Use SQL to query data
The Microsoft Dataverse business layer provides a Tabular Data Stream (TDS) endpoint that emulates a SQL data connection. The SQL connection provides read-only access to the table data of the target Dataverse environment allowing you to execute SQL queries against the Dataverse data tables. No custom views of the data are provided. The Dataverse endpoint SQL connection uses the Dataverse security model for data access. Data can be obtained for all Dataverse tables to which a user has access.
Note
Only the SQL data connection through SQL Server Management Studio and .NET libraries is in preview. Power BI is generally available.
Prerequisites
The Enable TDS endpoint setting must be enabled in your environment. That setting is enabled by default. More information: Manage feature settings
To prevent data exfiltration, turn on the user level access control for TDS endpoint. Assign a least privilege security role with data access permission to only the tables that your users need to access, and grant the Allow user to access TDS endpoint miscellaneous privilege.
Applications support
TDS (SQL) endpoint applications support for Power BI and SQL Server Management Studio is described next.
SQL Server Management Studio (Preview)
You can also use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) version 18.12.1 or later with the Dataverse endpoint SQL connection. Examples of using SSMS with the SQL data connection are shown in the figure.
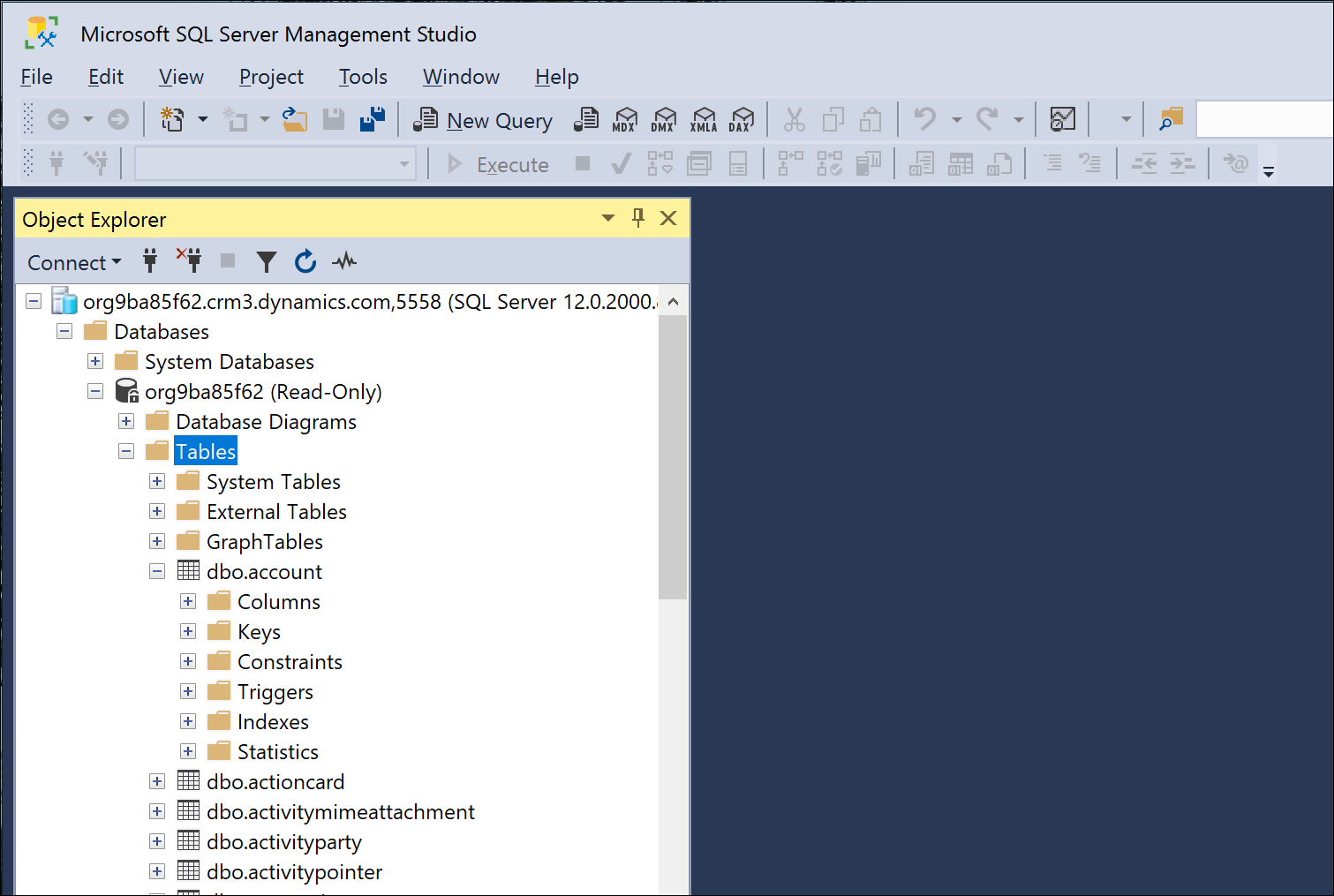
Security and authentication
Only Microsoft Entra ID authentication is supported. SQL authentication and Windows authentication aren't supported. The next figure shows an example of how to sign-in to the SQL connection in SSMS. Notice the server name is the organization address URL.
