撰寫 C# LINQ 查詢以查詢資料
在介紹 Language Integrated Query (LINQ) 的文件中,大多數查詢都是使用 LINQ 宣告式查詢語法撰寫。 C# 編譯程式會將查詢語法轉譯成方法呼叫。 這些方法呼叫會實作標準查詢運算符,並具有 Where、Select、GroupBy、Join、Max和 Average等名稱。 您可以使用方法語法來直接呼叫它們,而不是使用查詢語法。
查詢語法和方法語法在語意上相同,但查詢語法通常更簡單且更容易閱讀。 某些查詢必須以方法呼叫形式表示。 例如,您必須使用方法呼叫,來表示可擷取符合所指定條件的項目數的查詢。 您也必須針對擷取來源序列中具有最大值的項目的查詢,使用方法呼叫。 System.Linq 命名空間中標準查詢運算子的參考文件一般會使用方法語法。 您應該熟悉如何在查詢和在查詢運算式本身中使用方法語法。
標準查詢運算子擴充方法
下列範例示範簡單「查詢運算式」以及撰寫為「方法查詢」的語意對等查詢。
int[] numbers = [ 5, 10, 8, 3, 6, 12 ];
//Query syntax:
IEnumerable<int> numQuery1 =
from num in numbers
where num % 2 == 0
orderby num
select num;
//Method syntax:
IEnumerable<int> numQuery2 = numbers
.Where(num => num % 2 == 0)
.OrderBy(n => n);
foreach (int i in numQuery1)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine(System.Environment.NewLine);
foreach (int i in numQuery2)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
這兩個範例的輸出完全相同。 查詢變數的類型在這兩種形式中都相同:IEnumerable<T>。
在運算式的右側,請注意 where 子句現在會在 numbers 物件 (其類型為 IEnumerable<int>) 上被表示為執行個體方法。 如果您熟悉泛型 IEnumerable<T> 介面,就會知道它沒有 Where 方法。 不過,如果您在 Visual Studio IDE 中叫用 IntelliSense 完成清單,您不只會看到 Where 方法,還會看到許多其他方法 (例如 Select、SelectMany、Join 和 Orderby)。 這些方法會實作標準查詢運算子。
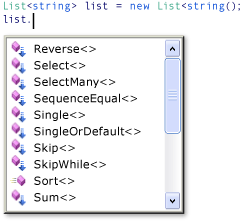
雖然 IEnumerable<T> 看起來似乎包含更多方法,但事實上並沒有。 標準查詢運算子會實作為擴充方法。 擴充方法會「擴充」現有類型,其呼叫方式就像它們是類型上的執行個體方法一樣。 標準查詢運算子可擴充 IEnumerable<T>,而且這是您可以撰寫 numbers.Where(...) 的原因。 您可以在呼叫擴充功能之前,先使用 using 指示詞將擴充功能帶入範圍。
如需擴充方法的詳細資訊,請參閱擴充方法。 如需標準查詢運算子的詳細資訊,請參閱標準查詢運算子概觀 (C#)。 有一些 LINQ 提供者 (例如 Entity Framework 和 LINQ to XML) 會為 IEnumerable<T> 以外的其他類型,實作自己的標準查詢運算子和擴充方法。
Lambda 運算式
在上述範例中,條件表達式(num % 2 == 0)會以行內引數的形式傳遞至 Enumerable.Where 方法:Where(num => num % 2 == 0). 此行內表達式是 lambda 表達式。 這是一種撰寫程式碼的便捷方法,否則必須以更繁瑣的形式編寫程式碼。 運算子左側的 num 是輸入變數,其對應到查詢運算式中的 num。 編譯器可以推斷 num 類型,因為它知道 numbers 是泛型 IEnumerable<T> 類型。 Lambda 主體與查詢語法中的運算式或任何其他 C# 運算式或語句的表達方式相同。 它可以包含方法呼叫和其他複雜的邏輯。 傳回值是表達式結果。 某些查詢只能以方法語法表示,而其中某些查詢需要 Lambda 表達式。 Lambda 運算式是 LINQ 工具箱中功能強大且彈性的工具。
查詢的編寫性
在上述程式碼範例中,使用小數點運算子於呼叫 Where時來叫用 Enumerable.OrderBy 方法。
Where 會產生篩選的序列,然後 Orderby 會排序 Where 所產生的序列。 因為查詢會傳回 IEnumerable,所以您可以將方法呼叫鏈結在一起,以在方法語法中撰寫它們。 當您使用查詢語法撰寫查詢時,編譯器會執行此撰寫。 因為查詢變數不會儲存查詢的結果,所以您隨時都可以修改它或使用它做為新查詢的基礎 (即使在執行它之後也一樣)。
下列範例示範一些基本 LINQ 查詢,使用之前提到的每種方法。
注意
這些查詢會在記憶體內部集合上運作;不過,語法與 LINQ to Entities 和 LINQ to XML 中使用的語法相同。
範例 - 查詢語法
您可以使用查詢語法來撰寫大部分的查詢,以建立查詢運算式。 下列範例示範三個查詢運算式。 第一個查詢運算式示範如何使用 where 子句套用條件來篩選或限制結果。 它會傳回值大於 7 或小於 3 的來源序列中的所有項目。 第二個運算式示範如何排序傳回的結果。 第三個運算式示範如何根據索引鍵來分組結果。 此查詢會根據單字的第一個字母來傳回兩個群組。
List<int> numbers = [ 5, 4, 1, 3, 9, 8, 6, 7, 2, 0 ];
// The query variables can also be implicitly typed by using var
// Query #1.
