1.3 Overview
The Windows Server Update Services (WSUS) protocols provides support for central publication and distribution of software components and software updates from server machines to client machines, and for hierarchical synchronization of available software components between servers.
This specification defines the Windows Server Update Services: Server-Server Protocol, which enables synchronization of updates within a hierarchical topology of update servers.
This protocol is a SOAP-based protocol that uses HTTP 1.1 as its transport.
The following figure shows a typical hierarchical topology of update servers and client computers. An upstream server (USS) in a hierarchy provides information on software and drivers to downstream servers (DSSs). Any update server in the hierarchy can serve simultaneously as a DSS with respect to its upstream server and as a USS with respect to its downstream servers. For example, in the following figure, update server C acts as a DSS when communicating with its upstream server A and acts as a USS when communicating with its downstream server D or E.
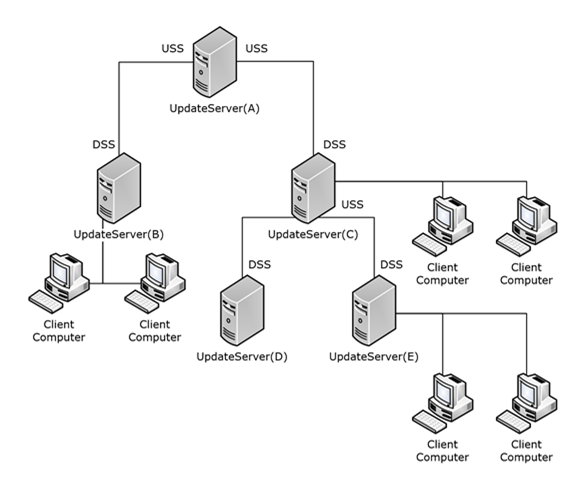
Figure 1: Typical hierarchical topology of update servers and client computers
An update server groups its client computers into target groups. An update server can be configured to deploy the updates to its client computers by assigning the updates to the target groups for deployment and, optionally, by specifying an installation or removal deadline. This mapping of the individual update revisions to target groups is known as a deployment.
There are two types of DSS defined by this protocol: autonomous and replica. Either type of DSS gets its updates from the USS. However, only a replica DSS gets the deployments from its USS. The autonomous DSS manages its deployments independently from the USS.
This specification describes the communication between two adjacent update servers in such a hierarchy.
This specification does not cover the format of self-update binaries, update metadata, and update content.<1>