在 C++ for UWP 應用程式中建立非同步作業
本文件說明當您使用工作類別在通用 Windows 執行階段 (UWP) 應用程式中產生以 Windows ThreadPool 為基礎的異步操作時,要記住的一些重點。
使用異步程式設計是 Windows 執行階段 應用程式模型中的重要元件,因為它可讓應用程式繼續回應用戶輸入。 您可以啟動長時間執行的工作,而不封鎖 UI 執行緒,而且可以稍後再接收工作的結果。 工作在背景執行時,您也可以取消工作和接收進度通知。 C++中的異步程式設計檔提供 Visual C++ 中可用來建立 UWP 應用程式的異步模式概觀。 該文件會教導如何同時取用和建立異步 Windows 執行階段 作業的鏈結。 本節說明如何使用 ppltasks.h 中的類型來產生另一個 Windows 執行階段 元件可以使用的異步操作,以及如何控制異步工作的執行方式。 也請考慮閱讀 Hilo 中的異步程式設計模式和秘訣(使用 C++ 和 XAML 的 Windows 市集應用程式),以瞭解如何使用工作類別在 Hilo 中實作異步操作,這是使用 C++ 和 XAML 的 Windows 執行階段 應用程式。
注意
您可以在 UWP 應用程式中使用 平行模式連結庫 (PPL) 和 異步代理程式連結庫 。 不過,您無法使用工作排程器或資源管理員。 本文件說明 PPL 提供的其他功能,僅適用於 UWP 應用程式,而不是傳統型應用程式。
重點
使用 concurrency::create_async 建立其他元件可以使用的非同步作業 (可能是以 C++ 以外的語言撰寫)。
使用 concurrency::progress_reporter 向呼叫您的非同步作業的元件回報進度通知。
使用取消語彙基元可讓內部非同步作業取消。
create_async函式的行為取決於所收到工作函式的傳回類型。 傳回工作 (task<T>或task<void>) 的工作函式會在呼叫create_async的內容中同步執行。 傳回T或void的工作函式則會在任意內容中執行。您可以使用 concurrency::task::then 方法建立逐一執行的工作鏈結。 在UWP應用程式中,工作接續的預設內容取決於該工作的建構方式。 如果工作是藉由傳遞非同步動作至工作建構函式所建立,或是藉由傳遞傳回非同步動作的 Lambda 運算式所建立,則該工作的所有預設接續內容都會是目前的內容。 如果未從異步動作建構工作,則預設會針對工作的接續使用任意內容。 您可以使用 concurrency::task_continuation_context 類別覆寫預設內容。
本文件內容
建立非同步作業
您可以在平行模式程式庫 (PPL) 中使用工作和接續模型,定義背景工作以及會在前一項工作完成時執行的工作。 這項功能是由 concurrency::task 類別所提供。 如需這個模型和 task 類別的詳細資訊,請參閱 Task Parallelism的內容中同步執行。
Windows 執行階段 是一種程式設計介面,可用來建立只在特殊操作系統環境中執行的 UWP 應用程式。 這類應用程式會使用授權的功能、資料類型和裝置,並且從 Microsoft Store 發佈。 Windows 執行階段 是由應用程式二進位介面 (ABI) 表示。 ABI 是基礎二進制合約,可讓 Windows 執行階段 API 可供 Visual C++ 等程式設計語言使用。
藉由使用 Windows 執行階段,您可以使用各種程式設計語言的最佳功能,並將其合併成一個應用程式。 例如,您可能在 JavaScript 中建立 UI,並且在 C++ 元件中執行密集運算的應用程式邏輯。 在背景執行這些密集運算作業的能力,就是讓 UI 保持回應的主要因素。 因為類別task是C++特有的,因此您必須使用 Windows 執行階段 介面,將異步操作傳達給其他元件(可能以C++以外的語言撰寫)。 Windows 執行階段 提供四個介面,可用來表示異步操作:
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncAction
表示非同步動作。
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncActionWithProgress TProgress<>
表示報告進度的非同步動作。
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncOperation<TResult>
表示傳回結果的非同步作業。
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncOperationWithProgress<TResult, TProgress>
表示傳回結果和報告進度的非同步作業。
「 動作 」(Action) 的概念表示,非同步工作沒有產生值 (想像傳回 void的函式)。 「 作業 」(Operation) 的概念表示,非同步工作會產生值。 「 進度 」(Progress) 的概念表示,工作可以向呼叫端報告進度訊息。 JavaScript、.NET Framework 和 Visual C++ 各提供了自己建立這些介面執行個體的方式,以供跨 ABI 界限使用。 針對 Visual C++,PPL 提供了 concurrency::create_async 函式。 此函式會建立代表工作完成的異步動作或作業 Windows 執行階段。 函create_async式會採用工作函式(通常是 Lambda 運算式),在內部建立 task 物件,並將該工作包裝在四個異步 Windows 執行階段 介面的其中一個。
