快速入門:在 Azure Stack Hub 中使用 PowerShell 建立 Linux 伺服器 VM
您可以使用 Azure Stack Hub PowerShell 建立 Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS 虛擬機(VM)。 在本文中,您會建立和使用虛擬機。 本文也會說明如何:
- 使用遠端用戶端連線到 VM。
- 安裝 NGINX 網頁伺服器並檢視預設首頁。
- 清除未使用的資源。
必要條件
Azure Stack Hub Marketplace 中的 Linux 映射。 根據預設,Azure Stack Hub Marketplace 沒有 Linux 映像。 讓 Azure Stack Hub 操作員提供您需要的 Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS 映像。 操作員可以使用將 Marketplace 專案從 Azure 下載至 Azure Stack Hub 中的指示。
Azure Stack Hub 需要特定版本的 Azure CLI 來建立和管理其資源。
- 如果您沒有針對 Azure Stack Hub 設定 PowerShell,請參閱 安裝適用於 Azure Stack Hub 的 PowerShell。
- 設定 Azure Stack Hub PowerShell 之後,您將連線到 Azure Stack Hub 環境。 如需指示,請參閱 以使用者身分使用 PowerShell 連線到 Azure Stack Hub。
公用安全殼層 (SSH) 金鑰,名稱 為 id_rsa.pub ,儲存在 Windows 使用者設定檔的 .ssh 目錄中。 如需建立 SSH 金鑰的詳細資訊,請參閱 搭配 Azure Stack Hub 使用 SSH 金鑰組。
建立資源群組
資源群組是一個邏輯容器,您可以在其中部署和管理 Azure Stack Hub 資源。 若要建立資源群組,請執行下列程式代碼區塊:
注意
我們已為下列程式代碼範例中的所有變數指派值。 不過,您可以指派自己的值。
# Create variables to store the location and resource group names.
$location = "local"
$ResourceGroupName = "myResourceGroup"
New-AzResourceGroup `
-Name $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location
建立儲存體資源
建立將用來儲存開機診斷輸出的記憶體帳戶。
# Create variables to store the storage account name and the storage account SKU information
$StorageAccountName = "mystorageaccount"
$SkuName = "Standard_LRS"
# Create a new storage account
$StorageAccount = New-AzStorageAccount `
-Location $location `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Type $SkuName `
-Name $StorageAccountName
Set-AzCurrentStorageAccount `
-StorageAccountName $storageAccountName `
-ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName
建立網路資源
建立虛擬網路、子網和公用IP位址。 這些資源可用來提供 VM 的網路連線。
# Create a subnet configuration
$subnetConfig = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig `
-Name mySubnet `
-AddressPrefix 192.168.1.0/24
# Create a virtual network
$vnet = New-AzVirtualNetwork `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location `
-Name MyVnet `
-AddressPrefix 192.168.0.0/16 `
-Subnet $subnetConfig
# Create a public IP address and specify a DNS name
$pip = New-AzPublicIpAddress `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location `
-AllocationMethod Static `
-IdleTimeoutInMinutes 4 `
-Name "mypublicdns$(Get-Random)"
