Manage multiple machines with Azure Update Manager
Applies to: ✔️ Windows VMs ✔️ Linux VMs ✔️ On-premises environment ✔️ Azure Arc-enabled servers.
This article describes the various features that Azure Update Manager offers to manage the system updates on your machines. By using the Update Manager, you can:
- Quickly assess the status of available operating system updates.
- Deploy updates.
- Set up a recurring update deployment schedule.
- Get insights on the number of machines managed.
- Obtain information on how they're managed and other relevant details.
Instead of performing these actions from a selected Azure VM or Azure Arc-enabled server, you can manage all your machines in the Azure subscription.
View update Manager status
Sign in to the Azure portal.
To view update assessment across all machines, including Azure Arc-enabled servers navigate to Azure Update Manager.
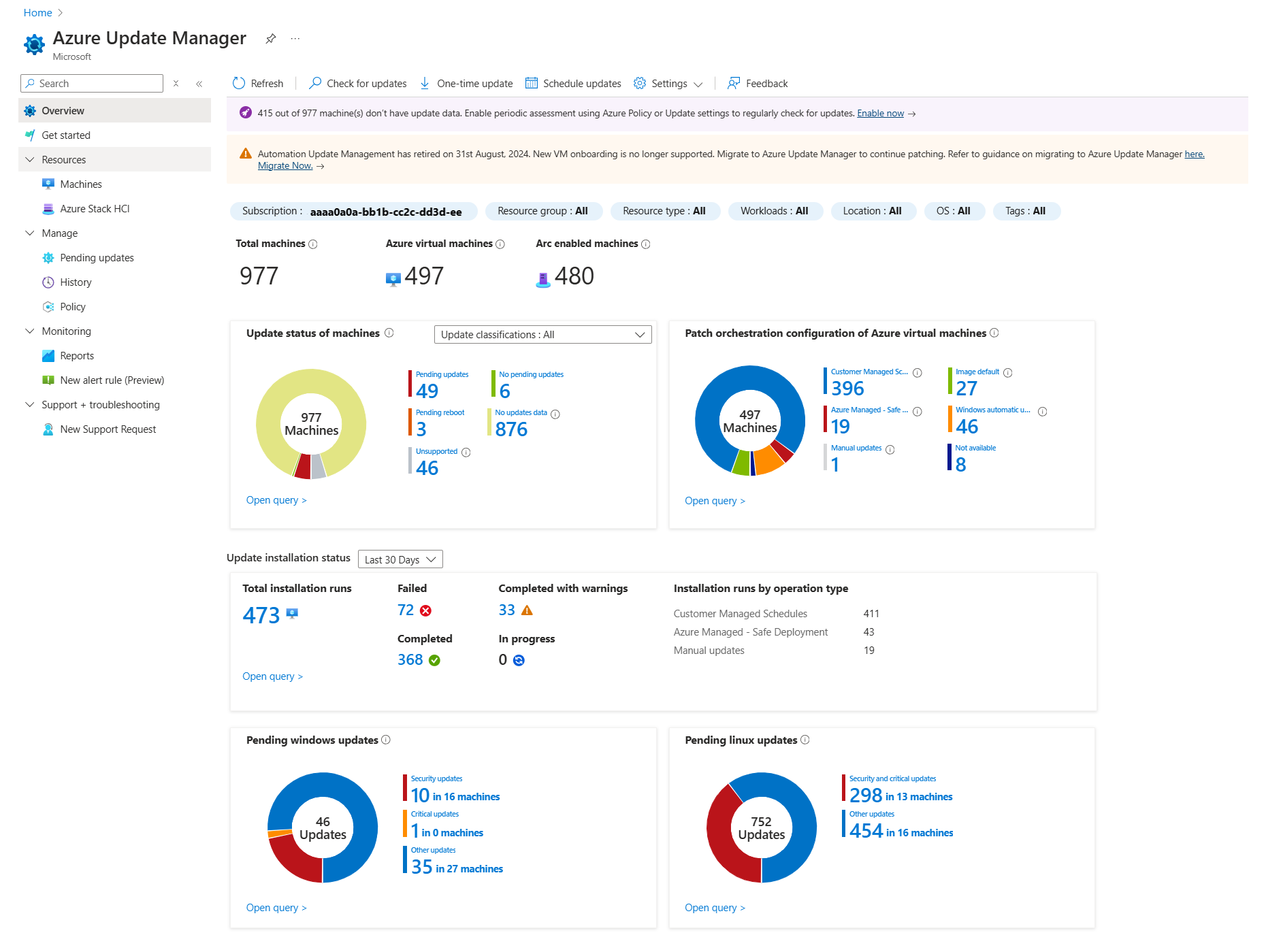
On the Overview page, the summary tiles show the following status:
Filters: Use filters to focus on a subset of your resources. The selectors above the tiles return Subscription, Resource group, Resource type (Azure VMs and Azure Arc-enabled servers), Location, and OS type (Windows or Linux) based on the Azure role-based access rights you've been granted. You can combine filters to scope to a specific resource.
