為 Azure App Service 設定 TLS 相互驗證
為 Azure App Service 應用程式啟用不同類型的驗證,即可限制其存取。 其中一個做法是:當用戶端要求透過 TLS/SSL 進行時,要求用戶端憑證並驗證該憑證。 此機制稱為傳輸層安全性 (TLS) 相互驗證或客戶端憑證驗證。 本文說明如何設定應用程式,以使用用戶端憑證驗證。
注意
您的應用程式程式碼會負責驗證用戶端憑證。 除了將它轉送至您的應用程式以外,App Service 不會使用此客戶端憑證執行任何動作。
如果您透過 HTTP 存取您的網站,而非 HTTPS,將不會收到任何用戶端憑證。 因此如果您的應用程式需要用戶端憑證,請勿允許透過 HTTP 傳入您應用程式的要求。
準備您的 Web 應用程式
若要為您的 App Service 應用程式建立自訂 TLS/SSL 繫結或啟用用戶端憑證,您的 App Service 方案 必須使用基本、標準、進階或隔離層。 若要確定 Web 應用程式在支援的定價層,請遵循下列步驟:
移至您的 Web 應用程式
在 Azure 入口網站的搜尋方塊中,尋找並選取 [App Service]。
![已選取 Azure 入口網站、搜尋方塊和 [應用程式服務] 的螢幕快照。](../includes/media/app-service-ssl-prepare-app/app-services.png)
在 [應用程式服務] 頁面上,選取您 Web 應用程式的名稱。
![Azure 入口網站 中 [應用程式服務] 頁面的螢幕快照,其中顯示所有執行中 Web 應用程式的清單,清單中第一個應用程式已醒目提示。](../includes/media/app-service-ssl-prepare-app/select-app.png)
您現在位於 Web 應用程式的管理頁面上。
檢查定價層
在 Web 應用程式左側功能表的 [設定] 區段底下,選取 [擴大 (App Service 方案)]。
![螢幕快照:已選取 [Web 應用程式] 功能表、[設定] 區段和 [相應增加][App Service 方案]。](../includes/media/app-service-ssl-prepare-app/scale-up-menu.png)
請確定您的 Web 應用程式不在 F1 或 D1 層中,這些階層不支援自訂 TLS/SSL。
如果您需要擴大,請遵循下一節中的步驟來進行。 否則,請關閉 [擴大] 頁面,並略過擴大 App Service 方案一節。
擴大您的 App Service 方案
選取任何非免費層,例如 B1、B2、B3 或生產類別中的任何一層。
完成後,請選取 [選取]。
出現下列訊息時,表示調整作業已完成。
啟用用戶端憑證
當您為應用程式啟用用戶端憑證時,您應該選取您選擇的客戶端憑證模式。 每個模式都會定義您的應用程式如何處理傳入客戶端憑證:
| 用戶端憑證模式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 必要 | 所有要求都需要客戶端憑證。 |
| 選擇性 | 根據預設,要求可能會或可能不會使用用戶端憑證,而且系統預設會提示用戶端輸入憑證。 例如,瀏覽器用戶端會顯示提示以選取憑證進行驗證。 |
| 選擇性的互動式使用者 | 根據預設,要求可能會或可能不會使用用戶端憑證,而且不會提示用戶端輸入憑證。 例如,瀏覽器用戶端不會顯示提示以選取憑證進行驗證。 |
若要將應用程式設定為在 Azure 入口網站 中要求客戶端憑證:
- 瀏覽至應用程式的管理頁面。
- 從應用程式管理頁面的左側導覽中,選取 [組態]>[一般設定]。
- 選取 所選的 [用戶端憑證模式 ]。 在頁面頂端,選取儲存。
排除路徑以不要求驗證
啟用應用程式的相互驗證時,應用程式根目錄下的所有路徑皆需要用戶端憑證,才能進行存取。 若要讓特定路徑免除此需求,請將排除路徑定義為應用程式組態的一部分。
注意
使用任何客戶端憑證排除路徑會觸發連入應用程式的 TLS 重新談判。
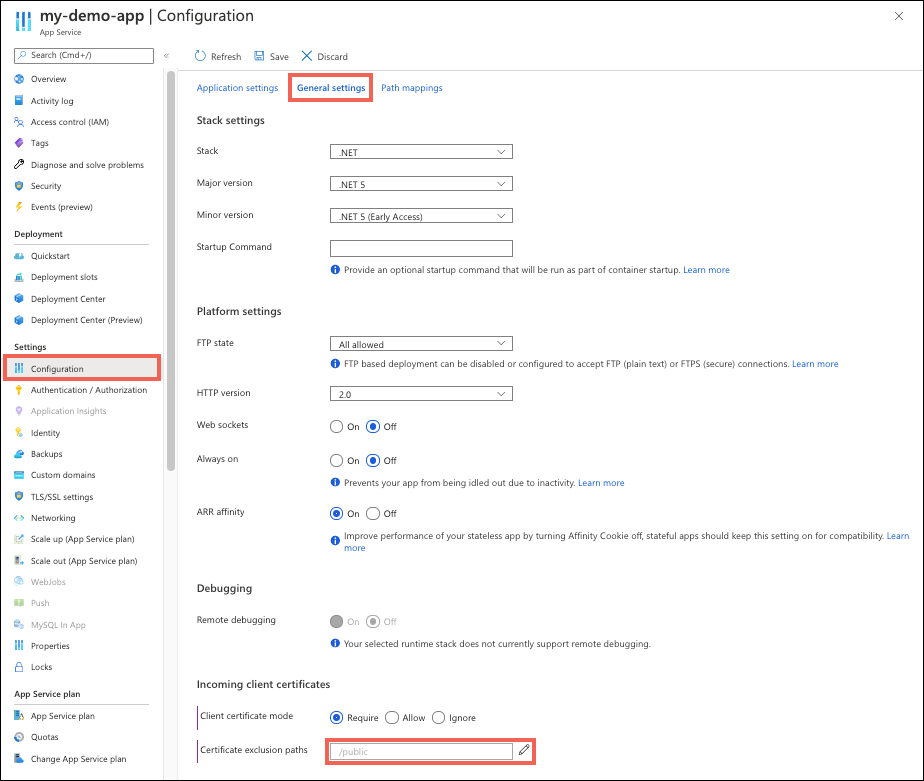
從應用程式管理頁面的左側導覽中,選取 [組態]>[一般設定]。
在 [憑證排除路徑] 旁,選取編輯圖示。
選取 [新增路徑]、指定路徑,或以 或
;分隔,的路徑清單,然後選取 [確定]。在頁面頂端,選取儲存。
在下列螢幕快照中,以 開頭 /public 的應用程式的任何路徑都不會要求客戶端憑證。 路徑比對不區分大小寫。
用戶端憑證和 TLS 重新談判
針對某些客戶端憑證設定,App Service 需要 TLS 重新談判才能讀取要求,才能知道是否提示客戶端憑證。 下列任一設定會觸發 TLS 重新談判:
- 使用「選擇互式使用者」客戶端憑證模式。
- 使用 客戶端憑證排除路徑。
注意
TLS 1.3 和 HTTP 2.0 不支援 TLS 重新談判。 如果您的應用程式已設定使用 TLS 重新談判的用戶端憑證設定,這些通訊協定將無法運作。
