Upgrade service applications to SharePoint Server 2016
APPLIES TO:  2013
2013  2016
2016  2019
2019  Subscription Edition
Subscription Edition  SharePoint in Microsoft 365
SharePoint in Microsoft 365
When you upgrade from SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) to SharePoint Server 2016, you must use a database attach upgrade, which means that you upgrade only the content for your environment and not the configuration settings. After you have configured the SharePoint Server 2016 environment, and copied the content and service application databases, you can upgrade the service applications to SharePoint Server 2016. This article contains the steps that you take to upgrade the service applications.
Phase 3 of the upgrade process: Upgrade service applications:
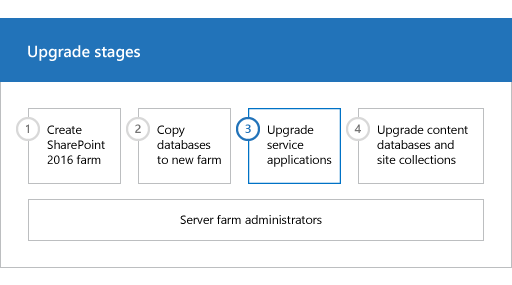
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| This is the third phase in the process to upgrade SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) data and sites to SharePoint Server 2016. The process includes the following phases that must be completed in order: Create the SharePoint Server 2016 farm for a database attach upgrade Copy databases to the new farm for upgrade to SharePoint Server 2016 Upgrade service applications to SharePoint Server 2016 (this phase) Upgrade content databases to SharePoint Server 2016 For an overview of the whole process, see Overview of the upgrade process to SharePoint Server 2016. |
Before you begin
Before you upgrade the service applications, review the following info and take any recommended actions.
Make sure that the account that you use to perform the steps in this article is a member of the Farm administrators group in Central Administration.
Decide which service application pool to use for the upgraded service applications. The procedures below use the default application pool for service applications which is "SharePoint Web Services Default". You can view a list of available service application pools by using the Get-SPServiceApplicationPool cmdlet in PowerShell. Or you can create a service application pool by using the New-SPServiceApplicationPool cmdlet. For more info, see Get-SPServiceApplicationPool and New-SPServiceApplicationPool.
Tip
Throughout this article, variables (such as $applicationPool, $sss, $upa, and so on) are used in the PowerShell cmdlets to save time and effort. You do not have to use these variables if you would prefer not to. However, if you do not use these variables, you must use IDs for the service applications and service application proxies when you specify the identity parameters. Each procedure has info about the variables used, or the alternate cmdlets to use to look up any IDs that are required. Also, many procedures in this article include a step to set the $applicationPool variable. If you are performing all of these procedures in the same session of PowerShell, and you want to use the same application pool for all service applications, you do not have to repeat this step in each procedure. Instead, you can set this variable once at the beginning and use it throughout the procedures in this article.
Note
For any Managed Properties in the SharePoint 2013 schema that are introduced in the SharePoint Server 2016 schema, prior to upgrading you must rename that Managed Property. For example, if you have created a Managed Property named SPWebURL, rename it to SPWebURL1 prior to the SharePoint Server 2016 upgrade. You may change the custom Managed Property name back to the original value (that is, rename SPWebURL1 to SPWebURL) after the upgrade has successfully completed. For a list of Managed Properties introduced in SharePoint Server 2016, see Managed Properties Added in SharePoint Server 2016.
About upgrading the service application databases
To upgrade a service application database, you create a new service application and provide the name of the existing database to use for the new service application. As the service application is created, the database is upgraded. This process has several steps.
Note
Word Automation Services and Machine Translation Services can't be upgraded. A new service instance will need to be created.
Important
The following steps outlining starting service instances only apply to the Custom server role type. For more info about server role types, see Planning for a MinRole server deployment in SharePoint Server 2016.
Start the service instances
The first step is to start service instances for the five service applications that you can upgrade: the Business Data Connectivity service, Managed Metadata Web Service, PerformancePoint Services service, Secure Store service, and Search service. Most of these service instances can be started from Central Administration. However the SharePoint Server Search service instance must be started by using PowerShell.