建立網路安全性群組和網路安全性群組規則
網路安全組會使用輸入和輸出規則來保護 VM。 建立埠 3389 的輸入規則,以允許連入遠端桌面連線,以及埠 80 的輸入規則,以允許連入的 Web 流量。
# Create variables to store the network security group and rules names.
$nsgName = "myNetworkSecurityGroup"
$nsgRuleSSHName = "myNetworkSecurityGroupRuleSSH"
$nsgRuleWebName = "myNetworkSecurityGroupRuleWeb"
# Create an inbound network security group rule for port 22
$nsgRuleSSH = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name $nsgRuleSSHName -Protocol Tcp `
-Direction Inbound -Priority 1000 -SourceAddressPrefix * -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix * `
-DestinationPortRange 22 -Access Allow
# Create an inbound network security group rule for port 80
$nsgRuleWeb = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name $nsgRuleWebName -Protocol Tcp `
-Direction Inbound -Priority 1001 -SourceAddressPrefix * -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix * `
-DestinationPortRange 80 -Access Allow
# Create a network security group
$nsg = New-AzNetworkSecurityGroup -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName -Location $location `
-Name $nsgName -SecurityRules $nsgRuleSSH,$nsgRuleWeb
建立 VM 的網路卡
網路卡會將 VM 連線到子網、網路安全組和公用IP位址。
# Create a virtual network card and associate it with public IP address and NSG
$nic = New-AzNetworkInterface `
-Name myNic `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location `
-SubnetId $vnet.Subnets[0].Id `
-PublicIpAddressId $pip.Id `
-NetworkSecurityGroupId $nsg.Id
建立 VM
建立 VM 組態。 此組態包含部署 VM 時要使用的設定(例如,使用者認證、大小和 VM 映射)。
# Define a credential object
$UserName='demouser'
$securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString ' ' -AsPlainText -Force
$cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ($UserName, $securePassword)
# Create the VM configuration object
$VmName = "VirtualMachinelatest"
$VmSize = "Standard_D1"
$VirtualMachine = New-AzVMConfig `
-VMName $VmName `
-VMSize $VmSize
$VirtualMachine = Set-AzVMOperatingSystem `
-VM $VirtualMachine `
-Linux `
-ComputerName "MainComputer" `
-Credential $cred
$VirtualMachine = Set-AzVMSourceImage `
-VM $VirtualMachine `
-PublisherName "Canonical" `
-Offer "UbuntuServer" `
-Skus "20.04-LTS" `
-Version "latest"
# Set the operating system disk properties on a VM
$VirtualMachine = Set-AzVMOSDisk `
-VM $VirtualMachine `
-CreateOption FromImage | `
Set-AzVMBootDiagnostic -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-StorageAccountName $StorageAccountName -Enable |`
Add-AzVMNetworkInterface -Id $nic.Id
# Configure SSH keys
$sshPublicKey = Get-Content "$env:USERPROFILE\.ssh\id_rsa.pub"
# Add the SSH key to the VM
Add-AzVMSshPublicKey -VM $VirtualMachine `
-KeyData $sshPublicKey `
-Path "/home/$UserName/.ssh/authorized_keys"
# Create the VM
New-AzVM `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location `
-VM $VirtualMachine
VM 快速建立:完整腳本
注意
此步驟基本上是上述程式代碼合併在一起,但使用密碼而非 SSH 金鑰進行驗證。
## Create a resource group
<#
A resource group is a logical container where you can deploy and manage Azure Stack Hub resources. From your development kit or the Azure Stack Hub integrated system, run the following code block to create a resource group. Though we've assigned values for all the variables in this article, you can use these values or assign new ones.
#>
# Edit your variables, if required
# Create variables to store the location and resource group names
$location = "local"
$ResourceGroupName = "myResourceGroup"
# Create variables to store the storage account name and the storage account SKU information
$StorageAccountName = "mystorageaccount"
$SkuName = "Standard_LRS"
# Create variables to store the network security group and rules names
$nsgName = "myNetworkSecurityGroup"
$nsgRuleSSHName = "myNetworkSecurityGroupRuleSSH"
$nsgRuleWebName = "myNetworkSecurityGroupRuleWeb"
# Create variable for VM password
$VMPassword = 'Password123!'
# End of variables - no need to edit anything past that point to deploy a single VM
# Create a resource group
New-AzResourceGroup `
-Name $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location
## Create storage resources
# Create a storage account, and then create a storage container for the Ubuntu Server 20.04 LTS image
# Create a new storage account
$StorageAccount = New-AzStorageAccount `
-Location $location `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Type $SkuName `
-Name $StorageAccountName
Set-AzCurrentStorageAccount `
-StorageAccountName $storageAccountName `
-ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName
# Create a storage container to store the VM image
$containerName = 'osdisks'
$container = New-AzureStorageContainer `
-Name $containerName `
-Permission Blob
## Create networking resources
# Create a virtual network, a subnet, and a public IP address, resources that are used provide network connectivity to the VM
# Create a subnet configuration
$subnetConfig = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig `
-Name mySubnet `
-AddressPrefix 192.168.1.0/24
# Create a virtual network
$vnet = New-AzVirtualNetwork `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location `
-Name MyVnet `
-AddressPrefix 192.168.0.0/16 `
-Subnet $subnetConfig
# Create a public IP address and specify a DNS name
$pip = New-AzPublicIpAddress `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location `
-AllocationMethod Static `
-IdleTimeoutInMinutes 4 `
-Name "mypublicdns$(Get-Random)"
### Create a network security group and a network security group rule
<#
The network security group secures the VM by using inbound and outbound rules. Create an inbound rule for port 3389 to allow incoming Remote Desktop connections and an inbound rule for port 80 to allow incoming web traffic.
