation, select on the name of that recommendation, and the Index recommendation details pane opens on the right side of the screen to surface all available details about the recommendation:
You can list index tuning recommendations produced by index tuning in an existing server via the az postgres flexible-server index-tuning list-recommendations command.
To list all CREATE INDEX recommendations, use this command:
az postgres flexible-server index-tuning list-recommendations --resource-group <resource_group> --server-name <server> --recommendation-type createindex
The command returns all information about the CREATE INDEX recommendations produced by index tuning, showing something similar to the following output:
[
{
"analyzedWorkload": {
"endTime": "2025-02-26T14:40:18.788628+00:00",
"queryCount": 18,
"startTime": "2025-02-26T13:40:18.788628+00:00"
},
"details": {
"databaseName": "<database>",
"includedColumns": "",
"indexColumns": "\"<table>\".\"<column>\"",
"indexName": "<index>",
"indexType": "BTREE",
"schema": "<schema>",
"table": "<table>"
},
"estimatedImpact": [
{
"absoluteValue": 0.3984375,
"dimensionName": "IndexSize",
"queryId": null,
"unit": "MB"
},
{
"absoluteValue": 62.86969111969111,
"dimensionName": "QueryCostImprovement",
"queryId": -555955670159268890,
"unit": "Percentage"
}
],
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/tuningOptions/index/recommendations/<recommendation_id>",
"implementationDetails": {
"method": "SQL",
"script": "create index concurrently <index> on <schema>.<table>(<column>)"
},
"improvedQueryIds": [
-555955670159268890
],
"initialRecommendedTime": "2025-02-26T14:40:19.707617+00:00",
"kind": "",
"lastRecommendedTime": "2025-02-26T14:40:19.707617+00:00",
"name": "CreateIndex_<database>_<schema>_<column>_idx",
"recommendationReason": "Column \"<table>\".\"<column>\" appear in Equal Predicate clause(s) in query -555955670159268890;",
"recommendationType": "CreateIndex",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"systemData": null,
"timesRecommended": 1,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/tuningOptions/index"
},
{
.
.
.
}
]
To list all DROP INDEX recommendations, use this command:
az postgres flexible-server index-tuning list-recommendations --resource-group <resource_group> --server-name <server> --recommendation-type dropindex
The command returns all information about the DROP INDEX recommendations produced by index tuning, showing something similar to the following output:
Using any PostgreSQL client tool of your preference:
Connect to the azure_sys database available in your server with any role that has permission to connect to the instance. Members of the public role can read from these views.
Execute queries on the sessions view to retrieve the details about recommendation sessions.
Execute queries on the recommendations view to retrieve the recommendations produced by index tuning for CREATE INDEX and DROP INDEX.
Views
Views in the azure_sys database provide a convenient way to access and retrieve index recommendations generated by index tuning. Specifically, the createindexrecommendations and dropindexrecommendations views contain detailed information about CREATE INDEX and DROP INDEX recommendations, respectively. These views expose data such as the session ID, database name, advisor type, start and stop times of the tuning session, recommendation ID, recommendation type, reason for the recommendation, and other relevant details. Users can query these views, to easily access and analyze the index recommendations produced by index tuning.
The sessions view exposes all the details for all index tuning sessions.
| column name |
data type |
Description |
| session_id |
uuid |
Globally Unique Identifier assigned to every new tuning session that is initiated. |
| database_name |
varchar(64) |
Name of the database in whose context the index tuning session was executed. |
| session_type |
intelligentperformance.recommendation_type |
Indicates the types of recommendations this index tuning session could produce. Possible values are: CreateIndex, DropIndex. Sessions of CreateIndex type can produce recommendations of CreateIndex type. Sessions of DropIndex type can produce recommendations of DropIndex or ReIndex types. |
| run_type |
intelligentperformance.recommendation_run_type |
Indicates the way in which this session was initiated. Possible values are: Scheduled. Sessions automatically executed as per the value of index_tuning.analysis_interval, are assigned a run type of Scheduled. |
| state |
intelligentperformance.recommendation_state |
Indicates the current state of the session. Possible values are: Error, Success, InProgress. Sessions whose execution failed are set as Error. Sessions that completed their execution correctly, whether or not they generated recommendations, are set as Success. Sessions which are still executing are set as InProgress. |
| start_time |
timestamp without timezone |
Timestamp at which the tuning session that produced this recommendation was started. |
| stop_time |
timestamp without timezone |
Timestamp at which the tuning session that produced this recommendation was started. NULL if the session is in progress or was aborted due to some failure. |
| recommendations_count |
integer |
Total number of recommendations produced in this session. |
The recommendations view exposes all the details for all recommendations generated on any tuning session whose data is still available in the underlying tables.