Create the service applications and upgrade the databases
After you have started the service instances, the next step is to create the service applications and upgrade the databases. You must use PowerShell to restore the service application databases.
Create proxies for the service applications
After you have upgraded the service application databases, you create the proxies for the service applications and add them to the default proxy group. You must create proxies for the following service applications:
Managed Metadata service application
Search service application
Secure Store service application
PerformancePoint Services service application
The Business Data Connectivity service application automatically creates a proxy and assigns it to the default proxy group when you create the service application.
Verify that the proxies are in the default group
The following sections provide procedures to complete these steps.
Start the service instances
The following procedures start the service instances.
To start service application instances from Central Administration:
Start SharePoint 2016 Central Administration.
For Windows Server 2012 R2:
On the Start screen, select SharePoint 2016 Central Administration.
If SharePoint 2016 Central Administration is not on the Start screen:
- Right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint 2016 Central Administration.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
In SharePoint 2016 Central Administration, on the Application Management page, in the Service Applications section, select Manage Services on Server.
Next to the Business Data Connectivity service, select Start.
Next to the Managed Metadata Web Service, select Start.
Next to the PerformancePoint Services service, select Start.
Next to the Secure Store Service, select Start.
The Search service instance must be started by using PowerShell because you cannot start it from Central Administration unless a Search Service application already exists.
To start the Search service instance by using PowerShell:
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note
If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2:
On the Start screen, select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
If SharePoint 2016 Management Shell is not on the Start screen:
- Right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
To start the Search service instance, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following commands and press ENTER after each one:
$SearchInst = Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceInstance # Stores the identity for the Search service instance on this server as a variableStart-SPServiceInstance $SearchInst # Starts the service instance
For more info, see Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceInstance and Start-SPServiceInstance.
Upgrade the Secure Store service application
To upgrade the Secure Store service application, you create the new service application and upgrade the database, create a proxy and add it to the default proxy group, and then restore the passphrase from the previous environment.
To upgrade the Secure Store service application by using PowerShell:
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note
If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2:
On the Start screen, select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
If SharePoint 2016 Management Shell is not on the Start screen:
- Right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2Windows Server 2012, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
To store the application pool that you want to use as a variable for this service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$applicationPool = Get-SPServiceApplicationPool -Identity 'SharePoint Web Services default'Where:
- SharePoint Web Services default is the name of the service application pool that will contain the new service applications. This is the default service application pool. You can specify a different service application pool.
This cmdlet sets the service application pool as a variable that you can use again in the cmdlets that follow. If you have multiple application pools and have to use a different application pool for a particular service application, repeat this step in the procedure to create each service application to use the appropriate application pool.
To upgrade the Secure Store service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$sss = New-SPSecureStoreServiceApplication -Name 'Secure Store' -ApplicationPool $applicationPool -DatabaseName 'SecureStore_Upgrade_DB' -AuditingEnabledWhere:
SecureStore is the name that you want to give the new Secure Store service application.
$applicationpool is the variable that you set earlier to identify the service application pool to use.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $applicationPool, then you must specify the name of an existing service application pool in the format ' Application Pool Name'. To view a list of service application pools, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplicationPool cmdlet.
SecureStore_Upgrade_DB is the name of the service application database that you want to upgrade.
This command sets a variable, $sss, that you use when you create the proxy later.
For more info, see New-SPSecureStoreApplication.
Type the following command to create a proxy for the Secure Store service application:
$sssp = New-SPSecureStoreServiceApplicationProxy -Name ProxyName -ServiceApplication $sss -DefaultProxyGroupWhere:
ProxyName is the proxy name that you want to use.
$sss is the variable that you set earlier to identify the new Secure Store service application.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $sss, then you must use an ID to identify the Secure Store service application instead of a name. To find the ID, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplication cmdlet to return a list of all service application IDs.
DefaultProxyGroup adds the Secure Store service application proxy to the default proxy group for the local farm.
