教程:在 Visual Studio 中创建简单的 C# 控制台应用(第 1 部分(共 2 部分)
在本教程中,你将使用 Visual Studio 创建和运行 C# 控制台应用,并探索 Visual Studio 集成开发环境(IDE)的某些功能。 本教程是两部分教程系列的第 1 部分。
在本教程中,你将完成以下任务:
- 创建 Visual Studio 项目。
- 创建 C# 控制台应用。
- 调试应用。
- 关闭应用。
- 检查您的完整代码。
在本教程的第 2 部分中,将扩展此应用以添加更多项目、了解调试技巧和引用非Microsoft包。
先决条件
必须安装 Visual Studio。
如果没有 Visual Studio,请转到 Visual Studio 下载 进行免费安装。
创建项目
若要开始,请创建 C# 应用程序项目。 项目类型附带所需的所有模板文件。
打开 Visual Studio,然后选择“开始”窗口中 创建新项目。
在“创建新项目 窗口中,从语言下拉列表中选择 C#。 从平台列表中选择 Windows,并从项目类型列表中选择 控制台。
应用语言、平台和项目类型筛选器后,选择 控制台应用程序 模板,然后选择“下一步”。
注意
如果未看到 控制台应用程序 模板,请选择 安装更多工具和功能。

在 Visual Studio 安装程序中,选择 .NET Core 跨平台开发 工作负荷。

在 Visual Studio 安装程序中选择 修改。 系统可能会提示你保存工作。 选择“继续”以安装该工作负载。
返回到 创建项目 过程中的步骤 2。
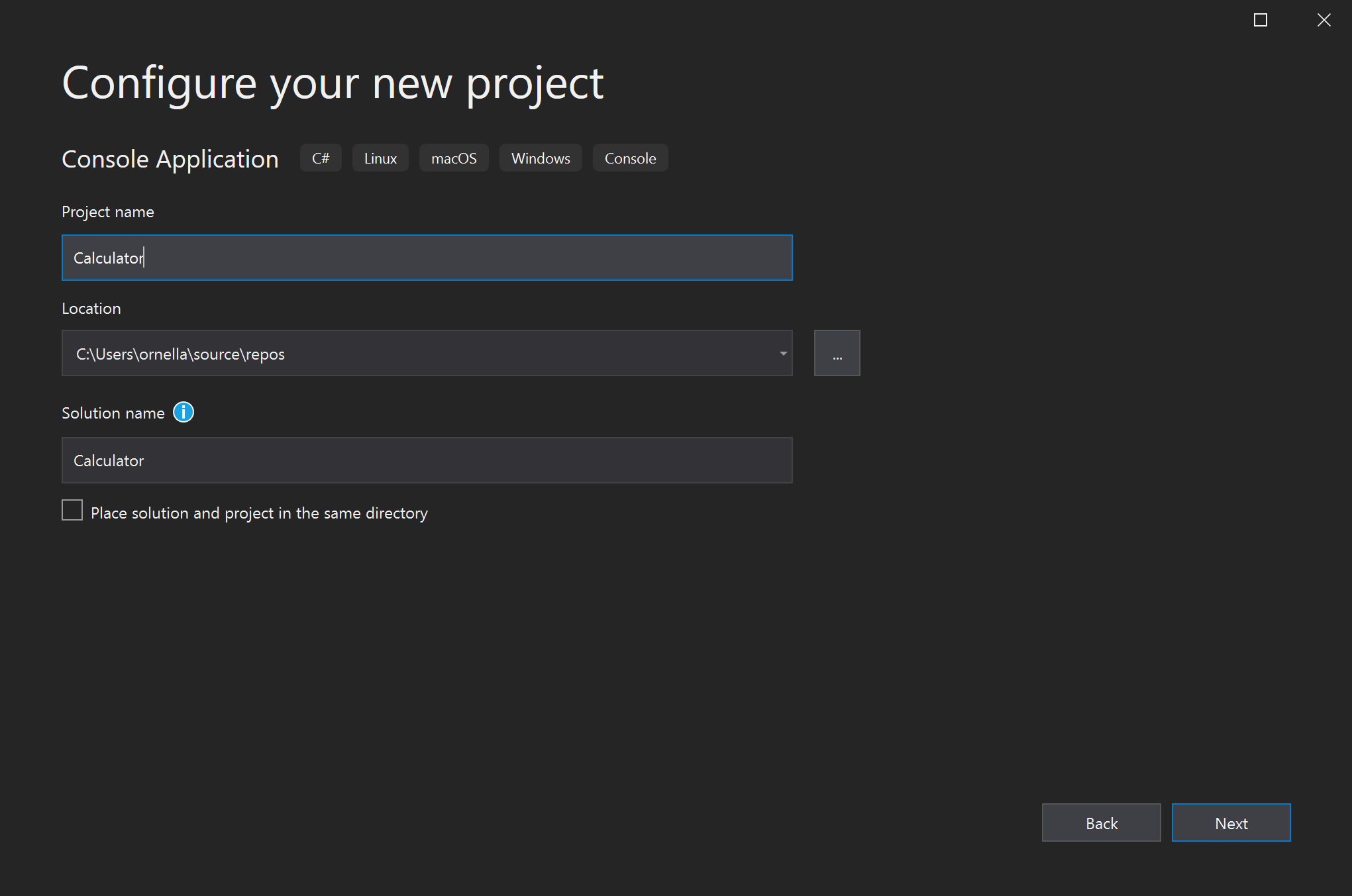
在 配置新项目 窗口中,在 项目名称 框中键入或输入 计算器。 然后选择下一步。
在“其他信息 窗口中,验证 .NET Core 3.1 是否显示在 目标框架 字段中。 然后选择“创建”。
Visual Studio 将打开新项目,其中包括默认 Hello World 代码。 若要在编辑器中查看该文件,请在解决方案资源管理器窗口中选择代码文件 Program.cs,该文件通常位于 Visual Studio 的右侧。
默认 Hello World 代码调用 WriteLine 方法,以在控制台窗口中显示字面字符串 Hello, World!。 如果按 F5,则可以在调试模式下运行默认程序。 应用程序在调试器中运行后,控制台窗口将保持打开状态。 按任意键关闭控制台窗口。
打开 Visual Studio,然后选择“开始”窗口中 创建新项目。
在“创建新项目 窗口中,从语言下拉列表中选择 C#。 从平台列表中选择 Windows,并从项目类型列表中选择 控制台。
应用语言、平台和项目类型筛选器后,选择 控制台应用 模板,然后选择“下一步”。
注意
如果未看到 控制台应用 模板,请选择 安装更多工具和功能。
在 Visual Studio 安装程序中,选择 .NET 桌面开发 工作负荷。
在 Visual Studio 安装程序中选择 修改。 系统可能会提示你保存工作。 选择 继续 安装工作负载。
返回到本 创建项目 过程的步骤二。
在“配置新项目”窗口中,在“项目名称”框中输入“计算器”,然后选择“下一步”。
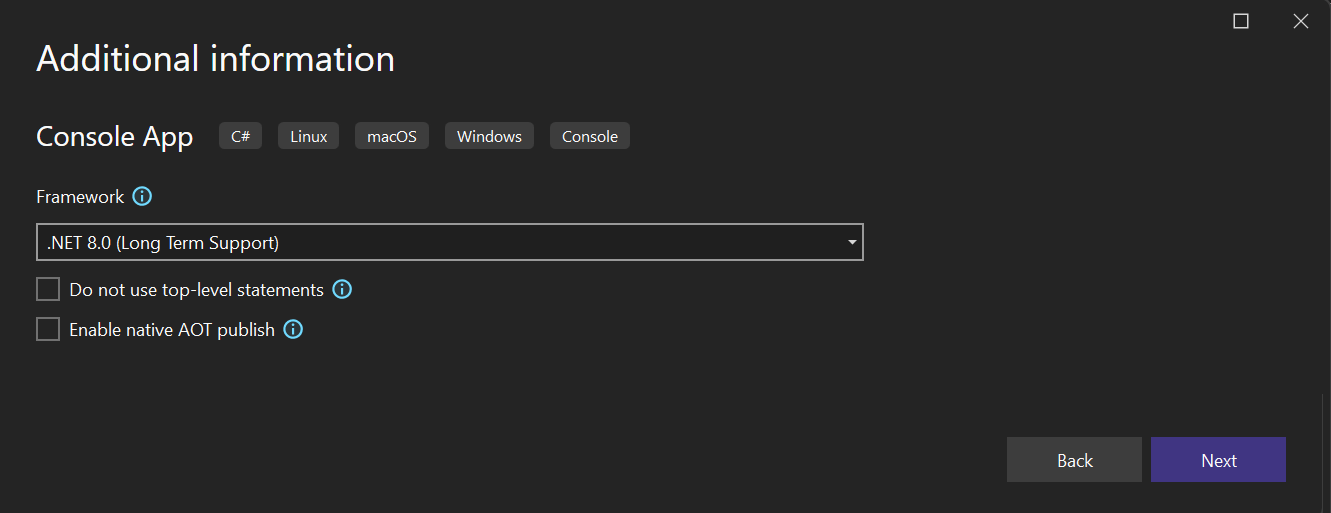
在“附加信息”窗口中,为 目标框架 字段选择 .NET 8.0。 然后,选择“创建”。
Visual Studio 将打开新项目,其中包括默认 Hello World 代码。 若要在编辑器中查看该文件,请在解决方案资源管理器窗口中选择代码文件 Program.cs,该文件通常位于 Visual Studio 的右侧。
单个代码语句调用 WriteLine 方法在控制台窗口中显示文本字符串 Hello, World!。 如果按 F5,则可以在调试模式下运行默认程序。 应用程序在调试器中运行后,控制台窗口将保持打开状态。 按任意键关闭控制台窗口。
注意
从 .NET 6 开始,使用控制台模板的新项目将生成与以前版本不同的代码。 若要了解详细信息,请参阅新的 C# 模板生成顶级语句。
创建应用
在本部分中,你将完成以下任务:
- 了解 C# 中的一些基本整数数学。
- 添加代码以创建基本计算器应用。
- 调试应用以查找和修复错误。
- 优化代码,使其更高效。
探索整数数学
从 C# 中的一些基本整数数学开始。
在右窗格中,选择 Program.cs 以在代码编辑器中显示文件。
在代码编辑器中,删除默认 Hello World 代码。
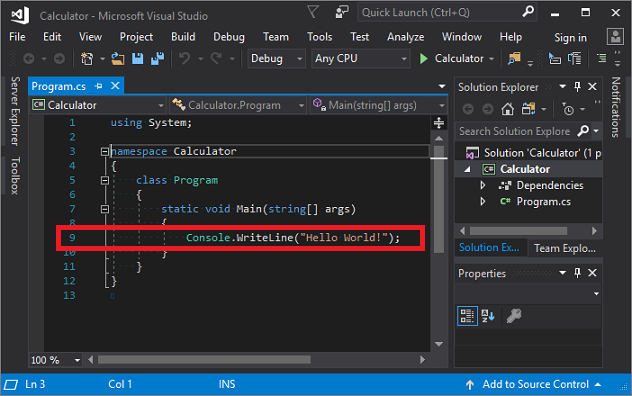
具体而言,请删除包含
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");的行。在其位置输入以下代码:
int a = 42; int b = 119; int c = a + b; Console.WriteLine(c); Console.ReadKey();请注意,输入代码时,Visual Studio 中的 IntelliSense 功能提供了自动完成条目的选项。
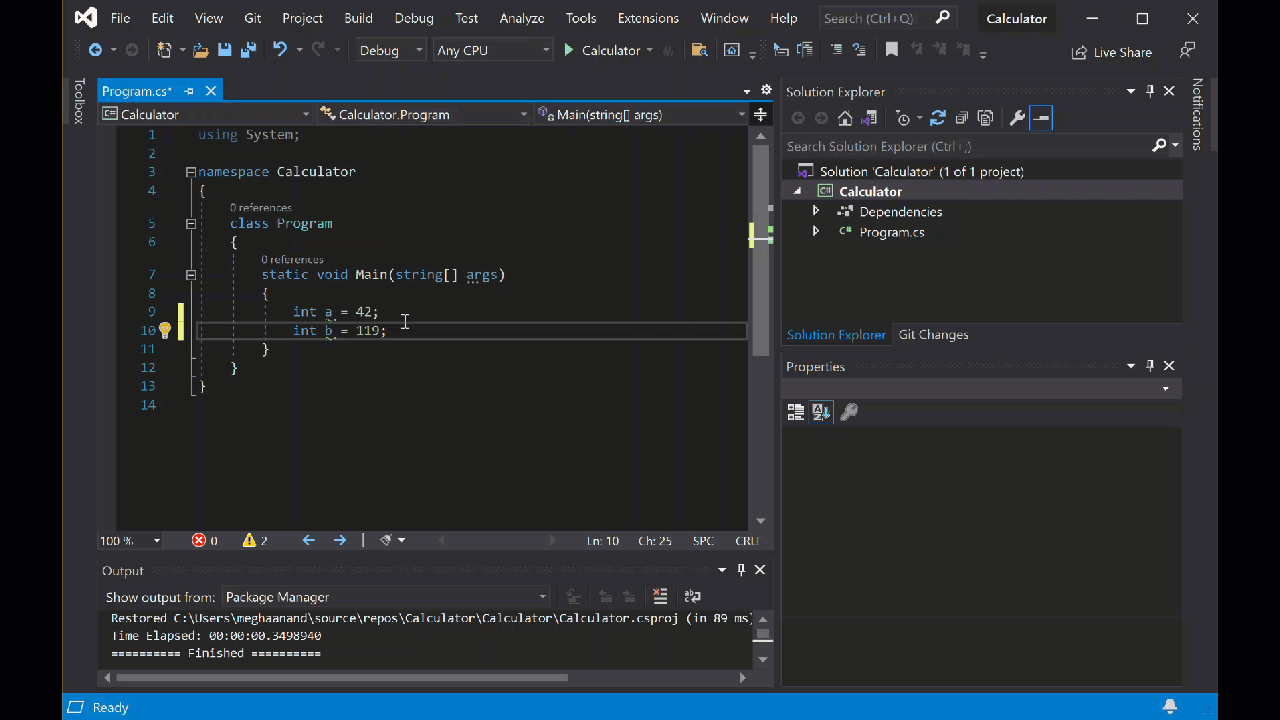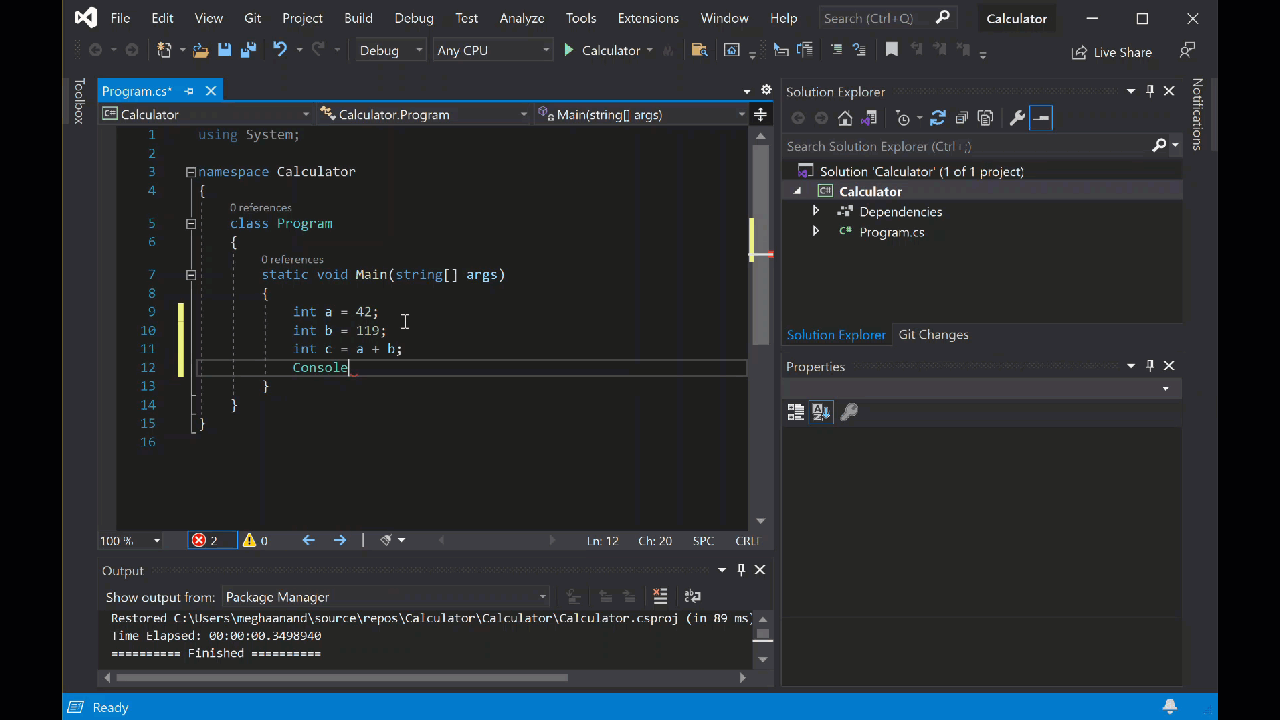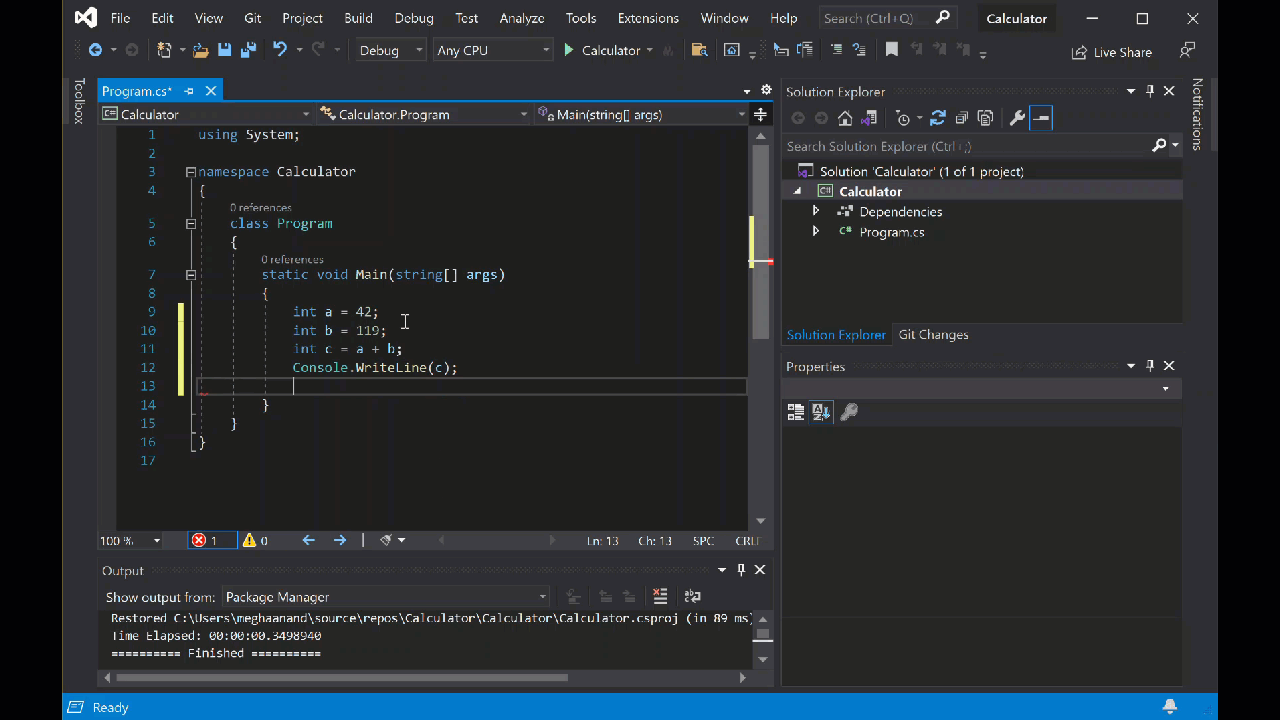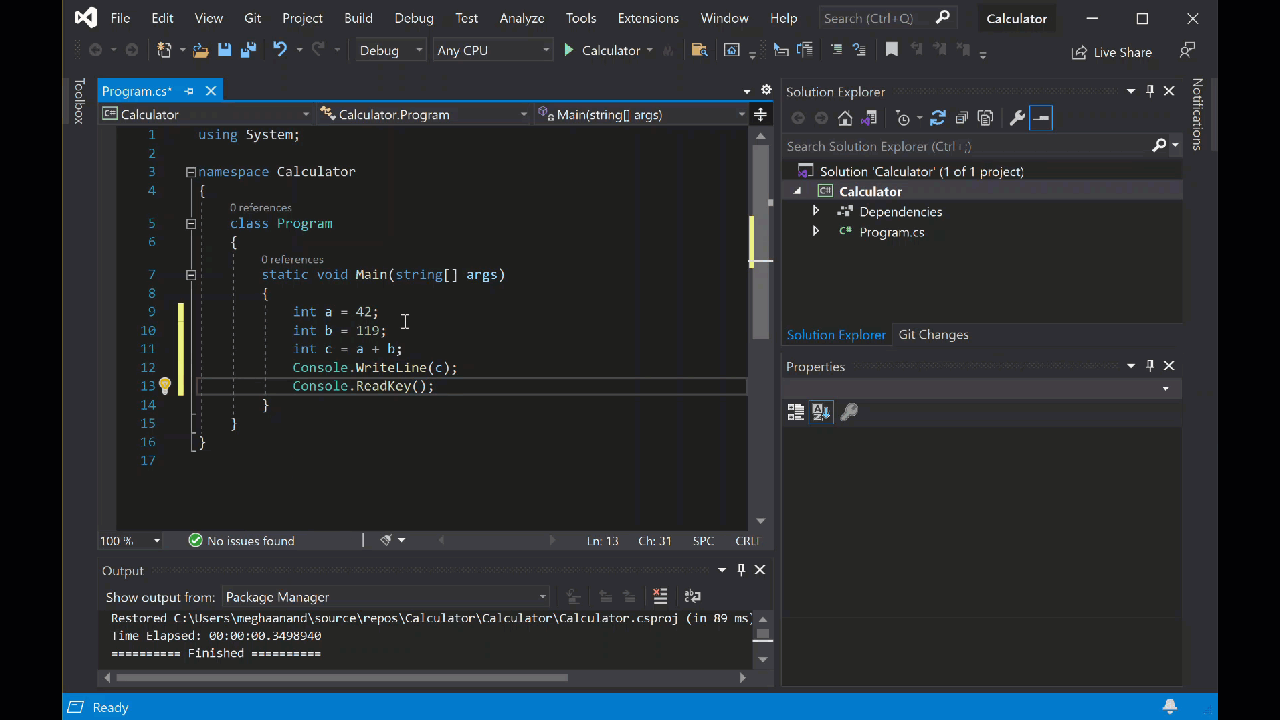
选择 计算器 旁边的绿色 “开始”按钮以生成和运行程序,或按 F5。
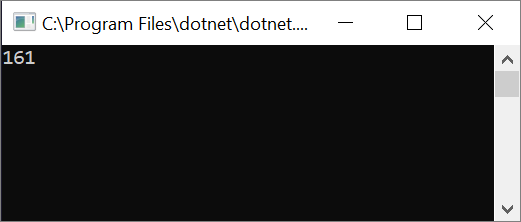
此时会打开一个控制台窗口,其中显示 42 + 119 的总和,161。
(可选) 可以更改运算符来更改结果。 例如,可以将代码行
int c = a + b;中的+运算符更改为减法-、乘法*或除法/。 然后,运行程序时,结果也会更改。关闭控制台窗口。
在 解决方案资源管理器的右窗格中,选择 Program.cs 在代码编辑器中显示文件。
在代码编辑器中,替换显示了
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");的默认“Hello World”代码。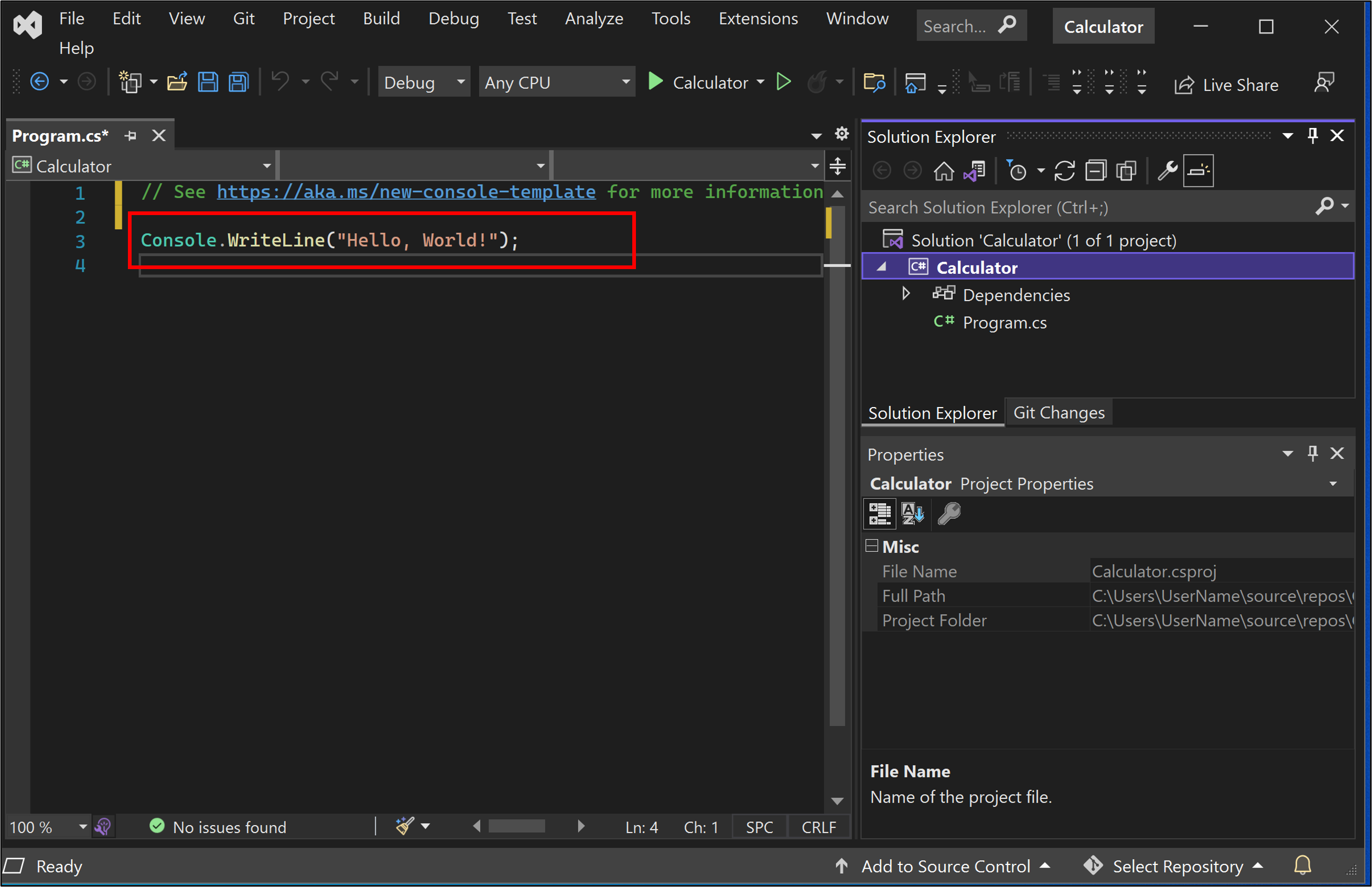
将行替换为以下代码:
int a = 42; int b = 119; int c = a + b; Console.WriteLine(c); Console.ReadKey();如果你输入代码,Visual Studio IntelliSense 功能将提供自动完成该条目的选项。
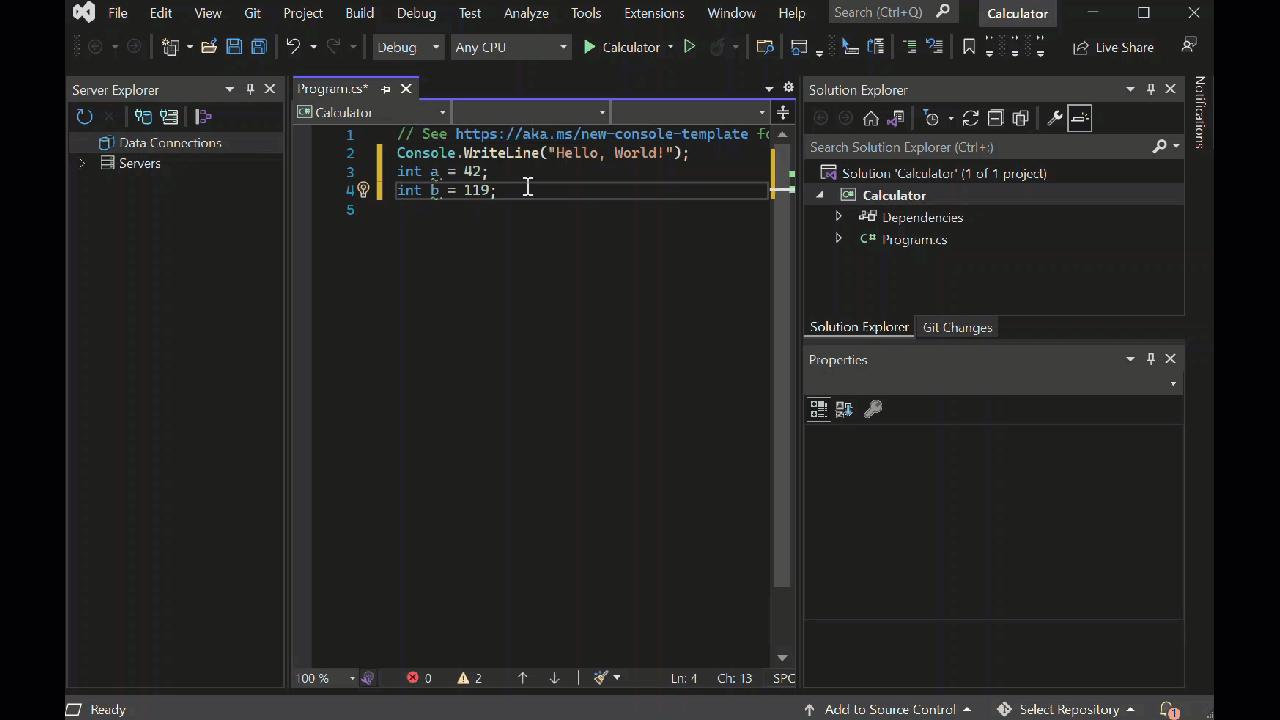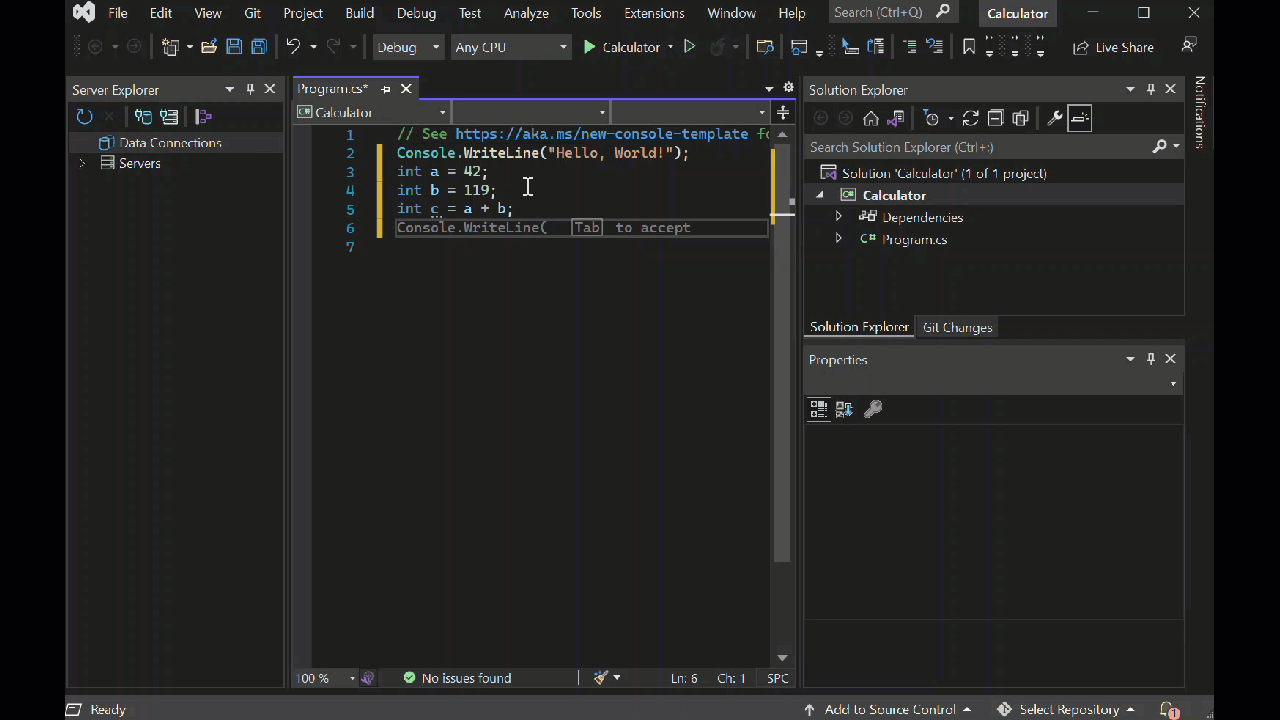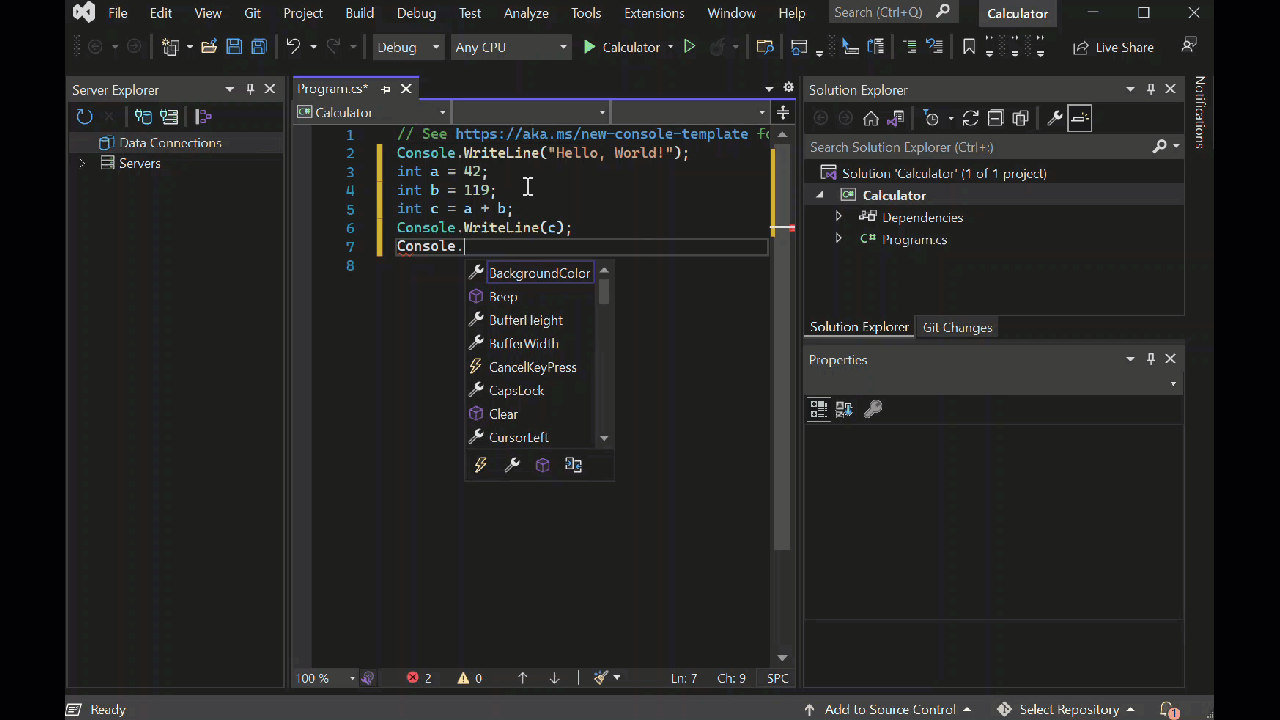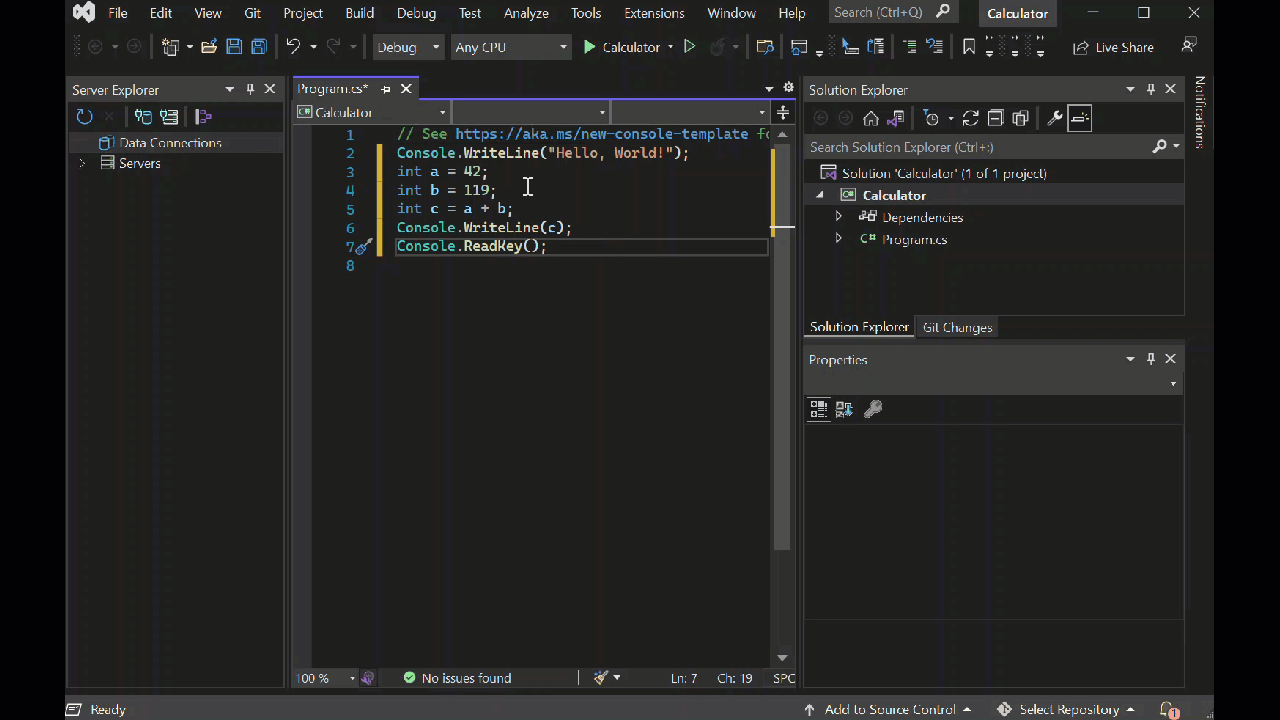
若要生成和运行应用,请按 F5,或选择顶部工具栏中名称 计算器 旁边的绿色箭头。
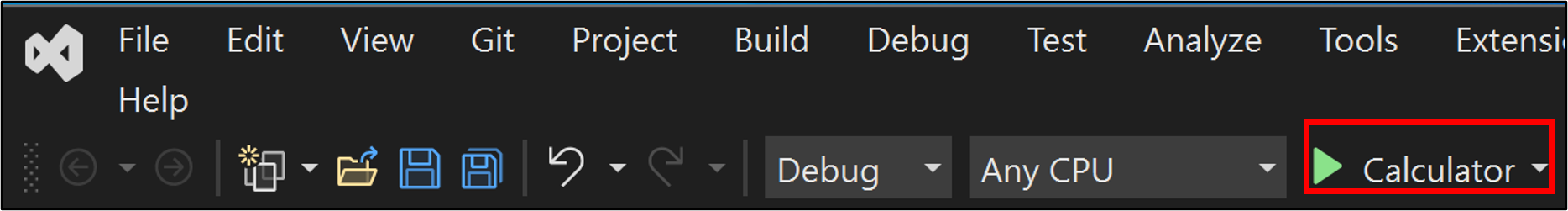
此时会打开一个控制台窗口,显示 42 + 119 的总和,161。
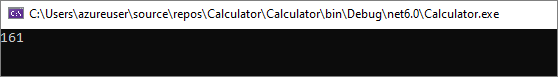
关闭控制台窗口。
(可选) 可以更改运算符来更改结果。 例如,可以将代码行
int c = a + b;中的+运算符更改为减法-、乘法*或除法/。 运行应用时,结果会相应地更改。
添加代码以创建计算器
继续向项目添加更复杂的计算器代码集。
在代码编辑器中,将 Program.cs 中的所有代码替换为以下新代码:
using System; namespace Calculator { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // Declare variables and then initialize to zero. int num1 = 0; int num2 = 0; // Display title as the C# console calculator app. Console.WriteLine("Console Calculator in C#\r"); Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n"); // Ask the user to type the first number. Console.WriteLine("Type a number, and then press Enter"); num1 = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); // Ask the user to type the second number. Console.WriteLine("Type another number, and then press Enter"); num2 = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); // Ask the user to choose an option. Console.WriteLine("Choose an option from the following list:"); Console.WriteLine("\ta - Add"); Console.WriteLine("\ts - Subtract"); Console.WriteLine("\tm - Multiply"); Console.WriteLine("\td - Divide"); Console.Write("Your option? "); // Use a switch statement to do the math. switch (Console.ReadLine()) { case "a": Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} + {num2} = " + (num1 + num2)); break; case "s": Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} - {num2} = " + (num1 - num2)); break; case "m": Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} * {num2} = " + (num1 * num2)); break; case "d": Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} / {num2} = " + (num1 / num2)); break; } // Wait for the user to respond before closing. Console.Write("Press any key to close the Calculator console app..."); Console.ReadKey(); } } }选择 计算器 按钮或按 F5 运行应用。
此时会打开控制台窗口。
在控制台窗口中,按照提示将数字 42 和 119 相加。
你的应用应类似于以下屏幕截图:
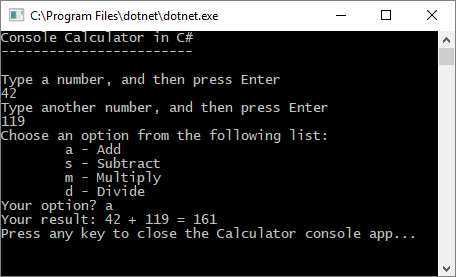
在代码编辑器中,将 Program.cs 中的所有代码替换为以下新代码:
// Declare variables and then initialize to zero. int num1 = 0; int num2 = 0; // Display title as the C# console calculator app. Console.WriteLine("Console Calculator in C#\r"); Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n"); // Ask the user to type the first number. Console.WriteLine("Type a number, and then press Enter"); num1 = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); // Ask the user to type the second number. Console.WriteLine("Type another number, and then press Enter"); num2 = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); // Ask the user to choose an option. Console.WriteLine("Choose an option from the following list:"); Console.WriteLine("\ta - Add"); Console.WriteLine("\ts - Subtract"); Console.WriteLine("\tm - Multiply"); Console.WriteLine("\td - Divide"); Console.Write("Your option? "); // Use a switch statement to do the math. switch (Console.ReadLine()) { case "a": Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} + {num2} = " + (num1 + num2)); break; case "s": Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} - {num2} = " + (num1 - num2)); break; case "m": Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} * {num2} = " + (num1 * num2)); break; case "d": Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} / {num2} = " + (num1 / num2)); break; } // Wait for the user to respond before closing. Console.Write("Press any key to close the Calculator console app..."); Console.ReadKey();选择 计算器 按钮或按 F5 运行应用。
此时会打开控制台窗口。
在控制台窗口中,按照提示将数字 42 和 119 相加。
你的应用应类似于以下屏幕截图:

添加十进制功能
现在,调整代码以添加更多功能。
当前计算器应用仅接受并返回整数。 例如,如果运行应用并将数字 42 除以数字 119,则结果为零,这并不精确。
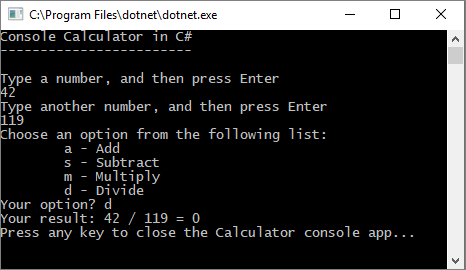
若要通过处理小数来修复代码以提高精度:
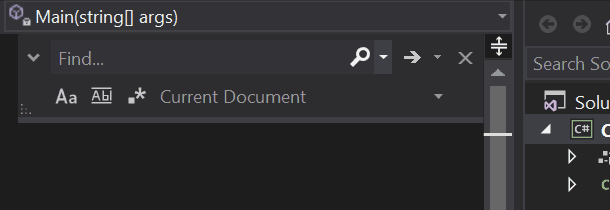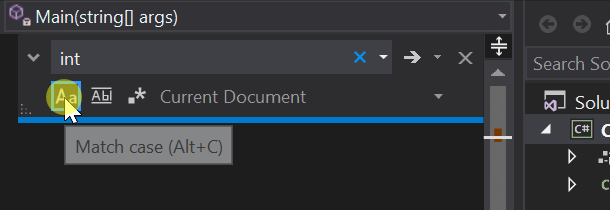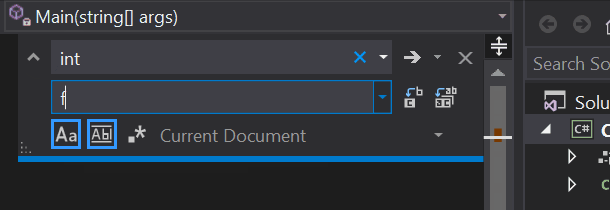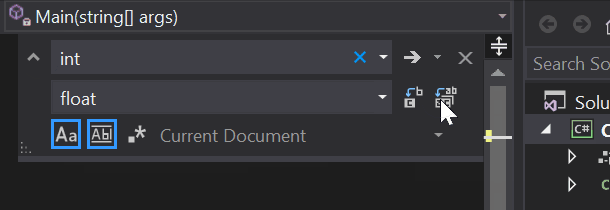
在 Visual Studio 编辑器中的 Program.cs 中,按 Ctrl +H 打开“查找和替换”控件。
在该控件中键入“int”,在“替换”字段中键入“float”。
在该控件中选择“匹配大小写”和“全字匹配”对应的图标,或者按 Alt+C 和 Alt+W。
选择“全部替换”图标或按 Alt+A 运行搜索和替换。
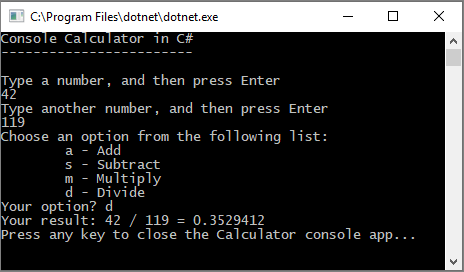
再次运行计算器应用,并将数字 42 除以数字 119。
应用现在返回十进制数而不是零。
现在,应用可以生成十进制结果。 对代码进行更多调整,以便应用也可以计算小数。
使用 查找和替换 控件将
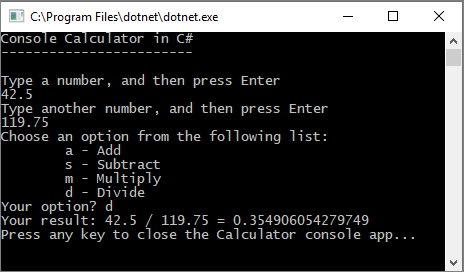
float变量的每个实例更改为double,并将Convert.ToInt32方法的每个实例更改为Convert.ToDouble。运行计算器应用,并将数字 42.5 除以数字 119.75。
应用现在接受十进制值,并返回较长的小数数字作为其结果。
在 修改代码 部分中,可减少结果中的小数位数。
调试应用
你改进了基本计算器应用,但应用尚未处理异常,例如用户输入错误。 例如,如果用户尝试除以零或输入意外字符,应用可能会停止工作、返回错误或返回意外的非数值结果。
让我们演练一些常见的用户输入错误,在调试器中查找它们(如果它们出现在那里)并在代码中修复它们。
提示
有关调试器及其工作原理的详细信息,请参阅 首先查看 Visual Studio 调试器。
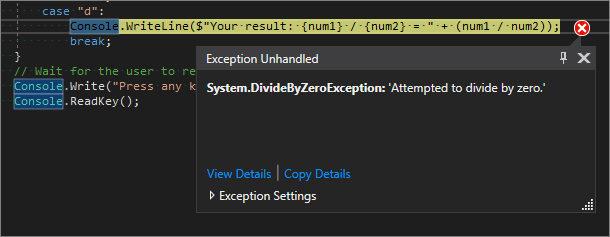
修复“被零除”错误
如果尝试将数字除以零,控制台应用可能会冻结,然后在代码编辑器中显示错误。
注意
有时,应用不会冻结且调试器不会显示“被零除”错误。 相反,应用可能会返回意外的非数值结果,例如无穷大符号。 以下代码修复仍适用。
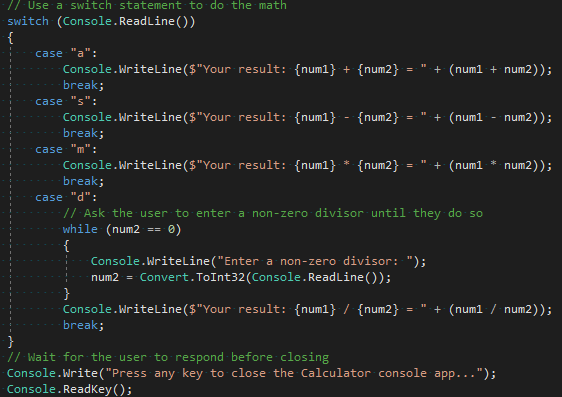
让我们更改代码来处理此错误。 在 Program.cs中,将 case "d": 的代码替换为以下代码:
// Ask the user to enter a non-zero divisor until they do so.
while (num2 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter a non-zero divisor: ");
num2 = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
}
Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} / {num2} = " + (num1 / num2));
break;
替换代码后,包含 switch 语句的部分看起来应与下图类似:
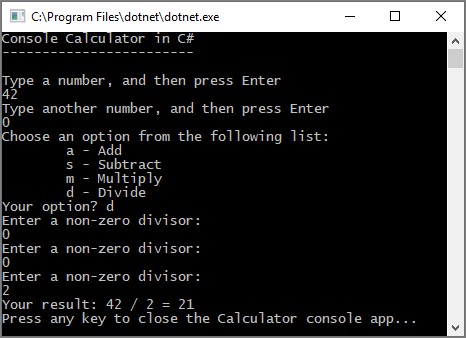
现在,当你将任意数字除以零时,应用会要求另一个数字,并不断询问,直到你提供非零数。
修复“格式”错误
如果在程序需要数字字符时输入了字母字符,程序将会冻结。 Visual Studio 指出代码编辑器中的错误。
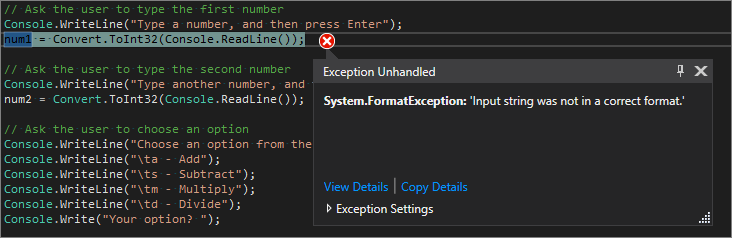
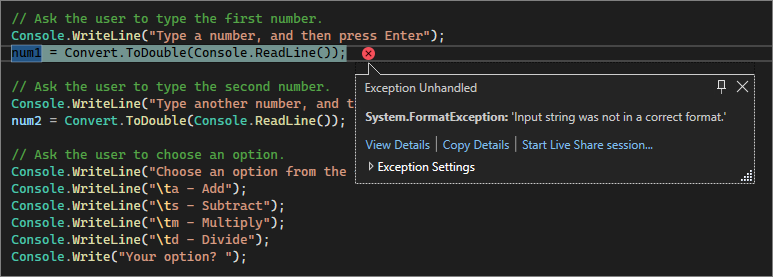
若要防止出现此异常,可以重构之前输入的代码。
修改代码
你可以将应用划分为两个类:Calculator 和 Program,而不是依赖 program 类来处理所有代码。
Calculator 类处理大部分计算工作,Program 类处理用户界面和错误处理工作。
让我们开始吧。
在 Program.cs中,删除所有内容并添加以下新
Calculator类:class Calculator { public static double DoOperation(double num1, double num2, string op) { double result = double.NaN; // Default value is "not-a-number" if an operation, such as division, could result in an error. // Use a switch statement to do the math. switch (op) { case "a": result = num1 + num2; break; case "s": result = num1 - num2; break; case "m": result = num1 * num2; break; case "d": // Ask the user to enter a non-zero divisor. if (num2 != 0) { result = num1 / num2; } break; // Return text for an incorrect option entry. default: break; } return result; } }另请添加新
Program类,如下所示:class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { bool endApp = false; // Display title as the C# console calculator app. Console.WriteLine("Console Calculator in C#\r"); Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n"); while (!endApp) { // Declare variables and set to empty. string numInput1 = ""; string numInput2 = ""; double result = 0; // Ask the user to type the first number. Console.Write("Type a number, and then press Enter: "); numInput1 = Console.ReadLine(); double cleanNum1 = 0; while (!double.TryParse(numInput1, out cleanNum1)) { Console.Write("This is not valid input. Please enter a numeric value: "); numInput1 = Console.ReadLine(); } // Ask the user to type the second number. Console.Write("Type another number, and then press Enter: "); numInput2 = Console.ReadLine(); double cleanNum2 = 0; while (!double.TryParse(numInput2, out cleanNum2)) { Console.Write("This is not valid input. Please enter a numeric value: "); numInput2 = Console.ReadLine(); } // Ask the user to choose an operator. Console.WriteLine("Choose an operator from the following list:"); Console.WriteLine("\ta - Add"); Console.WriteLine("\ts - Subtract"); Console.WriteLine("\tm - Multiply"); Console.WriteLine("\td - Divide"); Console.Write("Your option? "); string op = Console.ReadLine(); try { result = Calculator.DoOperation(cleanNum1, cleanNum2, op); if (double.IsNaN(result)) { Console.WriteLine("This operation will result in a mathematical error.\n"); } else Console.WriteLine("Your result: {0:0.##}\n", result); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine("Oh no! An exception occurred trying to do the math.\n - Details: " + e.Message); } Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n"); // Wait for the user to respond before closing. Console.Write("Press 'n' and Enter to close the app, or press any other key and Enter to continue: "); if (Console.ReadLine() == "n") endApp = true; Console.WriteLine("\n"); // Friendly linespacing. } return; } }选择 计算器 按钮或按 F5 运行应用。
按照提示操作,将数字 42 除以数字 119。 结果应类似于以下屏幕截图:
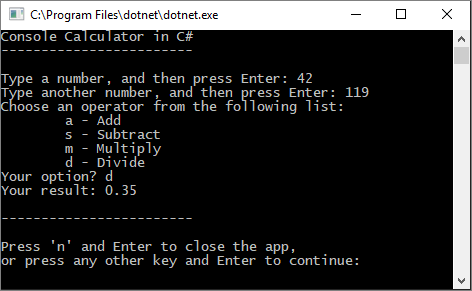
现在可以运行更多计算,直到选择关闭控制台应用。 结果中的小数位数也更少。 如果输入的字符不正确,则会收到相应的错误响应。
修改代码
你可以将应用划分为两个类:Calculator 和 Program,而不是依赖 program 类来处理所有代码。
Calculator 类处理大部分计算工作,Program 类处理用户界面和错误处理工作。
让我们开始吧。
在 Program.cs中,删除所有内容并添加以下新
Calculator类:class Calculator { public static double DoOperation(double num1, double num2, string op) { double result = double.NaN; // Default value is "not-a-number" if an operation, such as division, could result in an error. // Use a switch statement to do the math. switch (op) { case "a": result = num1 + num2; break; case "s": result = num1 - num2; break; case "m": result = num1 * num2; break; case "d": // Ask the user to enter a non-zero divisor. if (num2 != 0) { result = num1 / num2; } break; // Return text for an incorrect option entry. default: break; } return result; } }另请添加新
Program类,如下所示:class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { bool endApp = false; // Display title as the C# console calculator app. Console.WriteLine("Console Calculator in C#\r"); Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n"); while (!endApp) { // Declare variables and set to empty. // Use Nullable types (with ?) to match type of System.Console.ReadLine string? numInput1 = ""; string? numInput2 = ""; double result = 0; // Ask the user to type the first number. Console.Write("Type a number, and then press Enter: "); numInput1 = Console.ReadLine(); double cleanNum1 = 0; while (!double.TryParse(numInput1, out cleanNum1)) { Console.Write("This is not valid input. Please enter a numeric value: "); numInput1 = Console.ReadLine(); } // Ask the user to type the second number. Console.Write("Type another number, and then press Enter: "); numInput2 = Console.ReadLine(); double cleanNum2 = 0; while (!double.TryParse(numInput2, out cleanNum2)) { Console.Write("This is not valid input. Please enter a numeric value: "); numInput2 = Console.ReadLine(); } // Ask the user to choose an operator. Console.WriteLine("Choose an operator from the following list:"); Console.WriteLine("\ta - Add"); Console.WriteLine("\ts - Subtract"); Console.WriteLine("\tm - Multiply"); Console.WriteLine("\td - Divide"); Console.Write("Your option? "); string? op = Console.ReadLine(); // Validate input is not null, and matches the pattern if (op == null || ! Regex.IsMatch(op, "[a|s|m|d]")) { Console.WriteLine("Error: Unrecognized input."); } else { try { result = Calculator.DoOperation(cleanNum1, cleanNum2, op); if (double.IsNaN(result)) { Console.WriteLine("This operation will result in a mathematical error.\n"); } else Console.WriteLine("Your result: {0:0.##}\n", result); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine("Oh no! An exception occurred trying to do the math.\n - Details: " + e.Message); } } Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n"); // Wait for the user to respond before closing. Console.Write("Press 'n' and Enter to close the app, or press any other key and Enter to continue: "); if (Console.ReadLine() == "n") endApp = true; Console.WriteLine("\n"); // Friendly linespacing. } return; } }选择 计算器 按钮或按 F5 运行应用。
按照提示操作,将数字 42 除以数字 119。 结果应类似于以下屏幕截图:
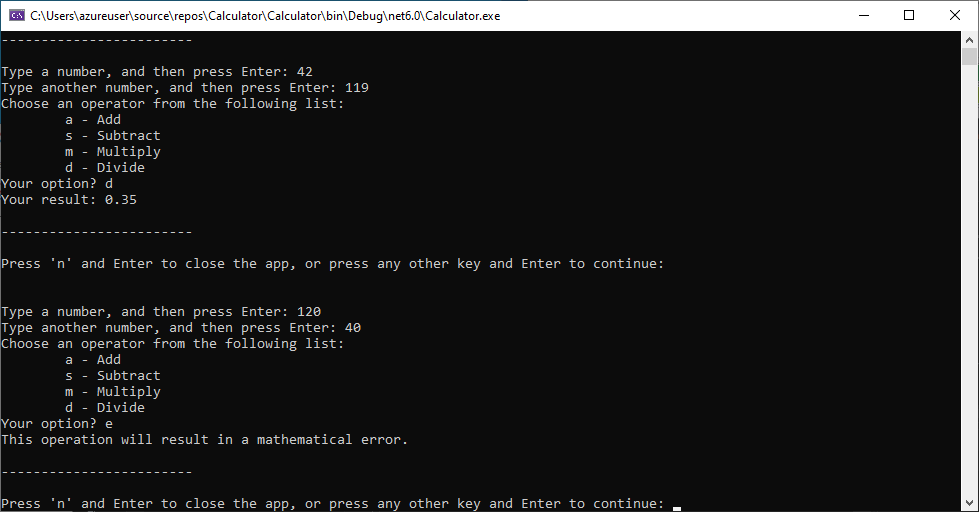
现在可以运行更多计算,直到选择关闭控制台应用。 结果中的小数位数也更少。 如果输入的字符不正确,则会收到相应的错误响应。
关闭应用
如果尚未这样做,请关闭计算器应用。
关闭 Visual Studio 中的 输出 窗格。
在 Visual Studio 中,按 Ctrl +S 保存应用。
添加 Git 源代码管理
有了应用程序后,你可能想要将其添加到 Git 存储库。 借助 Visual Studio,可以使用可直接从 IDE 使用的 Git 工具轻松完成此过程。
提示
Git 是最常用的新式版本控制系统。 无论你是专业开发人员还是学习如何编写代码,Git 都非常有用。 如果你不熟悉 Git,https://git-scm.com/ 网站是一个很好的起点。 你可以找到备忘单、热门在线书籍和 Git 基本信息视频。
若要将代码与 Git 相关联,请先创建代码所在的新 Git 存储库:
在 Visual Studio 右下角的状态栏中,选择 添加到源代码管理,然后选择 Git。
在 “创建 Git 存储库”对话框中,登录到 GitHub:
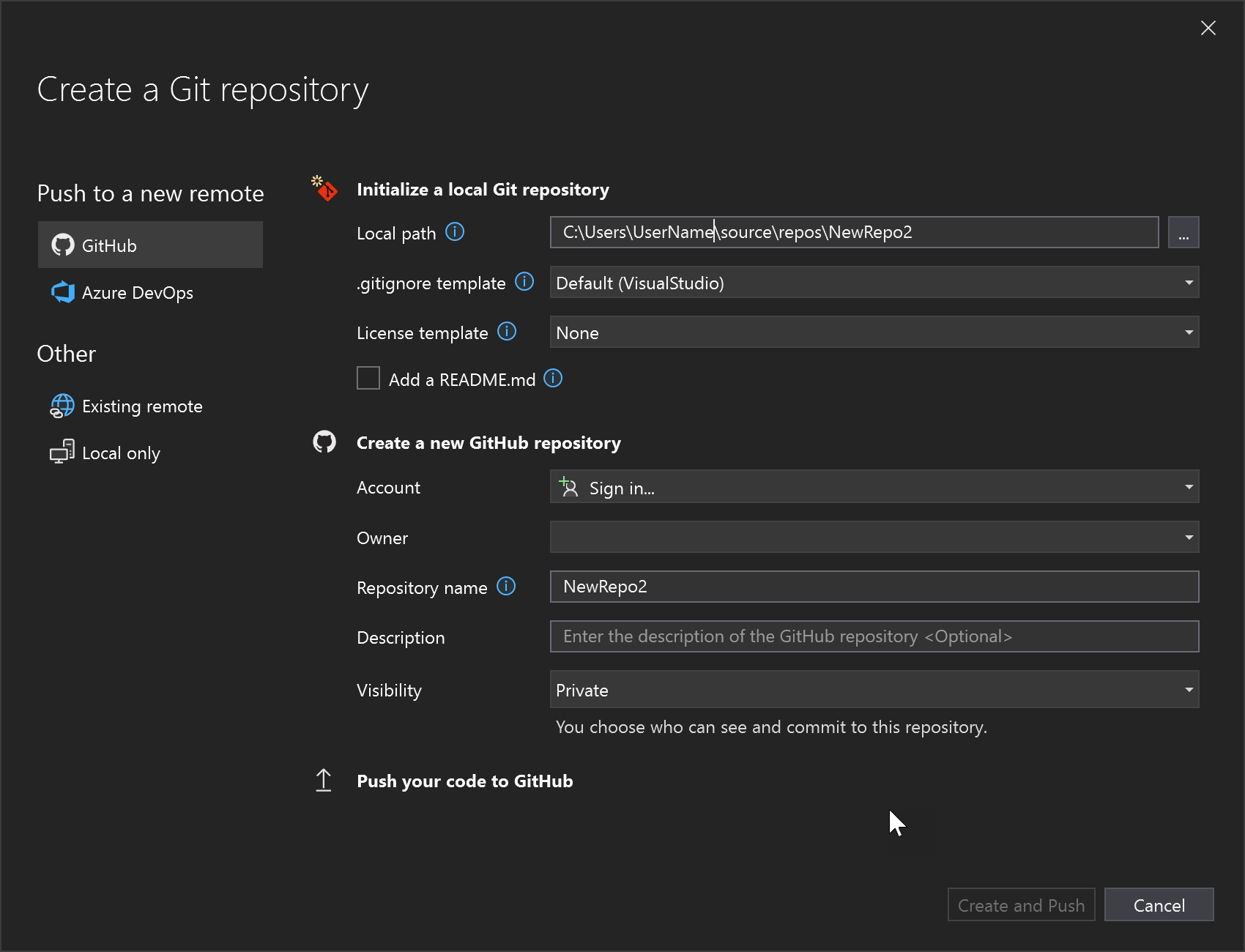
存储库名称根据文件夹位置自动填充。 默认情况下,新存储库是专用的,这意味着你是唯一可以访问它的人。
提示
无论存储库是公共的还是专用的,最好有一个安全存储在 GitHub 上的代码的远程备份。 即使你未与团队合作,远程存储库也会让你从任何计算机获得代码。
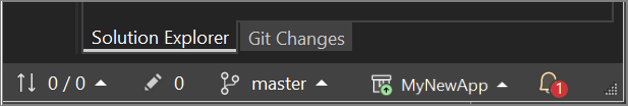
选择“创建并推送”。 创建存储库后,可在状态栏中看到状态详细信息:
在 Visual Studio 中使用 Git 操作
下面是 Visual Studio 状态栏中提供的 Git 操作的简要摘要:
向上/向下箭头显示当前分支中的传出/传入提交数。 可以使用此图标来拉取任何传入提交或推送任何传出提交。
若要查看特定提交,请选择向上/向下箭头,然后选择“查看传出/传入”。
铅笔显示代码的未提交更改数。 可以选择此图标,在 Git 更改 窗口中查看这些更改。
Git 菜单为文件上的存储库操作提供了工具。 在 Visual Studio中使用 git fetch、pull、push 和 sync 进行版本控制。
有关如何将 Git 与应用配合使用的详细信息,请参阅 Visual Studio 中的关于 Git。
审阅:代码已完成
在本教程中,你对计算器应用进行了许多更改。 应用现在更有效地处理计算资源,并处理大多数用户输入错误。
下面是完整的代码,全部放在一个位置:
class Calculator
{
public static double DoOperation(double num1, double num2, string op)
{
double result = double.NaN; // Default value is "not-a-number" which we use if an operation, such as division, could result in an error.
// Use a switch statement to do the math.
switch (op)
{
case "a":
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case "s":
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case "m":
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case "d":
// Ask the user to enter a non-zero divisor.
if (num2 != 0)
{
result = num1 / num2;
}
break;
// Return text for an incorrect option entry.
default:
break;
}
return result;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool endApp = false;
// Display title as the C# console calculator app.
Console.WriteLine("Console Calculator in C#\r");
Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n");
while (!endApp)
{
// Declare variables and set to empty.
string numInput1 = "";
string numInput2 = "";
double result = 0;
// Ask the user to type the first number.
Console.Write("Type a number, and then press Enter: ");
numInput1 = Console.ReadLine();
double cleanNum1 = 0;
while (!double.TryParse(numInput1, out cleanNum1))
{
Console.Write("This is not valid input. Please enter a numeric value: ");
numInput1 = Console.ReadLine();
}
// Ask the user to type the second number.
Console.Write("Type another number, and then press Enter: ");
numInput2 = Console.ReadLine();
double cleanNum2 = 0;
while (!double.TryParse(numInput2, out cleanNum2))
{
Console.Write("This is not valid input. Please enter a numeric value: ");
numInput2 = Console.ReadLine();
}
// Ask the user to choose an operator.
Console.WriteLine("Choose an operator from the following list:");
Console.WriteLine("\ta - Add");
Console.WriteLine("\ts - Subtract");
Console.WriteLine("\tm - Multiply");
Console.WriteLine("\td - Divide");
Console.Write("Your option? ");
string op = Console.ReadLine();
try
{
result = Calculator.DoOperation(cleanNum1, cleanNum2, op);
if (double.IsNaN(result))
{
Console.WriteLine("This operation will result in a mathematical error.\n");
}
else Console.WriteLine("Your result: {0:0.##}\n", result);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Oh no! An exception occurred trying to do the math.\n - Details: " + e.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n");
// Wait for the user to respond before closing.
Console.Write("Press 'n' and Enter to close the app, or press any other key and Enter to continue: ");
if (Console.ReadLine() == "n") endApp = true;
Console.WriteLine("\n"); // Friendly linespacing.
}
return;
}
}
class Calculator
{
public static double DoOperation(double num1, double num2, string op)
{
double result = double.NaN; // Default value is "not-a-number" which we use if an operation, such as division, could result in an error.
// Use a switch statement to do the math.
switch (op)
{
case "a":
result = num1 + num2;
break;
case "s":
result = num1 - num2;
break;
case "m":
result = num1 * num2;
break;
case "d":
// Ask the user to enter a non-zero divisor.
if (num2 != 0)
{
result = num1 / num2;
}
break;
// Return text for an incorrect option entry.
default:
break;
}
return result;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
bool endApp = false;
// Display title as the C# console calculator app.
Console.WriteLine("Console Calculator in C#\r");
Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n");
while (!endApp)
{
// Declare variables and set to empty.
// Use Nullable types (with ?) to match type of System.Console.ReadLine
string? numInput1 = "";
string? numInput2 = "";
double result = 0;
// Ask the user to type the first number.
Console.Write("Type a number, and then press Enter: ");
numInput1 = Console.ReadLine();
double cleanNum1 = 0;
while (!double.TryParse(numInput1, out cleanNum1))
{
Console.Write("This is not valid input. Please enter a numeric value: ");
numInput1 = Console.ReadLine();
}
// Ask the user to type the second number.
Console.Write("Type another number, and then press Enter: ");
numInput2 = Console.ReadLine();
double cleanNum2 = 0;
while (!double.TryParse(numInput2, out cleanNum2))
{
Console.Write("This is not valid input. Please enter a numeric value: ");
numInput2 = Console.ReadLine();
}
// Ask the user to choose an operator.
Console.WriteLine("Choose an operator from the following list:");
Console.WriteLine("\ta - Add");
Console.WriteLine("\ts - Subtract");
Console.WriteLine("\tm - Multiply");
Console.WriteLine("\td - Divide");
Console.Write("Your option? ");
string? op = Console.ReadLine();
// Validate input is not null, and matches the pattern
if (op == null || ! Regex.IsMatch(op, "[a|s|m|d]"))
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: Unrecognized input.");
}
else
{
try
{
result = Calculator.DoOperation(cleanNum1, cleanNum2, op);
if (double.IsNaN(result))
{
Console.WriteLine("This operation will result in a mathematical error.\n");
}
else Console.WriteLine("Your result: {0:0.##}\n", result);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Oh no! An exception occurred trying to do the math.\n - Details: " + e.Message);
}
}
Console.WriteLine("------------------------\n");
// Wait for the user to respond before closing.
Console.Write("Press 'n' and Enter to close the app, or press any other key and Enter to continue: ");
if (Console.ReadLine() == "n") endApp = true;
Console.WriteLine("\n"); // Friendly linespacing.
}
return;
}
}
下一步
继续学习本教程的第二部分: