SkiaSharp 中的 3D 旋轉
使用非仿射轉換在 3D 空間中旋轉 2D 物件。
非仿射轉換的一個常見應用是在 3D 空間中模擬 2D 物件的旋轉:
此作業牽涉到使用三維旋轉,然後衍生執行這些 3D 旋轉的非仿射 SKMatrix 轉換。
很難開發此 SKMatrix 轉換,只可在兩個維度內運作。 當這個 3 by-3 矩陣衍生自 3D 圖形中使用的 4 by-4 矩陣時,作業會變得更容易。 SkiaSharp 包含此用途的 SKMatrix44 類別,但需要 3D 圖形中的一些背景,才能瞭解 3D 旋轉和 4 位元組 4 轉換矩陣。
立體座標系統會在概念上新增第三個座標軸,稱為 Z。在概念上,Z 軸位於螢幕的直角。 3D 空間中的座標點以三個數位表示:(x、y、z)。 在本文中使用的 3D 座標系統中,X 的值會向右增加,而 Y 的值就會下降,就像在兩個維度中一樣。 增加正 Z 值會從畫面中取出。 原點是左上角,就像在 2D 圖形中一樣。 您可以將螢幕視為 XY 平面,其中 Z 軸位於此平面的直角。
這稱為左側座標系統。 如果您將左手的食指指向正 X 座標的方向(向右),而您的中指方向會增加 Y 座標(向下),則您的拇指指向增加 Z 座標的方向—從螢幕延伸出來。
在 3D 圖形中,轉換是以 4 by-4 矩陣為基礎。 以下是 4 by-4 身分識別矩陣:
| 1 0 0 0 | | 0 1 0 0 | | 0 0 1 0 | | 0 0 0 1 |
在使用 4 by-4 矩陣時,使用其數據列和數據行編號來識別儲存格是很方便的:
| M11 M12 M13 M14 | | M21 M22 M23 M24 | | M31 M32 M33 M34 | | M41 M42 M43 M44 |
不過,SkiaSharp Matrix44 類別有點不同。 在 中 SKMatrix44 設定或取得個別儲存格值的唯一方法是使用 Item 索引器。 數據列和數據行索引是以零起始,而不是以一為基底,而且會交換數據列和數據行。 上圖中的儲存格 M14 是使用物件中的SKMatrix44索引器[3, 0]來存取。
在 3D 圖形系統中,3D 點 (x, y, z) 會轉換成 1 by-4 矩陣,以乘以 4-by-4 轉換矩陣:
| M11 M12 M13 M14 |
| x y z 1 | × | M21 M22 M23 M24 | = | x' y' z' w' |
| M31 M32 M33 M34 |
| M41 M42 M43 M44 |
類似於在三個維度中發生的 2D 轉換,假設 3D 轉換會在四個維度中進行。 第四個維度稱為 W,而 3D 空間則假設存在於 W 座標等於 1 的 4D 空間內。 轉換公式如下所示:
x' = M11·x + M21·y + M31·z + M41
y' = M12·x + M22·y + M32·z + M42
z' = M13·x + M23·y + M33·z + M43
w' = M14·x + M24·y + M34·z + M44
從轉換公式中很明顯,單元格、 是 X、Y 和 Z 方向中的縮放因數,以及 M41、 和 ,以及 M43 是 X、Y 和 Z 方向中的轉譯因數。 M33M22M11M42
若要將這些座標轉換成 W 等於 1 的 3D 空間,x'、y'和 z' 座標全都除以 w':
x" = x' / w'
y" = y' / w'
z" = z' / w'
w" = w' / w' = 1
依 w' 的除法在 3D 空間中提供透視。 如果 w' 等於 1,則不會發生任何檢視方塊。
3D 空間中的旋轉可能相當複雜,但最簡單的旋轉是圍繞 X、Y 和 Z 軸的旋轉。 在 X 軸周圍α角度的旋轉是這個矩陣:
| 1 0 0 0 | | 0 cos(α) sin(α) 0 | | 0 –sin(α) cos(α) 0 | | 0 0 0 1 |
受此轉換約束時,X 的值會維持不變。 繞 Y 軸旋轉會保留 Y 的值不變:
| cos(α) 0 –sin(α) 0 | | 0 1 0 0 | | sin(α) 0 cos(α) 0 | | 0 0 0 1 |
