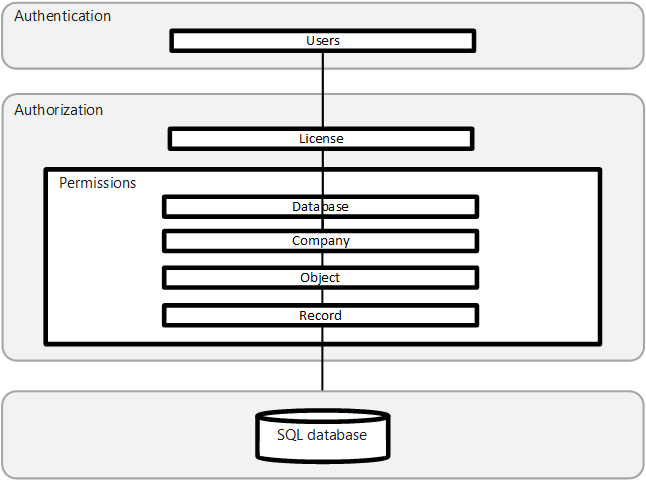
The Business Central security system allows you to control which objects or tables a user can access within each database. You can specify the type of access that each user has to these objects and tables, whether they're able to read, modify, or enter data.
You can specify which records are stored in the tables that each user is allowed to access. This means that permissions can be allocated at both the table level and the record level.
The security system contains information about the permissions that are granted to each user who can access a particular database.
This information includes the roles that the users have been assigned, and any permissions that they are granted to individual users.
Graphically, these can be represented as the layers, where the central layer is the records in the database.
The first layer of security when you open Business Central is database security.
After you start Business Central and attempt to open the database, your credentials are checked. For more information about granting a user permission to create or work with a Business Central database, see Setting Database Owner and Security Administration Permissions.
Database logins
Users are given a database sign in when they have their own user ID and password in Business Central. The user must enter the user ID and password to access the database.
Note
Database logins are only valid for connecting to the database from the Business Central.
How database logins work
Users must also have a sign in on SQL Server. SQL Server has its own authentication of the user's ID and password. SQL Server does this by checking whether a SQL Server sign in with this user's ID and password is created.
This sign in must first be created by a SQL Server administrator, with a SQL Server tool. If a SQL Server sign in hasn't been set up, authentication fails and the user receives an error. For more information, see Setting Database Owner and Security Administration Permissions.
The user is granted access to the server after their sign in is authenticated. Database security then validates the user's permissions by checking the database user accounts on the server. The permissions that the user has been granted to the various objects within the database, such as tables, are determined by the information contained in the user's database user account. This account also contains information about any extra permissions that the user might be granted to alter the database itself.
After you have gained access to the database, you can open the company that you want to work with.
Opening a company
In Business Central, you can only open companies in the current database that you have been given permission to access. A database can contain several companies. Each company can use its own tables and can also share tables with other companies.
Managing user access to companies
Users' access to companies is controlled by permission sets. When you assign a permission set to a user, you can specify a company to restrict the user's access for that permission set to that specific company. For more information, see Managing Users and Permissions in the Business Central application help.
When you open a company in Business Central, your ability to access information is determined by the security system.
Object-level security is the set of permissions on Business Central objects that constitute a permission set. Permission sets determine the access that users have and the tasks that users can perform on objects in the database.
Security system database objects
You can define permissions for all types of objects in a Business Central database.
| Object Type |
Description |
| Table Data |
The actual data that is stored in the tables. |
| Table |
The tables themselves. |
| Pages |
The pages that are used to view and enter data. |
| Report |
The reports that are used to present the data. |
| Codeunit |
The codeunits that are used in the database. |
| XMLport |
The XMLports that are used to import and export data. |
| Query |
The object that you use to specify a dataset from the database. |
| System |
The system tables in the database that allow the user to make backups, change license files, and so on. |
The various permission sets that exist in Business Central determine the actions that you can perform on these objects. For more information about permissions, see Permissions on Database Objects.
Permissions on database objects
This section provides an overview of permissions and permission sets in Business Central
Permissions
If you have been granted permission to read a page, then you can open the page and view the data that it displays. If, however, you don't have write permission, you aren't allowed to enter data into this page.
Sometimes, when you open a page it displays information from several tables. To access this page, you must have permission to view all the data displayed by the page. You might not have permission to read directly from all the tables that the page uses. In this case, you must have indirect permission to read from the tables in question. Having indirect permission to a table means that you can't open the table and read from it but can only view the data it contains indirectly through another object, such as a page or report, that you have direct permission to access.
Business Central has many standard predefined security permission sets. You can use these permission sets as defined or you can change a permission sets to suit your particular needs. You can also create your own permission sets and assign them the permissions that you want.
Permissions on objects
| Permission |
Description |
| Read |
You can read this object. |
| Insert |
You can insert data into this object. |
| Modify |
You can modify data in this object. |
| Delete |
You can delete data from this object. |
| Execute |
You can run this object. |
For more information, see Permissions on Database Objects.
Record-level security lets you limit the access that a user has to the data in a table.
You implement record-level security in Business Central by creating security filters on table data. A security filter describes a set of records in a table that a user has permission to access. You can specify, for example, that a user can only read the records that contain information about a particular customer. This means that the user can't access the records that contain information about other customers. For more information, see Security Filter Modes.
Record-level security filters are handled by SQL Server just like other filters that are applied by the user. They don't adversely affect performance unless the security filtering mode is Validated. When the security filtering mode for a record is Validated, then Business Central must validate whether each record is in the filter expression.
Users and credential types
Security considerations