Configure your Azure AI Search service in the Azure portal
Configuring your new Azure AI Search service involves several tasks to optimize security, access, and performance. This article provides a day-one checklist to help you set up your service in the Azure portal.
After you create a search service, we recommend that you:
Configure role-based access
Portal access is based on role assignments. By default, new search services have at least one service administrator or owner. Service administrators, co-administrators, and owners have permission to create more administrators and assign other roles. They also have access to all portal pages and operations on default search services.
Tip
By default, any administrator or owner can create or delete services. To prevent accidental deletions, consider locking your resources.
Each search service comes with API keys and uses key-based authentication by default. However, we recommend using Microsoft Entra ID and role-based access control (RBAC) for improved security. RBAC eliminates the need to store and pass API keys in plain text.
When you switch from key-based authentication to keyless authentication, service administrators must assign themselves data plane roles for full access to objects and data. These roles include Search Service Contributor, Search Index Data Contributor, and Search Index Data Reader.
To configure role-based access:
Enable roles on your search service. We recommend using both API keys and roles.
Assign data plane roles to replace the functionality lost when you disable API keys. An owner only needs Search Index Data Reader, but developers need more roles.
Role assignments can take several minutes to take effect. Until then, portal pages used for data plane operations display the following message:
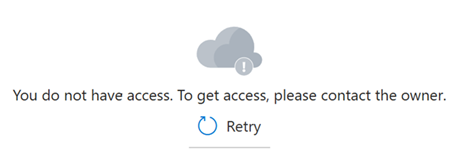
Assign more roles for solution developers and apps.
Configure a managed identity
If you plan to use indexers for automated indexing, applied AI, or integrated vectorization, you should configure your search service to use a managed identity. You can then assign roles on other Azure services that authorize your search service to access data and operations.
For integrated vectorization, your search service identity needs the following roles:
- Storage Blob Data Reader on Azure Storage
- Cognitive Services Data User on an Azure AI multiservice account
Role assignments can take several minutes to take effect.
Before you move on to network security, consider testing all points of connection to validate role assignments. Run either the Import data wizard or the Import and vectorize data wizard to test permissions.
Configure network security
By default, a search service accepts authenticated and authorized requests over public internet connections. You have two options for enhancing network security:
- Configure firewall rules to restrict network access by IP address.
- Configure a private endpoint to only allow traffic from Azure virtual networks. Note that when you turn off the public endpoint, the import wizards won't run.
To learn about inbound and outbound calls in Azure AI Search, see Security in Azure AI Search.
Check capacity and understand billing
By default, a search service is created with one replica and one partition. You can add capacity by adding replicas and partitions, but we recommend waiting until volumes require it. Many customers run production workloads on the minimum configuration.
Semantic ranker increases the cost of running your service. If you don't want to use this feature, you can disable semantic ranker at the service level.
To learn about other features that affect billing, see How you're charged for Azure AI Search.
Enable diagnostic logging
Enable diagnostic logging to track user activity. If you skip this step, you still get activity logs and platform metrics automatically. However, if you want index and query usage information, you should enable diagnostic logging and choose a destination for logged operations. We recommend Log Analytics Workspace for durable storage so that you can run system queries in the Azure portal.
Internally, Microsoft collects telemetry data about your service and the platform. To learn more about data retention, see Retention of metrics.
To learn more about data location and privacy, see Data residency.
Enable semantic ranker
Semantic ranker is free for the first 1,000 requests per month. It's enabled by default on newer search services.
To enable semantic ranker in the portal, select Settings > Semantic ranker from the left pane, and then select the Free plan. For more information, see Enable semantic ranker.
Provide connection information to developers
To connect to Azure AI Search, developers need:
- An endpoint or URL from the Overview page.
- An API key from the Keys page or a role assignment. We recommend Search Service Contributor, Search Index Data Contributor, and Search Index Data Reader.
We recommend portal access for the Import data wizard, the Import and vectorize data wizard, and Search explorer. You must be a contributor or higher to run the wizards.
Related content
For programmatic support for service administration, see the following APIs and modules:
You can also use the management client libraries in the Azure SDKs for .NET, Python, Java, and JavaScript.
There's feature parity across all modalities and languages, except for preview management features. As a general rule, preview management features are released through the Management REST API first.