注意
create_async只有當您必須建立可從另一種語言或另一個 Windows 執行階段元件存取的功能時,才使用 。 如果您清楚知道作業是在同一個元件中由 C++ 程式碼所產生和使用,則直接使用 task 類別。
create_async 的傳回類型取決於其引數的類型。 例如,如果您的工作函式不會傳回值,而且不會報告進度,則 create_async 會傳回 IAsyncAction。 如果您的工作函式不會傳回值,但是會報告進度,則 create_async 會傳回 IAsyncActionWithProgress。 若要報告進度,請提供 concurrency::progress_reporter 物件做為工作函式的參數。 報告進度的功能可讓您報告已執行多少工作,以及仍剩多少工作 (例如,以百分比表示)。 另外也可在結果產生時讓您報告結果。
IAsyncAction、 IAsyncActionWithProgress<TProgress>、 IAsyncOperation<TResult>和 IAsyncActionOperationWithProgress<TProgress, TProgress> 介面各提供了一個 Cancel 方法,可讓您取消非同步作業。 task 類別可與取消語彙基元一起使用。 當您使用取消語彙基元取消工作時,執行階段就不會啟動訂閱這個語彙基元的新工作。 已在進行的工作可以監視自己的取消語彙基元,並且在可以停止時停止。 這個機制將在 Cancellation in the PPL文件中進行詳細說明。 您可以使用兩種方式,將工作取消與 Windows 執行階段 Cancel 方法連線。 一種方式是定義傳遞至 create_async 以採用 concurrency::cancellation_token 物件的工作函式。 Cancel呼叫 方法時,會取消此取消標記,且一般取消規則會套用至支援create_async呼叫的基礎task物件。 如果您未提供 cancellation_token 物件,則基礎 task 物件會隱含定義該物件。 當您需要以合作方式回應工作函式中的取消時,請定義 cancellation_token 物件。 範例:使用 C++ 和 XAML 控制 Windows 執行階段 應用程式中的執行一節示範如何使用 C# 和使用自訂 Windows 執行階段 C++元件的 XAML 在 通用 Windows 平台 (UWP) 應用程式中執行取消。
警告
在工作接續鏈結中,一律清除狀態,然後在取消令牌取消時呼叫 並行::cancel_current_task 。 如果您提早傳回而不是呼叫 cancel_current_task,則作業會轉換成已完成狀態,而不是已取消狀態。
下表摘要說明可在您的應用程式中用來定義非同步作業的組合。
| 若要建立此 Windows 執行階段 介面 | 從 create_async傳回這個類型。 |
將這些參數類型傳遞至您的工作函式,以使用隱含取消語彙基元 | 將這些參數類型傳遞至您的工作函式,以使用明確取消語彙基元 |
|---|---|---|---|
IAsyncAction |
void 或 task<void> |
(無) | (cancellation_token) |
IAsyncActionWithProgress<TProgress> |
void 或 task<void> |
(progress_reporter) |
(progress_reporter, cancellation_token) |
IAsyncOperation<TResult> |
T 或 task<T> |
(無) | (cancellation_token) |
IAsyncActionOperationWithProgress<TProgress, TProgress> |
T 或 task<T> |
(progress_reporter) |
(progress_reporter, cancellation_token) |
您可以從傳遞至 task 函式的工作函式傳回值或 create_async 物件。 這些變化會產生不同的行為。 當您傳回值時,工作函式會包裝在 task 中,如此它就可以在背景執行緒上執行。 另外,基礎 task 會使用隱含取消語彙基元。 相反地,如果您傳回 task 物件,則工作函式會同步執行。 因此,如果您傳回 task 物件,請確認工作函式中所有冗長的作業也都做為工作執行,讓您的應用程式能夠保持回應。 另外,基礎 task 不會使用隱含取消語彙基元。 因此,如果您需要在從 cancellation_token 傳回 task 物件時支援取消,則需要定義自己的工作函式以接受 create_async物件。
下列範例示範建立另一IAsyncAction個 Windows 執行階段元件可取用之對象的各種方式。
// Creates an IAsyncAction object and uses an implicit cancellation token.
auto op1 = create_async([]
{
// Define work here.
});
// Creates an IAsyncAction object and uses no cancellation token.
auto op2 = create_async([]
{
return create_task([]
{
// Define work here.
});
});
// Creates an IAsyncAction object and uses an explicit cancellation token.
auto op3 = create_async([](cancellation_token ct)
{
// Define work here.
});
// Creates an IAsyncAction object that runs another task and also uses an explicit cancellation token.
auto op4 = create_async([](cancellation_token ct)
{
return create_task([ct]()
{
// Define work here.
});
});
範例:建立C++Windows 執行階段元件並從 C 取用它#
請考慮使用 XAML 和 C# 來定義 UI 和 C++ Windows 執行階段 元件來執行計算密集型作業的應用程式。 在這個範例中,C++ 元件會計算某個範圍中哪些數字是質數。 為了說明四個 Windows 執行階段 異步工作介面之間的差異,請在Visual Studio中建立空白解決方案並將它命名為 ,以Primes在Visual Studio中開始。 然後在方案中新增 [Windows 執行階段元件] 專案,並將它命名為 PrimesLibrary。 將下列程式碼加入至產生的 C++ 標頭檔 (這個範例會將 Class1.h 重新命名為 Primes.h)。 每個 public 方法都會定義四個非同步介面的其中一個。 傳回值的方法會傳回 Windows::Foundation::Collections::IVector<int> 物件。 報告進度的方法會產生 double 值,用以定義整體工作已完成的百分比。
#pragma once
namespace PrimesLibrary
{
public ref class Primes sealed
{
public:
Primes();
// Computes the numbers that are prime in the provided range and stores them in an internal variable.
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncAction^ ComputePrimesAsync(int first, int last);
// Computes the numbers that are prime in the provided range and stores them in an internal variable.
// This version also reports progress messages.
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncActionWithProgress<double>^ ComputePrimesWithProgressAsync(int first, int last);
// Gets the numbers that are prime in the provided range.
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncOperation<Windows::Foundation::Collections::IVector<int>^>^ GetPrimesAsync(int first, int last);
// Gets the numbers that are prime in the provided range. This version also reports progress messages.
Windows::Foundation::IAsyncOperationWithProgress<Windows::Foundation::Collections::IVector<int>^, double>^ GetPrimesWithProgressAsync(int first, int last);
};
}
注意
依照慣例,Windows 執行階段 中的異步方法名稱通常會以 「Async」 結尾。
將下列程式碼加入至產生的 C++ 原始程式檔 (這個範例會將 Class1.cpp 重新命名為 Primes.cpp)。 is_prime 函式會判斷其項目是否為質數。 其餘的方法會實作 Primes 類別。 每次呼叫 create_async 都會使用與從中進行呼叫的方法相容的簽章。 例如,由於 Primes::ComputePrimesAsync 會傳回 IAsyncAction,因此提供給 create_async 的工作函式不會傳回值,也不會使用 progress_reporter 物件做為其參數。
// PrimesLibrary.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include "Primes.h"
#include <atomic>
#include <collection.h>
#include <ppltasks.h>
#include <concurrent_vector.h>
using namespace concurrency;
using namespace std;
using namespace Platform;
using namespace Platform::Collections;
using namespace Windows::Foundation;
using namespace Windows::Foundation::Collections;
using namespace PrimesLibrary;
Primes::Primes()
{
}
// Determines whether the input value is prime.
bool is_prime(int n)
{
if (n < 2)
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 2; i < n; ++i)
{
if ((n % i) == 0)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// Adds the numbers that are prime in the provided range
// to the primes global variable.