| column name |
data type |
Description |
| recommendation_id |
integer |
Number that uniquely identifies a recommendation in the whole server. |
| last_known_session_id |
uuid |
Every index tuning session is assigned a Globally Unique Identifier. The value in this column represents that of the session which most recently produced this recommendation. |
| database_name |
varchar(64) |
Name of the database in whose context was produced the recommendation. |
| recommendation_type |
intelligentperformance.recommendation_type |
Indicates the type of the recommendation produced. Possible values are: CreateIndex, DropIndex, ReIndex. |
| initial_recommended_time |
timestamp without timezone |
Timestamp at which the tuning session that produced this recommendation was started. |
| last_recommended_time |
timestamp without timezone |
Timestamp at which the tuning session that produced this recommendation was started. |
| times_recommended |
integer |
Timestamp at which the tuning session that produced this recommendation was started. |
| reason |
text |
Reason justifying why this recommendation was produced. |
| recommendation_context |
json |
Contains the list of query identifiers for the queries affected by the recommendation, the type of index being recommended, the name of the schema and the name of the table on which the index is being recommended, the index columns, the index name, and the estimated size in bytes of the recommended index. |
Reasons for create index recommendations
When index tuning recommends the creation of an index, it does add at least one of the following reasons:
| Reason |
Column <column> appear in Join On clause(s) in query <queryId> |
Column <column> appear in Equal Predicate clause(s) in query <queryId> |
Column <column> appear in Non-Equal Predicate clause(s) in query <queryId> |
Column <column> appear in Group By clause(s) in query <queryId> |
Column <column> appear in Order By clause(s) in query <queryId> |
Reasons for drop index recommendations
When index tuning identifies any indexes which are marked as invalid, it proposes to drop it with the following reason:
The index is invalid and the recommended recovery method is to reindex.
To learn more about why and when indexes are marked as invalid, refer to the REINDEX in PostgreSQL official documentation.
Reasons for drop index recommendations
When index tuning detects an index which is unused for, at least, the number of days set in index_tuning.unused_min_period, it proposes to drop it with the following reason:
The index is unused in the past <days_unused> days.
When index tuning detects duplicate indexes, one of the duplicates survives, and it proposes to drop the remaining. The reason provided always has the following starting text:
Duplicate of <surviving_duplicate>.
Followed by another text which explains the reason why each of the duplicates has been chosen for drop:
| Reason |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" is a Primary key, while "<droppable_duplicate>" is not. |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" is a unique index, while "<droppable_duplicate>" is not. |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" is a constraint, while "<droppable_duplicate>" is not. |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" is a valid index, while "<droppable_duplicate>" is not. |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" has been chosen as replica identity, while "<droppable_duplicate>" is not. |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" was used to cluster the table, while "<droppable_duplicate>" was not. |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" has a smaller estimated size compared to "<droppable_duplicate>". |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" has more tuples compared to "<droppable_duplicate>". |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" has more index scans compared to "<droppable_duplicate>". |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" has been fetched more times compared to "<droppable_duplicate>". |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" has been read more times compared to "<droppable_duplicate>". |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" has a shorter length compared to "<droppable_duplicate>". |
The equivalent index "<surviving_duplicate>" has a smaller oid compared to "<droppable_duplicate>". |
If the index not only is removable due to duplication, but also is unused for, at least, the number of days set in index_tuning.unused_min_period, the following text is appended to the reason:
Also, the index is unused in the past <days_unused> days.
Index recommendations contain the SQL statement that you can execute to implement the recommendation.
The following section demonstrates how this statement can be obtained for a particular recommendation.
Once you have the statement, you can use any PostgreSQL client of your preference to connect to your server and apply the recommendation.