世界转换 (Direct3D 9)
世界转型的讨论介绍了基本概念,并详细介绍了如何设置世界转型。
什么是世界变革?
世界转换将坐标从模型空间(其中顶点相对于模型的本地原点定义)更改为“世界空间”,其中顶点相对于场景中所有对象通用的原点进行定义。 从本质上讲,世界将一个模型转化为世界:因此,它的名称。 下图显示了世界坐标系与模型本地坐标系之间的关系。
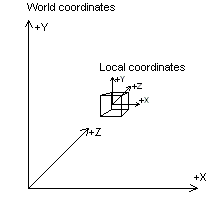
世界转换可以包括翻译、旋转和缩放的任意组合。
设置世界矩阵
与任何其他转换一样,通过将一系列矩阵串联成包含其效果总和的单个矩阵来创建世界转换。 最简单的情况是,当模型位于世界原点,其本地坐标轴面向世界空间时,世界矩阵是标识矩阵。 更常见的是,世界矩阵是转换为世界空间的组合,可能还有一个或多个旋转来根据需要转换模型。
下面的示例来自用 C++ 编写的虚构 3D 模型类,使用 D3DX 实用工具库中包括的帮助程序函数创建一个世界矩阵,该矩阵包含三个旋转来定位模型,以及一个转换,以相对于其在世界空间中的位置重新定位它。
/*
* For the purposes of this example, the following variables
* are assumed to be valid and initialized.
*
* The m_xPos, m_yPos, m_zPos variables contain the model's
* location in world coordinates.
*
* The m_fPitch, m_fYaw, and m_fRoll variables are floats that
* contain the model's orientation in terms of pitch, yaw, and roll
* angles, in radians.
*/
void C3DModel::MakeWorldMatrix( D3DXMATRIX* pMatWorld )
{
D3DXMATRIX MatTemp; // Temp matrix for rotations.
D3DXMATRIX MatRot; // Final rotation matrix, applied to
// pMatWorld.
// Using the left-to-right order of matrix concatenation,
// apply the translation to the object's world position
// before applying the rotations.
D3DXMatrixTranslation(pMatWorld, m_xPos, m_yPos, m_zPos);
D3DXMatrixIdentity(&MatRot);
// Now, apply the orientation variables to the world matrix
if(m_fPitch || m_fYaw || m_fRoll) {
// Produce and combine the rotation matrices.
D3DXMatrixRotationX(&MatTemp, m_fPitch); // Pitch
D3DXMatrixMultiply(&MatRot, &MatRot, &MatTemp);
D3DXMatrixRotationY(&MatTemp, m_fYaw); // Yaw
D3DXMatrixMultiply(&MatRot, &MatRot, &MatTemp);
D3DXMatrixRotationZ(&MatTemp, m_fRoll); // Roll
D3DXMatrixMultiply(&MatRot, &MatRot, &MatTemp);
// Apply the rotation matrices to complete the world matrix.
D3DXMatrixMultiply(pMatWorld, &MatRot, pMatWorld);
}
}
准备世界矩阵后,调用 IDirect3DDevice9::SetTransform 方法进行设置,为第一个参数指定 D3DTS_WORLD 宏。
注意
Direct3D 使用你设置的世界和视图矩阵来配置多个内部数据结构。 每次设置新的世界或视图矩阵时,系统都会重新计算关联的内部结构。 例如,频繁设置这些矩阵,即每个帧的数千次计算耗时。 通过将世界和视图矩阵串联为世界视图矩阵,然后将视图矩阵设置为世界矩阵,然后将视图矩阵设置为标识,可以最大程度地减少所需计算的数量。 保留单个世界和视图矩阵的缓存副本,以便根据需要修改、连接和重置世界矩阵。 为了清楚起见,本文档中的 Direct3D 示例很少采用此优化。
相关主题