IAsyncAction^ Primes::ComputePrimesAsync(int first, int last)
{
return create_async([this, first, last]
{
// Ensure that the input values are in range.
if (first < 0 || last < 0)
{
throw ref new InvalidArgumentException();
}
// Perform the computation in parallel.
parallel_for(first, last + 1, [this](int n)
{
if (is_prime(n))
{
// Perhaps store the value somewhere...
}
});
});
}
IAsyncActionWithProgress<double>^ Primes::ComputePrimesWithProgressAsync(int first, int last)
{
return create_async([first, last](progress_reporter<double> reporter)
{
// Ensure that the input values are in range.
if (first < 0 || last < 0)
{
throw ref new InvalidArgumentException();
}
// Perform the computation in parallel.
atomic<long> operation = 0;
long range = last - first + 1;
double lastPercent = 0.0;
parallel_for(first, last + 1, [&operation, range, &lastPercent, reporter](int n)
{
// Report progress message.
double progress = 100.0 * (++operation) / range;
if (progress >= lastPercent)
{
reporter.report(progress);
lastPercent += 1.0;
}
if (is_prime(n))
{
// Perhaps store the value somewhere...
}
});
reporter.report(100.0);
});
}
IAsyncOperation<IVector<int>^>^ Primes::GetPrimesAsync(int first, int last)
{
return create_async([this, first, last]() -> IVector<int>^
{
// Ensure that the input values are in range.
if (first < 0 || last < 0)
{
throw ref new InvalidArgumentException();
}
// Perform the computation in parallel.
concurrent_vector<int> primes;
parallel_for(first, last + 1, [this, &primes](int n)
{
// If the value is prime, add it to the global vector.
if (is_prime(n))
{
primes.push_back(n);
}
});
// Sort the results.
sort(begin(primes), end(primes), less<int>());
// Copy the results to an IVector object. The IVector
// interface makes collections of data available to other
// Windows Runtime components.
auto results = ref new Vector<int>();
for (int prime : primes)
{
results->Append(prime);
}
return results;
});
}
IAsyncOperationWithProgress<IVector<int>^, double>^ Primes::GetPrimesWithProgressAsync(int first, int last)
{
return create_async([this, first, last](progress_reporter<double> reporter) -> IVector<int>^
{
// Ensure that the input values are in range.
if (first < 0 || last < 0)
{
throw ref new InvalidArgumentException();
}
// Perform the computation in parallel.
concurrent_vector<int> primes;
long operation = 0;
long range = last - first + 1;
double lastPercent = 0.0;
parallel_for(first, last + 1, [&primes, &operation, range, &lastPercent, reporter](int n)
{
// Report progress message.
double progress = 100.0 * (++operation) / range;
if (progress >= lastPercent)
{
reporter.report(progress);
lastPercent += 1.0;
}
// If the value is prime, add it to the local vector.
if (is_prime(n))
{
primes.push_back(n);
}
});
reporter.report(100.0);
// Sort the results.
sort(begin(primes), end(primes), less<int>());
// Copy the results to an IVector object. The IVector
// interface makes collections of data available to other
// Windows Runtime components.
