Visual Studio Team Services - Creating a build pipeline (Part 3)
In part 1, a basic Azure Web App website was built and deployed using VSTS Build. Part 2 illustrated how additional files could be included when building a web project. In this post, Gulp will be added to the VSTS Build pipeline.
Gulp
Gulp is a task runner for automating routine development tasks. For example, a common use of Gulp is to minify the javascript and css files and/or perform other optimizations for a non-development environment. In this example we want to add the ability to alter the assembly version during the build.
Adding Gulp to Visual Studio
The ASP.Net template and Visual Studio added most of the references an setup we need to run Gulp. In order to add to our project, we need two files: Gulp.js and package.json. Gulp.js contains the defined tasks while package.json lists any referenced packages required. The first step is to add a Gulp.js and package.json file to your project (Add New Item -> Gulp Configuration File and Add New Item -> NPM Configuration File).
Depending on what install you have done you might need to perform an npm install gulp to get things to work. Please see references for how to get setup.
In the packages.json, we will bring in a couple of helpful packages for parsing supplied parameters (Yargs) and for updating the assembly file (DotNet Assembly Info):
[code lang="js"]
{
"version": "1.0.0",
"name": "ASP.NET",
"private": true,
"devDependencies": {
"gulp":"^3.9.1",
"gulp-dotnet-assembly-info": "^0.1.11",
"yargs": "^4.8.1"
}
}
Working with Gulp is surprisingly simple. The defined task below will apply the supplied version number against the assembly version and the file version.
[code lang="js"]
var gulp = require('gulp');
var assemblyInfo = require('gulp-dotnet-assembly-info');
var argv = require('yargs').argv;
gulp.task('version', function () {
-- only
if (argv.version != undefined) {
gulp.src('*/AssemblyInfo.cs')
.pipe(assemblyInfo({
version: function (value) { return argv.version; },
fileVersion: function (value) { return argv.version; },
}))
.pipe(gulp.dest('.'));
}
});
Tip: if you receive a Cannot find module error when running the Gulp task locally, verify you have have run npm install locally and the packages were downloaded successfully. You can review the modules in the node_modules sub-folder:
Adding Gulp to Build
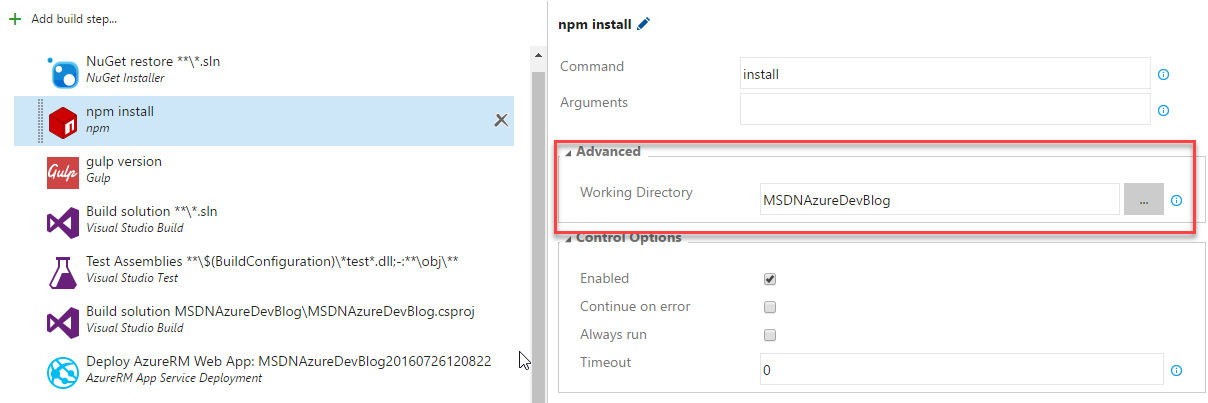
Once the files have been pushed to the server, we need to add two tasks to our Build pipeline. First npm will be run to install the modules required to run Gulp. In the sample, project the working directory of the package file was specified:
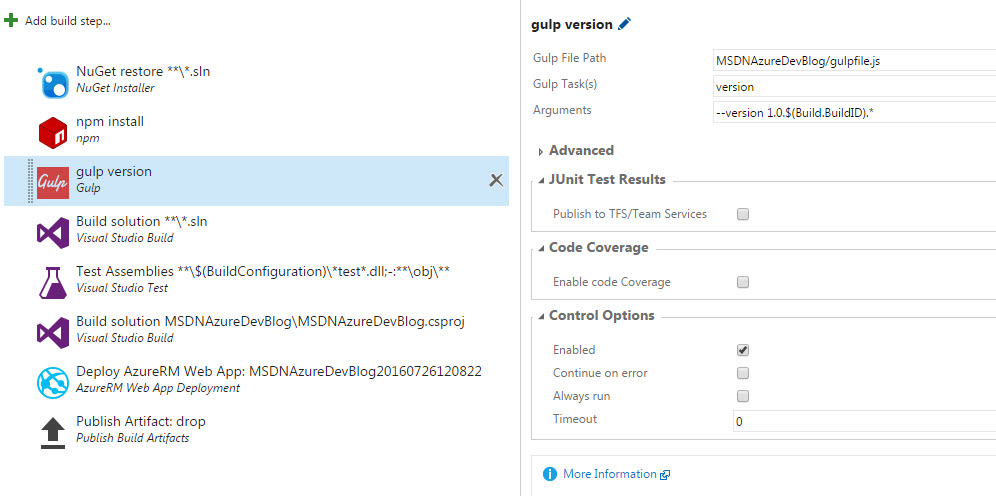
Next a Gulp task will be added to the build process. The version argument is specified to include the BuildID
References
- ASP.Net Using Gulp
- Introducing Gulp, Grunt, Bower, and npm support for Visual Studio
- No Gulp Tasks Found
- Gulp 101 - Getting LESS Up and Running in Visual Studio 2015
- How to use Gulp in Visual Studio
Summary
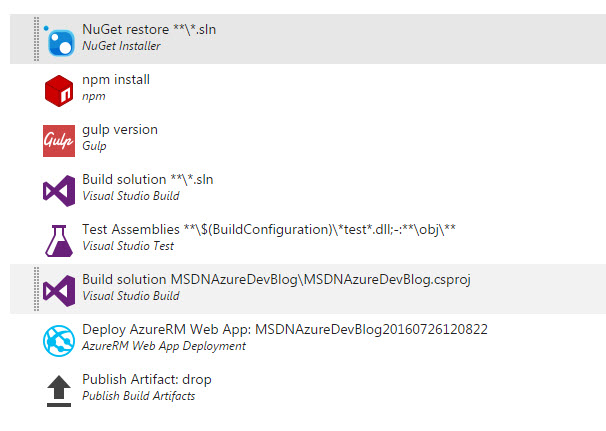
The following shows the current build pipeline:
Next Steps
In Part 4, Load Testing will be reviewed and brought into the build pipeline.
Comments
- Anonymous
August 18, 2016
Great scenario! - Anonymous
October 18, 2016
Hi chilberto, This series is really great to start learning DevOps. I really appreciate your work, but In part three after Gulp step I encountered a problem in Test Assemblies build step , the below is the error I got"The specified path, file name, or both are too long. The fully qualified file name must be less than 260 characters, and the directory name must be less than 248 characters. ---> System.IO.PathTooLongException: The specified path, file name, or both are too long. The fully qualified file name must be less than 260 characters, and the directory name must be less than 248 characters."I want to know how you solved this error? It will be help full if you add solution as well in the article. Can you please provide any solution for this, I tried all solutions available in online, stack overflow etc.- Anonymous
October 19, 2016
Hello Narendra, Sorry to hear about the issue. I uploaded the sample project I used to create the series of posts: https://code.msdn.microsoft.com/Visual-Studio-Creating-a-c36a1f40I have not encountered the error you described in your comment with Test Assemblies. I have come across path related issues with using Bower but I do not think this is related to the Test Assemblies build step: * https://github.com/npm/npm/issues/3697* https://github.com/nodejs/node-v0.x-archive/issues/6960The 7-Zip File Manager was used to solve this: http://superuser.com/questions/78434/how-to-delete-directories-with-path-names-too-long-for-normal-delete
- Anonymous