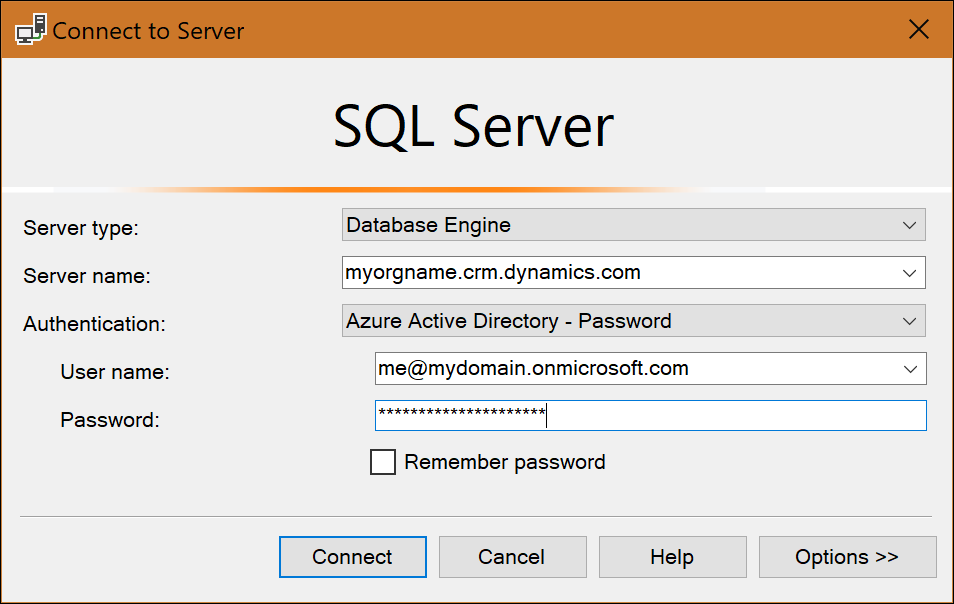
Note
Ports 1433 and/or 5558 need to be enabled to use the TDS endpoint from a client application such as SSMS. If you only enable port 5558, the user must append that port number to the server name in the Connect to Server dialog of SSMS - for example: myorgname.crm.dynamics.com,5558.
Information on endpoint encryption: In-transit data protection
Example table data queries
Here are a couple of example queries composed in SSMS. The first image shows a simple query using aliases and result ordering.