auto results = ref new Vector<int>();
for (int prime : primes)
{
results->Append(prime);
}
return results;
});
}
每個方法都會先執行驗證,以確保輸入參數為非負數。 如果輸入的值為負數,方法會擲回 Platform::InvalidArgumentException。 本結稍後將說明錯誤處理。
若要從 UWP 應用程式取用這些方法,請使用 Visual C# 空白應用程式 (XAML) 範本,將第二個專案新增至 Visual Studio 解決方案。 這個範例會將專案命名為 Primes。 然後從 Primes 專案中,新增 PrimesLibrary 專案的參考。
將下列程式碼加入至 MainPage.xaml。 這個程式碼會定義 UI,讓您能夠呼叫 C++ 元件並顯示結果。
<Page
x:Class="Primes.MainPage"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local="using:Primes"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
mc:Ignorable="d">
<Grid Background="{StaticResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="300"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="300"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="125"/>
<RowDefinition Height="125"/>
<RowDefinition Height="125"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="0" Grid.Row="0">
<Button Name="b1" Click="computePrimes">Compute Primes</Button>
<TextBlock Name="tb1"></TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="0">
<Button Name="b2" Click="computePrimesWithProgress">Compute Primes with Progress</Button>
<ProgressBar Name="pb1" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Width="100"></ProgressBar>
<TextBlock Name="tb2"></TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="0" Grid.Row="1">
<Button Name="b3" Click="getPrimes">Get Primes</Button>
<TextBlock Name="tb3"></TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="1">
<Button Name="b4" Click="getPrimesWithProgress">Get Primes with Progress</Button>
<ProgressBar Name="pb4" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Width="100"></ProgressBar>
<TextBlock Name="tb4"></TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="0" Grid.Row="2">
<Button Name="b5" Click="getPrimesHandleErrors">Get Primes and Handle Errors</Button>
<ProgressBar Name="pb5" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Width="100"></ProgressBar>
<TextBlock Name="tb5"></TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
<StackPanel Grid.Column="1" Grid.Row="2">
<Button Name="b6" Click="getPrimesCancellation">Get Primes with Cancellation</Button>
<Button Name="cancelButton" Click="cancelGetPrimes" IsEnabled="false">Cancel</Button>
<ProgressBar Name="pb6" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Width="100"></ProgressBar>
<TextBlock Name="tb6"></TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Page>
將下列程式碼加入至 MainPage.xaml 中的 MainPage 類別。 這個程式碼會定義 Primes 物件和按鈕事件處理常式。
private PrimesLibrary.Primes primesLib = new PrimesLibrary.Primes();
private async void computePrimes(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
b1.IsEnabled = false;
tb1.Text = "Working...";
var asyncAction = primesLib.ComputePrimesAsync(0, 100000);
await asyncAction;
tb1.Text = "Done";
b1.IsEnabled = true;
}
private async void computePrimesWithProgress(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
b2.IsEnabled = false;
tb2.Text = "Working...";
var asyncAction = primesLib.ComputePrimesWithProgressAsync(0, 100000);
asyncAction.Progress = new AsyncActionProgressHandler<double>((action, progress) =>
{
pb1.Value = progress;
});
await asyncAction;
tb2.Text = "Done";
b2.IsEnabled = true;
}
private async void getPrimes(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
b3.IsEnabled = false;
tb3.Text = "Working...";
