subrange class (C++標準連結庫)
提供範圍元素的檢視,如開始反覆運算器和 sentinel 所定義。
語法
template<input_or_output_iterator I, sentinel_for<I> S, subrange_kind K>
requires (K == subrange_kind::sized || !sized_sentinel_for<S, I>)
class subrange : public view_interface<subrange<I, S, K>>
範本參數
I
開始反覆運算器類型。 概 input_or_output_iterator 念可確保 I 是可讀取所有元素的反覆運算器。
K
子範圍的類型:用來 subrange_kind::sized 指定大小子範圍。 如果 sized_sentinel_for<S, I> 反覆運算器和 sentinel 可以減去以產生大小,請使用 。 需求 subrange_kind::sized || !sized_sentinel_for<S, I> 會將大小儲存在子範圍物件中,而且您必須使用採用 sized_range 的建構函式來建構子範圍, subrange_kind::sized 或透過採用 iterator、 sentinel和 size 的建構函式來 sized_sentinel_for<S, I> 建構子範圍。
S
結束反覆運算器類型。 概 sized_sentinel_for 念可確保 S 可以當做 sentinel I 使用,而且可以在常數時間計算 sentinel 與目前反覆運算器位置 I 之間的距離。
檢視特性
如需下列專案的描述,請參閱 檢視類別特性
| 特性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 範圍配接器 | views::counted |
| 基礎範圍 | 任何範圍 |
| 項目類型 | iter_reference_t<I> |
| 檢視反覆運算器類別 | 與 Is 類別相同 |
| 大小 | 如果 K 為 subrange::sized |
為 const-iterable |
如果 I 是可複製的 |
| 通用範圍 | 如果 I 和 S 是相同的類型。 |
| 借用範圍 | Yes |
成員
| 成員函式 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| 建構函式C++20 | subrange建構 。 |
operator PairLikeC++20 |
subrange將轉換成類似配對的類型。 |
advanceC++20 |
將反覆運算器移至指定的距離。 |
begin |
取得第一個專案的反覆運算器。 |
emptyC++20 |
測試 是否 subrange 為空白。 |
endC++20 |
取得 結尾的 subrangesentinel。 |
nextC++20 |
建立這個 subrange 的複本,但儲存的反覆運算器會往前移動指定的距離。 |
prevC++20 |
建立這個 subrange 的複本,但儲存的反覆運算器會移回指定的距離。 |
sizeC++20 |
取得項目數目。 |
繼承自 view_interface |
說明 |
backC++20 |
取得最後一個專案。 |
dataC++20 |
取得第一個專案的指標。 |
frontC++20 |
取得第一個專案。 |
operator[]C++20 |
取得位於指定位置的專案。 |
operator boolC++20 |
測試 是否 subrange 為空白。 |
備註
subrange當您有開始和結束反覆運算器,但想要改為傳遞單一物件時,會很有用。 例如,如果您想要呼叫範圍配接器,但有開始和結束反覆運算器,您可以使用 subrange 來包裝它們,並將 傳遞給 subrange 範圍配接器。
需求
標頭: <ranges> (自C++20起)
命名空間:std::ranges
需要編譯程式選項:/std:c++20或更新版本。
建構函式
建立 subrange。
1) subrange() requires default_initializable<I> = default;
2) template <Convertible_to_non_slicing<I> It>
constexpr subrange(It begin, S end) requires (!Store_size);
3) template <Convertible_to_non_slicing<I> It>
constexpr subrange(It begin, S end, const Size_type size) requires (K == subrange_kind::sized);
4) template <Not_same_as<subrange> rg>
requires borrowed_range<rg>
&& Convertible_to_non_slicing<iterator_t<rg>, I>
&& convertible_to<sentinel_t<rg>, S>
constexpr subrange(rg&& r) requires (!_Store_size || sized_range<rg>);
5) template <borrowed_range rg>
requires Convertible_to_non_slicing<iterator_t<rg>, I> && convertible_to<sentinel_t<rg>, S>
constexpr subrange(rg&& r, const _Size_type sizeHint) requires (K == subrange_kind::sized)
參數
begin
指向子範圍中第一個專案的反覆運算器。
end
Sentinel 指向子範圍的結尾。 它指向的專案不會包含在子範圍中。
sizeHint
元素中範圍的大小。 這可用來優化 size 成員函式,而且如果您想要從反覆運算器和 sentinel 建立大小 subrange ,且其類型不是模型 sized_sentinel_for,則為必要專案。
如需範本參數類型的相關信息,請參閱 範本參數。
傳回值
subrange 執行個體。
備註
1) 預設值會建構儲存的反覆運算器和 sentinel。 大小提示設定為 0。
2) 用來std::move()將反覆運算器和 end sentinel 移至begin儲存的反覆運算器和 sentinel。
3) 使用 std::move(begin)初始化預存反覆運算器、使用 的預存 sentinel std::move(end),以及具有 size的預存大小提示,這應該等於第一個自變數和第二個自變數之間的距離。
4) 從範圍建構 subrange 。
5) 如果 szHint != ranges::distance(rg),則不會定義行為。
counted範圍配接器可以建立 subrange。 該配接器會採用開始反覆運算器和計數。
範例: counted
// requires /std:c++20 or later
#include <ranges>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
auto pos5 = std::ranges::find(v, 5);
auto countedView = std::views::counted(pos5, 5);
for (auto e : countedView) // outputs 5 6 7 8 9
{
std::cout << e << ' ';
}
std::cout << '\n';
// You can pass the range directly if it supports input_or_output_iterator, in which case, the
// count starts from the first element
