IP addresses of Azure API Management
APPLIES TO: All API Management tiers
In this article we describe how to retrieve the IP addresses of Azure API Management service. IP addresses can be public or private if the service is in a virtual network. You can use IP addresses to create firewall rules, filter the incoming traffic to the backend services, or restrict the outbound traffic.
Public IP addresses
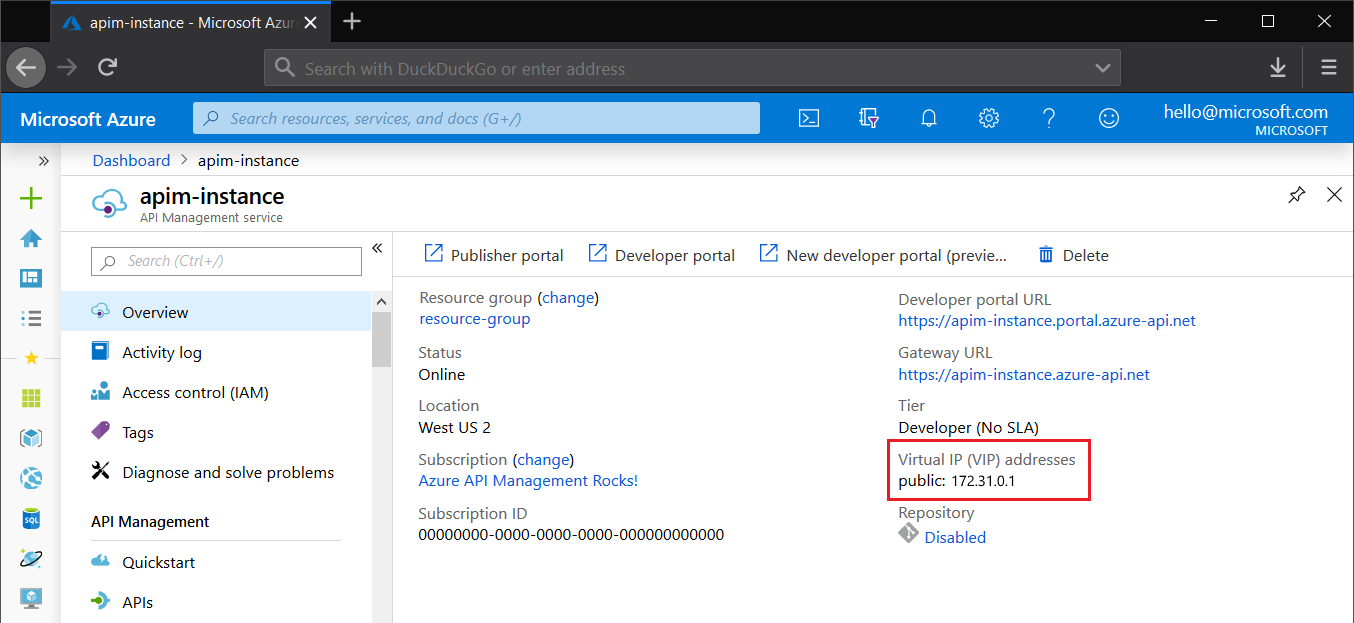
Every API Management service instance in Developer, Basic, Standard, or Premium tier has public IP addresses, which are exclusive only to that service instance (they are not shared with other resources).
You can retrieve the IP addresses from the overview dashboard of your resource in the Azure portal.
You can also fetch them programmatically with the following API call:
GET https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<subscription-id>/resourceGroups/<resource-group>/providers/Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/<service-name>?api-version=<api-version>
Public IP addresses will be part of the response:
{
...
"properties": {
...
"publicIPAddresses": [
"172.31.0.1"
],
...
}
...
}
In multi-regional deployments, each regional deployment has one public IP address.
IP addresses of API Management service in VNet
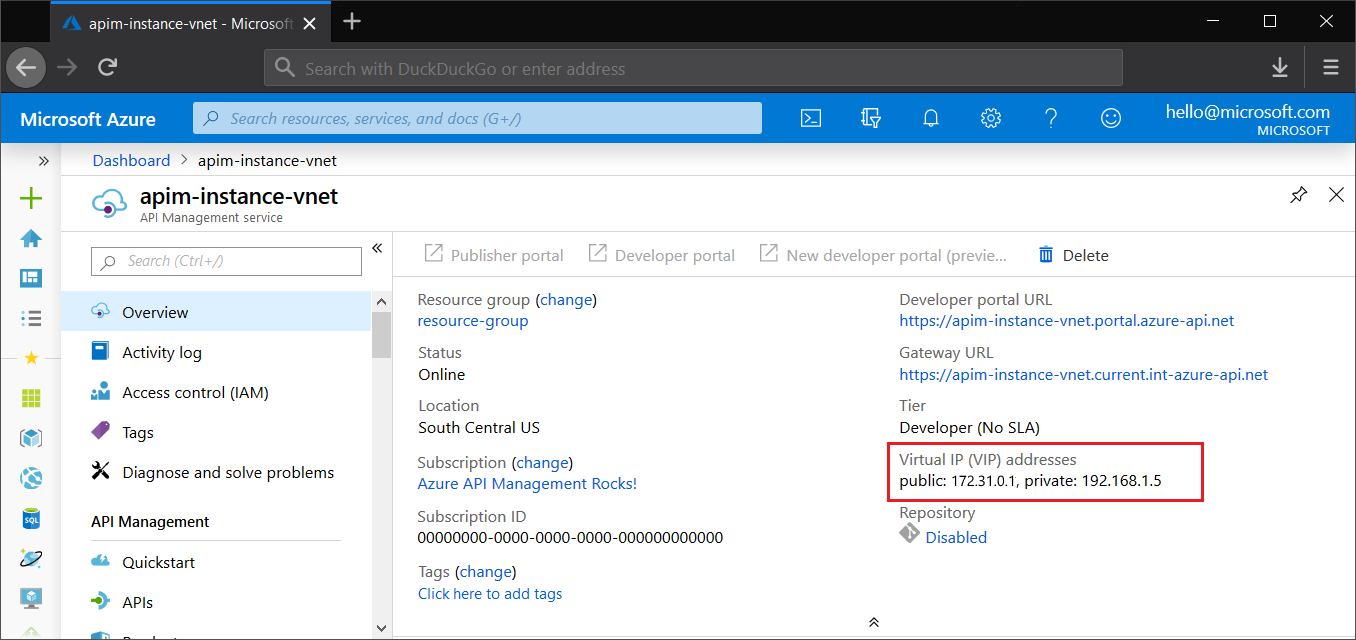
If your API Management service is inside a virtual network, it will have two types of IP addresses: public and private.
Public IP addresses are used for internal communication on port
3443- for managing configuration (for example, through Azure Resource Manager). In the external VNet configuration, they are also used for runtime API traffic. In the internal VNet configuration, public IP addresses are only used for Azure internal management operations and don't expose your instance to the internet.Private virtual IP (VIP) addresses, available only in the internal VNet mode, are used to connect from within the network to API Management endpoints - gateways, the developer portal, and the management plane for direct API access. You can use them for setting up DNS records within the network.
You will see addresses of both types in the Azure portal and in the response of the API call:
GET https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<subscription-id>/resourceGroups/<resource-group>/providers/Microsoft.ApiManagement/service/<service-name>?api-version=<api-version>
{
...
"properties": {
...
"publicIPAddresses": [
"172.31.0.1"
],
"privateIPAddresses": [
"192.168.1.5"
],
...
},
...
}
Important
The private IP addresses of internal load balancer and API Management units are assigned dynamically. Therefore, it is impossible to anticipate the private IP of the API Management instance prior to its deployment. Additionally, changing to a different subnet and then returning may cause a change in the private IP address.
IP addresses for outbound traffic
API Management uses a public IP address for a connection outside the VNet or a peered VNet, and it uses a private IP address for a connection in the VNet or a peered VNet.
When API Management is deployed in an external or internal virtual network and API Management connects to private (intranet-facing) backends, internal IP addresses (dynamic IP, or DIP addresses) from the subnet are used for the runtime API traffic. When a request is sent from API Management to a private backend, a private IP address will be visible as the origin of the request.
Therefore, if IP restriction lists secure resources within the VNet or a peered VNet, it is recommended to use the whole API Management subnet range with an IP rule - and (in internal mode) not just the private IP address associated with the API Management resource.
When a request is sent from API Management to a public (internet-facing) backend, a public IP address will always be visible as the origin of the request.
IP addresses of Consumption, Basic v2, Standard v2, and Premium v2 tier API Management service
If your API Management instance is created in a service tier that runs on a shared infrastructure, it doesn't have a dedicated IP address. Currently, instances in the following service tiers run on a shared infrastructure and without a deterministic IP address: Consumption, Basic v2, Standard v2, Premium v2.
If you need to add the outbound IP addresses used by your Consumption, Basic v2, Standard v2, or Premium v2 tier instance to an allowlist, you can add the instance's data center (Azure region) to an allowlist. You can download a JSON file that lists IP addresses for all Azure data centers. Then find the JSON fragment that applies to the region that your instance runs in.
For example, the following JSON fragment is what the allowlist for Western Europe might look like:
{
"name": "AzureCloud.westeurope",
"id": "AzureCloud.westeurope",
"properties": {
"changeNumber": 9,
"region": "westeurope",
"platform": "Azure",
"systemService": "",
"addressPrefixes": [
"13.69.0.0/17",
"13.73.128.0/18",
... Some IP addresses not shown here
"213.199.180.192/27",
"213.199.183.0/24"
]
}
}
For information about when this file is updated and when the IP addresses change, expand the Details section of the Download Center page.
Changes to the IP addresses
In the Developer, Basic, Standard, and Premium tiers of API Management, the public IP address or addresses (VIP) and private VIP addresses (if configured in the internal VNet mode) are static for the lifetime of a service, with the following exceptions:
The API Management service is deleted and then re-created.
The service subscription is disabled or warned (for example, for nonpayment) and then reinstated. Learn more about subscription states
(Developer and Premium tiers) Azure Virtual Network is added to or removed from the service.
(Developer and Premium tiers) API Management service is switched between external and internal VNet deployment mode.
(Developer and Premium tiers) API Management service is moved to a different subnet, migrated from the
stv1to thestv2compute platform, or configured with a different public IP address resource.(Premium tier) Availability zones are enabled, added, or removed.
(Premium tier) In multi-regional deployments, the regional IP address changes if a region is vacated and then reinstated.
Important
When changing from an internal to external virtual network, updating an API Management instance in a VNet by migrating from the
stv1tostv2platform, or changing subnets in the network, you can configure a different public IP address. If you don't provide one, an Azure-managed public IP address is automatically configured.