建立簡單的 Direct2D 應用程式
本主題將逐步引導您完成建立 DemoApp 類別的程式,此類別會建立視窗,並使用 Direct2D 來繪製內容。 在本教學課程中,您將瞭解如何建立 Direct2D 資源,以及繪製基本圖形。 您也會瞭解如何將資源建立降至最低,以建構應用程式以增強效能。
若要遵循本教學課程,您可以使用 Microsoft Visual Studio 來建立 Win32 專案,然後將主要應用程式標頭和 .cpp 檔案中的程式碼取代為本教學課程中所述的程式碼。
另請參閱 GitHub 上的簡單 Direct2D 應用程式範例應用程式。
注意
如果您想要建立使用 Direct2D 的 通用 Windows 平臺 (UWP) app,請參閱適用于 Windows 8 的 Direct2D 快速入門主題。
如需可用來建立 Direct2D 內容的介面概觀,請參閱 Direct2D API 概觀。
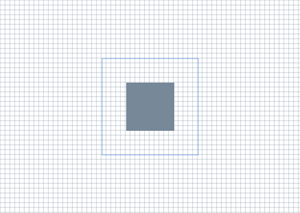
完成本教學課程之後, DemoApp 類別會產生下圖所示的輸出。
第 1 部分:建立 DemoApp 標頭
在此步驟中,您會新增必要的標頭和宏,將應用程式設定為使用 Direct2D。 您也會宣告您將在本教學課程稍後部分使用的方法和資料成員。
在應用程式標頭檔中,包含下列常用標頭。
// Windows Header Files: #include <windows.h> // C RunTime Header Files: #include <stdlib.h> #include <malloc.h> #include <memory.h> #include <wchar.h> #include <math.h> #include <d2d1.h> #include <d2d1helper.h> #include <dwrite.h> #include <wincodec.h>宣告發行介面的其他函式,以及用於錯誤處理和擷取模組基底位址的宏。
template<class Interface> inline void SafeRelease( Interface **ppInterfaceToRelease) { if (*ppInterfaceToRelease != NULL) { (*ppInterfaceToRelease)->Release(); (*ppInterfaceToRelease) = NULL; } } #ifndef Assert #if defined( DEBUG ) || defined( _DEBUG ) #define Assert(b) do {if (!(b)) {OutputDebugStringA("Assert: " #b "\n");}} while(0) #else #define Assert(b) #endif //DEBUG || _DEBUG #endif #ifndef HINST_THISCOMPONENT EXTERN_C IMAGE_DOS_HEADER __ImageBase; #define HINST_THISCOMPONENT ((HINSTANCE)&__ImageBase) #endif宣告方法以初始化 類別、建立和捨棄資源、處理訊息迴圈、轉譯內容和視窗程式。
class DemoApp { public: DemoApp(); ~DemoApp(); // Register the window class and call methods for instantiating drawing resources HRESULT Initialize(); // Process and dispatch messages void RunMessageLoop(); private: // Initialize device-independent resources. HRESULT CreateDeviceIndependentResources(); // Initialize device-dependent resources. HRESULT CreateDeviceResources(); // Release device-dependent resource. void DiscardDeviceResources(); // Draw content. HRESULT OnRender(); // Resize the render target. void OnResize( UINT width, UINT height ); // The windows procedure. static LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc( HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam ); };做為類別成員,宣告 ID2D1Factory 物件的指標、 ID2D1HwndRenderTarget 物件,以及兩個 ID2D1SolidColorBrush 物件。
private: HWND m_hwnd; ID2D1Factory* m_pDirect2dFactory; ID2D1HwndRenderTarget* m_pRenderTarget; ID2D1SolidColorBrush* m_pLightSlateGrayBrush; ID2D1SolidColorBrush* m_pCornflowerBlueBrush;
第 2 部分:實作類別基礎結構
在此部分中,您會實作 DemoApp 建構函式和解構函式、其初始化和訊息迴圈方法,以及 WinMain 函式。 這些方法大多看起來與任何其他 Win32 應用程式中找到的方法相同。 唯一的例外是 Initialize 方法,它會呼叫 CreateDeviceIndependentResources 方法 (您將在下一個部分定義) ,這會建立數個 Direct2D 資源。
在類別實作檔案中,實作類別建構函式和解構函式。 建構函式應該將其成員初始化為
NULL。 解構函式應該釋放儲存為類別成員的任何介面。DemoApp::DemoApp() : m_hwnd(NULL), m_pDirect2dFactory(NULL), m_pRenderTarget(NULL), m_pLightSlateGrayBrush(NULL), m_pCornflowerBlueBrush(NULL) {} DemoApp::~DemoApp() { SafeRelease(&m_pDirect2dFactory); SafeRelease(&m_pRenderTarget); SafeRelease(&m_pLightSlateGrayBrush); SafeRelease(&m_pCornflowerBlueBrush); }實作 DemoApp::RunMessageLoop 方法,此方法會轉譯和分派訊息。