Update status of machines: Shows the update status information for assessed machines that had applicable or needed updates. You can filter the results based on classification types. By default, all classifications are selected. According to the classification selection, the tile is updated.
The graph provides a snapshot for all your machines in your subscription, regardless of whether you've used Update Manager for that machine. This assessment data comes from Azure Resource Graph, and it stores the most recent assessment data for seven days.
From the assessment data available, machines are classified into the following categories:
- No updates available: No updates are pending for these machines and these machines are up to date.
- Updates available: Updates are pending for these machines and these machines aren't up to date.
- Reboot required: Pending a reboot for the updates to take effect.
- No updates data: No assessment data is available for these machines.
The following reasons could explain why there's no assessment data:
- No assessment has been done over the last seven days.
- The machine has an unsupported OS.
- The machine is in an unsupported region and you can't perform an assessment.
Patch orchestration configuration of Azure virtual machines: All the Azure machines inventoried in the subscription are summarized by each update orchestration method. Values are:
- Customer Managed Schedules—enables schedule patching on your existing VMs.
- Azure Managed - Safe Deployment—this mode enables automatic VM guest patching for the Azure virtual machine. Subsequent patch installation is orchestrated by Azure.
- Image Default—for Linux machines, it uses the default patching configuration.
- OS orchestrated—the OS automatically updates the machine.
- Manual updates—you control the application of patches to a machine by applying patches manually inside the machine. In this mode, automatic updates are disabled for Windows OS.
For more information about each orchestration method see, automatic VM guest patching for Azure VMs.
For more information about each orchestration method, see Automatic VM guest patching for Azure VMs.
- Update installation status: By default, the tile shows the status for the last 30 days. By using the Time picker, you can choose a different range. The values are:
- Failed: One or more updates in the deployment have failed.
- Completed: The deployment ends successfully by the time range selected.
- Completed with warnings: The deployment is completed successfully but had warnings.
- In progress: The deployment is currently running.
- Select Update status of machines or Patch orchestration configuration of Azure virtual machines to go to the Machines page.
- Select Update installation status to go to the History page.
- Pending Windows updates: Status of pending updates for Windows machines in your subscription.
- Pending Linux updates: Status of pending updates for Linux machines in your subscription.
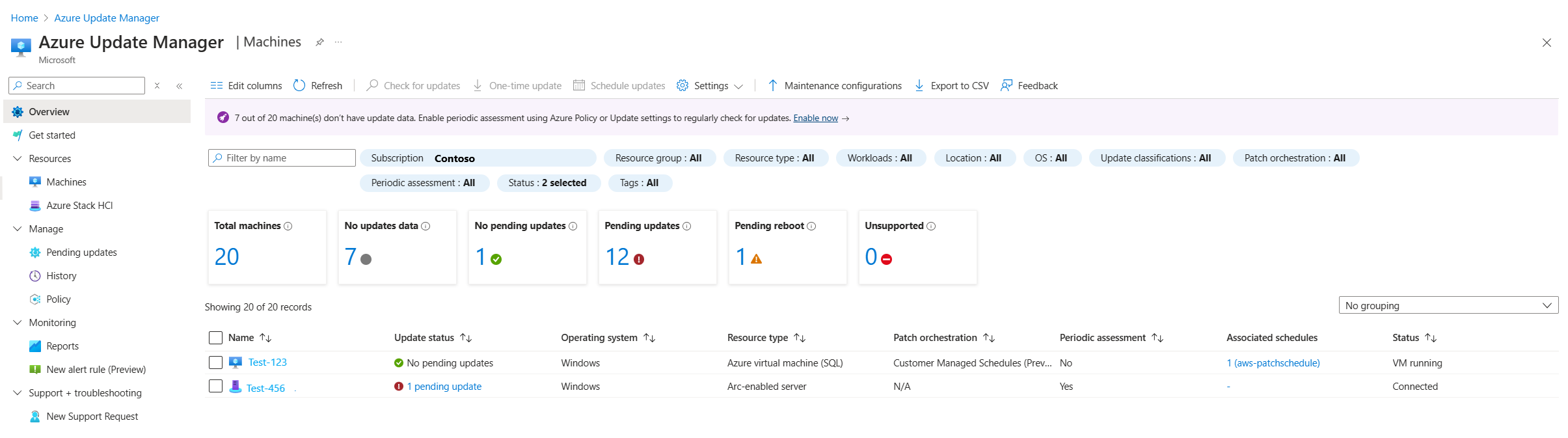
Summary of machine status
Update Manager in Azure enables you to browse information about your Azure VMs and Arc-enabled servers across your Azure subscriptions relevant to Update Manager. The section shows how you can filter information to understand the update status of your machine resources, and for multiple machines, initiate an update assessment, update deployment, and manage their update settings.