select top 5 a.name as [VIP customer], a.address1_postalcode as [ZIP code] from account a order by a.address1_postalcode desc
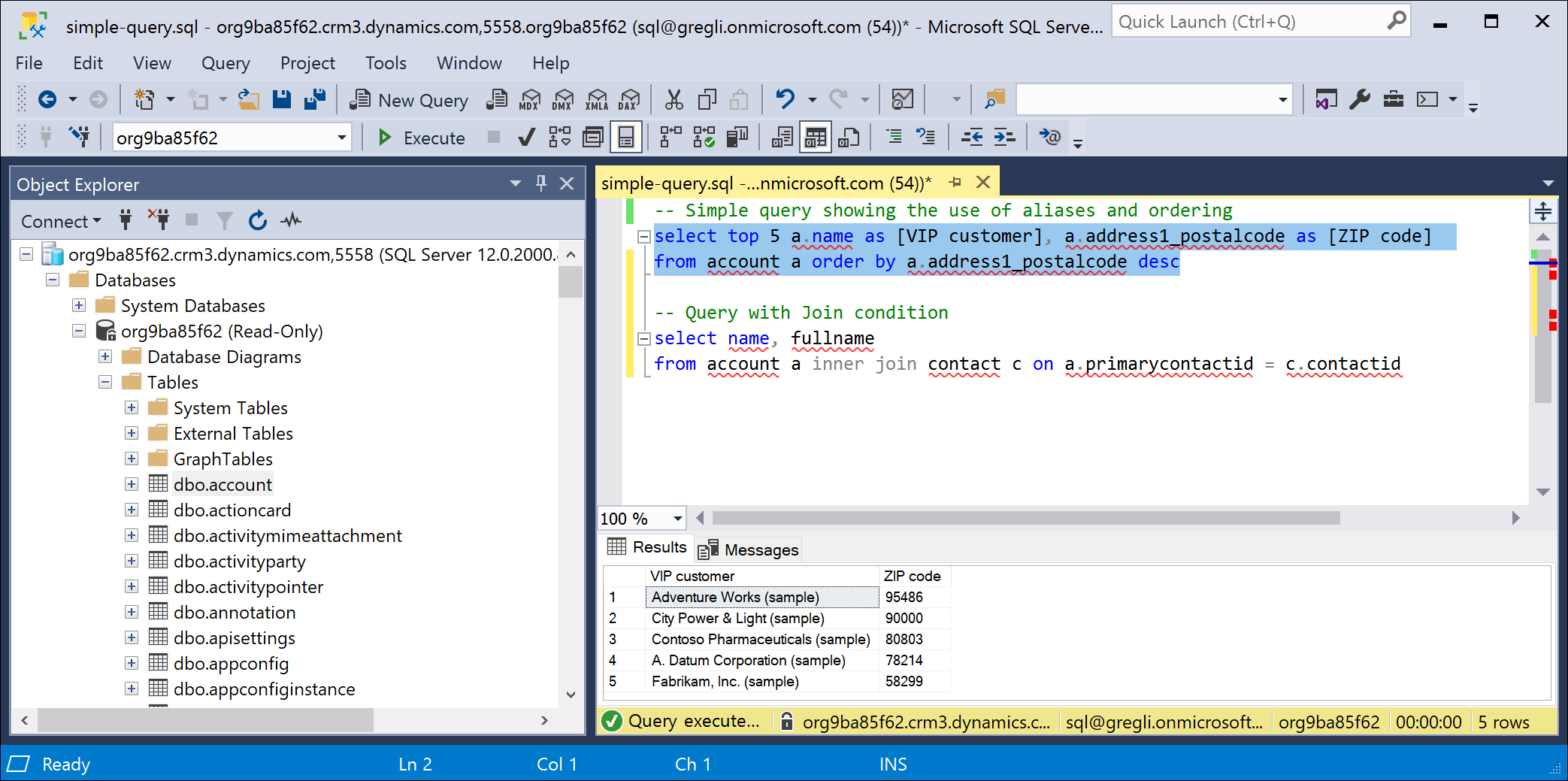
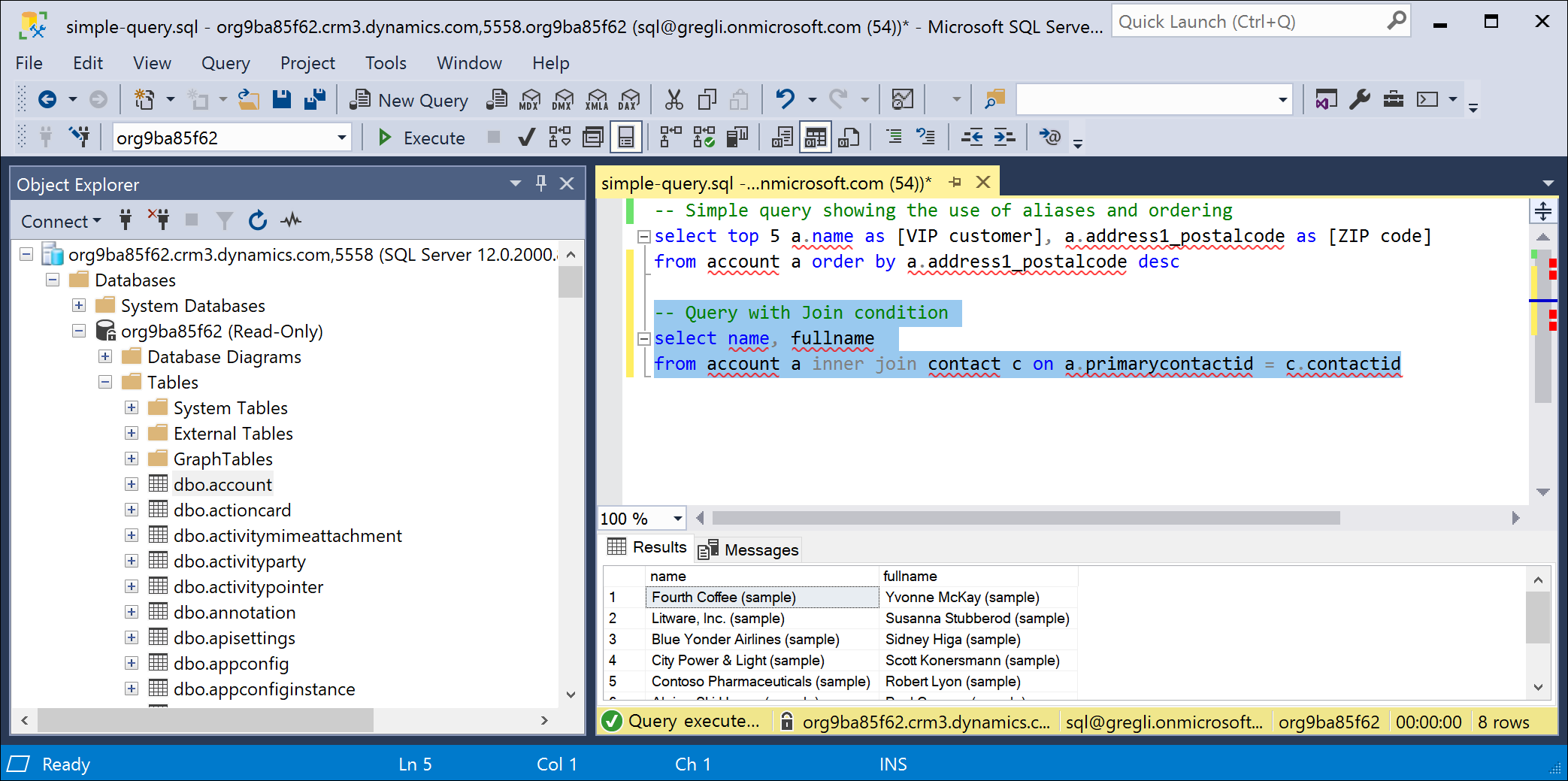
This next query shows a JOIN.
select name, fullname from account a inner join contact c on a.primarycontactid = c.contactid
Power BI (General Availability)
You can use the Analyze in Power BI option (Data > Tables > Analyze in Power BI) in Power Apps (https://make.powerapps.com) to use the Dataverse connector to analyze data in Power BI Desktop. More information: View table data in Power BI Desktop
Note
To enable this feature, see the TDS endpoint setting in Manage feature settings. Once enabled you should see a button Analyze in Power BI in the command bar of Power Apps.
Supported operations and data types
Any operation that attempts to modify data (that is, INSERT, UPDATE) doesn't work with this read-only SQL data connection. For a detailed list of supported SQL operations on the Dataverse endpoint, see How Dataverse SQL differs from Transact-SQL.
The following Dataverse datatypes aren't supported with the SQL connection: binary, image, sql_variant, varbinary, virtual, HierarchyId, managedproperty, file, xml, partylist, timestamp, choices. In addition, tables types 'virtual' and 'audit' aren't supported at this time.
Tip
partylist attributes can instead be queried by joining to the activityparty table as shown in this next example.
select act.activityid, act.subject, string_agg([to].partyidname, ', ')
from activitypointer as act
left outer join activityparty as [to] on act.activityid = [to].activityid and [to].participationtypemask = 2
group by act.activityid, act.subject
Lookup column type behaviors
Dataverse lookup columns are represented as <lookup>id and <lookup>name in a result set.
Choice column type behaviors
Dataverse choice columns are represented as <choice>Name and <choice>Label in a result set.
Tip
After making changes to labels for a choice column, the table needs to have customizations published.
Note
Including a large number of choice labels in your query will have significant impact on performance. It is best to use less than 10 labels if possible. Because choice labels are localized, the localized string is more expensive to return.
Reported SQL version
The Dataverse TDS endpoint emulates Microsoft SQL Server read-only query capabilities over the Dataverse business logic. Dataverse returns the current SQL Azure version 12.0.2000.8 for select @@version.
Performance guidance
When you retrieve data through through the TDS endpoint, there are a few key query patterns that should be used. Described in the next sections, these query patterns manage performance and size of result sets.
Only necessary columns
When building a query, only return the necessary columns. This technique helps both execution of the query and also transferring the results back to the client application. In general, keeping a query under 100 columns is recommended.
Choice columns
Choice columns are flattened into two columns, which help usability. However, it's important to do any aggregates and filters against the value portion of the choice column. The value portion can have indexes and is stored in the base table. However, the label portion ('choicecolumn' name) is stored separately, which cost more to retrieve and can't be indexed. Using a significant number of choice label columns may generate a slower performing query.
Use Top X
It's important to use a top clause in your queries to prevent trying to return the whole table of data. For example, use Select Top 1000 accountid,name From account Where revenue > 50000 limits the results to the first 1,000 accounts.
Don't use NOLOCK
When building queries, don't use the table hint NOLOCK. This hint prevents Dataverse from optimizing queries.
Limitations
The Dataverse TDS endpoint no longer has a hard maximum size limit. Instead, there's a fixed five (5) minute timeout. With the introduction of data streaming, you can retrieve as much data as can be completed in the fixed five (5) minute timeout. Consider using data integration tools such as Azure Synapse Link for Dataverse and dataflows for large data queries that require more than five (5) minutes to complete. More information: Importing and exporting data
Tip
To help keep the size of the returned data within acceptable limits, use as few multi-line text columns and choice columns as possible.
Warning
The five (5) minute timeout can be adjusted to two (2) minutes depending on the query complexity. For example, queries containing SELECT *, NESTED FROMs and/or JOINs will automatically adjust the timeout limit to two (2) minutes as those queries put too much pressure on the server when left running for a long time. It is advised to avoid using these patterns in SQL for maximum performance.
Dates returned in query results are formatted as Universal Time Coordinated (UTC). Previously, dates were returned in local time.
Querying data using SQL doesn't trigger any plug-ins registered on the RetrieveMultipleRequest or RetrieveRequest messages. Any rewriting of the query or results that are normally performed by such a plug-in don't take effect for a SQL query.
Queries using the TDS endpoint execute under the service protection API limits.
The TDS endpoint can't be used with elastic tables. More information: Elastic tables
Troubleshooting connection problems
Let's take a look at some known error conditions and how to resolve them.
Note
Ports 1433 and/or 5558 need to be enabled to use the TDS endpoint from a client application such as SSMS. If you only enable port 5558, the user must append that port number to the server name in the Connect to Server dialog of SSMS - for example: myorgname.crm.dynamics.com,5558.