var asyncOperation = primesLib.GetPrimesAsync(0, 100000);
await asyncOperation;
tb3.Text = "Found " + asyncOperation.GetResults().Count + " primes";
b3.IsEnabled = true;
}
private async void getPrimesWithProgress(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
b4.IsEnabled = false;
tb4.Text = "Working...";
var asyncOperation = primesLib.GetPrimesWithProgressAsync(0, 100000);
asyncOperation.Progress = new AsyncOperationProgressHandler<IList<int>, double>((operation, progress) =>
{
pb4.Value = progress;
});
await asyncOperation;
tb4.Text = "Found " + asyncOperation.GetResults().Count + " primes";
b4.IsEnabled = true;
}
private async void getPrimesHandleErrors(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
b5.IsEnabled = false;
tb5.Text = "Working...";
var asyncOperation = primesLib.GetPrimesWithProgressAsync(-1000, 100000);
asyncOperation.Progress = new AsyncOperationProgressHandler<IList<int>, double>((operation, progress) =>
{
pb5.Value = progress;
});
try
{
await asyncOperation;
tb5.Text = "Found " + asyncOperation.GetResults().Count + " primes";
}
catch (ArgumentException ex)
{
tb5.Text = "ERROR: " + ex.Message;
}
b5.IsEnabled = true;
}
private IAsyncOperationWithProgress<IList<int>, double> asyncCancelableOperation;
private async void getPrimesCancellation(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
b6.IsEnabled = false;
cancelButton.IsEnabled = true;
tb6.Text = "Working...";
asyncCancelableOperation = primesLib.GetPrimesWithProgressAsync(0, 200000);
asyncCancelableOperation.Progress = new AsyncOperationProgressHandler<IList<int>, double>((operation, progress) =>
{
pb6.Value = progress;
});
try
{
await asyncCancelableOperation;
tb6.Text = "Found " + asyncCancelableOperation.GetResults().Count + " primes";
}
catch (System.Threading.Tasks.TaskCanceledException)
{
tb6.Text = "Operation canceled";
}
b6.IsEnabled = true;
cancelButton.IsEnabled = false;
}
private void cancelGetPrimes(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
cancelButton.IsEnabled = false;
asyncCancelableOperation.Cancel();
}
在非同步作業完成後,這些方法會使用 async 和 await 關鍵字更新 UI。 如需 UWP 應用程式中異步編碼的相關信息,請參閱 線程和異步程序設計。
getPrimesCancellation 和 cancelGetPrimes 方法可一起使用,讓使用者取消作業。 當用戶選擇 [ 取消] 按鈕時,方法會 cancelGetPrimes 呼叫 IAsyncOperationWithProgress<TResult、TProgress>::Cancel 來取消作業。 管理基礎異步操作的並行運行時間會擲回 Windows 執行階段 攔截的內部例外狀況類型,以傳達取消已完成。 如需取消模型的詳細資訊,請參閱 取消。
重要
若要讓PPL正確地向已取消作業的 Windows 執行階段 報告,請勿攔截此內部例外狀況類型。 這表示,您不應該攔截所有例外狀況 (catch (...))。 如果您必須攔截所有例外狀況,請重新擲回例外狀況,以確保 Windows 執行階段 可以完成取消作業。
下圖顯示選擇每個選項之後的 Primes 應用程式。
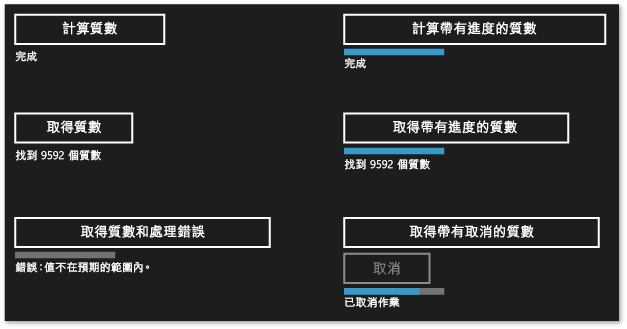
如需使用 create_async 來建立其他語言可取用之異步工作的範例,請參閱 Bing 地圖服務車程優化器範例中的使用C++。
控制執行緒
Windows 執行階段 會使用 COM 線程模型。 在這個模型中,物件會根據它們處理同步處理的方式裝載於不同的 Apartment。 安全執行緒物件裝載於多執行緒 Apartment (MTA) 中。 必須由單一執行緒存取的物件裝載於單一執行緒 Apartment (STA) 中。
在有 UI 的應用程式中,ASTA (應用程式 STA) 執行緒負責提取視窗訊息,而且是處理序中唯一可更新 STA 裝載 UI 控制項的執行緒。 這有兩種結果。 首先,為了讓應用程式保持回應,所有 CPU 密集和 I/O 作業都不應該在 ASTA 執行緒上執行。 其次,來自背景執行緒的結果必須封送處理回 ASTA 才能更新 UI。 在 C++ UWP 應用程式中, MainPage 以及其他 XAML 頁面都會在 ATSA 上執行。 因此根據預設,在 ASTA 上宣告的工作接續都會在該處執行,所以您可以直接在接續主體中更新控制項。 不過,如果您是以巢狀方式處理工作,則該巢狀工作上的任何接續都會在 MTA 中執行。 因此,您需要考慮是否要明確指定這些接續要在哪些內容上執行。
從非同步作業建立的工作 (例如 IAsyncOperation<TResult>) 會使用特殊語意協助您忽略執行緒的詳細資料。 雖然作業可能會在背景執行緒上執行 (或沒有任何執行緒支援它),但是根據預設,其接續仍保證能在啟動接續作業的 Appartment 上執行 (換句話說,就是從呼叫 task::then的 Apartment)。 您可以使用 concurrency::task_continuation_context 類別來控制接續的執行內容。 使用這些靜態 Helper 方法建立 task_continuation_context 物件:
