虚拟化技术的选择
Architect for Success – Infrastructure Planning and Design Series
随着Windows Server 2008发布倒计时,越来越丰富的虚拟化技术逐渐走入实际应用。究竟该如何区别和选择不同的虚拟化技术或者结合使用,可以下载上面这个解决方案。
其中有一篇 "Selecting the Right Virtualization Technology"
Contents
The Infrastructure Planning and Design Series Approach. 1
Microsoft Virtualization Technologies. 2
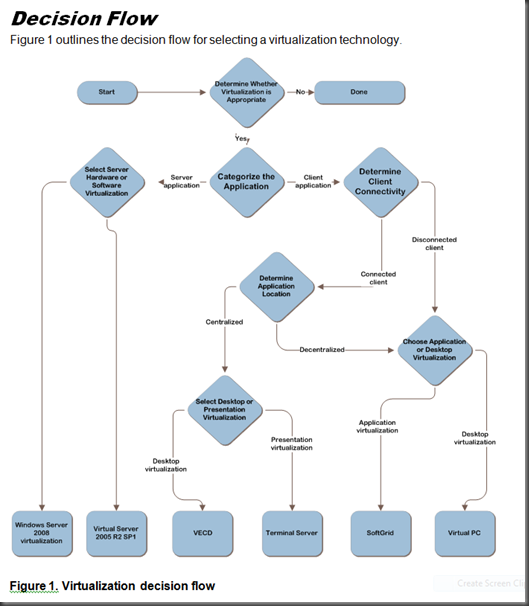
Step 1: Determine Whether Virtualization Is Appropriate. 7
Step 2: Categorize the Application. 7
Step 3: Select Server Hardware or Software Virtualization. 7
Step 4: Determine Client Connectivity. 9
Step 5: Determine Application Location. 10
Step 6: Select Desktop or Presentation Virtualization. 10
Step 7: Choose Application or Desktop Virtualization. 11
Combining Virtualization Technologies. 12
Virtualization Types
There are several different forms of virtualization that need to be understood as a basis for making the right technology choice.
· Server Hardware Virtualization. Also known as a hypervisor, Server Hardware Virtualization runs a very lightweight core operating system. The hypervisor can host independent virtual machines (VMs). This form of virtualization requires hardware that has embedded virtualization awareness capabilities. Since the hypervisor is very lightweight, there is little overhead in the system, which allows for more scalability in the virtual machines.
· Server Software Virtualization. An operating system, such as Windows Server® 2003 or Windows Server 2008, runs an application that is able to host virtual machines. Each virtual machine runs a completely separate operating system and application set.
· Presentation Virtualization. Centralized systems host multiple user sessions, and all processing is done on those host systems. The user sessions are isolated from each other. Only the presentation information, such as keyboard and mouse inputs, and video updates are sent between the client and the host system. The client can be a full Windows-based workstation or a Windows-based terminal device.
· Application Virtualization. An application is isolated from the underlying operating system by means of wrapper software that encapsulates it. This allows multiple applications that may have conflicting dynamic link libraries (DLLs) or other incompatibilities to run on the same machine without affecting each other.
· Desktop Virtualization. This is similar to Server Software Virtualization, but it runs on client systems such as Windows Vista®. The client operating system runs a virtualization application that hosts virtual machines. This is often used when a specific person needs to run one or a limited number of legacy applications on a legacy operating system.
Microsoft Virtualization Technologies
Microsoft has a comprehensive portfolio of virtualization technologies that can be used either independently or together to enable the widest variety of desktop and server virtualization scenarios.
详细内容,请参考文档。
Comments
- Anonymous
January 01, 2003
PingBack from http://geeklectures.info/2007/12/18/%e8%99%9a%e6%8b%9f%e5%8c%96%e6%8a%80%e6%9c%af%e7%9a%84%e9%80%89%e6%8b%a9/