使用路徑和區域裁剪
使用路徑將圖形裁剪到特定區域,以及建立區域
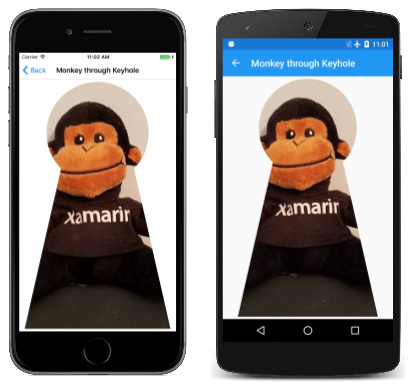
有時必須將圖形轉譯限制為特定區域。 這稱為 裁剪。 您可以針對特殊效果使用裁剪,例如透過鑰匙孔看到的猴子影像:

裁剪區域是呈現圖形的畫面區域。 不會轉譯在裁剪區域外部顯示的任何專案。 裁剪區域通常是由矩形或 SKPath 物件定義,但您也可以使用 SKRegion 對象來定義裁剪區域。 這兩種類型的物件一開始似乎相關,因為您可以從路徑建立區域。 不過,您無法從區域建立路徑,而且它們在內部非常不同:路徑包含一系列線條和曲線,而區域是由一系列水平掃描線所定義。
上圖是由 猴子透過Keyhole 頁面建立的。 類別 MonkeyThroughKeyholePage 會使用 SVG 資料定義路徑,並使用建構函式從程式資源載入點陣圖:
public class MonkeyThroughKeyholePage : ContentPage
{
SKBitmap bitmap;
SKPath keyholePath = SKPath.ParseSvgPathData(
"M 300 130 L 250 350 L 450 350 L 400 130 A 70 70 0 1 0 300 130 Z");
public MonkeyThroughKeyholePage()
{
Title = "Monkey through Keyhole";
SKCanvasView canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
string resourceID = "SkiaSharpFormsDemos.Media.SeatedMonkey.jpg";
Assembly assembly = GetType().GetTypeInfo().Assembly;
using (Stream stream = assembly.GetManifestResourceStream(resourceID))
{
bitmap = SKBitmap.Decode(stream);
}
}
...
}
keyholePath雖然物件描述鑰匙孔的外框,但座標是完全任意的,並反映設計路徑數據時方便什麼。 基於這個理由, PaintSurface 處理程式會取得此路徑的界限,並呼叫 Translate ,並將 Scale 路徑移至畫面中央,並使它幾乎與螢幕一樣高:
public class MonkeyThroughKeyholePage : ContentPage
{
...
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
// Set transform to center and enlarge clip path to window height
SKRect bounds;
keyholePath.GetTightBounds(out bounds);
canvas.Translate(info.Width / 2, info.Height / 2);
canvas.Scale(0.98f * info.Height / bounds.Height);
canvas.Translate(-bounds.MidX, -bounds.MidY);
// Set the clip path
canvas.ClipPath(keyholePath);
// Reset transforms
canvas.ResetMatrix();
// Display monkey to fill height of window but maintain aspect ratio
canvas.DrawBitmap(bitmap,
new SKRect((info.Width - info.Height) / 2, 0,
(info.Width + info.Height) / 2, info.Height));
}
}
但是路徑不會轉譯。 相反地,在轉換之後,路徑會使用這個語句來設定裁剪區域:
canvas.ClipPath(keyholePath);
處理程式 PaintSurface 接著會使用呼叫 ResetMatrix 重設轉換,並繪製位圖以延伸至螢幕的完整高度。 此程式代碼假設位圖是正方形,這是這個特定位圖。 點陣圖只會在裁剪路徑所定義的區域內轉譯:
當呼叫 方法時 ClipPath ,裁剪路徑會受到轉換的影響,而不是在顯示圖形物件(例如點陣圖)時生效的轉換。 裁剪路徑是畫布狀態的一部分,該狀態會與方法一起 Save 儲存,並使用 方法還原 Restore 。
結合裁剪路徑
嚴格來說,裁剪區域不是由 ClipPath 方法「設定」。 相反地,它會與現有的裁剪路徑結合,其開頭為矩形,大小等於畫布。 您可以使用 屬性或 DeviceClipBounds 屬性,取得裁剪區域的LocalClipBounds矩形界限。 屬性 LocalClipBounds 會傳回值 SKRect ,反映任何可能生效的轉換。 屬性 DeviceClipBounds 會傳 RectI 回值。 這是具有整數維度的矩形,並描述實際圖元維度中的裁剪區域。
將裁剪區域與新區域結合,以 ClipPath 減少裁剪區域的任何呼叫。 方法的完整語法 ClipPath ,結合裁剪區域與矩形:
public Void ClipRect(SKRect rect, SKClipOperation operation = SKClipOperation.Intersect, Boolean antialias = false);
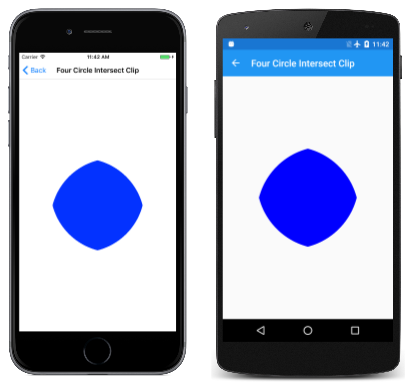
根據預設,結果裁剪區域是現有裁剪區域和 SKPath 或 SKRectClipRect 方法中指定的 ClipPath 交集。 這會在 [四個圓形交集剪輯 ] 頁面中示範。 類別 PaintSurface 中的 FourCircleInteresectClipPage 處理程式會重複使用相同的 SKPath 物件來建立四個重疊的圓形,每一個都會透過連續呼叫 ClipPath來減少裁剪區域:
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
float size = Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height);
float radius = 0.4f * size;
float offset = size / 2 - radius;
// Translate to center
canvas.Translate(info.Width / 2, info.Height / 2);
using (SKPath path = new SKPath())
{
path.AddCircle(-offset, -offset, radius);
canvas.ClipPath(path, SKClipOperation.Intersect);
path.Reset();
path.AddCircle(-offset, offset, radius);
canvas.ClipPath(path, SKClipOperation.Intersect);
path.Reset();
path.AddCircle(offset, -offset, radius);
canvas.ClipPath(path, SKClipOperation.Intersect);
path.Reset();
path.AddCircle(offset, offset, radius);
canvas.ClipPath(path, SKClipOperation.Intersect);
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
paint.Style = SKPaintStyle.Fill;
paint.Color = SKColors.Blue;
canvas.DrawPaint(paint);
}
}
}
剩下的是這四個圓形的交集:
列舉 SKClipOperation 只有兩個成員:
Difference從現有的裁剪區域移除指定的路徑或矩形Intersect與現有裁剪區域交集指定的路徑或矩形
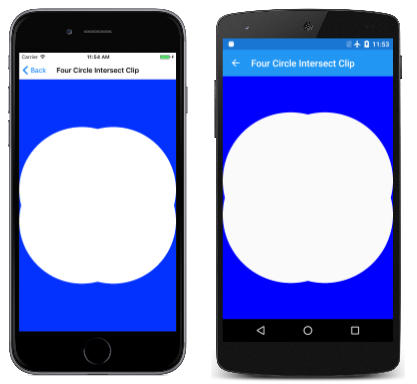
如果您將類別中的FourCircleIntersectClipPage四SKClipOperation.Intersect個自變數取代為 SKClipOperation.Difference,您會看到下列內容:
已從裁剪區域移除四個重疊的圓形。
[ 剪輯作業 ] 頁面說明這兩個作業與一對圓形之間的差異。 左邊的第一個圓形會新增至具有默認剪輯作業 Intersect的裁剪區域,而右邊的第二個圓圈會新增至裁剪區域,並加上文字捲標所指示的剪輯作業:
類別 ClipOperationsPage 會將兩個 SKPaint 物件定義為字段,然後將螢幕分成兩個矩形區域。 這些區域會根據手機處於直向或橫向模式而有所不同。 接著,類別 DisplayClipOp 會以兩個圓形路徑顯示文字和呼叫 ClipPath ,以說明每個剪輯作業:
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
float x = 0;
float y = 0;
foreach (SKClipOperation clipOp in Enum.GetValues(typeof(SKClipOperation)))
{
// Portrait mode
if (info.Height > info.Width)
{
DisplayClipOp(canvas, new SKRect(x, y, x + info.Width, y + info.Height / 2), clipOp);
y += info.Height / 2;
}
// Landscape mode
else
{
DisplayClipOp(canvas, new SKRect(x, y, x + info.Width / 2, y + info.Height), clipOp);
x += info.Width / 2;
}
}
}
void DisplayClipOp(SKCanvas canvas, SKRect rect, SKClipOperation clipOp)
{
float textSize = textPaint.TextSize;
canvas.DrawText(clipOp.ToString(), rect.MidX, rect.Top + textSize, textPaint);
rect.Top += textSize;
float radius = 0.9f * Math.Min(rect.Width / 3, rect.Height / 2);
float xCenter = rect.MidX;
float yCenter = rect.MidY;
canvas.Save();
using (SKPath path1 = new SKPath())
{
path1.AddCircle(xCenter - radius / 2, yCenter, radius);
canvas.ClipPath(path1);
using (SKPath path2 = new SKPath())
{
path2.AddCircle(xCenter + radius / 2, yCenter, radius);
canvas.ClipPath(path2, clipOp);
canvas.DrawPaint(fillPaint);
}
}
canvas.Restore();
}
呼叫 DrawPaint 通常會讓整個畫布填滿該 SKPaint 物件,但在此情況下,方法只會在裁剪區域內繪製。
探索區域
您也可以在物件方面 SKRegion 定義裁剪區域。
新建立 SKRegion 的物件描述空白區域。 通常物件上的第一次呼叫是 SetRect 讓區域描述矩形區域。 的 參數 SetRect 是一個值, 一個 SKRectI 具有整數座標的矩形,因為它會以像素為單位指定矩形。 接著,您可以使用物件呼叫 SetPathSKPath 。 這會建立與路徑內部相同的區域,但裁剪到初始矩形區域。
您也可以呼叫其中 Op 一個方法多載來修改區域,例如:
public Boolean Op(SKRegion region, SKRegionOperation op)
列舉 SKRegionOperation 類似於 SKClipOperation ,但它有更多成員:
DifferenceIntersectUnionXORReverseDifferenceReplace
您 Op 進行呼叫的區域會結合以成員為基礎的指定為參數的區域 SKRegionOperation 。 當您最後取得適合裁剪的區域時,您可以使用 的 方法來SKCanvas將該區域設定為畫布ClipRegion的裁剪區域:
public void ClipRegion(SKRegion region, SKClipOperation operation = SKClipOperation.Intersect)
下列螢幕快照顯示根據六個區域作業裁剪區域。 左圓圈是呼叫 方法的區域 Op ,而右圓形則是傳遞至 Op 方法的區域:
這些都是結合這兩個圓形的可能性嗎? 將產生的影像視為三個元件的組合,這本身會顯示在、 Intersect和 ReverseDifference 作業中Difference。 組合總數為 2 到第三個乘冪,或 8 個。 遺漏的兩個是原始區域(完全不是呼叫 Op 的結果)和完全空白的區域。
更難使用區域進行裁剪,因為您需要先建立路徑,再從該路徑建立區域,然後結合多個區域。 [區域作業] 頁面的整體結構與剪輯作業非常類似,但 RegionOperationsPage 類別會將畫面分成六個區域,並顯示使用此作業使用區域所需的額外工作:
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
float x = 0;
float y = 0;
float width = info.Height > info.Width ? info.Width / 2 : info.Width / 3;
float height = info.Height > info.Width ? info.Height / 3 : info.Height / 2;
foreach (SKRegionOperation regionOp in Enum.GetValues(typeof(SKRegionOperation)))
{
DisplayClipOp(canvas, new SKRect(x, y, x + width, y + height), regionOp);
if ((x += width) >= info.Width)
{
x = 0;
y += height;
}
}
}
void DisplayClipOp(SKCanvas canvas, SKRect rect, SKRegionOperation regionOp)
{
float textSize = textPaint.TextSize;
canvas.DrawText(regionOp.ToString(), rect.MidX, rect.Top + textSize, textPaint);
rect.Top += textSize;
float radius = 0.9f * Math.Min(rect.Width / 3, rect.Height / 2);
float xCenter = rect.MidX;
float yCenter = rect.MidY;
SKRectI recti = new SKRectI((int)rect.Left, (int)rect.Top,
(int)rect.Right, (int)rect.Bottom);
using (SKRegion wholeRectRegion = new SKRegion())
{
wholeRectRegion.SetRect(recti);
using (SKRegion region1 = new SKRegion(wholeRectRegion))
using (SKRegion region2 = new SKRegion(wholeRectRegion))
{
using (SKPath path1 = new SKPath())
{
path1.AddCircle(xCenter - radius / 2, yCenter, radius);
region1.SetPath(path1);
}
using (SKPath path2 = new SKPath())
{
path2.AddCircle(xCenter + radius / 2, yCenter, radius);
region2.SetPath(path2);
}
region1.Op(region2, regionOp);
canvas.Save();
canvas.ClipRegion(region1);
canvas.DrawPaint(fillPaint);
canvas.Restore();
}
}
}
方法與 ClipRegion 方法之間ClipPath有很大的差異:
重要
ClipPath不同於方法,ClipRegion方法不會受到轉換的影響。
若要瞭解此差異的理由,瞭解區域是什麼很有説明。 如果您已考慮如何在內部實作剪輯作業或區域作業,則看起來可能非常複雜。 有數個可能非常複雜的路徑正在結合,而結果路徑的外框可能是演算法噩夢。
如果每個路徑都縮減為一系列水平掃描線,例如舊式真空管電視,這項工作就會大幅簡化。 每個掃描線都是具有起點和終點的水平線。 例如,半徑為 10 像素的圓圈可以分解成 20 個水平掃描線,每一行都會從圓形的左部分開始,並結束於右部分。 將兩個圓形與任何區域作業結合會變得非常簡單,因為它只是檢查每對對應掃描線的開始和結束座標。
這就是區域:定義區域的一系列水平掃描線。
不過,當區域縮減為一系列掃描線時,這些掃描線會以特定的圖元維度為基礎。 嚴格來說,區域不是向量圖形物件。 它本質上比路徑更接近壓縮的單色位圖。 因此,區域無法縮放或旋轉,而不會失去逼真度,因此它們不會在用於裁剪區域時進行轉換。
不過,您可以針對繪製目的將轉換套用至區域。 “區域 小畫家”節目生動地展示了區域的內部本質。 類別RegionPaintPageSKRegion會根據 SKPath 10單位半徑圓形的 建立物件。 接著,轉換會展開該圓形以填滿頁面:
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
int radius = 10;
// Create circular path
using (SKPath circlePath = new SKPath())
{
circlePath.AddCircle(0, 0, radius);
// Create circular region
using (SKRegion circleRegion = new SKRegion())
{
circleRegion.SetRect(new SKRectI(-radius, -radius, radius, radius));
circleRegion.SetPath(circlePath);
// Set transform to move it to center and scale up
canvas.Translate(info.Width / 2, info.Height / 2);
canvas.Scale(Math.Min(info.Width / 2, info.Height / 2) / radius);
// Fill region
using (SKPaint fillPaint = new SKPaint())
{
fillPaint.Style = SKPaintStyle.Fill;
fillPaint.Color = SKColors.Orange;
canvas.DrawRegion(circleRegion, fillPaint);
}
// Stroke path for comparison
using (SKPaint strokePaint = new SKPaint())
{
strokePaint.Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke;
strokePaint.Color = SKColors.Blue;
strokePaint.StrokeWidth = 0.1f;
canvas.DrawPath(circlePath, strokePaint);
}
}
}
}
呼叫會 DrawRegion 以橙色填滿區域,而呼叫會 DrawPath 以藍色筆劃原始路徑進行比較:
區域顯然是一系列的離散座標。
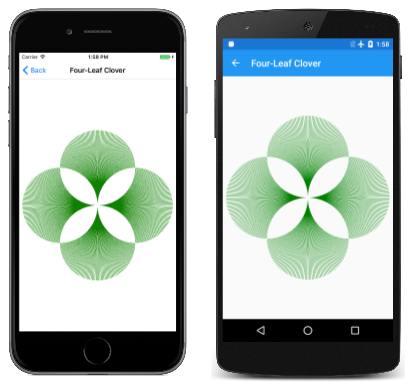
