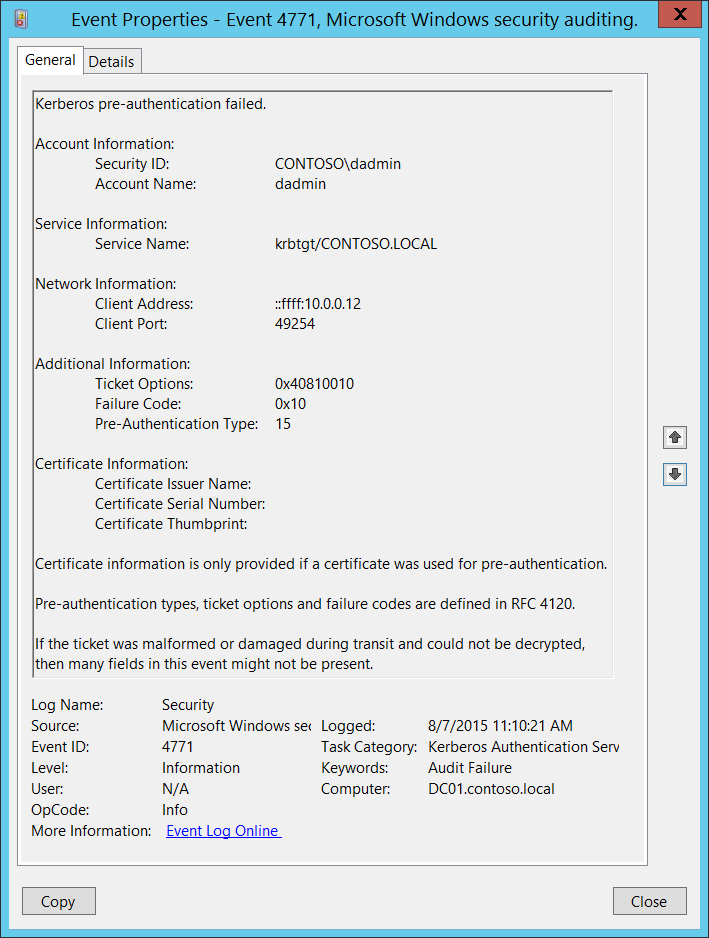
4771(F): Kerberos pre-authentication failed.
Subcategory: Audit Kerberos Authentication Service
Event Description:
This event generates every time the Key Distribution Center fails to issue a Kerberos Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT). This problem can occur when a domain controller doesn't have a certificate installed for smart card authentication (for example, with a "Domain Controller" or "Domain Controller Authentication" template), the user's password has expired, or the wrong password was provided.
This event generates only on domain controllers.
This event is not generated if "Do not require Kerberos preauthentication" option is set for the account.
Note For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
- <Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event">
- <System>
<Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing" Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" />
<EventID>4771</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>14339</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8010000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2015-08-07T18:10:21.495462300Z" />
<EventRecordID>166708</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID="520" ThreadID="1084" />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>DC01.contoso.local</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
- <EventData>
<Data Name="TargetUserName">dadmin</Data>
<Data Name="TargetSid">S-1-5-21-3457937927-2839227994-823803824-1104</Data>
<Data Name="ServiceName">krbtgt/CONTOSO.LOCAL</Data>
<Data Name="TicketOptions">0x40810010</Data>
<Data Name="Status">0x10</Data>
<Data Name="PreAuthType">15</Data>
<Data Name="IpAddress">::ffff:10.0.0.12</Data>
<Data Name="IpPort">49254</Data>
<Data Name="CertIssuerName" />
<Data Name="CertSerialNumber" />
<Data Name="CertThumbprint" />
</EventData>
</Event>
Required Server Roles: Active Directory domain controller.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Account Information:
Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of account object for which (TGT) ticket was requested. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.
For example: CONTOSO\dadmin or CONTOSO\WIN81$.
Note A security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers.
Account Name: [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of account, for which (TGT) ticket was requested. Computer account name ends with $ character.
User account example: dadmin
Computer account example: WIN81$
Service Information:
Service Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the service in the Kerberos Realm to which TGT request was sent. Typically has one of the following formats:
krbtgt/DOMAIN_NETBIOS_NAME. Example: krbtgt/CONTOSO
krbtgt/DOMAIN_FULL_NAME. Example: krbtgt/CONTOSO.LOCAL
Network Information:
Client Address [Type = UnicodeString]: IP address of the computer from which the TGT request was received. Here are some examples of formats:
IPv6 or IPv4 address.
::ffff:IPv4_address.
::1 - localhost.
Client Port [Type = UnicodeString]: source port number of client network connection (TGT request connection).
- 0 for local (localhost) requests.
Additional Information:
Ticket Options: [Type = HexInt32]: this set of different Ticket Flags is in hexadecimal format.
Example:
Ticket Options: 0x40810010
Binary view: 01000000100000010000000000010000
Using MSB 0-bit numbering, we have bit 1, 8, 15 and 27 set = Forwardable, Renewable, Canonicalize, Renewable-ok.
Note In the table below "MSB 0" bit numbering is used, because RFC documents use this style. In "MSB 0" style bit numbering begins from left.
The most common values:
0x40810010 - Forwardable, Renewable, Canonicalize, Renewable-ok
0x40810000 - Forwardable, Renewable, Canonicalize
0x60810010 - Forwardable, Forwarded, Renewable, Canonicalize, Renewable-ok
| Bit | Flag Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Reserved | - |
| 1 | Forwardable | (TGT only). Tells the ticket-granting service that it can issue a new TGT—based on the presented TGT—with a different network address based on the presented TGT. |
| 2 | Forwarded | Indicates either that a TGT has been forwarded or that a ticket was issued from a forwarded TGT. |
| 3 | Proxiable | (TGT only). Tells the ticket-granting service that it can issue tickets with a network address that differs from the one in the TGT. |
| 4 | Proxy | Indicates that the network address in the ticket is different from the one in the TGT used to obtain the ticket. |
| 5 | Allow-postdate | Postdated tickets SHOULD NOT be supported in KILE (Microsoft Kerberos Protocol Extension). |
| 6 | Postdated | Postdated tickets SHOULD NOT be supported in KILE (Microsoft Kerberos Protocol Extension). |
| 7 | Invalid | This flag indicates that a ticket is invalid, and it must be validated by the KDC before use. Application servers must reject tickets that have this flag set. |
| 8 | Renewable | Used in combination with the End Time and Renew Till fields to cause tickets with long life spans to be renewed at the KDC periodically. |
| 9 | Initial | Indicates that a ticket was issued using the authentication service (AS) exchange and not issued based on a TGT. |
| 10 | Pre-authent | Indicates that the client was authenticated by the KDC before a ticket was issued. This flag usually indicates the presence of an authenticator in the ticket. It can also flag the presence of credentials taken from a smart card logon. |
| 11 | Opt-hardware-auth | This flag was originally intended to indicate that hardware-supported authentication was used during pre-authentication. This flag is no longer recommended in the Kerberos V5 protocol. KDCs MUST NOT issue a ticket with this flag set. KDCs SHOULD NOT preserve this flag if it is set by another KDC. |
| 12 | Transited-policy-checked | KILE MUST NOT check for transited domains on servers or a KDC. Application servers MUST ignore the TRANSITED-POLICY-CHECKED flag. |
| 13 | Ok-as-delegate | The KDC MUST set the OK-AS-DELEGATE flag if the service account is trusted for delegation. |
| 14 | Request-anonymous | KILE does not use this flag. |
| 15 | Name-canonicalize | To request referrals, the Kerberos client MUST explicitly request the "canonicalize" KDC option for the AS-REQ or TGS-REQ. |
| 16-25 | Unused | - |
| 26 | Disable-transited-check | By default the KDC will check the transited field of a TGT against the policy of the local realm before it will issue derivative tickets based on the TGT. If this flag is set in the request, checking of the transited field is disabled. Tickets issued without the performance of this check will be noted by the reset (0) value of the TRANSITED-POLICY-CHECKED flag, indicating to the application server that the transited field must be checked locally. KDCs are encouraged but not required to honor the DISABLE-TRANSITED-CHECK option. Should not be in use, because Transited-policy-checked flag is not supported by KILE. |
| 27 | Renewable-ok | The RENEWABLE-OK option indicates that a renewable ticket will be acceptable if a ticket with the requested life cannot otherwise be provided, in which case a renewable ticket may be issued with a renew-till equal to the requested end time. The value of the renew-till field may still be limited by local limits, or limits selected by the individual principal or server. |
| 28 | Enc-tkt-in-skey | No information. |
| 29 | Unused | - |
| 30 | Renew | The RENEW option indicates that the present request is for a renewal. The ticket provided is encrypted in the secret key for the server on which it is valid. This option will only be honored if the ticket to be renewed has its RENEWABLE flag set and if the time in its renew-till field has not passed. The ticket to be renewed is passed in the padata field as part of the authentication header. |
| 31 | Validate | This option is used only by the ticket-granting service. The VALIDATE option indicates that the request is to validate a postdated ticket. Should not be in use, because postdated tickets are not supported by KILE. |
Table 6. Kerberos ticket flags.