IEnumerable<int> filteringQuery =
from num in numbers
where num is < 3 or > 7
select num;
// Query #2.
IEnumerable<int> orderingQuery =
from num in numbers
where num is < 3 or > 7
orderby num ascending
select num;
// Query #3.
string[] groupingQuery = ["carrots", "cabbage", "broccoli", "beans", "barley"];
IEnumerable<IGrouping<char, string>> queryFoodGroups =
from item in groupingQuery
group item by item[0];
查詢類型是 IEnumerable<T>。 使用 var 可以撰寫所有這些查詢,如下列範例所示︰
var query = from num in numbers...
在每個上述範例中,除非您逐一查看 foreach 陳述式或其他陳述式中的查詢變數,否則不會實際執行查詢。
範例 - 方法語法
某些查詢作業必須以方法呼叫形式表示。 最常見的此類方法是傳回單一數值的方法,例如 Sum、Max、Min、Average 等等。 這些方法必須一律在任何查詢中最後呼叫,因為它們會傳回單一值,而且無法做為其他查詢作業的來源。 下列範例示範查詢運算式中的方法呼叫:
List<int> numbers1 = [ 5, 4, 1, 3, 9, 8, 6, 7, 2, 0 ];
List<int> numbers2 = [ 15, 14, 11, 13, 19, 18, 16, 17, 12, 10 ];
// Query #4.
double average = numbers1.Average();
// Query #5.
IEnumerable<int> concatenationQuery = numbers1.Concat(numbers2);
如果方法具有 System.Action 或 System.Func<TResult> 參數,則這些引數會以 Lambda 運算式的形式提供,如下列範例所示:
// Query #6.
IEnumerable<int> largeNumbersQuery = numbers2.Where(c => c > 15);
在先前的查詢中,只會立即執行 Query #4,因為它會傳回單一值,而不是泛型 IEnumerable<T> 集合。 方法本身會使用 foreach 或類似的程式碼來計算其值。
搭配使用隱含類型與 var,可以撰寫每個先前的查詢,如下列範例所示︰
// var is used for convenience in these queries
double average = numbers1.Average();
var concatenationQuery = numbers1.Concat(numbers2);
var largeNumbersQuery = numbers2.Where(c => c > 15);
範例 - 混合查詢和方法語法
這個範例示範如何在查詢子句結果上使用方法語法。 只需要用括號括住查詢運算式,然後套用點運算子並呼叫方法。 在下列範例中,查詢 #7 會傳回其值介於 3 與 7 之間的數字計數。
// Query #7.
// Using a query expression with method syntax
var numCount1 = (
from num in numbers1
where num is > 3 and < 7
select num
).Count();
// Better: Create a new variable to store
// the method call result
IEnumerable<int> numbersQuery =
from num in numbers1
where num is > 3 and < 7
select num;
var numCount2 = numbersQuery.Count();
因為查詢 #7 會傳回單一值,而不是集合,所以會立即執行查詢。
搭配使用隱含類型與 var,可以撰寫前一個查詢,如下列所示︰
var numCount = (from num in numbers...