This command sets a variable, $sssp, for the service application proxy that you use when you restore the passphrase.
For more info, see New-SPSecureStoreServiceApplicationProxy.
After you create the Secure Store service application and the proxy, you have to refresh the encryption key. For info about how to refresh the encryption key, see Refresh the Secure Store encryption key.
Type the following command to restore the passphrase for the Secure Store service application:
Update-SPSecureStoreApplicationServerKey -Passphrase <Passphrase> -ServiceApplicationProxy $ssspWhere:
<Passphrase> is the Passphrase for the Secure Store service application from your previous environment.
$sssp is a variable that you set earlier to identify the new Secure Store service application proxy.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $sssp, then you must use an ID to identify the Secure Store service application proxy instead of a name. To find the ID, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy cmdlet to return a list of all service application proxy IDs.
For more info, see Update-SPSecureStoreApplicationServerKey.
Upgrade the Business Data Connectivity service application
To upgrade the Business Data Connectivity service application, you create the new service application and upgrade the database. You do not have to create a proxy for the Business Data Connectivity service application. The Business Data Connectivity service application automatically creates a proxy and assigns it to the default proxy group when you create the service application.
To upgrade the Business Data Connectivity service application by using PowerShell:
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note
If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2:
On the Start screen, select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
If SharePoint 2016 Management Shell is not on the Start screen:
- Right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
To store the application pool that you want to use as a variable for this service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$applicationPool = Get-SPServiceApplicationPool -Identity 'SharePoint Web Services default'Where:
- SharePoint Web Services default is the name of the service application pool that will contain the new service applications.
This cmdlet sets the service application pool as a variable that you can use again in the cmdlets that follow. If you have multiple application pools and have to use a different application pool for a particular service application, repeat this step in the procedure to create each service application to use the appropriate application pool.
To upgrade the Business Data Connectivity service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
New-SPBusinessDataCatalogServiceApplication -Name 'BDC Service' -ApplicationPool $applicationPool -DatabaseName 'BDC_Service_DB'Where:
BDC Service is the name that you want to give the new Business Data Connectivity service application.
$applicationpool is the variable that you set earlier to identify the service application pool to use.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $applicationPool, then you must specify the name of an existing service application pool in the format ' Application Pool Name'. To view a list of service application pools, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplicationPool cmdlet.
BDC_Service_DB is name of the service application database that you want to upgrade.
For more info, see New-SPBusinessDataCatalogServiceApplication.
Upgrade the Managed Metadata service application
To upgrade the Managed Metadata service application, you create the new service application and upgrade the database, and then create a proxy and add it to the default proxy group.
To upgrade the Managed Metadata service application by using PowerShell:
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note
If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2:
On the Start screen, select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
If SharePoint 2016 Management Shell is not on the Start screen:
- Right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
To store the application pool that you want to use as a variable for this service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$applicationPool = Get-SPServiceApplicationPool -Identity 'SharePoint Web Services default'Where:
- SharePoint Web Services default is the name of the service application pool that will contain the new service applications.
This cmdlet sets the service application pool as a variable that you can use again in the cmdlets that follow. If you have multiple application pools and have to use a different application pool for a particular service application, repeat this step in the procedure to create each service application to use the appropriate application pool.
To upgrade the Managed Metadata service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$mms = New-SPMetadataServiceApplication -Name 'Managed Metadata Service Application' -ApplicationPool $applicationPool -DatabaseName 'Managed Metadata Service_DB'Where:
Managed Metadata Service Application is the name that you want to give the new Managed Metadata service application.
$applicationpool is the variable that you set earlier to identify the service application pool to use.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $applicationPool, then you must specify the name of an existing service application pool in the format ' Application Pool Name'. To view a list of service application pools, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplicationPool cmdlet.
Managed Metadata Service_DB is name of the service application database that you want to upgrade.
This command sets a variable, $mms, that you use when you create the proxy later.
For more info, see New-SPMetadataServiceApplication.