- Failure Code [Type = HexInt32]: hexadecimal failure code of failed TGT issue operation. The table below contains the list of the error codes for this event as defined in RFC 4120:
| Code | Code Name | Description | Possible causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0 | KDC_ERR_NONE | No error | |
| 0x1 | KDC_ERR_NAME_EXP | Client's entry in database has expired | |
| 0x2 | KDC_ERR_SERVICE_EXP | Server's entry in database has expired | |
| 0x3 | KDC_ERR_BAD_PVNO | Requested protocol version number not supported | |
| 0x4 | KDC_ERR_C_OLD_MAST_KVNO | Client's key encrypted in old master key | |
| 0x5 | KDC_ERR_S_OLD_MAST_KVNO | Server's key encrypted in old master key | |
| 0x6 | KDC_ERR_C_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN | Client not found in Kerberos database | |
| 0x7 | KDC_ERR_S_PRINCIPAL_UNKNOWN | Server not found in Kerberos database | |
| 0x8 | KDC_ERR_PRINCIPAL_NOT_UNIQUE | Multiple principal entries in database | |
| 0x9 | KDC_ERR_NULL_KEY | The client or server has a null key | |
| 0xa | KDC_ERR_CANNOT_POSTDATE | Ticket not eligible for postdating | |
| 0xb | KDC_ERR_NEVER_VALID | Requested starttime is later than end time | |
| 0xc | KDC_ERR_POLICY | KDC policy rejects request | |
| 0xd | KDC_ERR_BADOPTION | KDC cannot accommodate requested option | |
| 0xe | KDC_ERR_ETYPE_NOSUPP | KDC has no support for encryption type | |
| 0xf | KDC_ERR_SUMTYPE_NOSUPP | KDC has no support for checksum type | |
| 0x10 | KDC_ERR_PADATA_TYPE_NOSUPP | KDC has no support for PADATA type (pre-authentication data) | Smart card logon is being attempted and the proper certificate cannot be located. This problem can happen because the wrong certification authority (CA) is being queried or the proper CA cannot be contacted in order to get Domain Controller or Domain Controller Authentication certificates for the domain controller. It can also happen when a domain controller doesn't have a certificate installed for smart cards (Domain Controller or Domain Controller Authentication templates). |
| 0x11 | KDC_ERR_TRTYPE_NOSUPP | KDC has no support for transited type | |
| 0x12 | KDC_ERR_CLIENT_REVOKED | Clients credentials have been revoked | |
| 0x13 | KDC_ERR_SERVICE_REVOKED | Credentials for server have been revoked | |
| 0x14 | KDC_ERR_TGT_REVOKED | TGT has been revoked | |
| 0x15 | KDC_ERR_CLIENT_NOTYET | Client not yet valid; try again later | |
| 0x16 | KDC_ERR_SERVICE_NOTYET | Server not yet valid; try again later | |
| 0x17 | KDC_ERR_KEY_EXPIRED | Password has expired—change password to reset | The user's password has expired. |
| 0x18 | KDC_ERR_PREAUTH_FAILED | Pre-authentication information was invalid | The wrong password was provided. |
| 0x19 | KDC_ERR_PREAUTH_REQUIRED | Additional pre-authentication required | |
| 0x1a | KDC_ERR_SERVER_NOMATCH | Requested server and ticket don't match | |
| 0x1b | KDC_ERR_MUST_USE_USER2USER | Server principal valid for user2user only | |