若要停用 TLS 重新談判,並在 TLS 交握期間讓應用程式交涉用戶端憑證,您必須使用 下列所有 設定來設定您的應用程式:
- 將用戶端憑證模式設定為 [必要] 或 [選擇性]
- 拿掉所有客戶端憑證排除路徑
使用 TLS 重新談判上傳大型檔案
使用 TLS 重新談判的用戶端憑證組態無法支援因緩衝區大小限制而大於 100 kb 的大型檔案連入要求。 在此案例中,超過 100 kb 的任何 POST 或 PUT 要求都會失敗,並出現 403 錯誤。 此限制無法設定且無法增加。
若要解決 100 kb 的限制,請考慮下列替代解決方案:
- 停用 TLS 重新談判。 使用 下列所有 設定更新應用程式的用戶端憑證組態:
- 將用戶端憑證模式設定為 [必要] 或 [選擇性]
- 拿掉所有客戶端憑證排除路徑
- 在 PUT/POST 要求之前傳送 HEAD 要求。 HEAD 要求會處理客戶端憑證。
- 將標頭
Expect: 100-Continue新增至您的要求。 這會導致用戶端等到伺服器在傳送要求本文之前回應100 Continue,以略過緩衝區。
存取用戶端憑證
在 App Service 中,要求的 TLS 終止會在前端負載平衡器上發生。 當 App Service 將要求轉送至已啟用用戶端憑證的應用程式程式代碼時,它會將要求標頭插入X-ARR-ClientCert用戶端憑證。 除了將它轉送至您的應用程式以外,App Service 不會使用此客戶端憑證執行任何動作。 您的應用程式程式碼會負責驗證用戶端憑證。
ASP.NET 的用戶端憑證可透過 HttpRequest.ClientCertificate 屬性取得。
若為其他應用程式堆疊 (Node.js、PHP 等),則可透過 X-ARR-ClientCert 要求標頭中的 base64 編碼值取得用戶端憑證。
ASP.NET Core 範例
ASP.NET Core 可使用中介軟體來剖析轉送的憑證。 為使用轉送的通訊協定標頭,系統會提供不同的中介軟體。 兩者皆須存在,才能接受轉送的憑證。 您可在 CertificateAuthentication 選項中放置自訂憑證驗證邏輯。
public class Startup
{
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddControllersWithViews();
// Configure the application to use the protocol and client ip address forwarded by the frontend load balancer
services.Configure<ForwardedHeadersOptions>(options =>
{
options.ForwardedHeaders =
ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedFor | ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedProto;
// Only loopback proxies are allowed by default. Clear that restriction to enable this explicit configuration.
options.KnownNetworks.Clear();
options.KnownProxies.Clear();
});
// Configure the application to client certificate forwarded the frontend load balancer
services.AddCertificateForwarding(options => { options.CertificateHeader = "X-ARR-ClientCert"; });
// Add certificate authentication so when authorization is performed the user will be created from the certificate
services.AddAuthentication(CertificateAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme).AddCertificate();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseForwardedHeaders();
app.UseCertificateForwarding();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseAuthentication()
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
ASP.NET WebForms 範例
using System;
using System.Collections.Specialized;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
using System.Web;
namespace ClientCertificateUsageSample
{
public partial class Cert : System.Web.UI.Page
{
public string certHeader = "";
public string errorString = "";
private X509Certificate2 certificate = null;
public string certThumbprint = "";
public string certSubject = "";
public string certIssuer = "";
public string certSignatureAlg = "";
public string certIssueDate = "";
public string certExpiryDate = "";
public bool isValidCert = false;
//
// Read the certificate from the header into an X509Certificate2 object
// Display properties of the certificate on the page
//
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
NameValueCollection headers = base.Request.Headers;
certHeader = headers["X-ARR-ClientCert"];
if (!String.IsNullOrEmpty(certHeader))
{
try
{
byte[] clientCertBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(certHeader);
certificate = new X509Certificate2(clientCertBytes);
certSubject = certificate.Subject;
certIssuer = certificate.Issuer;
certThumbprint = certificate.Thumbprint;
certSignatureAlg = certificate.SignatureAlgorithm.FriendlyName;
certIssueDate = certificate.NotBefore.ToShortDateString() + " " + certificate.NotBefore.ToShortTimeString();
certExpiryDate = certificate.NotAfter.ToShortDateString() + " " + certificate.NotAfter.ToShortTimeString();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
errorString = ex.ToString();
}
finally
{
isValidCert = IsValidClientCertificate();
if (!isValidCert) Response.StatusCode = 403;
else Response.StatusCode = 200;
}
}
else
{
certHeader = "";
}
}
//
// This is a SAMPLE verification routine. Depending on your application logic and security requirements,
// you should modify this method
//
private bool IsValidClientCertificate()
{
// In this example we will only accept the certificate as a valid certificate if all the conditions below are met:
// 1. The certificate isn't expired and is active for the current time on server.