At the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command to create a proxy for the Managed Metadata service application:
New-SPMetadataServiceApplicationProxy -Name ProxyName -ServiceApplication $mms -DefaultProxyGroupWhere:
ProxyName is the proxy name that you want to use.
$mms is the variable that you set earlier to identify the new Managed Metadata service application.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $mms, then you must use an ID to identify the Managed Metadata service application proxy instead of a name. To find the ID, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplication cmdlet to return a list of all service application IDs.
DefaultProxyGroup adds the Managed Metadata service application proxy to the default proxy group for the local farm.
For more info, see New-SPMetadataServiceApplicationProxy.
Upgrade the PerformancePoint Services service application
To upgrade the PerformancePoint Services service application, you create the new service application and upgrade the database, and then create a proxy and add it to the default proxy group.
To upgrade the PerformancePoint Services service application by using PowerShell:
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note
If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2:
On the Start screen, select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
If SharePoint 2016 Management Shell is not on the Start screen:
- Right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
To store the application pool that you want to use as a variable for this service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$applicationPool = Get-SPServiceApplicationPool -Identity 'SharePoint Web Services default'Where:
- SharePoint Web Services default is the name of the service application pool that will contain the new service applications.
This cmdlet sets the service application pool as a variable that you can use again in the cmdlets that follow. If you have multiple application pools and have to use a different application pool for a particular service application, repeat this step in the procedure to create each service application to use the appropriate application pool.
To upgrade the PerformancePoint Services service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$pps = New-SPPerformancePointServiceApplication -Name 'PerformancePoint Service' -ApplicationPool $applicationPool -DatabaseName 'PerformancePoint Service Application_DB'Where:
PerformancePoint Service is the name that you want to give the new PerformancePoint Services service application.
$applicationpool is the variable that you set earlier to identify the service application pool to use.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $applicationPool, then you must specify the name of an existing service application pool in the format ' Application Pool Name'. To view a list of service application pools, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplicationPool cmdlet.
PerformancePoint Service Application_DB is name of the PerformancePoint Services service application database that you want to upgrade.
This command sets a variable, $pps, that you use when you create the proxy later.
For more info, see New-SPPerformancePointServiceApplication.
Type the following command to create a proxy for the PerformancePoint Services service application:
New-SPPerformancePointServiceApplicationProxy -Name ProxyName -ServiceApplication $pps -DefaultWhere:
ProxyName is the proxy name that you want to use.
$pps is the variable that you set earlier to identify the new PerformancePoint Services service application.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $pps, then you must use an ID to identify the PerformancePoint Services service application instead of a name. To find the ID, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplication cmdlet to return a list of all service application IDs.
Default adds the PerformancePoint Services service application proxy to the default proxy group for the local farm.
For more info, see New-SPPerformancePointServiceApplicationProxy.
Upgrade the User Profile service application
Upgrade the Managed Metadata service application before you upgrade the User Profile service application.
To upgrade the User Profile service application, you copy the Profile and Social databases in your SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm to your SharePoint Server 2016 farm and create a new User Profile service application from your SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm in your SharePoint Server 2016 farm. The restore triggers SharePoint Server 2016 to create a new User Profile service application in the SharePoint Server 2016 farm and point it to the copied User Profile databases. To complete the upgrade of the User Profile service application, you create a proxy and add it to the default proxy group.
Note
As SharePoint Server 2016 does not have the User Profile Synchronization Service, you do not copy the Synchronization database. Instead, a new database will be created with an empty schema.
To upgrade the User Profile service application by using PowerShell:
Copy the Profile and Social databases in the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm to the SharePoint Server 2016 farm by following these steps:
Important
Perform these steps in the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) environment.
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note
If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2: On the Start screen, select SharePoint Management Shell.
If SharePoint Management Shell is not on the Start screen, right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
Set the User Profile databases to read-only. In the second phase of the process to upgrade SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) data and sites to SharePoint Server 2016, you set all the other databases to read-only.
Copy the Profile and Social databases in the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm to the SharePoint Server 2016 farm, follow the procedures in Copy databases to the new farm for upgrade to SharePoint Server 2016 for the search administration database only.