void DemoApp::RunMessageLoop() { MSG msg; while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0)) { TranslateMessage(&msg); DispatchMessage(&msg); } }實作 Initialize 方法,這個方法會建立視窗、顯示視窗,並呼叫 DemoApp::CreateDeviceIndependentResources 方法。 您將在下一節中實作 CreateDeviceIndependentResources 方法。
HRESULT DemoApp::Initialize() { HRESULT hr; // Initialize device-independent resources, such // as the Direct2D factory. hr = CreateDeviceIndependentResources(); if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { // Register the window class. WNDCLASSEX wcex = { sizeof(WNDCLASSEX) }; wcex.style = CS_HREDRAW | CS_VREDRAW; wcex.lpfnWndProc = DemoApp::WndProc; wcex.cbClsExtra = 0; wcex.cbWndExtra = sizeof(LONG_PTR); wcex.hInstance = HINST_THISCOMPONENT; wcex.hbrBackground = NULL; wcex.lpszMenuName = NULL; wcex.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION); wcex.lpszClassName = L"D2DDemoApp"; RegisterClassEx(&wcex); // In terms of using the correct DPI, to create a window at a specific size // like this, the procedure is to first create the window hidden. Then we get // the actual DPI from the HWND (which will be assigned by whichever monitor // the window is created on). Then we use SetWindowPos to resize it to the // correct DPI-scaled size, then we use ShowWindow to show it. m_hwnd = CreateWindow( L"D2DDemoApp", L"Direct2D demo application", WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW, CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, 0, 0, NULL, NULL, HINST_THISCOMPONENT, this); if (m_hwnd) { // Because the SetWindowPos function takes its size in pixels, we // obtain the window's DPI, and use it to scale the window size. float dpi = GetDpiForWindow(m_hwnd); SetWindowPos( m_hwnd, NULL, NULL, NULL, static_cast<int>(ceil(640.f * dpi / 96.f)), static_cast<int>(ceil(480.f * dpi / 96.f)), SWP_NOMOVE); ShowWindow(m_hwnd, SW_SHOWNORMAL); UpdateWindow(m_hwnd); } } return hr; }實作 WinMain 方法,做為應用程式進入點。 初始化 DemoApp的實例,類別並開始其訊息迴圈。
int WINAPI WinMain( HINSTANCE /* hInstance */, HINSTANCE /* hPrevInstance */, LPSTR /* lpCmdLine */, int /* nCmdShow */ ) { // Use HeapSetInformation to specify that the process should // terminate if the heap manager detects an error in any heap used // by the process. // The return value is ignored, because we want to continue running in the // unlikely event that HeapSetInformation fails. HeapSetInformation(NULL, HeapEnableTerminationOnCorruption, NULL, 0); if (SUCCEEDED(CoInitialize(NULL))) { { DemoApp app; if (SUCCEEDED(app.Initialize())) { app.RunMessageLoop(); } } CoUninitialize(); } return 0; }
第 3 部分:建立 Direct2D 資源
在此部分中,您會建立用來繪製的 Direct2D 資源。 Direct2D 提供兩種類型的資源:裝置獨立資源,可在應用程式期間持續,以及裝置相依資源。 裝置相依資源與特定轉譯裝置相關聯,如果移除該裝置,將會停止運作。
實作 DemoApp::CreateDeviceIndependentResources 方法。 在 方法中,建立 ID2D1Factory,這是建立其他 Direct2D 資源的裝置獨立資源。
m_pDirect2DdFactory使用類別成員來儲存處理站。HRESULT DemoApp::CreateDeviceIndependentResources() { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // Create a Direct2D factory. hr = D2D1CreateFactory(D2D1_FACTORY_TYPE_SINGLE_THREADED, &m_pDirect2dFactory); return hr; }實作 DemoApp::CreateDeviceResources 方法。 這個方法會建立視窗的裝置相依資源、轉譯目標,以及兩個筆刷。 擷取工作區的大小,並建立與視窗HWND相同大小的ID2D1HwndRenderTarget。 將轉譯目標儲存在類別成員中