繞 Z 軸旋轉與 2D 圖形相同:
| cos(α) sin(α) 0 0 | | –sin(α) cos(α) 0 0 | | 0 0 1 0 | | 0 0 0 1 |
旋轉方向是由座標系統的手部所隱含。 這是一個左手系統,因此,如果您將左手的拇指指向特定座標軸的遞增值-向右旋轉 X 軸,向下旋轉 Y 軸,朝您方向旋轉 Z 軸,則其他手指的曲線表示正角度的旋轉方向。
SKMatrix44 具有一般化的靜態 CreateRotation 和 CreateRotationDegrees 方法,可讓您指定旋轉周圍的軸:
public static SKMatrix44 CreateRotationDegrees (Single x, Single y, Single z, Single degrees)
若要繞 X 軸旋轉,請將前三個自變數設定為 1,0, 0。 若為繞 Y 軸旋轉,請將它們設定為 0、1、0,以及繞 Z 軸旋轉,將它們設定為 0、0、1。
4 by-4 的第四個數據行適用於檢視方塊。 SKMatrix44沒有建立檢視方塊轉換的方法,但您可以使用下列程式代碼自行建立:
SKMatrix44 perspectiveMatrix = SKMatrix44.CreateIdentity();
perspectiveMatrix[3, 2] = -1 / depth;
自變數名稱 depth 的原因很快就會明顯。 該程式代碼會建立矩陣:
| 1 0 0 0 | | 0 1 0 0 | | 0 0 1 -1/depth | | 0 0 0 1 |
轉換公式會產生下列 w『計算:
w' = –z / depth + 1
當 Z 的值小於零時,這會減少 X 和 Y 座標(在 XY 平面後方),並增加 Z 正值的 X 和 Y 座標。當 Z 座標等於 depth時,則 w' 為零,座標會變成無限。 立體圖形系統是圍繞相機隱喻所建置的, depth 此處的值代表相機與座標系統原點之間的距離。 如果圖形物件具有與原點單位相等的 Z 座標 depth ,則會在概念上觸碰相機的鏡頭,並變成無限大。
請記住,您可能將此值 perspectiveMatrix 與旋轉矩陣搭配使用。 如果旋轉的圖形物件具有 X depth或 Y 座標大於 ,則此物件在 3D 空間中的旋轉可能會涉及大於 depth的 Z 座標。 這必須避免! 當您建立 perspectiveMatrix 時,不論圖形物件中的旋轉方式為何,都想要設定 depth 為大小足以容納圖形物件中所有座標的值。 這可確保絕不會有零除法。
結合 3D 旋轉和透視需要將 4 乘以 4 矩陣相乘。 為此, SKMatrix44 定義串連方法。 如果 A 與 B 物件 SKMatrix44 ,則下列程式代碼會將 A 設定為 A 等於 A × B:
A.PostConcat(B);
在 2D 圖形系統中使用 4 by-4 轉換矩陣時,它會套用至 2D 物件。 這些對像是平面的,並假設 Z 座標為零。 轉換乘法比稍早顯示的轉換簡單一點:
| M11 M12 M13 M14 |
| x y 0 1 | × | M21 M22 M23 M24 | = | x' y' z' w' |
| M31 M32 M33 M34 |
| M41 M42 M43 M44 |
z 的這個 0 值會產生轉換公式,這些公式不包含矩陣第三個數據列中的任何儲存格:
x' = M11·x + M21·y + M41
y' = M12·x + M22·y + M42
z' = M13·x + M23·y + M43
w' = M14·x + M24·y + M44
此外,z 的座標也在這裡無關緊要。 當 3D 對象顯示在 2D 圖形系統中時,它會忽略 Z 座標值,折疊成二維物件。 轉換公式實際上只是這兩個:
x" = x' / w'
y" = y' / w'
這表示可以忽略 4 位元組 4 矩陣的第三列 和第 三欄。
但是,如果這是這樣,為什麼 4 比 4 矩陣在一開始甚至是必要的?
雖然 4 對 4 的第三個數據列和第三個數據行與二維轉換無關,但第三個數據列和數據行 會在 各種 SKMatrix44 值相乘時扮演角色。 例如,假設您將旋轉角度乘以 Y 軸與透視轉換:
| cos(α) 0 –sin(α) 0 | | 1 0 0 0 | | cos(α) 0 –sin(α) sin(α)/depth | | 0 1 0 0 | × | 0 1 0 0 | = | 0 1 0 0 | | sin(α) 0 cos(α) 0 | | 0 0 1 -1/depth | | sin(α) 0 cos(α) -cos(α)/depth | | 0 0 0 1 | | 0 0 0 1 | | 0 0 0 1 |
在產品中,儲存格 M14 現在包含檢視方塊值。 如果您想要將該矩陣套用至 2D 物件,則會排除第三個數據列和數據行,以將它轉換成 3 by-3 矩陣:
| cos(α) 0 sin(α)/depth | | 0 1 0 | | 0 0 1 |
現在可用來轉換 2D 點:
| cos(α) 0 sin(α)/depth |
| x y 1 | × | 0 1 0 | = | x' y' z' |
| 0 0 1 |
轉換公式如下:
x' = cos(α)·x
y' = y
z' = (sin(α)/depth)·x + 1
現在,將所有專案除以 z':
x" = cos(α)·x / ((sin(α)/depth)·x + 1)
y" = y / ((sin(α)/depth)·x + 1)
當 2D 物件繞 Y 軸旋轉正角度時,正 X 值會回到背景,而負 X 值則來到前景。 X 值似乎更接近 Y 軸(由餘弦值控管),因為距離 Y 軸最遠的座標會變小或更大,因為它們會從查看器進一步移動,或更接近查看器。
使用 SKMatrix44時,會乘以各種 SKMatrix44 值來執行所有 3D 旋轉和檢視方塊作業。 然後,您可以使用 類別的 SKMatrix44 屬性,從 4-by-4 矩陣擷取二維 3-by-3 矩陣Matrix。 這個屬性會傳回熟悉 SKMatrix 的值。
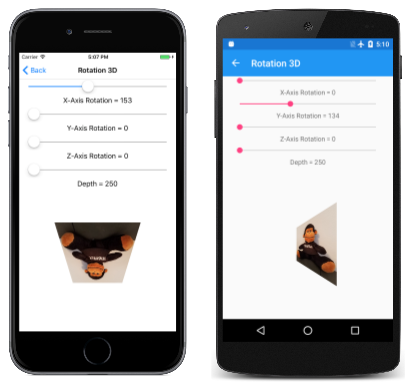
[ 旋轉 3D] 頁面可讓您實驗 3D 旋轉。 Rotation3DPage.xaml 檔案會具現化四個滑桿,以設定圍繞 X、Y 和 Z 軸的旋轉,以及設定深度值:
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:skia="clr-namespace:SkiaSharp.Views.Forms;assembly=SkiaSharp.Views.Forms"
x:Class="SkiaSharpFormsDemos.Transforms.Rotation3DPage"
Title="Rotation 3D">
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.Resources>
<ResourceDictionary>
<Style TargetType="Label">
<Setter Property="HorizontalTextAlignment" Value="Center" />
</Style>
<Style TargetType="Slider">
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="20, 0" />
<Setter Property="Maximum" Value="360" />
</Style>
</ResourceDictionary>
</Grid.Resources>
<Slider x:Name="xRotateSlider"
Grid.Row="0"
ValueChanged="OnSliderValueChanged" />
<Label Text="{Binding Source={x:Reference xRotateSlider},
Path=Value,
StringFormat='X-Axis Rotation = {0:F0}'}"
Grid.Row="1" />
<Slider x:Name="yRotateSlider"
Grid.Row="2"
ValueChanged="OnSliderValueChanged" />
<Label Text="{Binding Source={x:Reference yRotateSlider},
Path=Value,
StringFormat='Y-Axis Rotation = {0:F0}'}"
Grid.Row="3" />
<Slider x:Name="zRotateSlider"
Grid.Row="4"
ValueChanged="OnSliderValueChanged" />
<Label Text="{Binding Source={x:Reference zRotateSlider},
Path=Value,
StringFormat='Z-Axis Rotation = {0:F0}'}"
Grid.Row="5" />
<Slider x:Name="depthSlider"
Grid.Row="6"
Maximum="2500"
Minimum="250"
ValueChanged="OnSliderValueChanged" />
<Label Grid.Row="7"
Text="{Binding Source={x:Reference depthSlider},
Path=Value,
StringFormat='Depth = {0:F0}'}" />
<skia:SKCanvasView x:Name="canvasView"
Grid.Row="8"
PaintSurface="OnCanvasViewPaintSurface" />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
請注意, depthSlider 初始化 值為 Minimum 250。 這表示要在這裡旋轉的 2D 物件具有 X 和 Y 座標,限制在原點周圍 250 像素半徑所定義的圓形。 此物件在 3D 空間中的任何旋轉,一律會導致座標值小於 250。
Rotation3DPage.cs程式代碼後置檔案會在 300 像素平方的點陣圖中載入:
public partial class Rotation3DPage : ContentPage
{
SKBitmap bitmap;
public Rotation3DPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
string resourceID = "SkiaSharpFormsDemos.Media.SeatedMonkey.jpg";