| 0x1c | KDC_ERR_PATH_NOT_ACCEPTED | KDC Policy rejects transited path | |
| 0x1d | KDC_ERR_SVC_UNAVAILABLE | A service is not available | |
| 0x1f | KRB_AP_ERR_BAD_INTEGRITY | Integrity check on decrypted field failed | |
| 0x20 | KRB_AP_ERR_TKT_EXPIRED | Ticket expired | |
| 0x21 | KRB_AP_ERR_TKT_NYV | Ticket not yet valid | |
| 0x22 | KRB_AP_ERR_REPEAT | Request is a replay | |
| 0x23 | KRB_AP_ERR_NOT_US | The ticket isn't for us | |
| 0x24 | KRB_AP_ERR_BADMATCH | Ticket and authenticator don't match | |
| 0x25 | KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW | Clock skew too great | |
| 0x26 | KRB_AP_ERR_BADADDR | Incorrect net address | |
| 0x27 | KRB_AP_ERR_BADVERSION | Protocol version mismatch | |
| 0x28 | KRB_AP_ERR_MSG_TYPE | Invalid msg type | |
| 0x29 | KRB_AP_ERR_MODIFIED | Message stream modified | |
| 0x2a | KRB_AP_ERR_BADORDER | Message out of order | |
| 0x2c | KRB_AP_ERR_BADKEYVER | Specified version of key is not available | |
| 0x2d | KRB_AP_ERR_NOKEY | Service key not available | |
| 0x2e | KRB_AP_ERR_MUT_FAIL | Mutual authentication failed | |
| 0x2f | KRB_AP_ERR_BADDIRECTION | Incorrect message direction | |
| 0x30 | KRB_AP_ERR_METHOD | Alternative authentication method required | |
| 0x31 | KRB_AP_ERR_BADSEQ | Incorrect sequence number in message | |
| 0x32 | KRB_AP_ERR_INAPP_CKSUM | Inappropriate type of checksum in message | |
| 0x33 | KRB_AP_PATH_NOT_ACCEPTED | Policy rejects transited path | |
| 0x34 | KRB_ERR_RESPONSE_TOO_BIG | Response too big for UDP; retry with TCP | |
| 0x3c | KRB_ERR_GENERIC | Generic error (description in e-text) | |
| 0x3d | KRB_ERR_FIELD_TOOLONG | Field is too long for this implementation | |
| 0x3e | KDC_ERROR_CLIENT_NOT_TRUSTED | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x3f | KDC_ERROR_KDC_NOT_TRUSTED | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x40 | KDC_ERROR_INVALID_SIG | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x41 | KDC_ERR_KEY_TOO_WEAK | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x42 | KDC_ERR_CERTIFICATE_MISMATCH | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x43 | KRB_AP_ERR_NO_TGT | No TGT available to validate USER-TO-USER | |
| 0x44 | KDC_ERR_WRONG_REALM | Reserved for future use | |
| 0x45 | KRB_AP_ERR_USER_TO_USER_REQUIRED | Ticket must be for USER-TO-USER | |
| 0x46 | KDC_ERR_CANT_VERIFY_CERTIFICATE | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x47 | KDC_ERR_INVALID_CERTIFICATE | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x48 | KDC_ERR_REVOKED_CERTIFICATE | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x49 | KDC_ERR_REVOCATION_STATUS_UNKNOWN | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x4a | KDC_ERR_REVOCATION_STATUS_UNAVAILABLE | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x4b | KDC_ERR_CLIENT_NAME_MISMATCH | Reserved for PKINIT | |
| 0x4c | KDC_ERR_KDC_NAME_MISMATCH | Reserved for PKINIT |
- Pre-Authentication Type [Type = UnicodeString]: the code of pre-Authentication type that was used in TGT request.