它可以撰寫於方法語法中,如下所示:
var numCount = numbers.Count(n => n is > 3 and < 7);
它可以使用明確類型進行撰寫,如下所示:
int numCount = numbers.Count(n => n is > 3 and < 7);
在執行階段動態指定述詞篩選
在某些情況下,您要到執行階段才知道在 where 子句中必須套用多少述詞至來源項目。 動態指定多個述詞篩選的其中一個方式是使用 Contains 方法,如下列範例所示。 查詢會根據執行查詢時的 id 值而傳回不同的結果。
int[] ids = [ 111, 114, 112 ];
var queryNames = from student in students
where ids.Contains(student.ID)
select new
{
student.LastName,
student.ID
};
foreach (var name in queryNames)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{name.LastName}: {name.ID}");
}
/* Output:
Garcia: 114
O'Donnell: 112
Omelchenko: 111
*/
// Change the ids.
ids = [ 122, 117, 120, 115 ];
// The query will now return different results
foreach (var name in queryNames)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{name.LastName}: {name.ID}");
}
/* Output:
Adams: 120
Feng: 117
Garcia: 115
Tucker: 122
*/
注意
此範例使用下列資料來源和數據:
record City(string Name, long Population);
record Country(string Name, double Area, long Population, List<City> Cities);
record Product(string Name, string Category);
static readonly City[] cities = [
new City("Tokyo", 37_833_000),
new City("Delhi", 30_290_000),
new City("Shanghai", 27_110_000),
new City("São Paulo", 22_043_000),
new City("Mumbai", 20_412_000),
new City("Beijing", 20_384_000),
new City("Cairo", 18_772_000),
new City("Dhaka", 17_598_000),
new City("Osaka", 19_281_000),
new City("New York-Newark", 18_604_000),
new City("Karachi", 16_094_000),
new City("Chongqing", 15_872_000),
new City("Istanbul", 15_029_000),
new City("Buenos Aires", 15_024_000),
new City("Kolkata", 14_850_000),
new City("Lagos", 14_368_000),
new City("Kinshasa", 14_342_000),
new City("Manila", 13_923_000),
new City("Rio de Janeiro", 13_374_000),
new City("Tianjin", 13_215_000)
];
static readonly Country[] countries = [
new Country ("Vatican City", 0.44, 526, [new City("Vatican City", 826)]),
new Country ("Monaco", 2.02, 38_000, [new City("Monte Carlo", 38_000)]),
new Country ("Nauru", 21, 10_900, [new City("Yaren", 1_100)]),
new Country ("Tuvalu", 26, 11_600, [new City("Funafuti", 6_200)]),
new Country ("San Marino", 61, 33_900, [new City("San Marino", 4_500)]),
new Country ("Liechtenstein", 160, 38_000, [new City("Vaduz", 5_200)]),
new Country ("Marshall Islands", 181, 58_000, [new City("Majuro", 28_000)]),
new Country ("Saint Kitts & Nevis", 261, 53_000, [new City("Basseterre", 13_000)])
];
您可以使用 if... else 或 switch 這類控制流程陳述式,以在預先決定的替代查詢之間進行選取。 在下列範例中,如果 studentQuery 的執行階段值為 where 或 oddYear,則 true 會使用不同的 false 子句。
void FilterByYearType(bool oddYear)
{
IEnumerable<Student> studentQuery = oddYear
? (from student in students
where student.Year is GradeLevel.FirstYear or GradeLevel.ThirdYear
select student)
: (from student in students
where student.Year is GradeLevel.SecondYear or GradeLevel.FourthYear
select student);
var descr = oddYear ? "odd" : "even";
Console.WriteLine($"The following students are at an {descr} year level:");
foreach (Student name in studentQuery)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{name.LastName}: {name.ID}");
}
}
FilterByYearType(true);
/* Output:
The following students are at an odd year level:
Fakhouri: 116
Feng: 117
Garcia: 115
Mortensen: 113
Tucker: 119
Tucker: 122
*/
FilterByYearType(false);
/* Output:
The following students are at an even year level:
Adams: 120
Garcia: 114
Garcia: 118
O'Donnell: 112
