Polygon Class
Note
Bing Maps Web Control SDK retirement
Bing Maps Web Control SDK is deprecated and will be retired. Free (Basic) account customers can continue to use Bing Maps Web Control SDK until June 30th, 2025. Enterprise account customers can continue to use Bing Maps Web Control SDK until June 30th, 2028. To avoid service disruptions, all implementations using Bing Maps Web Control SDK will need to be updated to use Azure Maps Web SDK by the retirement date that applies to your Bing Maps for Enterprise account type. For detailed migration guidance, see Migrate from Bing Maps Web Control SDK and Migrate Bing Maps Enterprise applications to Azure Maps with GitHub Copilot.
Azure Maps is Microsoft's next-generation maps and geospatial services for developers. Azure Maps has many of the same features as Bing Maps for Enterprise, and more. To get started with Azure Maps, create a free Azure subscription and an Azure Maps account. For more information about azure Maps, see Azure Maps Documentation. For migration guidance, see Bing Maps Migration Overview.
A polygon is an area defined by a closed ring of locations. A simple polygon consists of an array of Location objects that form a boundary. This is useful for showing an area of interest on a map. In some applications there may be a need to for more complex polygons, such as polygons that have a hole in them. Take for instance the country of South Africa, which has a land locked country, Lesotho, within its main border. To represent South Africa on a map we need to be able to cut a hole in the polygon that represents its boundary to exclude the area of Lesotho. The first array of locations in a polygon represent the main border and is often called the exterior ring. All additional arrays of locations in a polygon are used to represent holes in the main polygon and are often called interior rings. Here is what the borders of South Africa look like.
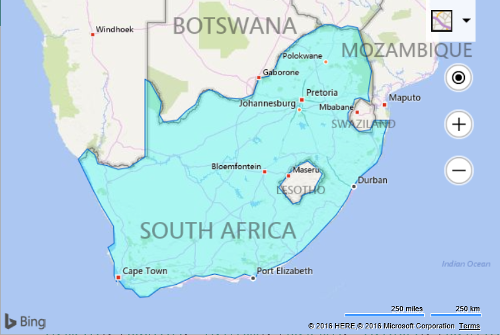
The Polygon class derives from the IPrimitive interface. When creating a polygon at least one array of Location objects must be passed as an argument to the constructor. An array of Location arrays can be passed in when creating complex polygons. Optionally, polygon options can also be passed as an argument.
Constructor
Polygon(rings: Location[] | Location[][], options?: PolygonOptions)
Methods
The Polygon class has the following methods.
| Name | Return Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
getCursor() |
string | Gets the css cursor value when the polygon has mouse events on it. |
getGeneralizable() |
boolean | Returns whether the polygon is generalizable based on zoom level or not. |
getFillColor() |
string or Color | Returns the color of the inside of the polygon. |
getLocations() |
Location[] | Returns the first ring of locations that define the polygon. If multiple rings were used to create the polygon, this method will return the first ring in the array. |
getRings() |
Returns an array of location arrays, where each location array defines a ring of the polygon. | |
getStrokeColor() |
string or Color | Returns the color of the outline of the polygon. |
getStrokeDashArray() |
string or number[] | Returns the string that represents the stroke/gap sequence used to draw the outline of the polygon. |
getStrokeThickness() |
number | Returns the thickness of the outline of the polygon. |
getVisible() |
boolean | Returns whether the polygon is visible. A value of false indicates that the polygon is hidden, although it is still an entity on the map. |
| setLocations(Location[]) | Sets the locations that define the polygon. Overwrites the rings value. | |
| setOptions(opt: PolygonOptions) | Sets options for the polygon. | |
| setRings(rings: Location[] or Location[][]) | Sets an array of location arrays, where each location array defines a ring of the polygon. |
Properties
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
metadata |
object | Information that is linked to the polygon. Some modules such as the GeoJSON and Spatial Data Service modules will also often add information to this property. |
Events
| Name | Arguments | Description |
|---|---|---|
changed |
IPrimitiveChangedEventArgs | Occurs when the locations/rings or options of the polygon has changed. |
click |
MouseEventArgs | Occurs when the mouse is used to click the polygon. |
dblclick |
MouseEventArgs | Occurs when the mouse is used to double click the polygon. |
mousedown |
MouseEventArgs | Occurs when the left mouse button is pressed when the mouse is over the polygon. |
mouseout |
MouseEventArgs | Occurs when the mouse cursor moves out of the area covered by the polygon. |
mouseover |
MouseEventArgs | Occurs when the mouse is over the polygon. |
mouseup |
MouseEventArgs | Occurs when the left mouse button is lifted up when the mouse is over the polygon. |