In the Azure Update Manager page, select Machines from the left menu.
On the Update Manager page, select Machines from the left menu.
The table lists all the machines in the specified subscription, and for each machine it helps you understand the following details that show up based on the latest assessment:
- Customer Managed Schedules—enables schedule patching on your existing VMs. The new patch orchestration option enables the two VM properties - Patch mode = AutomaticByPlatform and BypassPlatformSafetyChecksOnUserSchedule = TRUE on your behalf after receiving your consent.
- Azure Managed - Safe Deployment—for a group of virtual machines undergoing an update, the Azure platform will orchestrate updates. The VM is set to automatic VM guest patching.(i.e), the patch mode is AutomaticByPlatform.
- Automatic by OS—the machine is automatically updated by the OS.
- Image Default—for Linux machines, its default patching configuration is used.
- Manual—you control the application of patches to a machine by applying patches manually inside the machine. In this mode automatic updates are disabled for Windows OS.
The Patch orchestration column in the machine's patch mode has the following values:
- Customer Managed Schedules (preview): Enables schedule patching on your existing VMs. The new patch orchestration option enables the two VM properties:
Patch mode = AutomaticByPlatformandBypassPlatformSafetyChecksOnUserSchedule = TRUEon your behalf after receiving your consent. - Azure Managed - Safe Deployment: For a group of virtual machines undergoing an update, the Azure platform orchestrates updates. The VM is set to automatic VM guest patching. For example, the patch mode is
AutomaticByPlatform. - Automatic by OS: The machine is automatically updated by the OS.
- Image default: For Linux machines, its default patching configuration is used.
- Manual: You control the application of patches to a machine by applying patches manually inside the machine. In this mode, automatic updates are disabled for Windows OS.
The machine's status: For an Azure VM, it shows its power state. For an Azure Arc-enabled server, it shows if it's connected or not.
Use filters to focus on a subset of your resources. The selectors above the tiles return subscriptions, resource groups, resource types (that is, Azure VMs and Azure Arc-enabled servers), and regions. They're based on the Azure role-based access rights you've been granted. You can combine filters to scope to a specific resource.
The summary tiles at the top of the page summarize the number of machines that have been assessed and their update status.
To manage the machine's update settings, see Manage update configuration settings.