const char chars[] = { 'H','i',' ','t','h','e','r','e' };
for (char c : std::views::counted(chars, 2))
{
std::cout << c; // outputs Hi
}
}
5 6 7 8 9
Hi
operator PairLike
subrange將轉換成模型pair-like的類型。
template<not-same-as<subrange> PairLike>
requires pair-like-convertible-from<PairLike, const I&, const S&>
constexpr operator PairLike() const;
參數
無。
如需範本參數類型的相關信息,請參閱 範本參數。
傳回值
PairLike使用預存反覆運算器和 sentinel 直接初始化的值。
配對中的最後一個值將是 sentinel。
請記住,sentinel 已 超過 子範圍中的最後一個專案,如下列範例所示。
備註
這項轉換對於接受(第一個、最後一個)配對的舊 Boost::Ranges 版程序代碼很有用,以表示範圍。
此轉換適用於將子範圍 pair 轉換成 或 tuple 模型的其他類型 pair_like。 類型的 pair_like 一些範例包括:
std::array<T, 2>
std::pair<T, U>
std::ranges::subrange<I, S, K>
std::tuple<T, U>
範例: operator PairLike()
// requires /std:c++20 or later
#include <iostream>
#include <ranges>
#include <vector>
#include <utility>
int main()
{
constexpr int a[] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
std::ranges::subrange rg(a);
rg.advance(2);
const std::pair<const int*, const int*> p = rg;
for (auto e : rg)
{
std::cout << e << ' ';
}
// because the sentinel points after the last element, subtract one to get the last element
std::cout << '\n' << *p.first << ':' << *(p.second - 1) << '\n'; // outputs 2:5
}
2 3 4 5
2:5
advance
依n元素調整這個subrange的反覆運算器。
constexpr subrange& advance(const iter_difference_t<I> n);
參數
n
要調整反覆運算器的項目數目。 n 可以是正數(向前移動),或者,如果 I 是雙向的,則為負數(向後移動)。
備註
此函式會修改 中 subrange反覆運算器的目前狀態。
如果您前進到 的結尾 subrange,反覆運算器會設定為 結尾的 sentinel subrange。
如果您前進到 開頭 (使用負n數 subrange ),則如果您從 中建立subrange的範圍沒有專案,則會收到無效的參數例外狀況。
例 advance
// requires /std:c++20 or later
#include <iostream>
#include <ranges>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
void print(const std::string &msg, auto &&v)
{
std::cout << msg << '\n';
for (auto& x : v)
{
std::cout << x << ' ';
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
int main()
{
std::vector v = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
print("Original vector: ", v); // outputs 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
// create a subrange 3 4 5 6
std::ranges::subrange theSubrange{ std::ranges::find(v,3), std::ranges::find(v, 7) };
print("The subrange: ", theSubrange); // outputs 3 4 5 6
auto sr = theSubrange.advance(2); // get a subrange 2 positions to the right of the current iterator location
print("theSubrange.advance(2): ", sr); // outputs 5 6
print("Note that subrange's iterator moved during advance(): ", sr); // outputs 5 6
sr = theSubrange.advance(-3); // Moving before the subrange, but onto a valid element in the original range
print("theSubrange.advance(-3): ", sr); // outputs 2 3 4 5 6
}
Original vector:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
The subrange:
3 4 5 6
theSubrange.advance(2):
5 6
Note that subrange's iterator moved during advance():
5 6
theSubrange.advance(-3):
2 3 4 5 6
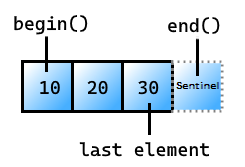
begin
取得 中第一個專案的 subrange反覆運算器。
1) constexpr I begin() const requires copyable<I>;
2) [[nodiscard]] constexpr I begin() requires (!std::copyable<I>);
參數
無。
傳回值
指向 中第一個專案的 subrange反覆運算器。
如果反覆運算器無法複製,則會使用 std::move()傳回。 如果反覆運算器已移動,則預存反覆運算器的狀態取決於的移動建構函 I式實作。
empty
測試 是否 subrange 為空白。
constexpr bool empty() const;
參數
無。
傳回值
如果沒有專案,subrange則傳true回 。 否則傳回 false。
end
在結尾取得 sentinel subrange
[[nodiscard]] constexpr S end() const;
參數
無。
傳回值
緊接在 中最後一個項目後面的 subrangesentinel:

sentinel 是從儲存的 sentinel 複製建構的。
next
建立這個 subrange 的複本,但儲存的反覆運算器會往前移動指定的距離。
1) [[nodiscard]] constexpr subrange next(iter_difference_t<I> n = 1) const & requires forward_iterator<I>;
2) [[nodiscard]] constexpr subrange next(iter_difference_t<I> n = 1) &&;
