使用 Windows ML API 在 Windows 应用中部署数据分析模型
在本教程的上一部分中,你已了解如何构建并以 ONNX 格式导出模型。 接下来,我们将介绍如何将导出的模型嵌入到 Windows 应用程序中,并通过调用 Windows ML API 在设备的本地运行该模型。
完成此部分后,你将拥有一个可工作的数据分析应用。
关于示例应用程序
在本教程的该步骤中,你将创建一个可分析鸢尾花表格数据的应用。 通过该应用,你可添加具有所需输入信息的 Excel 文件,或者手动填写输入参数 - 鸢尾花花瓣的长度和宽度(以厘米为单位)。这些特征将由你在上一部分构建和训练过的本地存储的神经网络 ONNX 模型进行处理。 根据模型输出,应用将显示正确的鸢尾花类型。
在本部分中,我们将指导你完成该过程。
注意
如果选择使用预定义的代码示例,可以克隆解决方案文件。 克隆存储库,导航到此示例,然后使用 Visual Studio 打开 Iris Data Analysis.csproj 文件。跳到此页面的“启动应用程序”部分以查看它的使用情况。
下面,我们将指导你如何创建应用并添加 Windows ML 代码。
创建 Windows ML 桌面 (C#) 应用
若要创建可以工作的 Windows ML 应用,需要执行以下操作:
- 加载机器学习模型。
- 绑定模型的输入和输出。
- 评估模型并显示有意义的结果。
还需要创建一个基本 UI,以提供更好的用户体验。
在 Visual Studio 中打开新项目
- 现在就开始吧。 打开 Visual Studio 并选择
Create a new project。
- 在搜索栏中,选择
C#作为语言,选择Windows作为目标平台,选择Dektop作为项目类型。 选择NUnit Test Project (.NET Core)作为项目类型,并选择next来打开项目的配置窗口。
- 在配置窗口中执行以下操作:
- 为项目命名。 在此处,我们将它称为“鸢尾花数据分析”。
- 选择项目的位置。
- 如果使用的是 VS 2019,请确保选中
Create directory for solution。 - 如果使用的是 VS2017,请确保未勾选
Place solution and project in the same directory。
按 create 创建项目。 可能会弹出最低目标版本窗口。 请确保将最低版本设置为“Windows 10 版本 1809 (10.0;内部版本 17763)”或更高版本。
- 创建项目后,导航到项目文件夹,打开资产文件夹
[….\DataClassifier\Assets],然后将Network.onnx文件复制到该位置。
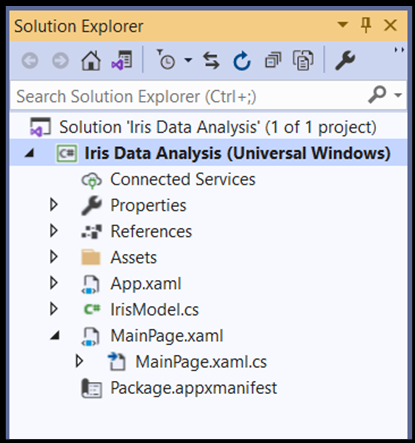
探索项目解决方案
让我们探索项目解决方案。
Visual Studio 在解决方案资源管理器中自动创建了几个 cs 代码文件。 MainPage.xaml 包含 GUI 的 XAML 代码,MainPage.xaml.cs 包含应用程序代码。 如果之前已创建 UWP 应用,你应该对这些文件非常熟悉。
虽然我们在“资产”文件夹中添加了 Network.onnx,但需要将其适当地添加到此项目。
- 在解决方案资源管理器中右键单击“资产”文件夹,然后选择
Add > Existing Item。 - 导航到
Iris Data Analysis [….\Iris Data Analysis \Assets]中的“资产”文件夹,找到之前复制到该文件夹中的Network.onnx model,然后选择Add。 - 若要确保在编译应用程序时生成模型,请右键单击
Network.onnx文件,然后选择Properties。 将Build Action设置为Content。
还需要创建一个新的 cs-code 类文件来保存额外的一些机器学习代码,这包含将调用 Windows ML API 的类和方法。
- 在 Visual Studio 中右键单击解决方案名称,然后选择
add和new item。 在打开的窗口中,选择Class,然后为其指定一个名称 - 此处使用IrisModel.cs。 你的项目下将出现一个新的类文件。
 。
。
创建机器学习代码
在此步骤中,我们将创建要调用 Windows 机器学习 API 的所有类和方法。 这样你可将 ONNX 机器学习模型加载和绑定到项目中并对其进行评估。
双击
IrisModel.cs文件。将 using 语句替换为以下内容,以访问所需的全部 API。
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Windows.AI.MachineLearning;
using Windows.Storage;
将机器学习类初始化
我们将需要将多个类添加到 IrisModel.cs,来帮助你与 Windows 机器学习 API 进行交互。
我们将使用 LearningModel 类来访问经过训练的机器学习模型。 此类是 Windows.AI.MachineLearning 命名空间的一部分,它表示经过训练的机器学习模型。 实例化后,LearningModel 是用于与 Windows ML API 交互的主要对象。
若要评估学习模型,必须创建评估会话。 为此,请使用 LearningModelSession 类。 此类用于评估机器学习模型,并将该模型绑定到一个设备上,然后运行和评估该模型。 使用此 API 创建会话时,还可选择一台设备来执行模型(默认为 CPU)。