Important
Perform the next steps in the SharePoint Server 2016 environment.
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note
If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2: On the Start screen, select SharePoint Management Shell.
If SharePoint Management Shell is not on the Start screen, right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
To store the application pool that you want to use as a variable for this service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$applicationPool = Get-SPServiceApplicationPool -Identity 'SharePoint Web Services default'Where:
- SharePoint Web Services default is the name of the service application pool that will contain the new service applications.
This cmdlet sets the service application pool as a variable that you can use again in the cmdlets that follow. If you have multiple application pools and have to use a different application pool for a particular service application, repeat this step in the procedure to create each service application to use the appropriate application pool.
To restore the User Profile service application and upgrade the Profile and Social databases, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
New-SPProfileServiceApplication -Name '<UserProfileApplicationName>' -ApplicationPool $applicationPool -ProfileDBName '<ProfileDBName>' -SocialDBName '<SocialDBName>' -ProfileSyncDBName '<SyncDBName>'Where:
UserProfileApplicationName is the name of the User Profile service application.
$applicationpool is the variable that you set to identify the service application pool to use.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $applicationPool, then you must specify the name of an existing service application pool in the format ' Application Pool Name'. To view a list of service application pools, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplicationPool cmdlet.
ProfileDBName is the name of the Profile database that you want to upgrade.
SocialDBName is the name of the Social database that you want to upgrade.
SyncDBName is the name of the new Synchronization database that you want to upgrade.
Create the User Profile service application proxy and add it to the default proxy group by completing these actions:
Type the following command to get the ID for the User Profile service application and store it as a variable:
$sa = Get-SPServiceApplication | ?{$_.TypeName -eq 'User Profile Service Application'}For more info, see Get-SPServiceApplication.
Type the following command to create a proxy for the User Profile service application:
New-SPProfileServiceApplicationProxy -Name ProxyName -ServiceApplication $saWhere:
ProxyName is the proxy name that you want to use.
$sa is the variable that you set earlier to identify the new User Profile service application.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $sa, then you must use an ID to identify the User Profile service application instead of a name. To find the ID, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplication cmdlet to return a list of all service application IDs.
For more info, see New-SPProfileServiceApplicationProxy.
Type the following command to get the Search service application proxy ID for the proxy you just created and set it as the variable $ssap:
$proxy = Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy | ?{$_.TypeName -eq 'User Profile Service Application Proxy'}For more info, see Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy.
Type the following command to add the User Profile service application proxy to the default proxy group:
Add-SPServiceApplicationProxyGroupMember -member $proxy -identity ""Where:
$proxy is the variable that you set earlier to identify the ID for the proxy you just created for the User Profile service application.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $proxy, then you must use an ID to identify the User Profile service application proxy instead of a name. To find the ID, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy cmdlet to return a list of all service application proxy IDs.
You use an empty Identity parameter ("") to add it to the default group.
For more info, see Add-SPServiceApplicationProxyGroupMember.
Upgrade the Search service application
Upgrade the User Profile service application and the Managed Metadata service application before you upgrade the Search service application.
To upgrade the Search service application, you copy the search administration database in your SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm to your SharePoint Server 2016 farm and restore the Search service application from your SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm in your SharePoint Server 2016 farm. The restore triggers SharePoint Server 2016 to create a new Search service application in the SharePoint Server 2016 farm and point it to the copied search administration database. To complete the upgrade of the Search service application you create a proxy and add it to the default proxy group and you ensure that the new Links Database and the new search topology is configured the same way as in the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm.
SharePoint Server 2016 normally creates a new search topology with all the search components and databases when it creates a the new Search service application. During a restore of a Search service application, SharePoint Server 2016 creates a new search topology, but upgrades the restored Search Administration database instead of creating a new Search Administration database. The upgraded Search Administration database retains any additions or modifications made to the search schema, result sources and query rules from the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm.
Note
During this upgrade, search doesn't crawl content in your SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1). If freshness of search results is important, save time by familiarizing yourself with these steps before starting the upgrade.