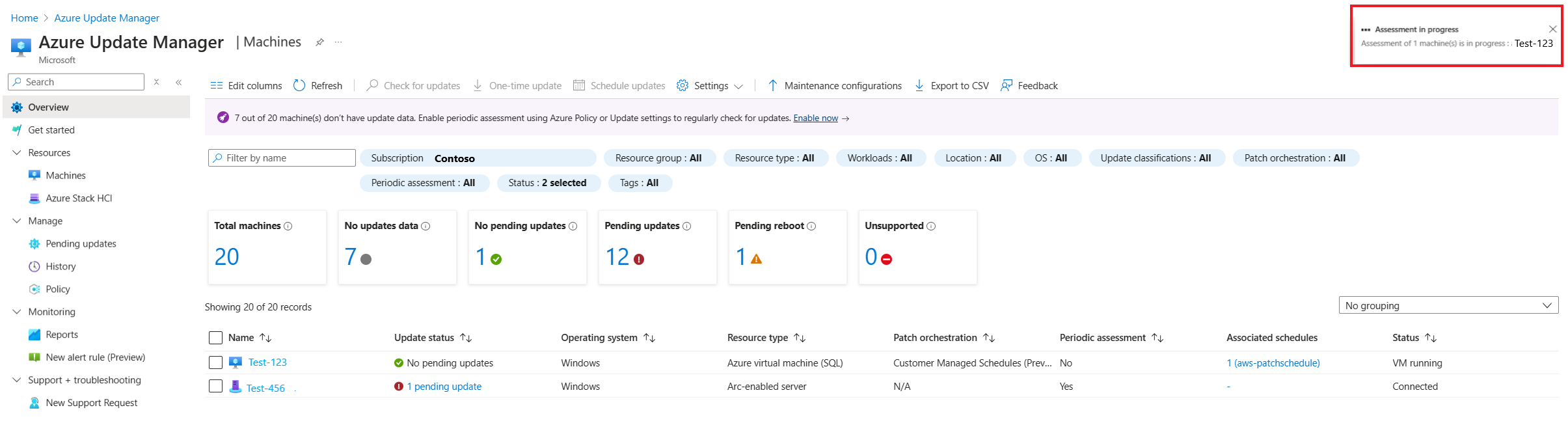
Check for updates
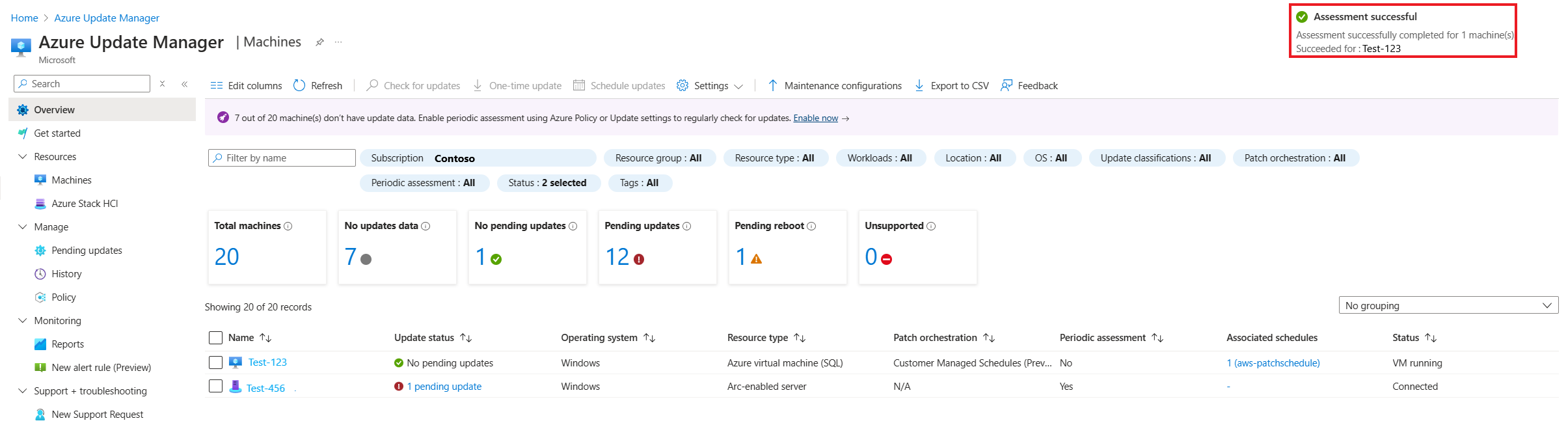
For machines that haven't had a compliance assessment scan for the first time, you can select one or more of them from the list. Then select Check for updates. You receive status messages as the configuration is performed.
Otherwise, a compliance scan begins and the results are forwarded and stored in Azure Resource Graph. This process takes several minutes. When the assessment is finished, a confirmation message appears on the page.
Select a machine from the list to open Update Manager scoped to that machine. Here, you can view its detailed assessment status and update history, configure its patch orchestration options, and begin an update deployment.