此外,还需要指定机器学习模型的输出的标签。 稍后可将这些标签连接到模型的预测输出。
注意
若要详细了解 LearningModel 和 LearningModelSession 类,请查看 LearningModel 类文档和 LearningModelSession 类文档。
- 将以下代码复制到
IrisModel.cs文件。
class IrisModel
{
private LearningModel _learning_model;
private LearningModelSession _session;
private String[] _labels = { "Iris-setosa", "Iris-versicolor", "Iris-virginica"};
加载模型
接下来,需要加载机器学习模型并创建一个会话,你将在该会话中处理刚才定义的类。 若要加载模型,需使用 LearningModel 类的多个静态方法。在本例中,我们将使用 LoadFromStorageFileAsync,它可用于从 ISorageFile 异步加载 ONNX 模型。
注意
若要详细了解加载模型的其他方式,请查看“加载模型”文档。
- 将以下代码复制到
IrisModel.cs文件。
public async Task Initialize()
{
// Load and create the model and session
var modelFile = await StorageFile.GetFileFromApplicationUriAsync(new Uri($"ms-appx:///Assets//Network.onnx"));
_learning_model = await LearningModel.LoadFromStorageFileAsync(modelFile);
_session = new LearningModelSession(_learning_model);
}
定义模型输入张量
现在,我们将根据你的模型要求定义正确的输入。 你在上一部分生成的网络模型具有 4 个输入值。 每个输入值表示 4 种鸢尾花特征的可能大小,这些特征是花萼长度(厘米)、花萼宽度(厘米)、花瓣长度(厘米)、花瓣宽度(厘米)。根据此输入,模型将返回最符合这些参数的鸢尾花类型。 需要将输入值的大小限制为有效逻辑值 - 在本教程中,我们将使用以下值:
- 花萼长度 - 1-100 厘米
- 花萼宽度 - 1-8 厘米
- 花瓣长度 - 0.5-10 厘米
- 花瓣宽度 - 0.1-5 厘米
- 将以下代码复制到
IrisModel.cs文件。
private float _sepal_length = 1.0f;
public float Sepal_Length
{
get
{
return _sepal_length;
}
set
{
// validate range [1,10]
if (value >= 1 && value <= 10)
{
_sepal_length = value;
}
}
}
private float _sepal_width = 1.0f;
public float Sepal_Width
{
get
{
return _sepal_width;
}
set
{
// validate range [1, 8]
if (value >= 1 && value <= 8)
{
_sepal_width = value;
}
}
}
private float _petal_length = 0.5f;
public float Petal_Length
{
get
{
return _petal_length;
}
set
{
// validate range [0.5, 10]
if (value >= 0.5 && value <= 10)
{
_petal_length = value;
}
}
}
private float _petal_width = 0.1f;
public float Petal_Width
{
get
{
return _petal_width;
}
set
{
// validate range [0.1, 5]
if (value >= 0.1 && value <= 5)
{
_petal_width = value;
}
}
}
Windows ML API 接受 ONNX 模型支持的 4 个描述性类的输入值,这些类是张量、序列、地图和图像。 在本例中,模型需要一个形状为 float32[batch_size,4] 的 32 位张量浮点对象。 由于批大小是 1,因此输入张量形状是 [1x4]。
若要创建张量输入,请使用 TensorFloat 类。
TensorFloat 类是 Windows.AI.MachineLearning 命名空间的一部分,它用于定义 32 位浮点张量对象(即 32 位浮点值的张量)。 此类包含几种用于生成张量的有用方法。 在本例中,你将使用 CreateFromArray 方法生成一个大小恰好是模型所需大小的张量输入。 我们将在评估方法中添加此调用。
绑定并评估模型
现在你已定义了模型输入张量,还将经过训练的模型和会话实例化,接下来可创建一个方法来绑定和评估经过训练的机器学习模型。
此方法是机器学习应用的关键部分。 它包括输入值的张量化和模型输入的绑定。 稍后,你将在应用程序中使用此模型来评估你的模型。
若要绑定输入和输出,请使用 LearningModelBinding 类。 机器学习模型具有输入和输出特征,用于将信息传入和传出模型。 请注意,Windows ML API 必须支持必需的功能。 在 LearningModelSession 上应用 LearningModelBinding 类以将值绑定到已命名的输入和输出特征。
LearningModelBinding 类具有多个预定义的方法,你可使用它们将值绑定到这些命名特征。 在这里,你将使用 Bind 方法将值绑定到模型。
若要评估模型并从其接收结果,请从 LearningModelSession 调用相关的预定义评估方法。在本例中,是 Evaluate 方法。 此方法将提供你需要的功能,使用 LearningModelBinding 类提供的特征值评估机器学习模型。
注意
要了解用于运行模型的其他评估方法,请通过查看 LearningModelSession 类文档,检查哪些方法可以在 LearningModelSession 上实现。
提取并显示结果
模型以张量浮点输出的形式返回张量格式的预测值。 现在需要提取模型输出并显示正确的结果。 为此,需要对预测的输出运行 GetAsVectorView() 函数,将张量格式转换为矢量。
模型会返回 3 个概率值,每个值表示一种特定的鸢尾花类型。 需要返回概率最高的标签。
- 将以下代码复制到
IrisModel.cs文件。
internal String Evaluate()
{
// input tensor shape is [1x4]
long[] shape = new long[2];
shape[0] = 1;
shape[1] = 4;
// set up the input tensor
float[] input_data = new float[4];
input_data[0] = _sepal_length;
input_data[1] = _sepal_width;
input_data[2] = _petal_length;
input_data[3] = _petal_width;
TensorFloat tensor_float = TensorFloat.CreateFromArray(shape, input_data);
// bind the tensor to "input"
var binding = new LearningModelBinding(_session);
binding.Bind("input", tensor_float);
// evaluate
var results = _session.Evaluate(binding, "");
// get the results
TensorFloat prediction = (TensorFloat)results.Outputs.First().Value;
var prediction_data = prediction.GetAsVectorView();
// find the highest predicted value
int max_index = 0;
float max_value = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prediction_data.Count; i++)
{
var val = prediction_data.ElementAt(i);
if (val > max_value)
{
max_value = val;
max_index = i;
}
}
// return the label corresponding to the highest predicted value
return _labels.ElementAt(max_index);
}
你现在已完成代码的机器学习部分。 接下来可轻松地将模型与 Windows 应用程序集成。 在本教程的最后一个部分,我们提供了一个基本的 Windows GUI 和控制代码,便于使用你已创建的方法测试模型。
创建应用程序 GUI
若要为应用创建 GUI 应用代码,请双击
MainPage.xaml代码文件,并打开 GUI 的预定义模板。将以下代码复制粘贴到
“Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}" " Height="939">行下的MainPage.xaml中。
<Grid Margin="30,30,30,30">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<TextBlock x:Name="title" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Text="Data Analysis App - Windows ML" TextWrapping="Wrap" VerticalAlignment="Top" FontSize="32" TextDecorations="Underline" FontWeight="Bold"/>
<TextBlock x:Name="subtitle" HorizontalAlignment="Left" Text="Provide the input :" TextWrapping="Wrap" VerticalAlignment="Top" FontSize="20" Grid.Row="1" FontWeight="Bold"/>
<Grid Grid.Row="2">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto"/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBlock x:Name="sepal_length" Text="sepal length in mm [range of 10 - 100]:" VerticalAlignment="Center"/>
<TextBlock x:Name="sepal_width" Text="sepal width in mm [range of 10 - 80]:" VerticalAlignment="Center" Grid.Row="1"/>
<TextBlock x:Name="petal_length" Text="petal length in mm [range of 5 - 100]:" VerticalAlignment="Center" Grid.Row="2"/>
<TextBlock x:Name="petal_width" Text="sepal width in mm [range of 1 - 50]:" VerticalAlignment="Center" Grid.Row="3"/>
<Slider x:Name="sepal_length_input" Minimum="10" Maximum="100" Orientation="Horizontal" Grid.Column="1" Width="200" ValueChanged="sepal_length_input_ValueChanged"/>
<Slider x:Name="sepal_width_input" Minimum="10" Maximum="80" Orientation="Horizontal" Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Width="200" ValueChanged="sepal_width_input_ValueChanged"/>
<Slider x:Name="petal_length_input" Minimum="5" Maximum="100" Orientation="Horizontal" Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1" Width="200" ValueChanged="petal_length_input_ValueChanged"/>
<Slider x:Name="petal_width_input" Minimum="1" Maximum="50" Orientation="Horizontal" Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="1" Width="200" ValueChanged="petal_width_input_ValueChanged"/>
</Grid>
<TextBlock x:Name="output" Text="Output:" FontSize="20" FontWeight="Bold" Grid.Row="3"/>
<Grid Grid.Row="4">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto"/>
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<TextBlock x:Name="output_subtitle" Text="Based on the information provided, the Iris type is:"/>
<TextBlock x:Name="model_output" Text="Model output" FontStyle="Italic" Grid.Column="1" Margin="10,0,0,0"/>
</Grid>
</Grid>
创建应用程序控件
应用程序控制代码 MainPage.xaml.cs 包含用于运行应用的主要方法,还包含运行模型和执行输出的几个步骤:
- 将之前在本教程中创建的
IrisModel类的新对象进行实例化。 - 对模型调用在上一部分中生成的
Evaluate()方法。 此方法将应用 4 次,对每个输入参数(花萼长度、花萼宽度、花瓣长度和花瓣宽度)应用一次。
应用将根据机器学习预测算法显示结果。
- 若要创建应用程序控制代码,请双击
MainPage.xaml.cs代码文件并添加以下代码。
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls.Primitives;
// The Blank Page item template is documented at https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=402352&clcid=0x409
namespace Iris_Data_Analysis
{
/// <summary>
/// An empty page that can be used on its own or navigated to within a Frame.
/// </summary>
public sealed partial class MainPage : Page
{
private IrisModel _iris_model;
public MainPage()
{
this.InitializeComponent();
_iris_model = new IrisModel();
#pragma warning disable CS4014 // Because this call is not awaited, execution of the current method continues before the call is completed
_iris_model.Initialize();
#pragma warning restore CS4014 // Because this call is not awaited, execution of the current method continues before the call is completed
}
private void sepal_length_input_ValueChanged(object sender, RangeBaseValueChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (_iris_model != null)
{
_iris_model.Sepal_Length = (float)sepal_length_input.Value / 10.0f;
model_output.Text = _iris_model.Evaluate();
}
}
private void sepal_width_input_ValueChanged(object sender, RangeBaseValueChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (_iris_model != null)
{
_iris_model.Sepal_Width = (float)sepal_width_input.Value / 10.0f;
model_output.Text = _iris_model.Evaluate();
}
}
private void petal_length_input_ValueChanged(object sender, RangeBaseValueChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (_iris_model != null)
{
_iris_model.Petal_Length = (float)petal_length_input.Value / 10.0f;
model_output.Text = _iris_model.Evaluate();
}
}
private void petal_width_input_ValueChanged(object sender, RangeBaseValueChangedEventArgs e)
{
if (_iris_model != null)
{
_iris_model.Petal_Width = (float)petal_width_input.Value / 10.0f;
model_output.Text = _iris_model.Evaluate();
}
}
}
}
启动应用程序
现在你可启动应用程序并查看结果了。
启用开发人员模式并从 Visual Studio 测试应用程序。 确保顶部工具栏中的下拉菜单设置为 Debug。 将解决方案平台更改为 x64(如果设备是 64 位的)或 x86(如果设备是 32 位的)以在你的本地计算机上运行该项目。
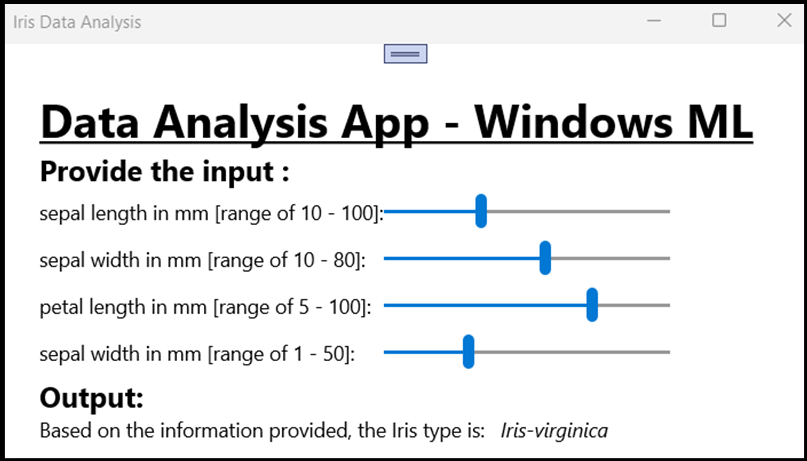
应用 GUI 包含 4 个滑块,用于更改所需参数的输入。 输入中的任何更改都将根据预测算法生成一个新的输出。 输出显示在输入滑块的下方。
可以看到,假设花萼长度是 40 毫米、花萼宽度是 50、花瓣长度是 75,而花瓣宽度是 15,则应用生成 Iris-versicolor 类型的输入!
总结
你刚刚完成了首个 Windows 机器学习应用从模型创建到成功执行的过程。
其他资源
若要详细了解本教程中所述的主题,请访问以下资源:
- Windows ML 工具:了解更多工具,例如 Windows ML 仪表板、WinMLRunner 和 mglen Windows ML 代码生成器。
- ONNX 模型:详细了解 ONNX 格式。
- Windows ML 性能和内存:详细了解如何使用 Windows ML 管理应用性能。
- Windows 机器学习 API 参考:详细了解 Windows ML API 的三个方面。