逐步解說:矩陣乘法
本逐步解說示範如何使用 C++ AMP 加速矩陣乘法的執行。 呈現兩種演算法,一個沒有並排,一個具有並排。
必要條件
在開始之前:
- 閱讀 C++ AMP 概觀。
- 讀取 使用磚。
- 請確定您至少執行 Windows 7 或 Windows Server 2008 R2。
注意
從 Visual Studio 2022 17.0 版開始,C++ AMP 標頭已被取代。
包含任何 AMP 標頭將會產生建置錯誤。 先定義 _SILENCE_AMP_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS ,再包含任何 AMP 標頭以讓警告無聲。
建立專案
建立新專案的指示會根據您已安裝的Visual Studio版本而有所不同。 若要查看您慣用 Visual Studio 版本的文件,請使用版本選取器控制項。 其位於此頁面目錄頂端。
在 Visual Studio 中建立專案
在功能表列上,選擇 [檔案]>[新增]>[專案],以開啟 [建立新專案] 對話方塊。
在對話方塊頂端,將 [語言] 設定為 C++,將 [平台] 設定為 Windows,並將 [專案類型] 設定為主控台。
從篩選的項目類型清單中,選擇 [ 空白專案 ],然後選擇 [ 下一步]。 在下一個頁面中,在 [名稱] 方塊中輸入 MatrixMultiply 以指定項目的名稱,並視需要指定專案位置。
![顯示 [建立新專案] 對話框的螢幕快照,其中已選取 [主控台應用程式] 範本。](../../build/media/mathclient-project-name-2019.png?view=msvc-160)
選擇 [建立] 按鈕以建立用戶端專案。
在 方案總管 中,開啟 [來源檔案] 的快捷方式功能表,然後選擇 [新增>專案]。
在 [新增專案] 對話框中,選取 [C++檔案][.cpp],在 [名稱] 方塊中輸入MatrixMultiply.cpp,然後選擇 [新增] 按鈕。
在 Visual Studio 2017 或 2015 中建立專案
在 Visual Studio 的功能表列上,選擇 [檔案] > [新增] > [專案]。
在 [範本] 窗格中的 [已安裝 ] 下,選取 [Visual C++]。
選取 [空白專案],在 [名稱] 方塊中輸入 MatrixMultiply,然後選擇 [確定] 按鈕。
選擇 [下一步] 按鈕。
在 方案總管 中,開啟 [來源檔案] 的快捷方式功能表,然後選擇 [新增>專案]。
在 [新增專案] 對話框中,選取 [C++檔案][.cpp],在 [名稱] 方塊中輸入MatrixMultiply.cpp,然後選擇 [新增] 按鈕。
沒有並排的乘法
在本節中,請考慮兩個矩陣 A 和 B 的乘法,其定義如下:
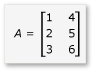

是 3 by-2 矩陣,B 是 2 by-3 矩陣。 乘以 B 乘 A 的乘積是下列 3-by-3 矩陣。 乘以 B 元素數據行乘以 A 的數據列來計算產品。

在沒有使用 C++ AMP 的情況下相乘
開啟MatrixMultiply.cpp,並使用下列程式代碼來取代現有的程序代碼。
#include <iostream> void MultiplyWithOutAMP() { int aMatrix[3][2] = {{1, 4}, {2, 5}, {3, 6}}; int bMatrix[2][3] = {{7, 8, 9}, {10, 11, 12}}; int product[3][3] = {{0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0}, {0, 0, 0}}; for (int row = 0; row < 3; row++) { for (int col = 0; col < 3; col++) { // Multiply the row of A by the column of B to get the row, column of product. for (int inner = 0; inner < 2; inner++) { product[row][col] += aMatrix[row][inner] * bMatrix[inner][col]; } std::cout << product[row][col] << " "; } std::cout << "\n"; } } int main() { MultiplyWithOutAMP(); getchar(); }演算法是矩陣乘法定義的直接實作。 它不會使用任何平行或線程演算法來減少計算時間。
在功能表列上,依序選擇 [檔案]>[全部儲存]。
選擇 F5 鍵盤快捷方式以開始偵錯,並確認輸出正確無誤。
選擇 Enter 以結束應用程式。
若要使用 C++ AMP 乘以
在 MatrixMultiply.cpp 中,在方法之前
main新增下列程序代碼。void MultiplyWithAMP() { int aMatrix[] = { 1, 4, 2, 5, 3, 6 }; int bMatrix[] = { 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 }; int productMatrix[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; array_view<int, 2> a(3, 2, aMatrix); array_view<int, 2> b(2, 3, bMatrix); array_view<int, 2> product(3, 3, productMatrix); parallel_for_each(product.extent, [=] (index<2> idx) restrict(amp) { int row = idx[0]; int col = idx[1]; for (int inner = 0; inner <2; inner++) { product[idx] += a(row, inner)* b(inner, col); } }); product.synchronize(); for (int row = 0; row <3; row++) { for (int col = 0; col <3; col++) { //std::cout << productMatrix[row*3 + col] << " "; std::cout << product(row, col) << " "; } std::cout << "\n"; } }AMP 程式代碼類似於非 AMP 程式代碼。 呼叫