Important
Because the search topology in the SharePoint Server 2016 farm is new, the index is empty. You have to perform a full crawl of the entire indexed corpus after you have upgraded all content sources (the fourth phase in the process to upgrade SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) data and sites to SharePoint Server 2016).
To upgrade the Search service application by using PowerShell:
Copy the search administration database in the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm to the SharePoint Server 2016 farm by following these steps:
Note
You copied all other content and service databases in your SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) environment in an earlier step of the process for upgrading to SharePoint Server 2016. We recommend copying the Search Administration database at this later stage because you have to pause the Search service application in your SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) environment while copying the Search Administration database.
Important
Perform these steps in the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) environment.
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note
If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2: On the Start screen, select SharePoint Management Shell.
If SharePoint Management Shell is not on the Start screen, right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
Set the Search Administration database to read-only. In the second phase of the process to upgrade SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) data and sites to SharePoint Server 2016, you set all the other databases to read-only. Follow the same instructions now for the Search Administration database.
Pause the Search service application. At the Windows PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$ssa = Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplication <SearchServiceApplicationName> Suspend-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplication -Identity $ssaWhere:
- SearchServiceApplicationName is the name of the Search service application you want to pause.
Note
While the Search service application is paused, the index in the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) environment isn't updated. This means that during the upgrade to SharePoint Server 2016, search results might be less fresh.
Copy the search administration database in the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm to the SharePoint Server 2016 farm, follow the procedures in Copy databases to the new farm for upgrade to SharePoint Server 2016 for the search administration database only.
Important
Perform the next steps in the SharePoint Server 2016 environment.
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note
If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2: On the Start screen, select SharePoint Management Shell.
If SharePoint Management Shell is not on the Start screen, right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
To store the application pool that you want to use as a variable for this service application, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$applicationPool = Get-SPServiceApplicationPool -Identity 'SharePoint Web Services default'Where:
- SharePoint Web Services default is the name of the service application pool that will contain the new service applications.
This cmdlet sets the service application pool as a variable that you can use again in the cmdlets that follow. If you have multiple application pools and have to use a different application pool for a particular service application, repeat this step in the procedure to create each service application to use the appropriate application pool.
To restore the Search service application and upgrade the Search Administration database, at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$searchInst = Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceInstance -local # Gets the Search service instance and sets a variable to use in the next command Restore-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplication -Name '<SearchServiceApplicationName>' -applicationpool $applicationPool -databasename '<SearchServiceApplicationDBName>' -databaseserver <ServerName> -AdminSearchServiceInstance $searchInstWhere:
SearchServiceApplicationName is the name of the Search service application.
$applicationpool is the variable that you set to identify the service application pool to use.
Tip
If you do not use the variable $applicationPool, then you must specify the name of an existing service application pool in the format ' Application Pool Name'. To view a list of service application pools, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplicationPool cmdlet.
SearchServiceApplicationDBName is the name of the search administration database that you want to upgrade, and that this Search service application shall use.
$searchInst is the variable that you set to identify the new Search Service application instance.
Note: A Search service application upgrade might fail, for example due to network or SQL Server latency. If an error message appears during the upgrade, do the following:
Delete the Search Administration database that you were trying to upgrade.
Using the backup copy that you made of the Search Administration database, repeat the following procedures in this article for the Search service application only:
Type the command to upgrade the Search service application again at the Microsoft PowerShell command prompt.
For more info, see Restore-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplication.
Create the Search service application proxy and add it to the default proxy group by completing these actions:
Type the following command to get the ID for the Search service application and store it as a variable:
$ssa = Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplicationFor more info, see Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplication.
Type the following command to create a proxy for the Search service application:
New-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplicationProxy -Name ProxyName -SearchApplication $ssaWhere:
ProxyName is the proxy name that you want to use.
$ssa is the variable that you set earlier to identify the new Search service application.
Tip: If you do not use the variable $ssa, then you must use an ID to identify the Search service application instead of a name. To find the ID, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplication cmdlet to return a list of all service application IDs.