使用 concurrency::task_continuation_context::use_arbitrary 指定接續在背景執行緒上執行。
使用 concurrency::task_continuation_context::use_current 指定接續在呼叫
task::then的執行緒上執行。
您可以將 task_continuation_context 物件傳遞至 task::then 方法,藉此明確控制接續的執行內容,您也可以將工作傳遞至另一個 Apartment,然後呼叫 task::then 方法隱含控制執行內容。
重要
由於UWP應用程式的主要UI線程會在STA下執行,因此您預設在該STA上建立的接續會在STA上執行。 同樣地,您在 MTA 上建立的接續工作也會在 MTA 上執行。
下一節將示範從磁碟讀取檔案、在該檔案中尋找最常見的字詞,然後在 UI 中顯示結果的應用程式。 最後的作業是更新 UI,它會在 UI 執行緒上發生。
重要
此行為專屬於 UWP 應用程式。 如果是傳統型應用程式,您不用控制接續工作執行的位置。 而是由排程器選擇執行每個接續工作所在的背景工作執行緒。
重要
不要在 STA 上執行的接續主體中呼叫 concurrency::task::wait 。 否則,因為這個方法會封鎖目前的執行緒,而且可能會導致應用程式沒有回應,所以執行階段會擲回 concurrency::invalid_operation 。 不過,您可以呼叫 concurrency::task::get 方法來以工作為基礎連續的形式接收前項工作的結果。
範例:使用 C++ 和 XAML 控制 Windows 執行階段 應用程式中的執行
假設有一個 C++ XAML 應用程式,它會從硬碟讀取檔案、尋找該檔案中最常見的字詞,然後在 UI 中顯示結果。 若要建立此應用程式,請在 Visual Studio 中建立空白應用程式 (通用 Windows) 專案,並將它命名為 CommonWords。 在您的應用程式資訊清單中指定 [ 文件庫 ] 功能,讓應用程式能夠存取 [我的文件] 資料夾。 另外在應用程式資訊清單的宣告區段中加入 [文字 (.txt)] 檔案類型。 如需應用程式功能和宣告的詳細資訊,請參閱 Windows 應用程式的封裝、部署和查詢。
將 MainPage.xaml 中的 Grid 項目更新,以包含 ProgressRing 項目和 TextBlock 項目。 ProgressRing 會指出作業正在進行,而 TextBlock 會顯示計算的結果。
<Grid Background="{StaticResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<ProgressRing x:Name="Progress"/>
<TextBlock x:Name="Results" FontSize="16"/>
</Grid>
將下列 #include 語句新增至 pch.h。
#include <sstream>
#include <ppltasks.h>
#include <concurrent_unordered_map.h>
將下列方法宣告加入至 MainPage 類別 (MainPage.h)。
private:
// Splits the provided text string into individual words.
concurrency::task<std::vector<std::wstring>> MakeWordList(Platform::String^ text);
// Finds the most common words that are at least the provided minimum length.
concurrency::task<std::vector<std::pair<std::wstring, size_t>>> FindCommonWords(const std::vector<std::wstring>& words, size_t min_length, size_t count);
// Shows the most common words on the UI.
void ShowResults(const std::vector<std::pair<std::wstring, size_t>>& commonWords);
將下列 using 陳述式加入至 MainPage.cpp。
using namespace concurrency;
using namespace std;
using namespace Windows::Storage;
using namespace Windows::Storage::Streams;
在 MainPage.cpp 中,實作 MainPage::MakeWordList、 MainPage::FindCommonWords和 MainPage::ShowResults 方法。 MainPage::MakeWordList 和 MainPage::FindCommonWords 會執行密集運算的作業。 MainPage::ShowResults 方法會在 UI 中顯示計算的結果。
// Splits the provided text string into individual words.
task<vector<wstring>> MainPage::MakeWordList(String^ text)
{
return create_task([text]() -> vector<wstring>
{
vector<wstring> words;
// Add continuous sequences of alphanumeric characters to the string vector.
wstring current_word;
for (wchar_t ch : text)
{
if (!iswalnum(ch))
{
if (current_word.length() > 0)
{
words.push_back(current_word);
current_word.clear();
}
}
else
{
current_word += ch;
}
}
return words;
});
}
// Finds the most common words that are at least the provided minimum length.
task<vector<pair<wstring, size_t>>> MainPage::FindCommonWords(const vector<wstring>& words, size_t min_length, size_t count)
{
return create_task([words, min_length, count]() -> vector<pair<wstring, size_t>>
{
typedef pair<wstring, size_t> pair;
// Counts the occurrences of each word.
concurrent_unordered_map<wstring, size_t> counts;
parallel_for_each(begin(words), end(words), [&counts, min_length](const wstring& word)
{
// Increment the count of words that are at least the minimum length.
if (word.length() >= min_length)
{
// Increment the count.