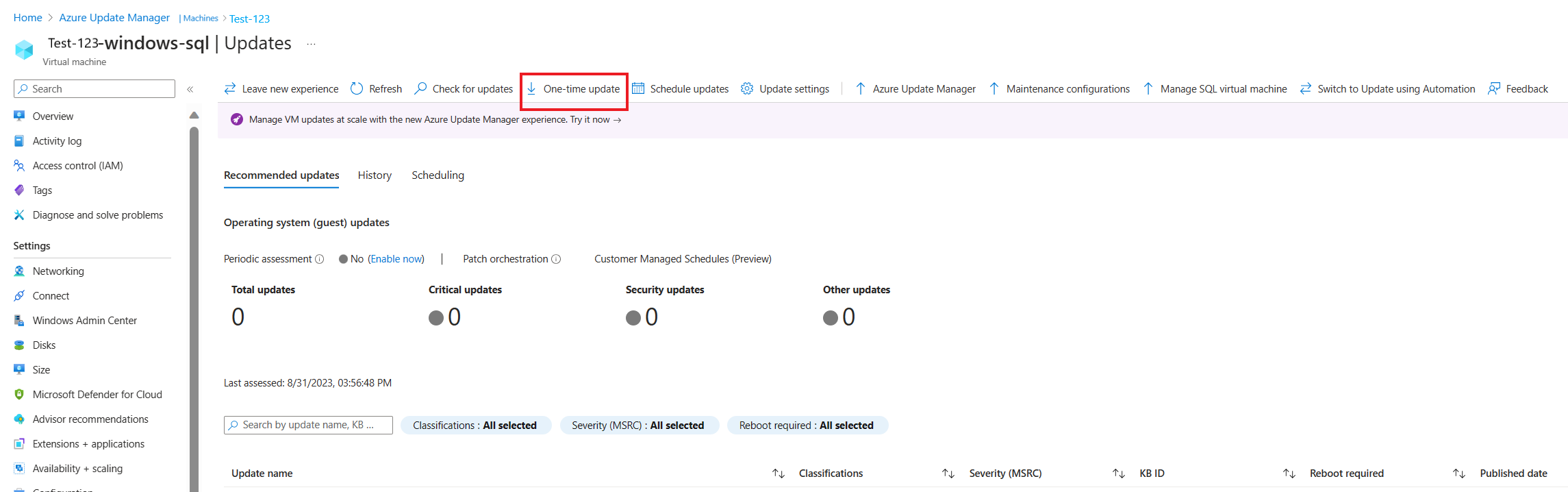
Deploy the updates
For assessed machines that are reporting updates available, select one or more of the machines from the list and begin an update deployment that starts immediately. Select the machine and go to One-time update.
A notification confirms when an activity starts and another tells you when it's finished. After it's successfully finished, the installation operation results are available to view. You can use the Update history tab, when you select the machine from the Machines page. You can also select the History page. You're redirected to this page automatically after you begin the update deployment. You can view the status of the operation at any time from the Azure activity log.
Set up a recurring update deployment
You can create a recurring update deployment for your machines. Select your machine and select Scheduled updates. A Create new maintenance configuration flow opens.
Update deployment history
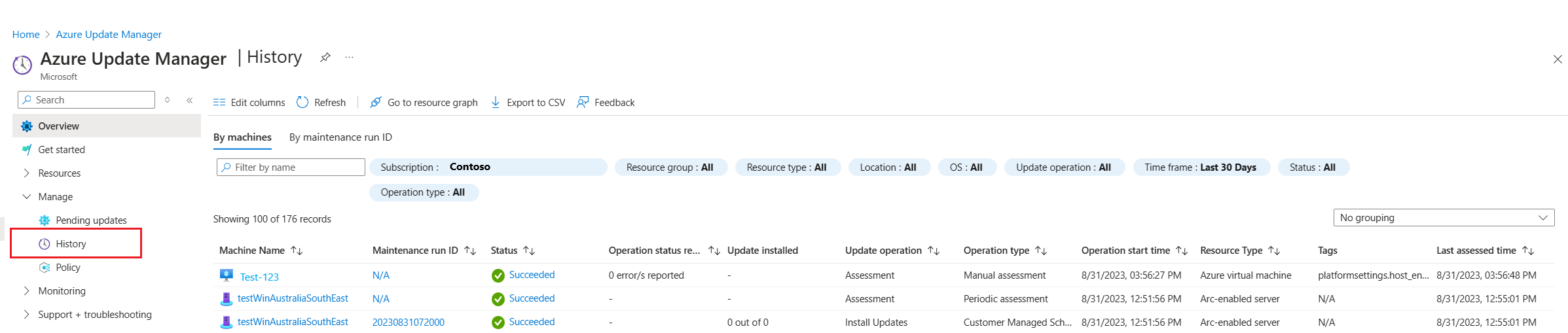
Update Manager enables you to browse information about your Azure VMs and Azure Arc-enabled servers across your Azure subscriptions relevant to Update Manager. You can filter information to understand the update assessment and deployment history for multiple machines. On the Update Manager page, select History from the left menu.