#>
# Create an inbound network security group rule for port 22
$nsgRuleSSH = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name $nsgRuleSSHName -Protocol Tcp `
-Direction Inbound -Priority 1000 -SourceAddressPrefix * -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix * `
-DestinationPortRange 22 -Access Allow
# Create an inbound network security group rule for port 80
$nsgRuleWeb = New-AzNetworkSecurityRuleConfig -Name $nsgRuleWebName -Protocol Tcp `
-Direction Inbound -Priority 1001 -SourceAddressPrefix * -SourcePortRange * -DestinationAddressPrefix * `
-DestinationPortRange 80 -Access Allow
# Create a network security group
$nsg = New-AzNetworkSecurityGroup -ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName -Location $location `
-Name $nsgName -SecurityRules $nsgRuleSSH,$nsgRuleWeb
### Create a network card for the VM
# The network card connects the VM to a subnet, network security group, and public IP address.
# Create a virtual network card and associate it with public IP address and NSG
$nic = New-AzNetworkInterface `
-Name myNic `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location `
-SubnetId $vnet.Subnets[0].Id `
-PublicIpAddressId $pip.Id `
-NetworkSecurityGroupId $nsg.Id
## Create a VM
<#
Create a VM configuration. This configuration includes the settings used when deploying the VM. For example: user credentials, size, and the VM image.
#>
# Define a credential object
$UserName='demouser'
$securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $VMPassword -AsPlainText -Force
$cred = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential ($UserName, $securePassword)
# Create the VM configuration object
$VmName = "VirtualMachinelatest"
$VmSize = "Standard_D1"
$VirtualMachine = New-AzVMConfig `
-VMName $VmName `
-VMSize $VmSize
$VirtualMachine = Set-AzVMOperatingSystem `
-VM $VirtualMachine `
-Linux `
-ComputerName "MainComputer" `
-Credential $cred
$VirtualMachine = Set-AzVMSourceImage `
-VM $VirtualMachine `
-PublisherName "Canonical" `
-Offer "UbuntuServer" `
-Skus "20.04-LTS" `
-Version "latest"
$osDiskName = "OsDisk"
$osDiskUri = '{0}vhds/{1}-{2}.vhd' -f `
$StorageAccount.PrimaryEndpoints.Blob.ToString(),`
$vmName.ToLower(), `
$osDiskName
# Set the operating system disk properties on a VM
$VirtualMachine = Set-AzVMOSDisk `
-VM $VirtualMachine `
-Name $osDiskName `
-VhdUri $OsDiskUri `
-CreateOption FromImage | `
Add-AzVMNetworkInterface -Id $nic.Id
# Create the VM
New-AzVM `
-ResourceGroupName $ResourceGroupName `
-Location $location `
-VM $VirtualMachine
連線至 VM
部署 VM 之後,請為其設定 SSH 連線。 若要取得 VM 的公用 IP 位址,請使用 Get-AzPublicIpAddress 命令:
Get-AzPublicIpAddress -ResourceGroupName myResourceGroup | Select IpAddress
從已安裝 SSH 的客戶端系統中,使用下列命令來連線到 VM。 如果您正在使用 Windows,您可以使用 PuTTY 來建立連線。
ssh <Public IP Address>
出現提示時,請以 azureuser 身分登入。 如果您在建立 SSH 金鑰時使用複雜密碼,則必須提供複雜密碼。
安裝 NGINX 網頁伺服器
若要更新套件資源並安裝最新的 NGINX 套件,請執行下列腳本:
#!/bin/bash
# update package source
apt-get -y update
# install NGINX
apt-get -y install nginx
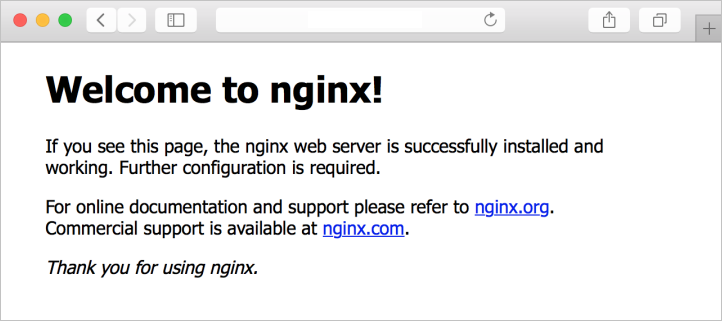
檢視 NGINX 歡迎頁面
安裝 NGINX 網頁伺服器,並在 VM 上開啟埠 80 后,您可以使用 VM 的公用 IP 位址來存取網頁伺服器。 開啟網頁瀏覽器,然後移至 http://<public IP address>。
清除資源
您可以使用 Remove-AzResourceGroup 命令來清除不再需要的資源。 若要刪除資源群組及其所有資源,請執行下列命令:
Remove-AzResourceGroup -Name myResourceGroup
下一步
在本快速入門中,您已部署基本的Linux伺服器 VM。 若要深入瞭解 Azure Stack Hub VM,請移至 Azure Stack Hub 中 VM 的考慮。