Administrative units
Administrative units let you subdivide your organization into smaller units and assign specific administrators that can manage only the members of those units. Microsoft Purview role groups allow you to assign admins to specific administrative units. Microsoft Purview solutions that support administrative unit will then restrict visibility and management permissions to the members of the unit.
For example, you could use administrative units to delegate permissions to administrators for each geographic region in a large multi-national organization, or for grouping administrator access by department within your organization. You can create region or department-specific policies or view user activity as a result of those policies and administrative unit assignment. You can also use administrative units as an initial scope for a policy, where the selection of users eligible for the policy depends on membership in administrative units.
If you are using adaptive scopes for compliance policies, see How adaptive scopes work with Microsoft Entra administrative units.
Administrative units support in Microsoft Purview
The following Microsoft Purview compliance solutions support administrative units:
The configuration for administrative units automatically flows down to the following features:
- Alerts: DLP alerts are visible only from users in assigned administrative units
- Activity explorer: Activity events are visible only from users in assigned administrative units
- Adaptive scopes:
- Restricted administrators can select, create, edit, and view adaptive scopes only for users in those administrators' assigned administrative units
- When a restricted administrator configures a policy that's using adaptive scopes, that administrator can only select adaptive scopes that are assigned to their administrative units
- Audit log search access
- Communication compliance:
- Policy lookup and configuration: Restricted administrators can create or manage policies only for users assigned to their administrative units.
- Alerts and policy matches: Restricted administrators can investigate user activities only for users within their assigned administrative units.
- Data lifecycle management and records management:
- Policy lookup: Restricted administrators will see policies only from users within their assigned administrative units
- Disposition review and verification: Restricted administrators are able to add reviewers only from within their assigned administrative units, and see disposition reviews and items disposed only from users within their assigned administrative units
- Insider risk management:
- Policy lookup and configuration: Restricted administrators can create or manage policies only for users assigned to their administrative units.
- User activities: Restricted administrators can start scoring activities or investigate user activities only for users within their assigned administrative units.
- Alerts and cases: Restricted administrators can view and investigate alerts and cases only for users within their assigned administrative units.
Note
Microsoft Defender XDR supports up to 100 administrative units.
To assign a role group member to an administrative unit, admins must be assigned the Role management role. To learn more about Microsoft Purview role groups and roles, see Role groups in Microsoft Purview.
You can assign role group members to administrative units within the following built-in role groups:
- Communication Compliance
- Communication Compliance Admins
- Communication Compliance Analysts
- Communication Compliance Investigators
- Compliance Administrator
- Compliance Data Administrators
- Global Reader
- Information Protection
- Information Protection Admins
- Information Protection Analyst
- Information Protection Investigators
- Information Protection Readers
- Insider Risk Management
- Insider Risk Management Admins
- Insider Risk Management Analysts
- Insider Risk Management Investigators
- Insider Risk Management Session Approvers
- Insider Risk Management Approvers
- Organization Management
- Records Management
- Security Administrator
- Security Operator
- Security Reader
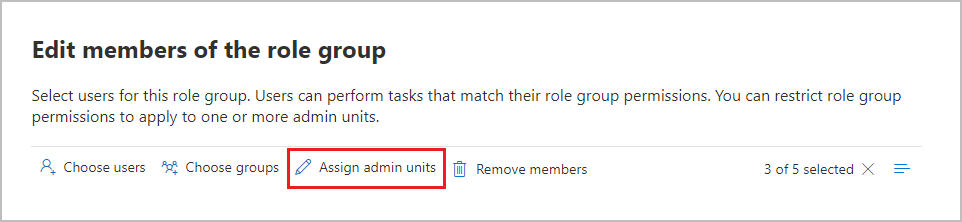
When you assign role groups, you can select individual members or groups, and then select the Assign admin units option to select administrative units that have been defined in Microsoft Entra ID:
Important
Assign admin units is always available when you've created custom role groups. You can assign administrative units for any custom role group.
These administrators, referred to as restricted administrators, can now select one or more of their assigned administrative units to automatically define the initial scope of policies that they create or edit. Only if administrators don't have administrative units assigned (unrestricted administrators), will they be able to assign policies to the entire directory without being required to select individual administrative units.
Important
After you've assigned administrative units to members of the role groups, these restricted administrators will no longer be able to see and edit existing policies. However, there's no operational change to these policies and they remain visible and can be edited by unrestricted administrators.
Restricted administrators will also no longer be able to see historical data using features that support administrative units, such as activity explorer and alerts. They remain visible to unrestricted administrators. Going forward, restricted administrators are able to see this related data for their assigned administrative units only.
Note
In addition to being able to configure and view alerts, users with the Information Protection Analyst and Information Protection Investigator roles can search audit logs using the Search-UnifiedAuditLog cmdlet.
Prerequisites for administrative units
Before configuring administrative units for Microsoft Purview compliance solutions, make sure your organization and users meet the following subscription and licensing requirements:
Microsoft Purview licensing:
- Microsoft 365 E5/A5/G5
- Microsoft 365 E5/A5/G5/F5 Compliance or F5 Security & Compliance
- Microsoft 365 E5/A5/G5/F5 Information Protection & Governance
- Microsoft 365 E5/A5/F5 Insider Risk Management
Configure and use administrative units
Complete the following steps to configure and use administrative units with Microsoft Purview compliance solutions:
Create administrative units to restrict the scope of role permissions in Microsoft Entra ID.
Add users and distribution groups to administrative units.
Important
Members of Dynamic Distribution Groups don't automatically become members of an administrative unit.
If creating a geographic region or department-based administrative units, configure administrative units with dynamic membership rules.
Note
You can't add groups to an administrative unit that uses dynamic membership rules. If needed, create two administrative units, one for users and one for groups.
Use any of the role groups from the Microsoft Purview compliance solutions that support administrative units to assign administrative units to members.
Now, when these restricted administrators create or edit policies that support administrative units, they can select administrative units so that only the users in those administrative units are eligible for the policy:
- Unrestricted administrators don't have to select administrative units as part of the policy configuration. They can keep the default of the entire directory, or select one or more administrative units.
- Restricted administrators must now select one or more administrative units as part of the policy configuration.
Further into the policy configuration, administrators who selected administrative units must then include or exclude (if supported) individual users and groups from the administrative units that they previously selected for the policy.
For information about administrative units that is specific to each supported solution, see the following sections:
- For audit: Scoping access to audit logs using administrative units
- For communication compliance: Consider administrative units if you want to scope user permissions to a region or department
- For data lifecycle management: Support for administrative units
- For DLP: Administrative Unit restricted policies
- For insider risk management: Consider administrative units if you want to scope user permissions to a region or department
- For records management: Support for administrative units
- For sensitivity labeling: Support for administrative units