Update deployment history by machines
The update deployment history provides a summarized status of update and assessment actions performed against your Azure VMs and Azure Arc-enabled servers. You can also drill into a specific machine to view update-related details and manage it directly. You can review the detailed update or assessment history for the machine and other related details in the table.
Each record shows:
- Machine Name
- Status
- Update installed
- Update operation
- Operation type
- Operation start time
- Resource Type
- Tags
- Last assessed time
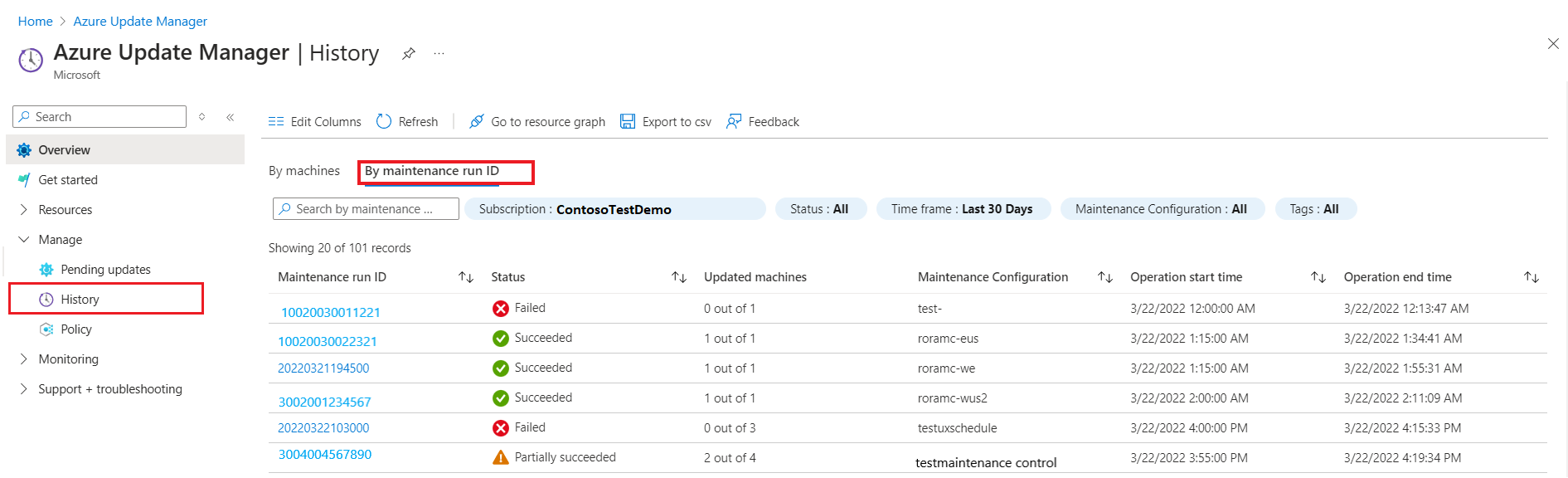
Update deployment history by maintenance run ID
On the History page, select By maintenance run ID to view the history of the maintenance run schedules.