Omelchenko: 111
Zabokritski: 121
*/
處理查詢運算式中的 Null 值
本例示範如何處理來源集合中可能有的 Null 值。 如 IEnumerable<T> 的物件集合,可以包含值為 null 的元素。 如果來源集合為 null 或包含其值為 null 的元素,而且您的查詢不處理 null 值,則當您執行查詢時會擲回 NullReferenceException。
下列範例會使用這些類型和靜態資料陣列:
record Product(string Name, int CategoryID);
record Category(string Name, int ID);
static Category?[] categories =
[
new ("brass", 1),
null,
new ("winds", 2),
default,
new ("percussion", 3)
];
static Product?[] products =
[
new Product("Trumpet", 1),
new Product("Trombone", 1),
new Product("French Horn", 1),
null,
new Product("Clarinet", 2),
new Product("Flute", 2),
null,
new Product("Cymbal", 3),
new Product("Drum", 3)
];
您可以謹慎撰寫程式碼以避免發生 Null 參考例外狀況,如下例所示︰
var query1 = from c in categories
where c != null
join p in products on c.ID equals p?.CategoryID
select new
{
Category = c.Name,
Name = p.Name
};
在上例中,where 子句會篩選掉類別序列中的所有 Null 項目。 這項技術不影響 join 子句中的 Null 檢查。 因為 Products.CategoryID 是 int? 類型 (即 Nullable<int> 的速記),所以具有 Null 的條件運算式在此範例中可以運作。
在 join 子句中,如果僅有一個比較索引鍵是可為 Null 的實值型別,則可以在查詢運算式中將其他的比較索引鍵轉換成可為 Null 的型別。 在下列範例中,假設 EmployeeID 是包含 int? 類型值的資料行:
var query =
from o in db.Orders
join e in db.Employees
on o.EmployeeID equals (int?)e.EmployeeID
select new { o.OrderID, e.FirstName };
在每個範例中,都會使用 equals 查詢關鍵字。 您也可以使用模式比對,其中包含 is null 與 is not null 的模式。 LINQ 查詢中不建議使用這些模式,因為查詢提供者可能無法正確解譯新的 C# 語法。 查詢提供者是一種程式庫,可將 C# 查詢運算式轉譯成原生資料格式,例如 Entity Framework Core。 查詢提供者會實作 System.Linq.IQueryProvider 介面,以建立實作 System.Linq.IQueryable<T> 介面的資料來源。
處理查詢運算式中的例外狀況
您可在查詢運算式的內容中呼叫任何方法。 請勿在查詢運算式中呼叫任何可能產生副作用 (例如修改資料來源的內容或擲回例外狀況) 的方法。 此範例顯示如何避免在查詢運算式中呼叫方法時引發例外狀況,卻不違反處理例外狀況的一般 .NET 方針。 這些指導方針指出,當您了解為何在特定情境中拋出例外狀況時,可以接受捕捉該例外狀況。 如需詳細資訊,請參閱例外狀況的最佳做法。
最後一個範例顯示如何處理這種當您在查詢執行期間必須擲回例外狀況的情況。
下例示範如何將例外狀況處理程式碼移到查詢運算式之外。 只有當該方法不依賴任何查詢區域變數時,才能進行此重構。 處理查詢運算式以外的例外狀況比較容易。
// A data source that is very likely to throw an exception!
IEnumerable<int> GetData() => throw new InvalidOperationException();
// DO THIS with a datasource that might
// throw an exception.
IEnumerable<int>? dataSource = null;
try
{
dataSource = GetData();
}
catch (InvalidOperationException)
{
Console.WriteLine("Invalid operation");
}
if (dataSource is not null)
{
// If we get here, it is safe to proceed.
var query = from i in dataSource
select i * i;
foreach (var i in query)
{
Console.WriteLine(i.ToString());
}
}
在上述範例的 catch (InvalidOperationException) 區塊中,請以適合您應用程式的方式處理 (或不要處理) 例外狀況。
在某些情況下,對從查詢中擲回的例外狀況的最佳回應,可能是立即停止執行查詢。 下例示範如何處理可能從查詢主體內擲回的例外狀況。 假設 SomeMethodThatMightThrow 可能造成需要停止執行查詢的例外狀況。
try 區塊會括住 foreach 迴圈,不是括住查詢本身。
foreach 迴圈是執行查詢的點。 執行查詢時會擲回執行階段例外狀況。 因此,必須在 foreach 迴圈中進行處理。
// Not very useful as a general purpose method.
string SomeMethodThatMightThrow(string s) =>
s[4] == 'C' ?
throw new InvalidOperationException() :
$"""C:\newFolder\{s}""";
// Data source.
string[] files = ["fileA.txt", "fileB.txt", "fileC.txt"];
// Demonstration query that throws.
var exceptionDemoQuery = from file in files
let n = SomeMethodThatMightThrow(file)
select n;
try
{
foreach (var item in exceptionDemoQuery)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Processing {item}");
}
}
catch (InvalidOperationException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
/* Output:
Processing C:\newFolder\fileA.txt
Processing C:\newFolder\fileB.txt
Operation is not valid due to the current state of the object.
*/
請記得在 finally 區塊中擷取任何您預期引發和/或進行任何必要清除的例外狀況。