參數
n
要向前移動反覆運算器的項目數目。 預設值為 1。 必須是正數。
傳回值
傳回從 *n*th 元素開始的 subrange 複本。
備註
不同於 advance(), next() 不會變更儲存在原始 subrange中之反覆運算器的位置。
傳回 subrange 的 具有原始子範圍擁有的所有元素,但反覆運算器位於不同的位置。
1) 傳回值與:
auto tmp = *this;
tmp.advance(n);
return tmp;
2) 傳回值與:
advance(n);
return std::move(*this);
範例: next
// requires /std:c++20 or later
#include <iostream>
#include <ranges>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
void print(const std::string &msg, auto &&v)
{
std::cout << msg << '\n';
for (auto& x : v)
{
std::cout << x << ' ';
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
int main()
{
std::vector v = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
print("Original vector:", v); // 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
// create a subrange from the front of v up to (but not including) the element 7
std::ranges::subrange theSubrange{ std::ranges::find(v,1), std::ranges::find(v, 7) };
print("The subrange:", theSubrange); // 1 2 3 4 5 6
auto forward = theSubrange.advance(3); // get a subrange 3 positions to the right of the current iterator location
print("theSubrange.advance(3):", forward); // 4 5 6
// prev()
auto previous = theSubrange.prev(2); // move back 2
print("theSubrange.prev(2):", previous); // 2 3 4 5 6
print("Note that the subrange's iterator did *not* move during prev():", theSubrange); // 4 5 6
}
Original vector:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
The subrange:
1 2 3 4 5 6
theSubrange.next(3):
4 5 6
Note that the original subrange's iterator did *not* move during next():
1 2 3 4 5 6
prev
建立這個 subrange的複本,但儲存的反覆運算器會移回指定的距離。
[[nodiscard]] constexpr subrange prev(std::iter_difference_t<I> n = 1 ) const
requires std::bidirectional_iterator<I>;
參數
n
將反覆運算器移回多少個元素。 預設值為 1。 必須是正數。
傳回值
傳回的複本, subrange 但反覆運算器已移回 n 元素。
備註
不同於 advance(), prev() 不會變更儲存在原始 subrange中之反覆運算器的位置。
傳回 subrange 的 具有原始子範圍擁有的所有元素,但反覆運算器只是在不同的位置。 您可以傳回值視為:
auto tmp = *this;
tmp.advance(-n);
return tmp;
例 prev
// requires /std:c++20 or later
#include <iostream>
#include <ranges>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
void print(const std::string &msg, auto &&v)
{
std::cout << msg << '\n';
for (auto& x : v)
{
std::cout << x << ' ';
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
int main()
{
std::vector v = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
print("Original vector:", v); // 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
// create a subrange from the front of v up to (but not including) the element 7
std::ranges::subrange theSubrange{std::ranges::find(v,1), std::ranges::find(v, 7)};
print("The subrange: ", theSubrange); // 1 2 3 4 5 6
auto forward = theSubrange.advance(3); // get a subrange 3 positions to the right of the current iterator location
print("theSubrange.advance(3):", forward); // 4 5 6
// prev()
auto previous = theSubrange.prev(2); // move back 2
print("theSubrange.prev(2):", previous); // 2 3 4 5 6
print("Note that the subrange's iterator did *not* move during prev():", theSubrange); // 4 5 6
}
Original vector:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
The subrange:
1 2 3 4 5 6
theSubrange.advance(3):
4 5 6
theSubrange.prev(2):
2 3 4 5 6
Note that the subrange's iterator did *not* move during prev():
4 5 6
size
取得中的 subrange項目數目。
constexpr size() const
requires (K == ranges::subrange_kind::sized);
參數
無。
傳回值
subrange 中的項目數。
如果未儲存大小,則為以指定的 和 std::sized_sentinel_for<S, I> 不符合建立 K == ranges::subrange_kind::sized 時subrange的情況,則會以開始和結束反覆運算器之間的距離傳回大小。
使用 變更反覆運算器的位置 begin , advance例如,變更報告的大小。