parallel_for_each會針對 中的每個product.extent項目啟動一個線程,並取代數據列和數據行的for迴圈。 數據列和數據行的數據格值可在 中使用idx。 您可以使用 運算子和索引變數,或是()運算符和數據行變數來存取 物件的[]元素array_view。 此範例示範這兩種方法。 方法array_view::synchronize會將變數productMatrix的值product複製到變數。在MatrixMultiply.cpp頂端新增下列
include和using語句。#include <amp.h> using namespace concurrency;main修改方法以呼叫MultiplyWithAMP方法。int main() { MultiplyWithOutAMP(); MultiplyWithAMP(); getchar(); }按 Ctrl+F5 鍵盤快捷方式以開始偵錯,並確認輸出正確無誤。
按空格鍵以結束應用程式。
具有並排的乘法
Tiling 是一種技術,可讓您將數據分割成大小相等的子集,也就是所謂的磚。 當您使用並排時,有三件事會變更。
您可以建立
tile_static變數。 存取空間中的數據tile_static可能會比存取全域空間中的數據快很多倍。 系統會為每個磚建立變數的tile_static實例,而磚中的所有線程都可以存取變數。 並排的主要優點是因為存取而獲得tile_static效能。您可以呼叫 tile_barrier::wait 方法,以在指定的程式代碼行停止一個圖格中的所有線程。 您無法保證線程執行的順序,只有一個圖格中的所有線程都會在呼叫
tile_barrier::wait時停止,才能繼續執行。您可以存取相對於整個
array_view物件的線程索引,以及相對於磚的索引。 藉由使用本機索引,您可以讓程式代碼更容易讀取和偵錯。
若要利用矩陣乘法中的並排,演算法必須將矩陣分割成磚,然後將磚數據 tile_static 複製到變數中,以便更快速地存取。 在此範例中,矩陣會分割成大小相等的子陣列。 乘以子數來找到產品。 此範例中的兩個矩陣及其產品如下:
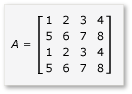
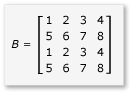
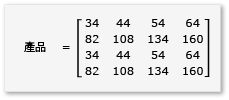
矩陣會分割成四個 2x2 矩陣,其定義如下:
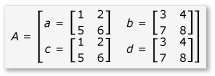
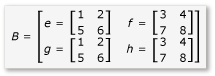
A 和 B 的乘積現在可以撰寫並計算如下:
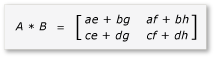
因為矩陣ah是 2x2 矩陣,因此所有產品和總和也是 2x2 矩陣。 此外,A 和 B 的乘積也如預期般是 4x4 矩陣。 若要快速檢查演算法,請計算產品中第一個數據列、第一個數據行中的元素值。 在此範例中,這會是 的第一個數據列和第一個 ae + bg數據行中元素的值。 您只需要計算每個字詞的第一個資料列、第一個資料列 ae 和 bg 。 的值為 ae (1 * 1) + (2 * 5) = 11。 的值 bg 是 (3 * 1) + (4 * 5) = 23。 最終值為 11 + 23 = 34,正確。
若要實作此演算法,程式代碼:
tiled_extent使用物件,extent而不是呼叫中的parallel_for_each物件。tiled_index使用物件,index而不是呼叫中的parallel_for_each物件。tile_static建立變數來保存子專案。tile_barrier::wait使用方法來停止線程來計算子系的產品。
若要乘以使用 AMP 和並排
在 MatrixMultiply.cpp 中,在方法之前
main新增下列程序代碼。void MultiplyWithTiling() { // The tile size is 2. static const int TS = 2; // The raw data. int aMatrix[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }; int bMatrix[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }; int productMatrix[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }; // Create the array_view objects. array_view<int, 2> a(4, 4, aMatrix); array_view<int, 2> b(4, 4, bMatrix); array_view<int, 2> product(4, 4, productMatrix); // Call parallel_for_each by using 2x2 tiles. parallel_for_each(product.extent.tile<TS, TS>(), [=] (tiled_index<TS, TS> t_idx) restrict(amp) { // Get the location of the thread relative to the tile (row, col) // and