| Type | Type Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | Logon without Pre-Authentication. |
| 2 | PA-ENC-TIMESTAMP | This type is normal for standard password authentication. |
| 11 | PA-ETYPE-INFO | The ETYPE-INFO pre-authentication type is sent by the KDC in a KRB-ERROR indicating a requirement for additional pre-authentication. It is usually used to notify a client of which key to use for the encryption of an encrypted timestamp for the purposes of sending a PA-ENC-TIMESTAMP pre-authentication value. Never saw this Pre-Authentication Type in Microsoft Active Directory environment. |
| 15 | PA-PK-AS-REP_OLD | Used for Smart Card logon authentication. |
| 16 | PA-PK-AS-REQ | Request sent to KDC in Smart Card authentication scenarios. |
| 17 | PA-PK-AS-REP | This type should also be used for Smart Card authentication, but in certain Active Directory environments, it is never seen. |
| 19 | PA-ETYPE-INFO2 | The ETYPE-INFO2 pre-authentication type is sent by the KDC in a KRB-ERROR indicating a requirement for additional pre-authentication. It is usually used to notify a client of which key to use for the encryption of an encrypted timestamp for the purposes of sending a PA-ENC-TIMESTAMP pre-authentication value. Never saw this Pre-Authentication Type in Microsoft Active Directory environment. |
| 20 | PA-SVR-REFERRAL-INFO | Used in KDC Referrals tickets. |
| 138 | PA-ENCRYPTED-CHALLENGE | Logon using Kerberos Armoring (FAST). Supported starting from Windows Server 2012 domain controllers and Windows 8 clients. |
| - | This type shows in Audit Failure events. |
Certificate Information:
Certificate Issuer Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of Certification Authority that issued smart card certificate. Populated in Issued by field in certificate. Always empty for 4771 events.
Certificate Serial Number [Type = UnicodeString]: smart card certificate's serial number. Can be found in Serial number field in the certificate. Always empty for 4771 events.
Certificate Thumbprint [Type = UnicodeString]: smart card certificate's thumbprint. Can be found in Thumbprint field in the certificate. Always empty for 4771 events.
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 4771(F): Kerberos pre-authentication failed.
| Type of monitoring required | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| High-value accounts: You might have high-value domain or local accounts for which you need to monitor each action. Examples of high-value accounts are database administrators, built-in local administrator account, domain administrators, service accounts, domain controller accounts and so on. |
Monitor this event with the "Security ID" that corresponds to the high-value account or accounts. |
| Anomalies or malicious actions: You might have specific requirements for detecting anomalies or monitoring potential malicious actions. For example, you might need to monitor for use of an account outside of working hours. | When you monitor for anomalies or malicious actions, use the "Security ID" (with other information) to monitor how or when a particular account is being used. |
| Non-active accounts: You might have non-active, disabled, or guest accounts, or other accounts that should never be used. | Monitor this event with the "Security ID" that corresponds to the accounts that should never be used. |
| Account allow list: You might have a specific allow list of accounts that are the only ones allowed to perform actions corresponding to particular events. | If this event corresponds to a "allow list-only" action, review the "Security ID" for accounts that are outside the allow list. |
| Account naming conventions: Your organization might have specific naming conventions for account names. | Monitor "Subject\Account Name" for names that don't comply with naming conventions. |
You can track all 4771 events where the Client Address is not from your internal IP range or not from private IP ranges.
If you know that Account Name should be used only from known list of IP addresses, track all Client Address values for this Account Name in 4771 events. If Client Address is not from the allow list, generate the alert.
All Client Address = ::1 means local authentication. If you know the list of accounts that should log on to the domain controllers, then you need to monitor for all possible violations, where Client Address = ::1 and Account Name is not allowed to log on to any domain controller.
All 4771 events with Client Port field value > 0 and < 1024 should be examined, because a well-known port was used for outbound connection.
Also monitor the fields shown in the following table, to discover the issues listed:
| Field | Issue to discover |
|---|---|
| Pre-Authentication Type | Value is not 15 when account must use a smart card for authentication. For more information, see Table 5. Kerberos Pre-Authentication types. |
| Pre-Authentication Type | Value is not 2 when only standard password authentication is in use in the organization. For more information, see Table 5. Kerberos Pre-Authentication types. |
| Pre-Authentication Type | Value is not 138 when Kerberos Armoring is enabled for all Kerberos communications in the organization. For more information, see Table 5. Kerberos Pre-Authentication types. |
| Failure Code | 0x10 (KDC has no support for PADATA type (pre-authentication data)). This error can help you to more quickly identify smart-card related problems with Kerberos authentication. |
| Failure Code | 0x18 ((Pre-authentication information was invalid), if you see, for example N events in last N minutes. This issue can indicate a brute-force attack on the account password, especially for highly critical accounts. |