Office UI elements for Office Add-ins
You can use several types of UI elements to extend the Office UI, including add-in commands and HTML containers. These UI elements look like a natural extension of Office and work across platforms. You can insert your custom web-based code into any of these elements.
The following image shows the types of Office UI elements that you can create.
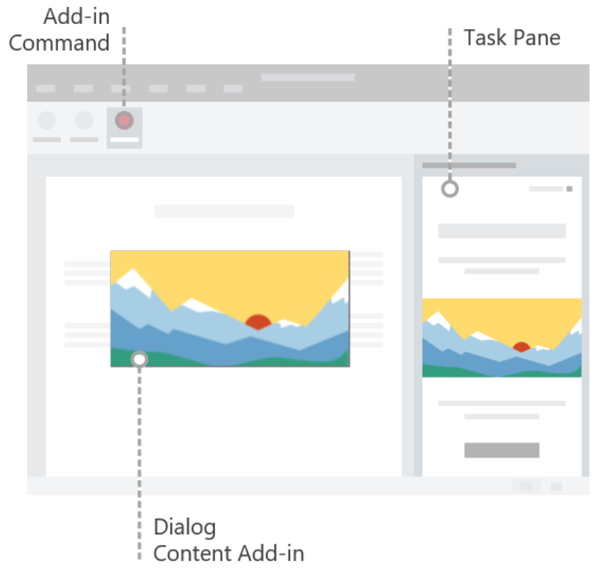
Add-in commands
Use add-in commands to add entry points to your add-in to the Office app ribbon. Commands start actions in your add-in either by running JavaScript code, or by launching an HTML container. You can create two types of add-in commands.
| Command type | Description |
|---|---|
| Ribbon buttons, menus, and tabs | Use to add custom buttons, menus (dropdowns), or tabs to the default ribbon in Office. Use buttons and menus to trigger an action in Office. Use tabs to group and organize buttons and menus. |
| Context menus | Use to extend the default context menu. Context menus are displayed when, for example, users right-click (or select and hold) text in an Office document or an object in Excel. |
HTML containers
Use HTML containers to embed HTML-based UI code within Office clients. These web pages can then reference the Office JavaScript API to interact with content in the document. You can create three types of HTML containers.
| HTML container | Description |
|---|---|
| Task panes | Display custom UI in the right pane of the Office document. Use task panes to allow users to interact with your add-in side-by-side with the Office document. |
| Content add-ins | Display custom UI embedded within Office documents. Use content add-ins to allow users to interact with your add-in directly within the Office document. For example, you might want to show external content such as videos or data visualizations from other sources. |
| Dialog boxes | Display custom UI in a dialog box that overlays the Office document. Use a dialog box for interactions that require focus and more real estate, and don't require a side-by-side interaction with the document. |