Assembly assembly = GetType().GetTypeInfo().Assembly;
using (Stream stream = assembly.GetManifestResourceStream(resourceID))
{
bitmap = SKBitmap.Decode(stream);
}
}
void OnSliderValueChanged(object sender, ValueChangedEventArgs args)
{
if (canvasView != null)
{
canvasView.InvalidateSurface();
}
}
...
}
如果 3D 轉換置中於此點陣圖上,則 X 和 Y 座標範圍介於 –150 和 150 之間,而邊角距離中心 212 圖元,因此一切都在 250 像素半徑內。
處理程式 PaintSurface 會 SKMatrix44 根據滑桿建立物件,並使用 PostConcat將其相乘。 SKMatrix從最終SKMatrix44物件擷取的值會以平移轉換為將旋轉置中於螢幕中央四周:
public partial class Rotation3DPage : ContentPage
{
SKBitmap bitmap;
public Rotation3DPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
string resourceID = "SkiaSharpFormsDemos.Media.SeatedMonkey.jpg";
Assembly assembly = GetType().GetTypeInfo().Assembly;
using (Stream stream = assembly.GetManifestResourceStream(resourceID))
{
bitmap = SKBitmap.Decode(stream);
}
}
void OnSliderValueChanged(object sender, ValueChangedEventArgs args)
{
if (canvasView != null)
{
canvasView.InvalidateSurface();
}
}
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
// Find center of canvas
float xCenter = info.Width / 2;
float yCenter = info.Height / 2;
// Translate center to origin
SKMatrix matrix = SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(-xCenter, -yCenter);
// Use 3D matrix for 3D rotations and perspective
SKMatrix44 matrix44 = SKMatrix44.CreateIdentity();
matrix44.PostConcat(SKMatrix44.CreateRotationDegrees(1, 0, 0, (float)xRotateSlider.Value));
matrix44.PostConcat(SKMatrix44.CreateRotationDegrees(0, 1, 0, (float)yRotateSlider.Value));
matrix44.PostConcat(SKMatrix44.CreateRotationDegrees(0, 0, 1, (float)zRotateSlider.Value));
SKMatrix44 perspectiveMatrix = SKMatrix44.CreateIdentity();
perspectiveMatrix[3, 2] = -1 / (float)depthSlider.Value;
matrix44.PostConcat(perspectiveMatrix);
// Concatenate with 2D matrix
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref matrix, matrix44.Matrix);
// Translate back to center
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref matrix,
SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(xCenter, yCenter));
// Set the matrix and display the bitmap
canvas.SetMatrix(matrix);
float xBitmap = xCenter - bitmap.Width / 2;
float yBitmap = yCenter - bitmap.Height / 2;
canvas.DrawBitmap(bitmap, xBitmap, yBitmap);
}
}
當您實驗第四個滑桿時,您會發現不同的深度設定不會將物件從查看器進一步移動,而是改變檢視方塊效果的範圍:
動畫旋轉 3D 也會使用 SKMatrix44 在 3D 空間中建立文字字串的動畫效果。 在建 textPaint 構函式中使用物件集做為欄位,以判斷文字的界限:
public class AnimatedRotation3DPage : ContentPage
{
SKCanvasView canvasView;
float xRotationDegrees, yRotationDegrees, zRotationDegrees;
string text = "SkiaSharp";
SKPaint textPaint = new SKPaint
{
Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke,
Color = SKColors.Black,
TextSize = 100,
StrokeWidth = 3,
};
SKRect textBounds;
public AnimatedRotation3DPage()
{
Title = "Animated Rotation 3D";
canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
// Measure the text
textPaint.MeasureText(text, ref textBounds);
}
...