m_pRenderTarget。RECT rc; GetClientRect(m_hwnd, &rc); D2D1_SIZE_U size = D2D1::SizeU( rc.right - rc.left, rc.bottom - rc.top); // Create a Direct2D render target. hr = m_pDirect2dFactory->CreateHwndRenderTarget( D2D1::RenderTargetProperties(), D2D1::HwndRenderTargetProperties(m_hwnd, size), &m_pRenderTarget);使用轉譯目標來建立灰色 ID2D1SolidColorBrush 和一個圓角花藍色 ID2D1SolidColorBrush。
if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { // Create a gray brush. hr = m_pRenderTarget->CreateSolidColorBrush( D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::LightSlateGray), &m_pLightSlateGrayBrush ); } if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { // Create a blue brush. hr = m_pRenderTarget->CreateSolidColorBrush( D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::CornflowerBlue), &m_pCornflowerBlueBrush ); }因為這個方法會重複呼叫,所以請新增
if語句,以檢查轉譯目標 (m_pRenderTarget) 是否存在。 下列程式碼顯示完整的 CreateDeviceResources 方法。HRESULT DemoApp::CreateDeviceResources() { HRESULT hr = S_OK; if (!m_pRenderTarget) { RECT rc; GetClientRect(m_hwnd, &rc); D2D1_SIZE_U size = D2D1::SizeU( rc.right - rc.left, rc.bottom - rc.top ); // Create a Direct2D render target. hr = m_pDirect2dFactory->CreateHwndRenderTarget( D2D1::RenderTargetProperties(), D2D1::HwndRenderTargetProperties(m_hwnd, size), &m_pRenderTarget ); if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { // Create a gray brush. hr = m_pRenderTarget->CreateSolidColorBrush( D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::LightSlateGray), &m_pLightSlateGrayBrush ); } if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) { // Create a blue brush. hr = m_pRenderTarget->CreateSolidColorBrush( D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::CornflowerBlue), &m_pCornflowerBlueBrush ); } } return hr; }實作 DemoApp::D iscardDeviceResources 方法。 在此方法中,釋放您在 DemoApp::CreateDeviceResources 方法中建立的轉譯目標和兩個筆刷。
void DemoApp::DiscardDeviceResources() { SafeRelease(&m_pRenderTarget); SafeRelease(&m_pLightSlateGrayBrush); SafeRelease(&m_pCornflowerBlueBrush); }
第 4 部分:轉譯 Direct2D 內容
在此部分中,您會實作視窗程式、 OnRender 方法 (繪製內容) ,以及 OnResize 方法 (,以在視窗調整大小時調整轉譯目標的大小) 。
實作 DemoApp::WndProc 方法來處理視窗訊息。 針對 WM_SIZE 訊息,呼叫 DemoApp::OnResize 方法,並將新的寬度和高度傳遞。 針對 WM_PAINT 和 WM_DISPLAYCHANGE 訊息,請呼叫 DemoApp::OnRender 方法來繪製視窗。 您將在後續步驟中實作 OnRender 和 OnResize 方法。
LRESULT CALLBACK DemoApp::WndProc(HWND hwnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam) { LRESULT result = 0; if (message == WM_CREATE) { LPCREATESTRUCT pcs = (LPCREATESTRUCT)lParam; DemoApp *pDemoApp = (DemoApp *)pcs->lpCreateParams; ::SetWindowLongPtrW( hwnd, GWLP_USERDATA, reinterpret_cast<LONG_PTR>(pDemoApp) ); result = 1; } else { DemoApp *pDemoApp = reinterpret_cast<DemoApp *>(static_cast<LONG_PTR>( ::GetWindowLongPtrW( hwnd, GWLP_USERDATA ))); bool wasHandled = false; if (pDemoApp) { switch (message) { case WM_SIZE: { UINT width = LOWORD(lParam); UINT height = HIWORD(lParam); pDemoApp->OnResize(width, height); } result = 0; wasHandled = true; break; case WM_DISPLAYCHANGE: { InvalidateRect(hwnd, NULL, FALSE); } result = 0; wasHandled = true; break; case WM_PAINT: { pDemoApp->OnRender(); ValidateRect(hwnd, NULL); } result = 0; wasHandled = true; break; case WM_DESTROY: { PostQuitMessage(0); } result = 1; wasHandled = true; break; } } if (!wasHandled) { result = DefWindowProc(hwnd, message, wParam, lParam); } } return result; }實作 DemoApp::OnRender 方法。 首先,定義 HRESULT。 然後呼叫 CreateDeviceResource 方法。 每次繪製視窗時都會呼叫該方法。 回想一下,在第 3 部分的步驟 4 中,您已新增
if語句,以防止方法在轉譯目標已經存在時執行任何工作。HRESULT DemoApp::OnRender() { HRESULT hr = S_OK; hr = CreateDeviceResources();確認 CreateDeviceResource 方法成功。 如果未執行,則請勿執行任何繪圖。
if (SUCCEEDED(hr)) {在您剛才新增的
if語句內,呼叫轉譯目標的 BeginDraw 方法來起始繪圖。 將轉譯目標的轉換設定為識別矩陣,然後清除視窗。m_pRenderTarget->BeginDraw(); m_pRenderTarget->SetTransform(D2D1::Matrix3x2F::Identity()); m_pRenderTarget->Clear(D2D1::ColorF(D2D1::ColorF::White));擷取繪圖區域的大小。
D2D1_SIZE_F rtSize = m_pRenderTarget->GetSize();使用
for迴圈和轉譯目標的 DrawLine 方法來繪製一數列線條,繪製格線背景。// Draw a grid background. int width = static_cast<int>(rtSize.width); int height = static_cast<int>(rtSize.height); for (int x = 0; x < width; x += 10) { m_pRenderTarget->DrawLine( D2D1::Point2F(static_cast<FLOAT>(x), 0.0f), D2D1::Point2F(static_cast<FLOAT>(x), rtSize.height), m_pLightSlateGrayBrush, 0.5f ); } for (int y = 0; y < height; y += 10) { m_pRenderTarget->DrawLine( D2D1::Point2F(0.0f, static_cast<FLOAT>(y)), D2D1::Point2F(rtSize.width, static_cast<FLOAT>(y)), m_pLightSlateGrayBrush, 0.5f ); }建立兩個以螢幕為中心的矩形基本類型。
// Draw two rectangles. D2D1_RECT_F rectangle1 = D2D1::RectF( rtSize.width/2 - 50.0f, rtSize.height/2 - 50.0f, rtSize.width/2 + 50.0f, rtSize.height/2 + 50.0f ); D2D1_RECT_F rectangle2 = D2D1::RectF( rtSize.width/2 - 100.0f, rtSize.height/2 - 100.0f, rtSize.width/2 + 100.0f, rtSize.height/2 + 100.0f );使用轉譯目標的 FillRectangle 方法,以灰色筆刷繪製第一個矩形的內部。
// Draw a filled rectangle. m_pRenderTarget->FillRectangle(&rectangle1, m_pLightSlateGrayBrush);使用轉譯目標的 DrawRectangle 方法,使用菜花藍色筆刷繪製第二個矩形的外框。
// Draw the outline of a rectangle. m_pRenderTarget->DrawRectangle(&rectangle2, m_pCornflowerBlueBrush);呼叫轉譯目標的 EndDraw 方法。 EndDraw方法會傳回HRESULT,以指出繪圖作業是否成功。 關閉您在步驟 3 中開始的
if語句範圍。hr = m_pRenderTarget->EndDraw(); }檢查EndDraw傳回的HRESULT。 如果它指出必須重新建立轉譯目標,請呼叫 DemoApp::D iscardDeviceResources 方法來釋放它;它會在下一次視窗收到 WM_PAINT 或 WM_DISPLAYCHANGE 訊息時重新建立。
if (hr == D2DERR_RECREATE_TARGET) { hr = S_OK; DiscardDeviceResources(); }傳回 HRESULT,並關閉方法的範圍。
return hr; }實作 DemoApp::OnResize 方法,以便將轉譯目標調整為視窗的新大小。
void DemoApp::OnResize(UINT width, UINT height) { if (m_pRenderTarget) { // Note: This method can fail, but it's okay to ignore the // error here, because the error will be returned again // the next time EndDraw is called. m_pRenderTarget->Resize(D2D1::SizeU(width, height)); } }
您現在已完成教學課程。
注意
若要使用 Direct2D,請確定您的應用程式包含 d2d1.h 標頭檔,並針對 d2d1.lib 程式庫進行編譯。 您可以在Windows SDK中找到 d2d1.h 和 d2d1.lib 。
摘要
在本教學課程中,您已瞭解如何建立 Direct2D 資源,以及繪製基本圖形。 您也瞭解如何建構應用程式,藉由將資源建立降至最低來增強效能。