the entire array_view (rowGlobal, colGlobal). int row = t_idx.local[0]; int col = t_idx.local[1]; int rowGlobal = t_idx.global[0]; int colGlobal = t_idx.global[1]; int sum = 0; // Given a 4x4 matrix and a 2x2 tile size, this loop executes twice for each thread. // For the first tile and the first loop, it copies a into locA and e into locB. // For the first tile and the second loop, it copies b into locA and g into locB. for (int i = 0; i < 4; i += TS) { tile_static int locA[TS][TS]; tile_static int locB[TS][TS]; locA[row][col] = a(rowGlobal, col + i); locB[row][col] = b(row + i, colGlobal); // The threads in the tile all wait here until locA and locB are filled. t_idx.barrier.wait(); // Return the product for the thread. The sum is retained across // both iterations of the loop, in effect adding the two products // together, for example, a*e. for (int k = 0; k < TS; k++) { sum += locA[row][k] * locB[k][col]; } // All threads must wait until the sums are calculated. If any threads // moved ahead, the values in locA and locB would change. t_idx.barrier.wait(); // Now go on to the next iteration of the loop. } // After both iterations of the loop, copy the sum to the product variable by using the global location. product[t_idx.global] = sum; }); // Copy the contents of product back to the productMatrix variable. product.synchronize(); for (int row = 0; row <4; row++) { for (int col = 0; col <4; col++) { // The results are available from both the product and productMatrix variables. //std::cout << productMatrix[row*3 + col] << " "; std::cout << product(row, col) << " "; } std::cout << "\n"; } }此範例與範例明顯不同,但不加磚。 程式代碼會使用這些概念步驟:
將 tile[0,0] 的項目
alocA複製到 。 將 tile[0,0] 的項目blocB複製到 。 請注意,product會並排顯示,而不是a和b。 因此,您會使用全域索引來存取a, b、 和product。 對的呼叫tile_barrier::wait至關重要。 它會停止磚中的所有線程,直到 填locA滿 和locB為止。將和 相乘
locA,並將locB結果product放入 中。將磚[0,1] 的項目
alocA複製到 。 將 圖格[1,0] 的項目blocB複製到 。將和 相乘
locA,locB並將其新增至中product已經的結果。tile[0,0] 的乘法已完成。
針對其他四個磚重複。 磚沒有特別編製索引,線程可以依任何順序執行。 當每個線程執行時
tile_static,會適當地為每個磚建立變數,以及控制程式流程的呼叫tile_barrier::wait。當您仔細檢查演算法時,請注意,每個子對象都會載入記憶體兩
tile_static次。 該數據傳輸確實需要時間。 不過,一旦數據在記憶體中tile_static,數據的存取速度會更快。 因為計算產品需要重複存取子目錄中的值,因此整體效能會有所提高。 針對每個演算法,必須進行實驗,才能尋找最佳的演算法和磚大小。
在非 AMP 和非磚範例中,A 和 B 的每個元素都會從全域記憶體取四次,以計算產品。 在圖格範例中,會從全域記憶體存取每個元素兩次,以及從
tile_static記憶體存取四次。 這不是顯著的效能提升。 不過,如果 A 和 B 是 1024x1024 矩陣,而磚大小為 16,將會有顯著的效能提升。 在此情況下,每個元素只會複製到tile_static記憶體 16 次,並從tile_static記憶體存取 1024 次。修改 main 方法以呼叫
MultiplyWithTiling方法,如下所示。int main() { MultiplyWithOutAMP(); MultiplyWithAMP(); MultiplyWithTiling(); getchar(); }按 Ctrl+F5 鍵盤快捷方式以開始偵錯,並確認輸出正確無誤。
按空格鍵結束應用程式。
另請參閱
C++ AMP (C++ Accelerated Massive Parallelism)
逐步解說:偵錯 C++ AMP 應用程式