Windows 365 中的警示
Windows 365 警示系統會在雲端計算機環境中發生特定事件時通知您,例如連線、布建或映射上傳失敗。 當您已達到或超過 Windows 365 Frontline 雲端電腦的最大並行閾值時,也會有警示通知您。 根據預設,警示會在 Microsoft Intune 系統管理中心中顯示為快顯通知 (您也可以開啟電子郵件通知) 。 您可以自訂內建警示規則:
- 設定觸發警示的條件和閾值。
- 定義警示的嚴重性。
- 開啟或關閉每個警示規則。
- 設定每個警示,以在主控台和/或透過電子郵件通知您。
如果電子郵件已開啟,則觸發警示規則時,會將一封電子郵件傳送至指定的電子郵件位址。 解決警示之後,如果再次觸發,則會將另一封電子郵件傳送至指定的位址。
需求
若要查看警示,您的帳戶必須符合下列需求:
- Windows 365 企業版
- 下列其中一個角色:
- Intune 系統管理員
- Windows 365系統管理員
檢視警示
若要檢視最近的警示清單,請登入 Microsoft Intune 系統管理中心>租用戶系統管理>警示。
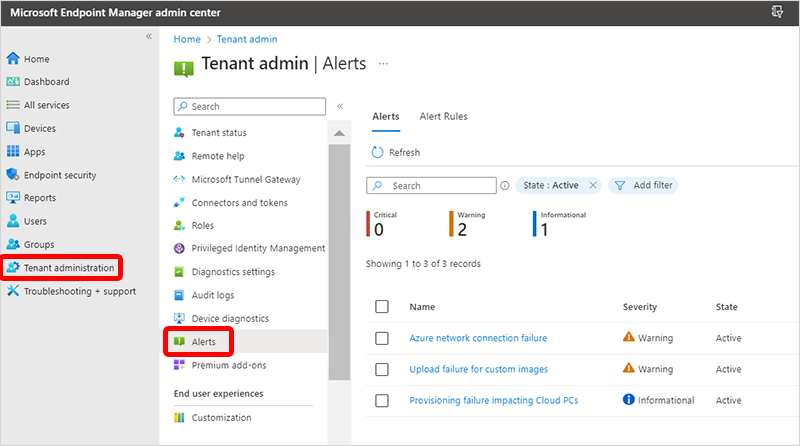
篩選
根據預設,只會顯示作用中的警示。 您可以使用 [新增篩選] 選項來篩選:
- 嚴重性
- 參考
- 警告
- 重大
- 狀態
- 作用中
- Resolved
警示摘要
您可以從清單中選取警示,以查看該警示的摘要。
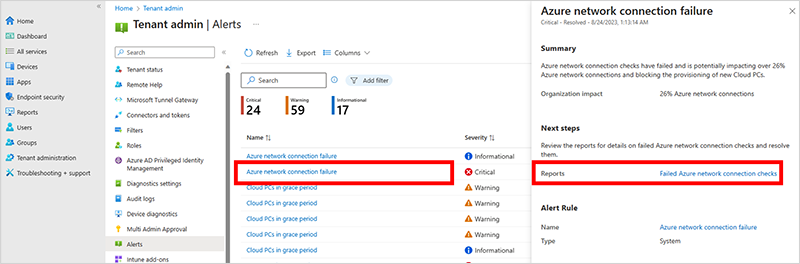
選取 [報表] 旁的連結,以查看更多詳細數據。
自訂警示規則
登入 Microsoft Intune 系統管理中心>租用戶系統管理>警示>規則。
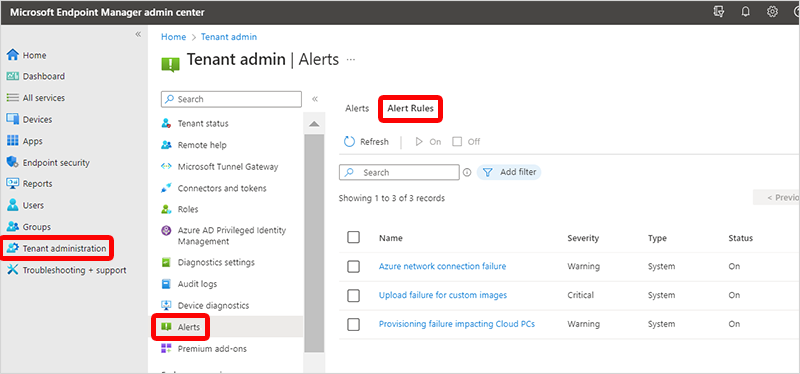
從清單中選取規則。
在 [ 系統規則] 頁面上,於 [ 條件]、[ 設定] 和 [ 通知 ] 區段中進行您想要的任何變更。
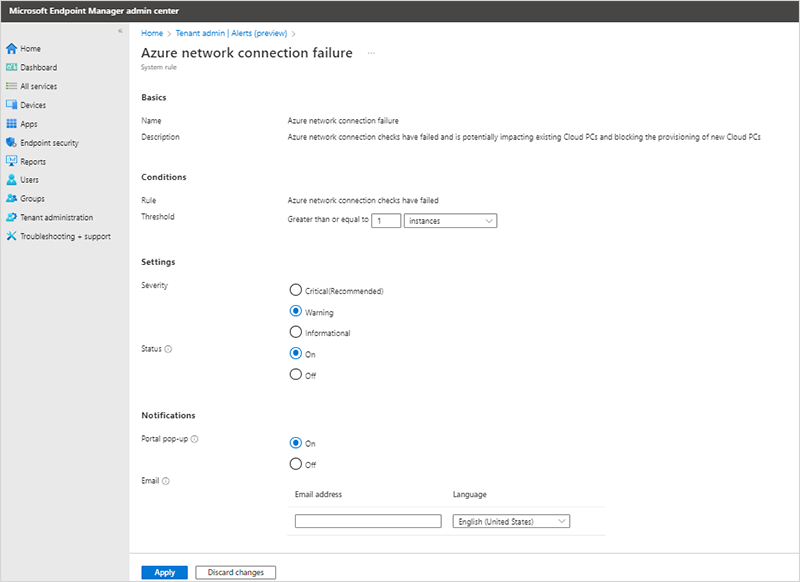
選 取 [套用 ] 以將變更儲存至規則。
後續步驟
如需詳細疑難解答資訊,請參閱 疑難解答。