Configure 3-tier deployment architecture using Application Request Routing
by IIS Team
Overview
This topic leads you through the steps to configure a 3-tier deployment architecture using Application Request Routing. The 3-tier deployment architecture consists of a Web tier, an application server tier, and a data tier, as shown below:
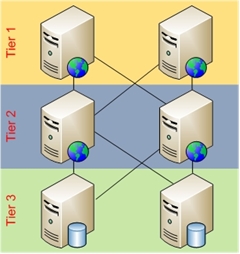
Typically in this deployment scenario, static content is served by the tier 1 servers while dynamic content is served by the business logic in tier 2 servers.
Goal
To configure 3-tier deployment architecture using Application Request Routing. In this walkthrough, the focus is on how to configure the ARR server to serve static content directly from the ARR server while forwarding the requests for dynamic content to the application servers.
Prerequisites
This walkthrough requires the following prerequisites:
- IIS 7.0 or above on Windows 2008 (any SKU) or newer
- Microsoft Application Request Routing Version 1 and dependent modules
- Minimum of two content servers with working sites and applications
- Static content available on the Application Request Routing server
Follow the steps outlined in this document to install Application Request Routing.
As another prerequisite, you must have defined and configured a server farm using the steps outlined in Define and Configure an Application Request Routing (ARR) Server Group.
Step 1 – Change URL rewrite rules to filter for static requests.
In this step, URL rewrite rules are changed so that requests for certain extensions or paths are served directly from the Application Request Routing server. Static requests can be identified by looking at the file extensions, such as .jpg or .gif. If the static resources are contained in certain folders, such as /images/, then the URL rewrite rules can look for the path in the URL.
In this walkthrough, you will change the URL rewrite rules to look for .jpg and .css extensions, along with the /images/ folder. If the requested resource has a .jpg or .css extension, it will be served directly from the ARR server. Similarly, if the requested URL contains /images/, then this request will be served from the ARR server. All other requests will be forwarded to application servers behind the ARR server.
Before proceeding, make sure that the static content is available on the ARR server to serve. The content can either be made available locally on the ARR server or shared content can be used.
To change URL rewrite rules using the UI:
- Launch IIS Manager.
- Select the server farm, myServerFarm, which was created in Define and Configure an Application Request Routing (ARR) Server Group.
- The following icons are shown:
- Double click Routing Rules. Type *.jpg and *.css in the Requests with the following extensions are not forwarded text box. The multiple extensions are comma (,) separated. To match the path in URL, type */image/* in the Requests with the following patterns are not forwarded text box. The wildcard character (*) is used to match any character before and after the path /image/.

- To verify that the static images are being served from the ARR server, inspect the logs. By default, the logs are in
c:\inetpub\logs\LogFiles\. On application servers behind the ARR server, there should not be any requests that reference *.jpg, *.css or */images/* in the log file.
To change URL rewrite rules using the command-line:
Open a command prompt with administrator privileges.
Navigate to
%windir%\system32\inetsrv.Clear all URL rewrite rules by entering:
appcmd.exe clear config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules
To change the routing rules so that requests for resources with extensions *.jpg and *.css and a path that matches */images/* are not forwarded to the application servers, enter:
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules /+"[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessing='True']" /commit:apphostappcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules /[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessing='True'].match.url:"*" /commit:apphostappcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules /+"[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessing='True'].conditions. [input='EXT_{URL}',negate='True',pattern='*.jpg']" /commit:apphostappcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules /+"[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessing='True'].conditions. [input='EXT_{URL}',negate='True',pattern='*.css']" /commit:apphostappcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules /+"[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessing='True'].conditions. [input='{URL}',negate='True',pattern='*/images/*']" /commit:apphostappcmd.exe set config -section:system.webServer/rewrite/globalRules /[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessing='True'].action.type:"Rewrite" /[name='ARR_myServerFarm_loadbalance',patternSyntax='Wildcard',stopProcessing='True'].action.url:"http://myServerFarm1/{R:0}" /commit:apphost
Summary
You have now successfully changed URL rewrite rules using the Application Request Routing UI to enable a 3-tier deployment architecture scenario. For additional Application Request Routing properties and capabilities, refer to the HTTP Load Balancing using Application Request Routing (ARR) walkthrough.
When ARR is used as a reverse proxy, the scenario can be further enhanced when used with URL Rewrite Version 2 which has the feature to rewrite the response headers and entity body.