// 2. The subject name of the certificate has the common name nildevecc
// 3. The issuer name of the certificate has the common name nildevecc and organization name Microsoft Corp
// 4. The thumbprint of the certificate is 30757A2E831977D8BD9C8496E4C99AB26CB9622B
//
// This example doesn't test that this certificate is chained to a Trusted Root Authority (or revoked) on the server
// and it allows for self signed certificates
//
if (certificate == null || !String.IsNullOrEmpty(errorString)) return false;
// 1. Check time validity of certificate
if (DateTime.Compare(DateTime.Now, certificate.NotBefore) < 0 || DateTime.Compare(DateTime.Now, certificate.NotAfter) > 0) return false;
// 2. Check subject name of certificate
bool foundSubject = false;
string[] certSubjectData = certificate.Subject.Split(new char[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
foreach (string s in certSubjectData)
{
if (String.Compare(s.Trim(), "CN=nildevecc") == 0)
{
foundSubject = true;
break;
}
}
if (!foundSubject) return false;
// 3. Check issuer name of certificate
bool foundIssuerCN = false, foundIssuerO = false;
string[] certIssuerData = certificate.Issuer.Split(new char[] { ',' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
foreach (string s in certIssuerData)
{
if (String.Compare(s.Trim(), "CN=nildevecc") == 0)
{
foundIssuerCN = true;
if (foundIssuerO) break;
}
if (String.Compare(s.Trim(), "O=Microsoft Corp") == 0)
{
foundIssuerO = true;
if (foundIssuerCN) break;
}
}
if (!foundIssuerCN || !foundIssuerO) return false;
// 4. Check thumbprint of certificate
if (String.Compare(certificate.Thumbprint.Trim().ToUpper(), "30757A2E831977D8BD9C8496E4C99AB26CB9622B") != 0) return false;
return true;
}
}
}
Node.js 範例
下列 Node.js 範例程式碼會取得 X-ARR-ClientCert 標頭,並使用 node-forge 將 base64 編碼的 PEM 字串轉換成憑證物件,並進行驗證:
import { NextFunction, Request, Response } from 'express';
import { pki, md, asn1 } from 'node-forge';
export class AuthorizationHandler {
public static authorizeClientCertificate(req: Request, res: Response, next: NextFunction): void {
try {
// Get header
const header = req.get('X-ARR-ClientCert');
if (!header) throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
// Convert from PEM to pki.CERT
const pem = `-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----${header}-----END CERTIFICATE-----`;
const incomingCert: pki.Certificate = pki.certificateFromPem(pem);
// Validate certificate thumbprint
const fingerPrint = md.sha1.create().update(asn1.toDer(pki.certificateToAsn1(incomingCert)).getBytes()).digest().toHex();
if (fingerPrint.toLowerCase() !== 'abcdef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef12') throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
// Validate time validity
const currentDate = new Date();
if (currentDate < incomingCert.validity.notBefore || currentDate > incomingCert.validity.notAfter) throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
// Validate issuer
if (incomingCert.issuer.hash.toLowerCase() !== 'abcdef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef12') throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
// Validate subject
if (incomingCert.subject.hash.toLowerCase() !== 'abcdef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef12') throw new Error('UNAUTHORIZED');
next();
} catch (e) {
if (e instanceof Error && e.message === 'UNAUTHORIZED') {
res.status(401).send();
} else {
next(e);
}
}
}
}
Java 範例
下列 JAVA 類別會將憑證從 X-ARR-ClientCert 編碼為 X509Certificate 執行個體。 certificateIsValid() 驗證憑證的指紋是否符合建構函式中指定的指紋,且該憑證尚未過期。
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.cert.*;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import sun.security.provider.X509Factory;
import javax.xml.bind.DatatypeConverter;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.Date;
public class ClientCertValidator {
private String thumbprint;
private X509Certificate certificate;
/**
* Constructor.
* @param certificate The certificate from the "X-ARR-ClientCert" HTTP header
* @param thumbprint The thumbprint to check against
* @throws CertificateException If the certificate factory cannot be created.