如果您不需要使用與裁剪區域相關聯的轉換,您可以使用區域進行裁剪,如 四葉 Clover 頁面所示範。 類別 FourLeafCloverPage 會從四個圓形區域建構複合區域、將複合區域設定為裁剪區域,然後從頁面中央繪製一系列 360 條直線:
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
float xCenter = info.Width / 2;
float yCenter = info.Height / 2;
float radius = 0.24f * Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height);
using (SKRegion wholeScreenRegion = new SKRegion())
{
wholeScreenRegion.SetRect(new SKRectI(0, 0, info.Width, info.Height));
using (SKRegion leftRegion = new SKRegion(wholeScreenRegion))
using (SKRegion rightRegion = new SKRegion(wholeScreenRegion))
using (SKRegion topRegion = new SKRegion(wholeScreenRegion))
using (SKRegion bottomRegion = new SKRegion(wholeScreenRegion))
{
using (SKPath circlePath = new SKPath())
{
// Make basic circle path
circlePath.AddCircle(xCenter, yCenter, radius);
// Left leaf
circlePath.Transform(SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(-radius, 0));
leftRegion.SetPath(circlePath);
// Right leaf
circlePath.Transform(SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(2 * radius, 0));
rightRegion.SetPath(circlePath);
// Make union of right with left
leftRegion.Op(rightRegion, SKRegionOperation.Union);
// Top leaf
circlePath.Transform(SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(-radius, -radius));
topRegion.SetPath(circlePath);
// Combine with bottom leaf
circlePath.Transform(SKMatrix.MakeTranslation(0, 2 * radius));
bottomRegion.SetPath(circlePath);
// Make union of top with bottom
bottomRegion.Op(topRegion, SKRegionOperation.Union);
// Exclusive-OR left and right with top and bottom
leftRegion.Op(bottomRegion, SKRegionOperation.XOR);
// Set that as clip region
canvas.ClipRegion(leftRegion);
// Set transform for drawing lines from center
canvas.Translate(xCenter, yCenter);
// Draw 360 lines
for (double angle = 0; angle < 360; angle++)
{
float x = 2 * radius * (float)Math.Cos(Math.PI * angle / 180);
float y = 2 * radius * (float)Math.Sin(Math.PI * angle / 180);
using (SKPaint strokePaint = new SKPaint())
{
strokePaint.Color = SKColors.Green;
strokePaint.StrokeWidth = 2;
canvas.DrawLine(0, 0, x, y, strokePaint);
}
}
}
}
}
}
它看起來並不像四葉樹葉草,但它是一個影像,否則可能很難轉譯而不裁剪:
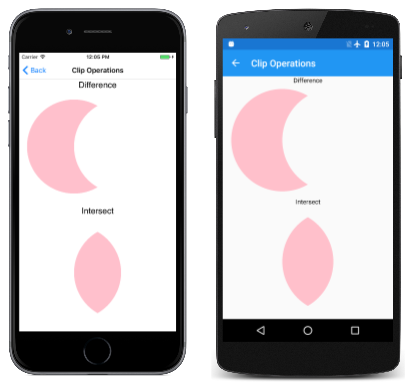
![[區域作業] 頁面的三重螢幕快照](clipping-images/regionoperations-small.png)
![[區域 小畫家] 頁面的三個螢幕快照](clipping-images/regionpaint-small.png)