Each record shows:
- Maintenance run ID
- Status
- Updated machines
- Maintenance Configuration
- Operation start time
- Operation end time
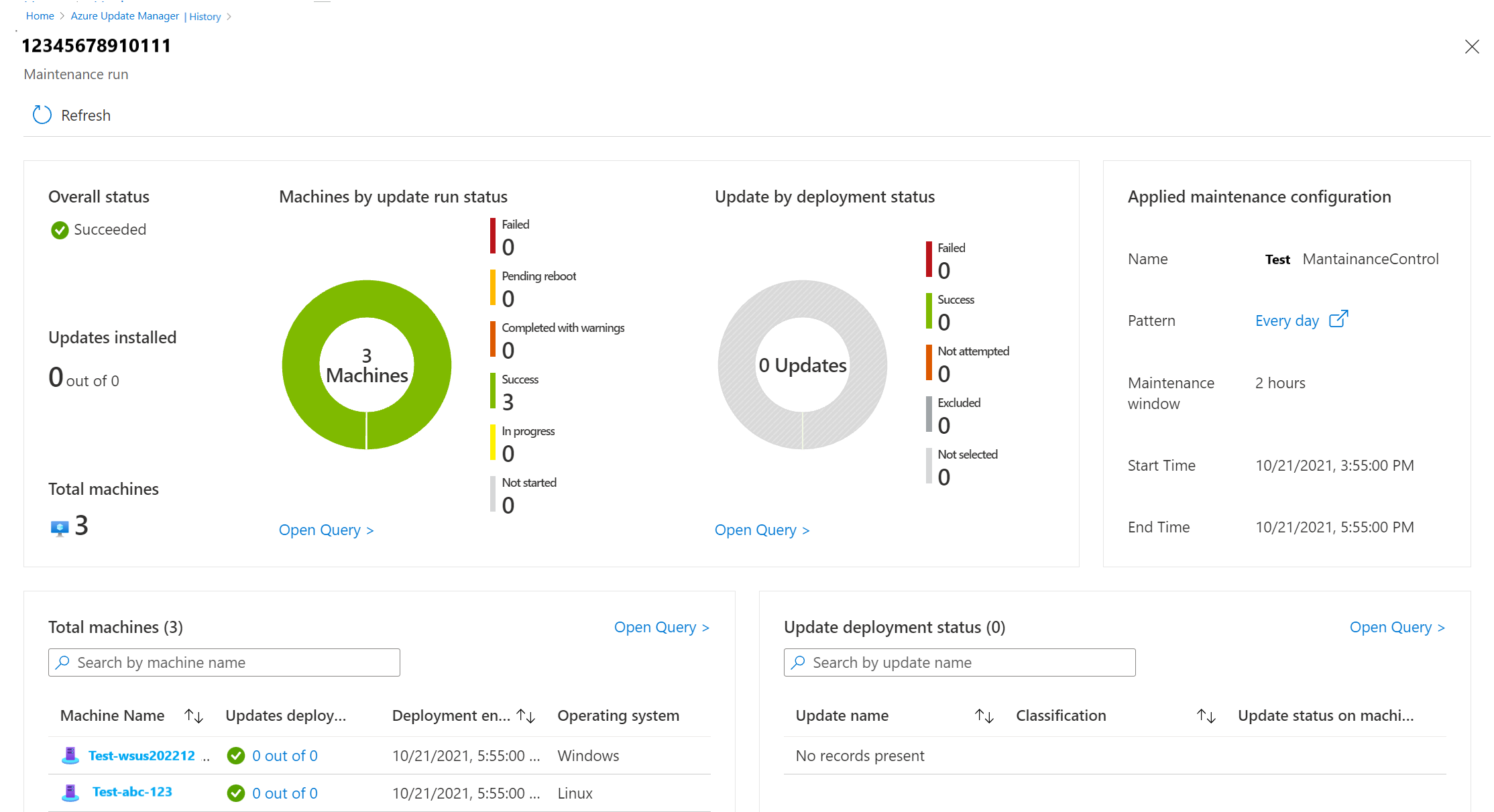
When you select any one maintenance run ID record, you can view an expanded status of the maintenance run. It contains information about machines and updates. It includes the number of machines that were updated and updates installed on them. A pie chart shows the status of each of the machines. At the end of the page, a list view shows both machines and updates that were a part of this maintenance run.
Resource Graph
The update assessment and deployment data are available for querying in Azure Resource Graph. You can apply this data to scenarios that include security compliance, security operations, and troubleshooting. Select Go to resource graph to go to the Azure Resource Graph Explorer. It enables running Resource Graph queries directly in the Azure portal. Resource Graph supports the Azure CLI, Azure PowerShell, Azure SDK for Python, and more. For more information, see First query with Azure Resource Graph Explorer.
When the Resource Graph Explorer opens, it's automatically populated with the same query used to generate the results presented in the table on the History page in Update Manager. Ensure that you review Overview of query logs in Azure Update Manager to learn about the log records and their properties, and the sample queries included.
Next steps
- To set up and manage recurring deployment schedules, see Schedule recurring updates.
- To view update assessment and deployment logs generated by Update Manager, see Query logs.