InterlockedIncrement(&counts[word]);
}
});
// Copy the contents of the map to a vector and sort the vector by the number of occurrences of each word.
vector<pair> wordvector;
copy(begin(counts), end(counts), back_inserter(wordvector));
sort(begin(wordvector), end(wordvector), [](const pair& x, const pair& y)
{
return x.second > y.second;
});
size_t size = min(wordvector.size(), count);
wordvector.erase(begin(wordvector) + size, end(wordvector));
return wordvector;
});
}
// Shows the most common words on the UI.
void MainPage::ShowResults(const vector<pair<wstring, size_t>>& commonWords)
{
wstringstream ss;
ss << "The most common words that have five or more letters are:";
for (auto commonWord : commonWords)
{
ss << endl << commonWord.first << L" (" << commonWord.second << L')';
}
// Update the UI.
Results->Text = ref new String(ss.str().c_str());
}
修改 MainPage 建構函式以建立接續工作鏈結,在 UI 中顯示荷馬 (Homer) 寫的《伊利亞德》( The Iliad ) 這本書中常見的字。 前兩個接續工作會將文字分割成單字並尋找常見字詞,不過非常耗時,因此明確設定為在背景執行。 最後一項接續工作是更新 UI,它不會指定接續內容,因此遵循 Apartment 執行緒規則。
MainPage::MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
// To run this example, save the contents of http://www.gutenberg.org/files/6130/6130-0.txt to your Documents folder.
// Name the file "The Iliad.txt" and save it under UTF-8 encoding.
// Enable the progress ring.
Progress->IsActive = true;
// Find the most common words in the book "The Iliad".
// Get the file.
create_task(KnownFolders::DocumentsLibrary->GetFileAsync("The Iliad.txt")).then([](StorageFile^ file)
{
// Read the file text.
return FileIO::ReadTextAsync(file, UnicodeEncoding::Utf8);
// By default, all continuations from a Windows Runtime async operation run on the
// thread that calls task.then. Specify use_arbitrary to run this continuation
// on a background thread.
}, task_continuation_context::use_arbitrary()).then([this](String^ file)
{
// Create a word list from the text.
return MakeWordList(file);
// By default, all continuations from a Windows Runtime async operation run on the
// thread that calls task.then. Specify use_arbitrary to run this continuation
// on a background thread.
}, task_continuation_context::use_arbitrary()).then([this](vector<wstring> words)
{
// Find the most common words.
return FindCommonWords(words, 5, 9);
// By default, all continuations from a Windows Runtime async operation run on the
// thread that calls task.then. Specify use_arbitrary to run this continuation
// on a background thread.
}, task_continuation_context::use_arbitrary()).then([this](vector<pair<wstring, size_t>> commonWords)
{
// Stop the progress ring.
Progress->IsActive = false;
// Show the results.
ShowResults(commonWords);
// We don't specify a continuation context here because we want the continuation
// to run on the STA thread.
});
}
注意
這個範例會示範如何指定執行內容以及如何撰寫接續鏈結。 前面說過,根據預設,從非同步作業建立的工作會在呼叫 task::then的 Apartment 上執行接續。 因此,這個範例會使用 task_continuation_context::use_arbitrary 指定不涉及 UI 的作業將在背景執行緒上執行。
下圖顯示 CommonWords 應用程式的結果。

在此範例中,可能會支援取消,因為 task 支持 create_async 的物件使用隱含取消標記。 如果您的工作需要以合作方式回應取消,請定義您的工作函式使其接受 cancellation_token 物件。 如需在 PPL 中取消的詳細資訊,請參閱 Cancellation in the PPL。