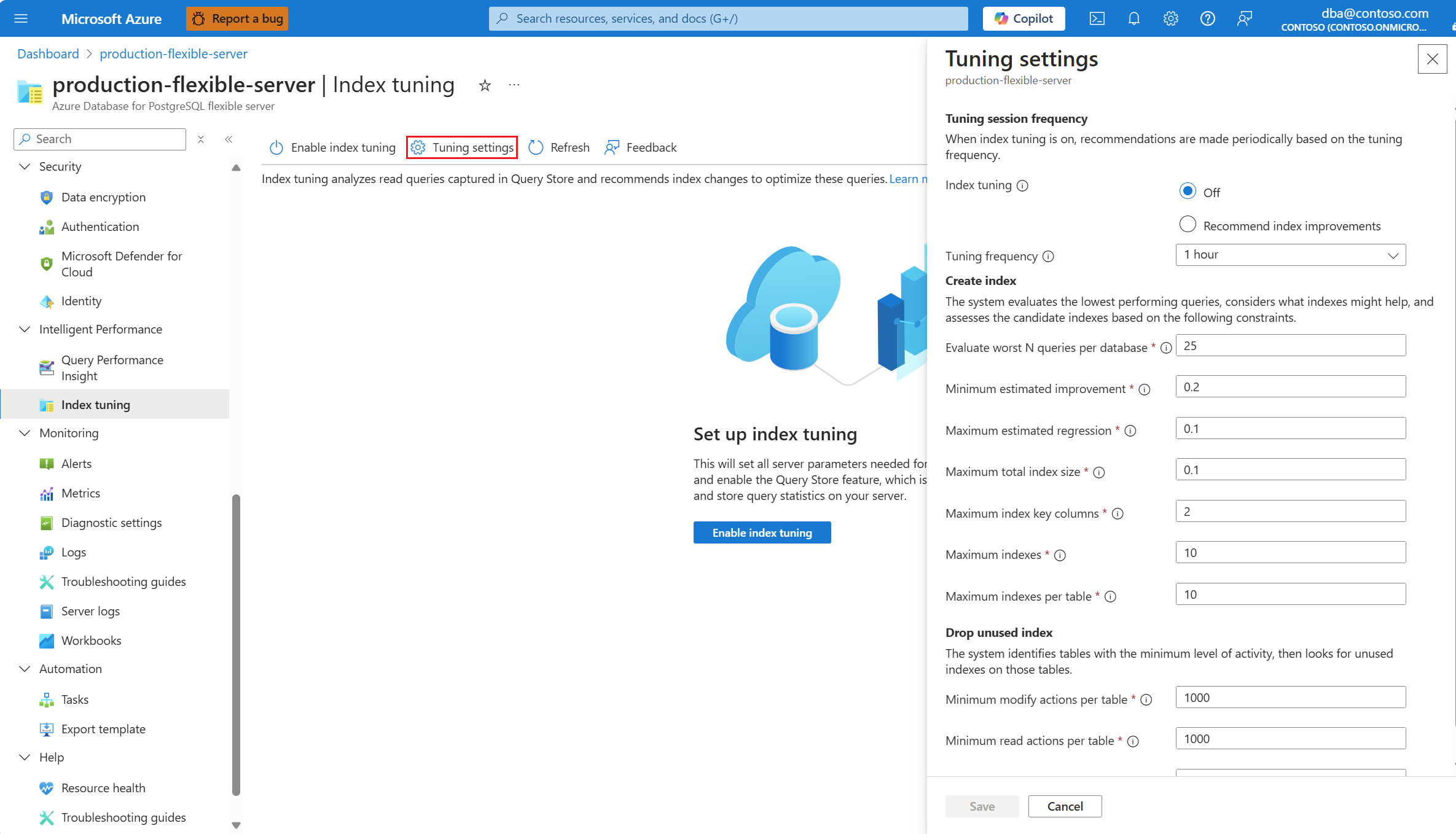
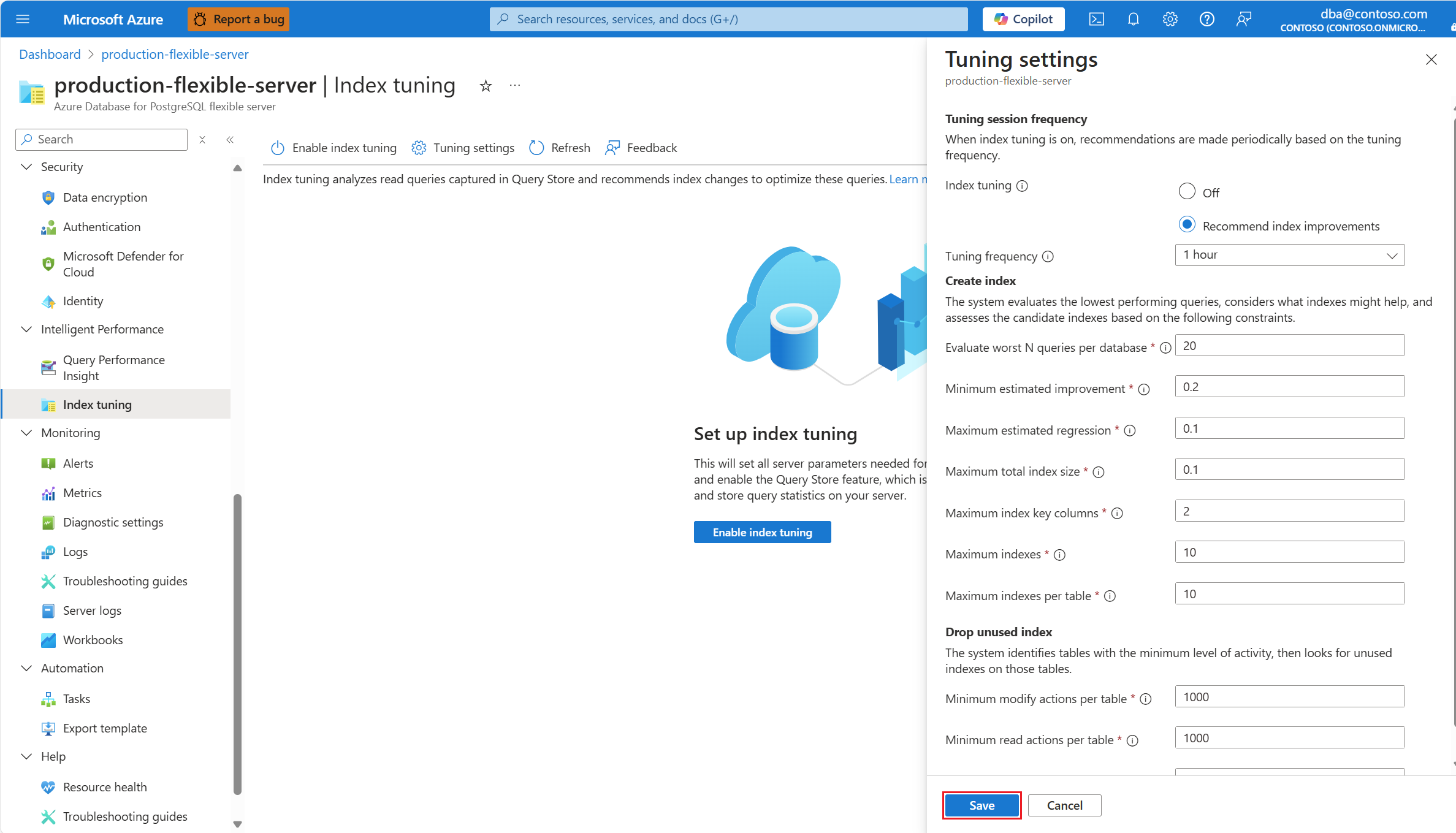
You can show the value of a single index tuning setting in an existing server via the az postgres flexible-server index-tuning show-settings command.
For example, to show the value of the index tuning setting called analyze_interval, use this command:
az postgres flexible-server index-tuning show-settings --resource-group <resource_group> --server-name <server> --name analyze_interval
The command returns all information about the server parameter corresponding to that setting of index tuning, and the output is similar to the following:
{
"allowedValues": "60-10080",
"dataType": "Integer",
"defaultValue": "720",
"description": "Sets the frequency at which each index optimization session is triggered when index_tuning.mode is set to 'REPORT'.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.analysis_interval",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.analysis_interval",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "user-override",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": "minutes",
"value": "720"
}
Also, you can show the list of all index tuning settings in an existing server via the az postgres flexible-server index-tuning list-settings command.