Authentication
Only Microsoft Entra ID authentication is supported on the Dataverse endpoint SQL connection. The preferred authentication mechanism is "Microsoft Entra ID – Universal" with multifactor authentication (MFA). However, "Microsoft Entra ID – Password" works if MFA isn't configured. If you try to use other forms of authentication, you could see errors like the following.
- Error returned when using Microsoft Entra ID – Integrated authentication.
"Login failed: The HTTP request was forbidden with client authentication scheme 'Anonymous'. RequestId: TDS;81d8a4f7-0d49-4d21-8f50-04364bddd370;2 Time: 2020-12-17T01:10:59.8628578Z (.Net SqlClient Data Provider)"
- Error returned when using SQL Server authentication.
"Login failed: Request is not authenticated. RequestId: TDS;918aa372-ccc4-438a-813e-91b086355343;1 Time: 2020-12-17T01:13:14.4986739Z (.Net SqlClient Data Provider)"
- Error returned when using Windows authentication.
"Login failed: Request is not authenticated. RequestId: TDS;fda17c60-93f7-4d5a-ad79-7ddfbb917979;1 Time: 2020-12-17T01:15:01.0497703Z (.Net SqlClient Data Provider)"
Blocked ports
A blocked port error can look something like the following.
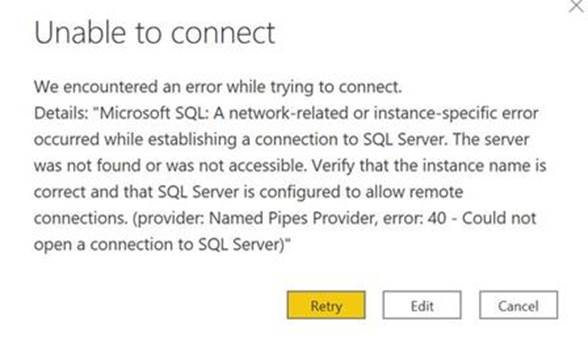
The solution is to verify the TCP ports 1433 or 5558 from the client are unblocked. Use one of the following methods to unblock the ports as described next.
Use PowerShell to validate connection with TDS endpoint
- Open a PowerShell command window.
- Run the Test-connection command.
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName <environment>.crm.dynamics.com -port 1433
If the connection is successful a line "TcpTestSucceeded : True" is returned.
In some cases, traffic can be blocked directly at the IP level. To validate the IP address is also working, take the IP address returned from the above domain test connection and replace the ComputerName parameter value with the IP address.
- Take the address returned from the above command as "RemoteAddress"
- Run the Test-NetConnection -ComputerName <RemoteAddress> -port 1433
This command should return "TcpTestSucceeded : True"
Establish a telnet session to the TDS endpoint
- On a Microsoft Windows computer, install/enable telnet.
- Choose Start.
- Select Control Panel.
- Choose Programs and features.
- Select Turn Windows features on or off.
- Choose the Telnet Client option.
- Select OK. A dialog box appears to confirm the installation. The telnet command should now be available.
- Run a telnet command in a Command window.
telnet <environmentname>.crm.dynamics.com 1433
If the connection is successful, you're placed in an active telnet session. If unsuccessful, you receive the error:
"Connecting to <environmentname>.crm.dynamics.com… Couldn't open connection to the host, on port 1433: connect failed."
This error message means the port is blocked at the client.
Port redirect from non-SSL to SSL
The TDS connection can fail when using third party applications due to port redirection from the 1433/5558 to 443. This failure happens because the SSL inspection rule can block communication, where the reason for the block being 'redirection from non-SSL port to SSL port'. The solution is to allowlist Dataverse TDS communication on web proxies using IP addresses.
For information on the official IP address values for accessing the service, see IP-Addreses-Required.
Allowlisting hostnames isn't sufficient when connecting to Dataverse TDS because port redirection between ports 1433/5558 to 433 is happening over IP address, not over hostname.
See also
How Dataverse SQL differs from Transact-SQL
Get started with virtual tables (entities)
Query data using FetchXml
Service Protection API Limits