Add Watch dialog box
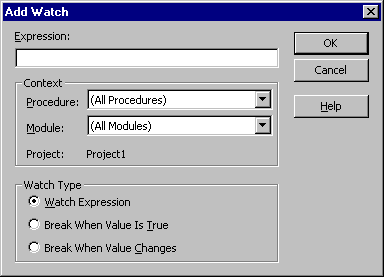
Use to enter a watch expression. The expression can be a variable, a property, a function call, or any other valid Basic expression.
Watch expressions are updated in the Watch window each time you enter break mode or after execution of each statement in the Immediate window.
You can drag selected expressions from the Code window into the Watch window.
Important
When selecting a context for a watch expression, use the narrowest scope that fits your needs. Selecting all procedures or all modules could slow down execution considerably because the expression is evaluated after execution of each statement. Selecting a specific procedure for a context affects execution only while the procedure is in the list of active procedure calls, which you can see by choosing the Call Stack command on the View menu.
The following table describes the dialog box options.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Expression | Displays the selected expression by default. The expression is a variable, a property, a function call, or any other valid expression. You may enter a different expression to evaluate. |
| Context | Sets the scope of the variables watched in the expression. - Procedure: Displays the procedure name where the selected term resides (default). Defines the procedure(s) in which the expression is evaluated. You may select all procedures or a specific procedure context in which to evaluate the variable. - Module: Displays the module name where the selected term resides (default). You may select all modules or a specific module context in which to evaluate the variable. - Project: Displays the name of the current project. Expressions can't be evaluated in a context outside of the current project. |
| Watch Type | Determines how Visual Basic responds to the watch expression. - Watch Expression: Displays the watch expression and its value in the Watch window. When you enter break mode, the value of the watch expression is automatically updated. - Break When Value Is True: Execution automatically enters break mode when the expression evaluates to true or is any nonzero value (not valid for string expressions). - Break When Value Changes: Execution automatically enters break mode when the value of the expression changes within the specified context. |
See also
Support and feedback
Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.