To list all index tuning settings, use this command:
az postgres flexible-server index-tuning list-settings --resource-group <resource_group> --server-name <server>
The command returns all server parameters that control the different settings of index tuning, and the output is similar to the following:
[
{
"allowedValues": "60-10080",
"dataType": "Integer",
"defaultValue": "720",
"description": "Sets the frequency at which each index optimization session is triggered when index_tuning.mode is set to 'REPORT'.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.analysis_interval",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.analysis_interval",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "user-override",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": "minutes",
"value": "720"
},
{
"allowedValues": "1-10",
"dataType": "Integer",
"defaultValue": "2",
"description": "Maximum number of columns that can be part of the index key for any recommended index.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.max_columns_per_index",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.max_columns_per_index",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": null,
"value": "2"
},
{
"allowedValues": "1-25",
"dataType": "Integer",
"defaultValue": "10",
"description": "Maximum number of indexes that can be recommended for each database during one optimization session.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.max_index_count",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.max_index_count",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": null,
"value": "10"
},
{
"allowedValues": "1-25",
"dataType": "Integer",
"defaultValue": "10",
"description": "Maximum number of indexes that can be recommended for each table.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.max_indexes_per_table",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.max_indexes_per_table",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": null,
"value": "10"
},
{
"allowedValues": "5-100",
"dataType": "Integer",
"defaultValue": "25",
"description": "Number of slowest queries per database for which indexes can be recommended.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.max_queries_per_database",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.max_queries_per_database",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": null,
"value": "25"
},
{
"allowedValues": "0.05-0.2",
"dataType": "Numeric",
"defaultValue": "0.1",
"description": "Acceptable regression introduced by a recommended index on any of the queries analyzed during one optimization session.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.max_regression_factor",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.max_regression_factor",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": "percentage",
"value": "0.1"
},
{
"allowedValues": "0-1.0",
"dataType": "Numeric",
"defaultValue": "0.1",
"description": "Maximum total size, in percentage of total disk space, that all recommended indexes for any given database can use.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.max_total_size_factor",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.max_total_size_factor",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": "percentage",
"value": "0.1"
},
{
"allowedValues": "0-20.0",
"dataType": "Numeric",
"defaultValue": "0.2",
"description": "Cost improvement that a recommended index must provide to at least one of the queries analyzed during one optimization session.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.min_improvement_factor",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.min_improvement_factor",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": "percentage",
"value": "0.2"
},
{
"allowedValues": "off,report",
"dataType": "Enumeration",
"defaultValue": "off",
"description": "Configures index optimization as disabled ('OFF') or enabled to only emit recommendation. Requires Query Store to be enabled by setting pg_qs.query_capture_mode to 'TOP' or 'ALL'.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.mode",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.mode",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "user-override",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": null,
"value": "off"
},
{
"allowedValues": "0-9999999",
"dataType": "Integer",
"defaultValue": "1000",
"description": "Minimum number of daily average DML operations affecting the table, so that their unused indexes are considered for dropping.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.unused_dml_per_table",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.unused_dml_per_table",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": null,
"value": "1000"
},
{
"allowedValues": "30-720",
"dataType": "Integer",
"defaultValue": "35",
"description": "Minimum number of days the index has not been used, based on system statistics, so that it is considered for dropping.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.unused_min_period",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.unused_min_period",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": "days",
"value": "35"
},
{
"allowedValues": "0-9999999",
"dataType": "Integer",
"defaultValue": "1000",
"description": "Minimum number of daily average read operations affecting the table, so that their unused indexes are considered for dropping.",
"documentationLink": "https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2274149",
"id": "/subscriptions/<subscription_id>/resourceGroups/<resource_group>/providers/Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/<server>/configurations/index_tuning.unused_reads_per_table",
"isConfigPendingRestart": false,
"isDynamicConfig": true,
"isReadOnly": false,
"name": "index_tuning.unused_reads_per_table",
"resourceGroup": "<resource_group>",
"source": "system-default",
"systemData": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforPostgreSQL/flexibleServers/configurations",
"unit": null,
"value": "1000"
}
]
 Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server