*/
public ClientCertValidator(String certificate, String thumbprint) throws CertificateException {
certificate = certificate
.replaceAll(X509Factory.BEGIN_CERT, "")
.replaceAll(X509Factory.END_CERT, "");
CertificateFactory cf = CertificateFactory.getInstance("X.509");
byte [] base64Bytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(certificate);
X509Certificate X509cert = (X509Certificate) cf.generateCertificate(new ByteArrayInputStream(base64Bytes));
this.setCertificate(X509cert);
this.setThumbprint(thumbprint);
}
/**
* Check that the certificate's thumbprint matches the one given in the constructor, and that the
* certificate hasn't expired.
* @return True if the certificate's thumbprint matches and hasn't expired. False otherwise.
*/
public boolean certificateIsValid() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, CertificateEncodingException {
return certificateHasNotExpired() && thumbprintIsValid();
}
/**
* Check certificate's timestamp.
* @return Returns true if the certificate hasn't expired. Returns false if it has expired.
*/
private boolean certificateHasNotExpired() {
Date currentTime = new java.util.Date();
try {
this.getCertificate().checkValidity(currentTime);
} catch (CertificateExpiredException | CertificateNotYetValidException e) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* Check the certificate's thumbprint matches the given one.
* @return Returns true if the thumbprints match. False otherwise.
*/
private boolean thumbprintIsValid() throws NoSuchAlgorithmException, CertificateEncodingException {
MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-1");
byte[] der = this.getCertificate().getEncoded();
md.update(der);
byte[] digest = md.digest();
String digestHex = DatatypeConverter.printHexBinary(digest);
return digestHex.toLowerCase().equals(this.getThumbprint().toLowerCase());
}
// Getters and setters
public void setThumbprint(String thumbprint) {
this.thumbprint = thumbprint;
}
public String getThumbprint() {
return this.thumbprint;
}
public X509Certificate getCertificate() {
return certificate;
}
public void setCertificate(X509Certificate certificate) {
this.certificate = certificate;
}
}
Python 範例
下列 Flask 和 Django Python 程式代碼範例會實作一 authorize_certificate 個名為 的裝飾專案,可在檢視函式上使用,只允許存取出示有效用戶端憑證的呼叫端。 其預期標頭中有 PEM 格式的 X-ARR-ClientCert 憑證,並使用 Python 密碼編譯 套件根據其指紋(指紋)、主體通用名稱、簽發者通用名稱和開始和到期日期來驗證憑證。 如果驗證失敗,裝飾專案可確保狀態代碼為 403 的 HTTP 回應會傳回給用戶端。
from functools import wraps
from datetime import datetime, timezone
from flask import abort, request
from cryptography import x509
from cryptography.x509.oid import NameOID
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes
def validate_cert(request):
try:
cert_value = request.headers.get('X-ARR-ClientCert')
if cert_value is None:
return False
cert_data = ''.join(['-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\n', cert_value, '\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n',])
cert = x509.load_pem_x509_certificate(cert_data.encode('utf-8'))
fingerprint = cert.fingerprint(hashes.SHA1())
if fingerprint != b'12345678901234567890':
return False
subject = cert.subject
subject_cn = subject.get_attributes_for_oid(NameOID.COMMON_NAME)[0].value
if subject_cn != "contoso.com":
return False
issuer = cert.issuer
issuer_cn = issuer.get_attributes_for_oid(NameOID.COMMON_NAME)[0].value
if issuer_cn != "contoso.com":
return False
current_time = datetime.now(timezone.utc)
if current_time < cert.not_valid_before_utc:
return False
if current_time > cert.not_valid_after_utc:
return False
return True
except Exception as e:
# Handle any errors encountered during validation
print(f"Encountered the following error during certificate validation: {e}")
return False
def authorize_certificate(f):
@wraps(f)
def decorated_function(*args, **kwargs):
if not validate_cert(request):
abort(403)
return f(*args, **kwargs)
return decorated_function
下列代碼段示範如何在 Flask 檢視函式上使用裝飾專案。
@app.route('/hellocert')
@authorize_certificate
def hellocert():
print('Request for hellocert page received')
return render_template('index.html')