将 PyTorch 训练模型转换为 ONNX
注意
为了获得更大的功能, PyTorch 还可用于 Windows 上的 DirectML。
在本教程的上一阶段中,我们使用 PyTorch 创建了机器学习模型。 但是,该模型是一个 .pth 文件。 若要将其与 Windows ML 应用集成,需要将模型转换为 ONNX 格式。
导出模型
要导出模型,你将使用 torch.onnx.export() 函数。 此函数执行模型,并记录用于计算输出的运算符的跟踪。
- 将 main 函数上方的以下代码复制到 Visual Studio 中的
PyTorchTraining.py文件中。
import torch.onnx
#Function to Convert to ONNX
def Convert_ONNX():
# set the model to inference mode
model.eval()
# Let's create a dummy input tensor
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, input_size, requires_grad=True)
# Export the model
torch.onnx.export(model, # model being run
dummy_input, # model input (or a tuple for multiple inputs)
"ImageClassifier.onnx", # where to save the model
export_params=True, # store the trained parameter weights inside the model file
opset_version=10, # the ONNX version to export the model to
do_constant_folding=True, # whether to execute constant folding for optimization
input_names = ['modelInput'], # the model's input names
output_names = ['modelOutput'], # the model's output names
dynamic_axes={'modelInput' : {0 : 'batch_size'}, # variable length axes
'modelOutput' : {0 : 'batch_size'}})
print(" ")
print('Model has been converted to ONNX')
在导出模型之前必须调用 model.eval() 或 model.train(False),因为这会将模型设置为“推理模式”。 这是必需的,因为 dropout 或 batchnorm 等运算符在推理和训练模式下的行为有所不同。
- 要运行到 ONNX 的转换,请将对转换函数的调用添加到 main 函数。 无需再次训练模型,因此我们将注释掉一些不再需要运行的函数。 main 函数将如下所示。
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Let's build our model
#train(5)
#print('Finished Training')
# Test which classes performed well
#testAccuracy()
# Let's load the model we just created and test the accuracy per label
model = Network()
path = "myFirstModel.pth"
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(path))
# Test with batch of images
#testBatch()
# Test how the classes performed
#testClassess()
# Conversion to ONNX
Convert_ONNX()
- 选择工具栏上的
Start Debugging按钮或按F5再次运行项目。 无需再次训练模型,只需从项目文件夹中加载现有模型即可。
输出将如下所示。
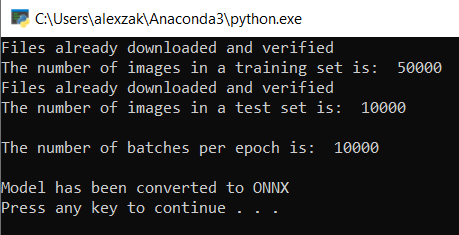
导航到项目位置并找到 .pth 模型旁边的 ONNX 模型。
注意
想要了解更多内容? 查看有关导出模型的 PyTorch 教程。
导出模型。
使用 Netron 打开
ImageClassifier.onnx模型文件。选择数据节点,打开模型属性。
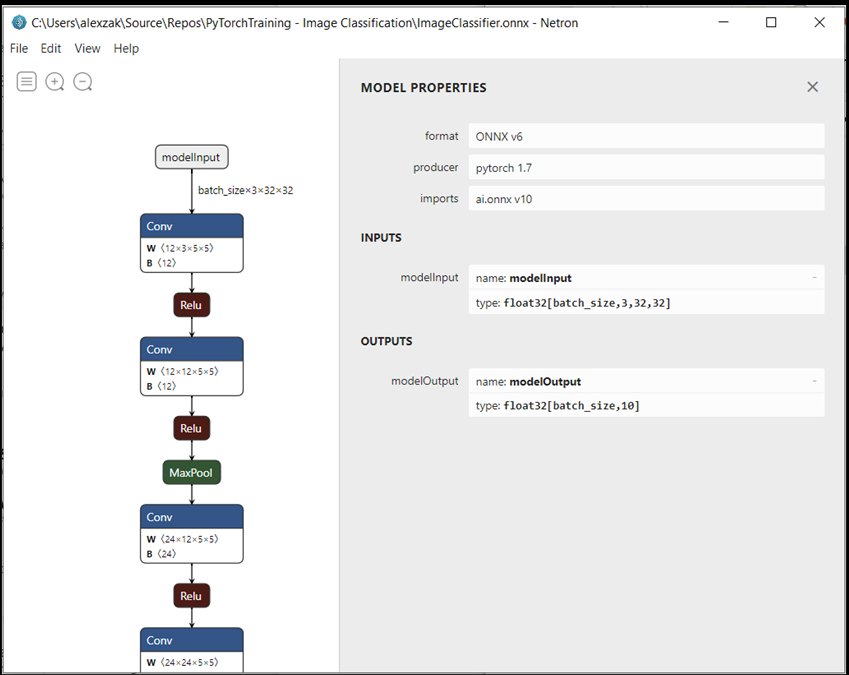
如你所见,该模型需要一个 32 位张量(多维数组)浮点对象作为输入,并返回一个 Tensor 浮点作为输出。 输出数组将包括每个标签的概率。 根据模型的构建方式,标签由 10 个数字表示,每个数字代表 10 个对象类别。
| 标签 0 | 标签 1 | 标签 2 | 标签 3 | 标签 4 | 标签 5 | 标签 6 | 标签 7 | 标签 8 | 标签 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 飞机 | car | bird | cat | 鹿 | 狗 | 青蛙 | 马 | 轮船 | 卡车 |
你将需要提取这些值来显示 Windows ML 应用的正确预测。
后续步骤
模型已准备就绪,可供部署。 接下来,主要事件是构建一个 Windows 应用程序并在 Windows 设备上在本地运行它。