For more info, see New-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplicationProxy.
Type the following command to get the Search service application proxy ID for the proxy you just created and set it as the variable $ssap:
$ssap = Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplicationProxyFor more info, see Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplicationProxy.
Type the following command to add the Search service application proxy to the default proxy group:
Add-SPServiceApplicationProxyGroupMember -member $ssap -identity ""Where:
$ssap is the variable that you set earlier to identify the ID for the proxy you just created for the Search service application.
Tip: If you do not use the variable $ssap, then you must use an ID to identify the Search service application proxy instead of a name. To find the ID, you can run the Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy cmdlet to return a list of all service application proxy IDs.
You use an empty Identity parameter ("") to add it to the default group.
For more info, see Add-SPServiceApplicationProxyGroupMember.
If the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm uses a Links Database that is partitioned, partition the Links Database in the SharePoint Server 2016 farm the same way. Learn how in Move-SPEnterpriseSearchLinksDatabases.
(Optional) Preserve search relevance settings from the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm. Because the upgraded Search service application has a new, empty index, search analytics data from the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm cannot be fully retained. Copy the Analytics Reporting database from the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm and attach it to the new Search service application in the SharePoint Server 2016 farm:
In the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm, backup the Analytics Reporting database.
In the SharePoint Server 2016 farm, restore the backed up database to the new database server.
In the SharePoint Server 2016 farm, attach the restored database to the new Search service application.
Verify that the search topology on the new SharePoint Server 2016 farm is alike that of the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) farm. If your requirements for search have changed, now is a good time to scale out the search topology of the new SharePoint Server 2016 farm.
Resume the Search service application in the SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) environment.
At the PowerShell command prompt, type the following command:
$ssa = Get-SPEnterpriseSearchServiceApplication <SearchServiceApplicationName> $ssa.Resume()Where:
- SearchServiceApplicationName is the name of the Search service application you want to resume.
Verify that all of the new proxies are in the default proxy group
Use the following procedure to verify that the steps to create the proxies and add them to the default proxy group worked.
To verify that all of the new proxies are in the default proxy group by using PowerShell:
Verify that you have the following memberships:
securityadmin fixed server role on the SQL Server instance.
db_owner fixed database role on all databases that are to be updated.
Administrators group on the server on which you are running the PowerShell cmdlets.
An administrator can use the Add-SPShellAdmin cmdlet to grant permissions to use SharePoint Server 2016 cmdlets.
Note: If you do not have permissions, contact your Setup administrator or SQL Server administrator to request permissions. For additional info about PowerShell permissions, see Add-SPShellAdmin.
Start the SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For Windows Server 2012 R2:
On the Start screen, select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
If SharePoint 2016 Management Shell is not on the Start screen, right-click Computer, select All apps, and then select SharePoint 2016 Management Shell.
For more info about how to interact with Windows Server 2012 R2, see Common Management Tasks and Navigation in Windows Server 2012.
At the PowerShell command prompt, type the following commands:
$pg = Get-SPServiceApplicationProxyGroup -Identity "" $pg.ProxiesWhere:
$pg is a variable you set to represent the default proxy group.
You use an empty Identity parameter ("") to specify the default proxy group.
This returns a list of all proxies in the default proxy group, their display names, type names, and IDs.
For more info, see Get-SPServiceApplicationProxyGroup.
Now that the service applications are upgraded, you can start the process to upgrade the content databases. The first step in that process is to create the web applications that are needed for each content database.
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| This is the third phase in the process to upgrade SharePoint Server 2013 with Service Pack 1 (SP1) data and sites to SharePoint Server 2016. For an overview of the whole process, see Overview of the upgrade process to SharePoint Server 2016. |
Next phase: Upgrade content databases to SharePoint Server 2016
See also
Concepts
Create the SharePoint Server 2016 farm for a database attach upgrade
Copy databases to the new farm for upgrade to SharePoint Server 2016
Upgrade content databases to SharePoint Server 2016
Services upgrade overview for SharePoint Server 2016