}
覆OnAppearing寫會定義三Xamarin.FormsAnimation個物件,以不同的速率建立 、 yRotationDegrees和 zRotationDegrees 欄位的動畫xRotationDegrees效果。 請注意,這些動畫的期間會設定為質數(5 秒、7 秒和 11 秒),因此整體組合只會每隔 385 秒重複一次,或超過 10 分鐘:
public class AnimatedRotation3DPage : ContentPage
{
...
protected override void OnAppearing()
{
base.OnAppearing();
new Animation((value) => xRotationDegrees = 360 * (float)value).
Commit(this, "xRotationAnimation", length: 5000, repeat: () => true);
new Animation((value) => yRotationDegrees = 360 * (float)value).
Commit(this, "yRotationAnimation", length: 7000, repeat: () => true);
new Animation((value) =>
{
zRotationDegrees = 360 * (float)value;
canvasView.InvalidateSurface();
}).Commit(this, "zRotationAnimation", length: 11000, repeat: () => true);
}
protected override void OnDisappearing()
{
base.OnDisappearing();
this.AbortAnimation("xRotationAnimation");
this.AbortAnimation("yRotationAnimation");
this.AbortAnimation("zRotationAnimation");
}
...
}
如同上一個程式, PaintCanvas 處理程式會 SKMatrix44 建立旋轉和檢視方塊的值,並將它們相乘:
public class AnimatedRotation3DPage : ContentPage
{
...
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
// Find center of canvas
float xCenter = info.Width / 2;
float yCenter = info.Height / 2;
// Translate center to origin
SKMatrix matrix = SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(-xCenter, -yCenter);
// Scale so text fits
float scale = Math.Min(info.Width / textBounds.Width,
info.Height / textBounds.Height);
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref matrix, SKMatrix.MakeScale(scale, scale));
// Calculate composite 3D transforms
float depth = 0.75f * scale * textBounds.Width;
SKMatrix44 matrix44 = SKMatrix44.CreateIdentity();
matrix44.PostConcat(SKMatrix44.CreateRotationDegrees(1, 0, 0, xRotationDegrees));
matrix44.PostConcat(SKMatrix44.CreateRotationDegrees(0, 1, 0, yRotationDegrees));
matrix44.PostConcat(SKMatrix44.CreateRotationDegrees(0, 0, 1, zRotationDegrees));
SKMatrix44 perspectiveMatrix = SKMatrix44.CreateIdentity();
perspectiveMatrix[3, 2] = -1 / depth;
matrix44.PostConcat(perspectiveMatrix);
// Concatenate with 2D matrix
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref matrix, matrix44.Matrix);
// Translate back to center
SKMatrix.PostConcat(ref matrix,
SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(xCenter, yCenter));
// Set the matrix and display the text
canvas.SetMatrix(matrix);
float xText = xCenter - textBounds.MidX;
float yText = yCenter - textBounds.MidY;
canvas.DrawText(text, xText, yText, textPaint);
}
}
這個 3D 旋轉會圍繞數個 2D 轉換,將旋轉中心移至螢幕中央,並調整文字字串的大小,使其與螢幕寬度相同: