练习 - 识别 CPU 使用率较高的计算机
在这里,你将编写 KQL 查询以从 Perf 表中检索和转换数据,以了解哪些计算机已达到或接近其总计算容量以及哪些计算机未得到充分利用。
1. 设定目标
若要解决性能问题、缓解潜在问题并确定提高操作效率的机会,需要分析 IT 环境中虚拟机的中央处理器 (CPU) 使用情况。
若要确定与 CPU 相关的性能问题和提高效率的机会,需要以下信息:
- 每个活动计算机的 CPU 使用率趋势。
- 处于高峰和清静时间的计算机的 CPU 使用率。
2. 评估日志
Windows 和 Linux 代理将在受监视计算机上运行的硬件组件、操作系统和应用程序的性能计数器发送到 Azure Monitor 中的 Perf 表。
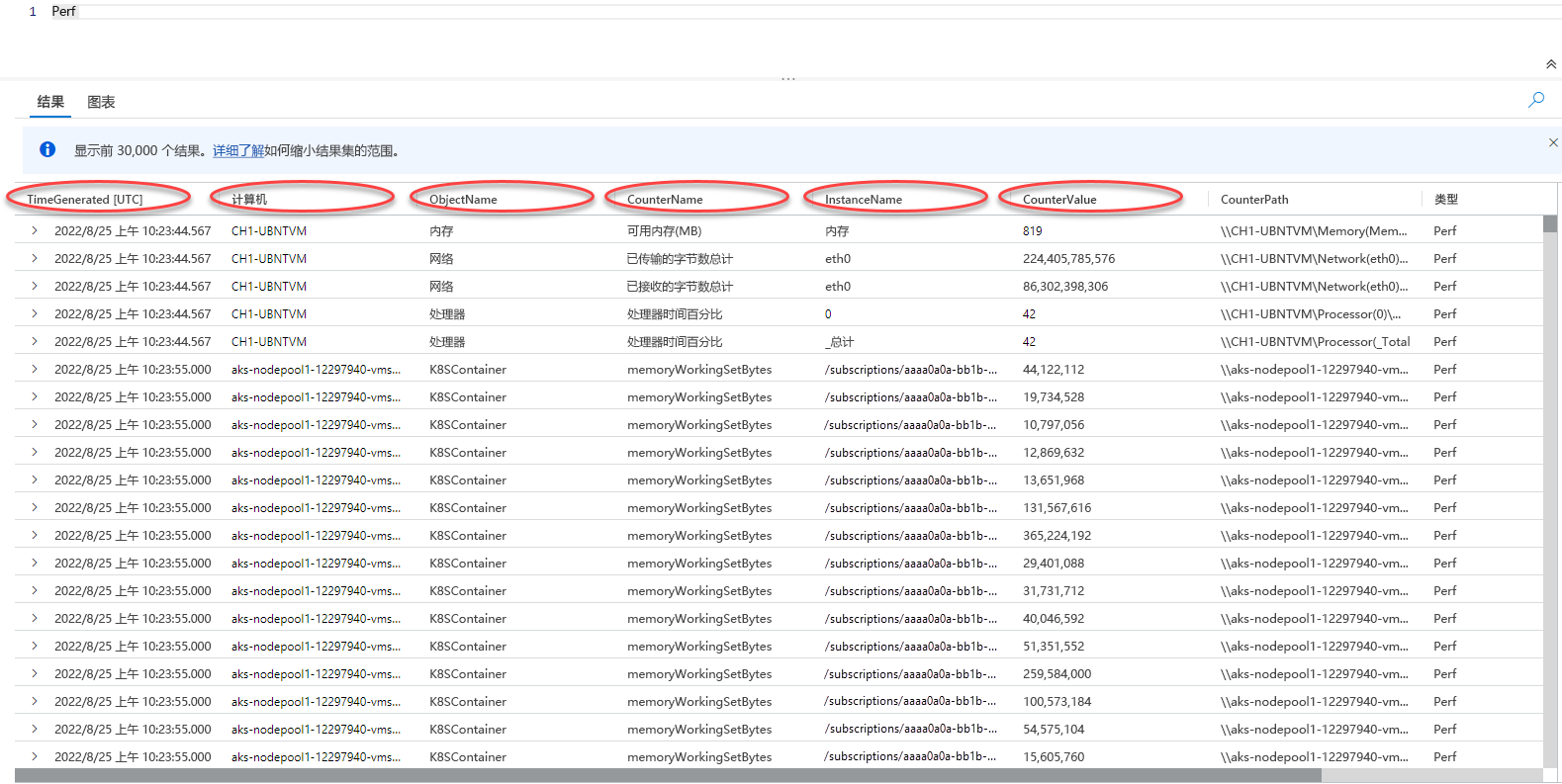
让我们对 Perf 表运行一个简单的查询,以检索过去 24 小时的日志,并了解表架构和表保存的数据:
Perf // The table you’re querying
| where TimeGenerated > ago(1d) // Filters for entries generated in the past day
你可以看到 TimeGenerated、Computer、ObjectName、CounterName、InstanceName 和 CounterValue 列包含与我们的分析相关的数据。
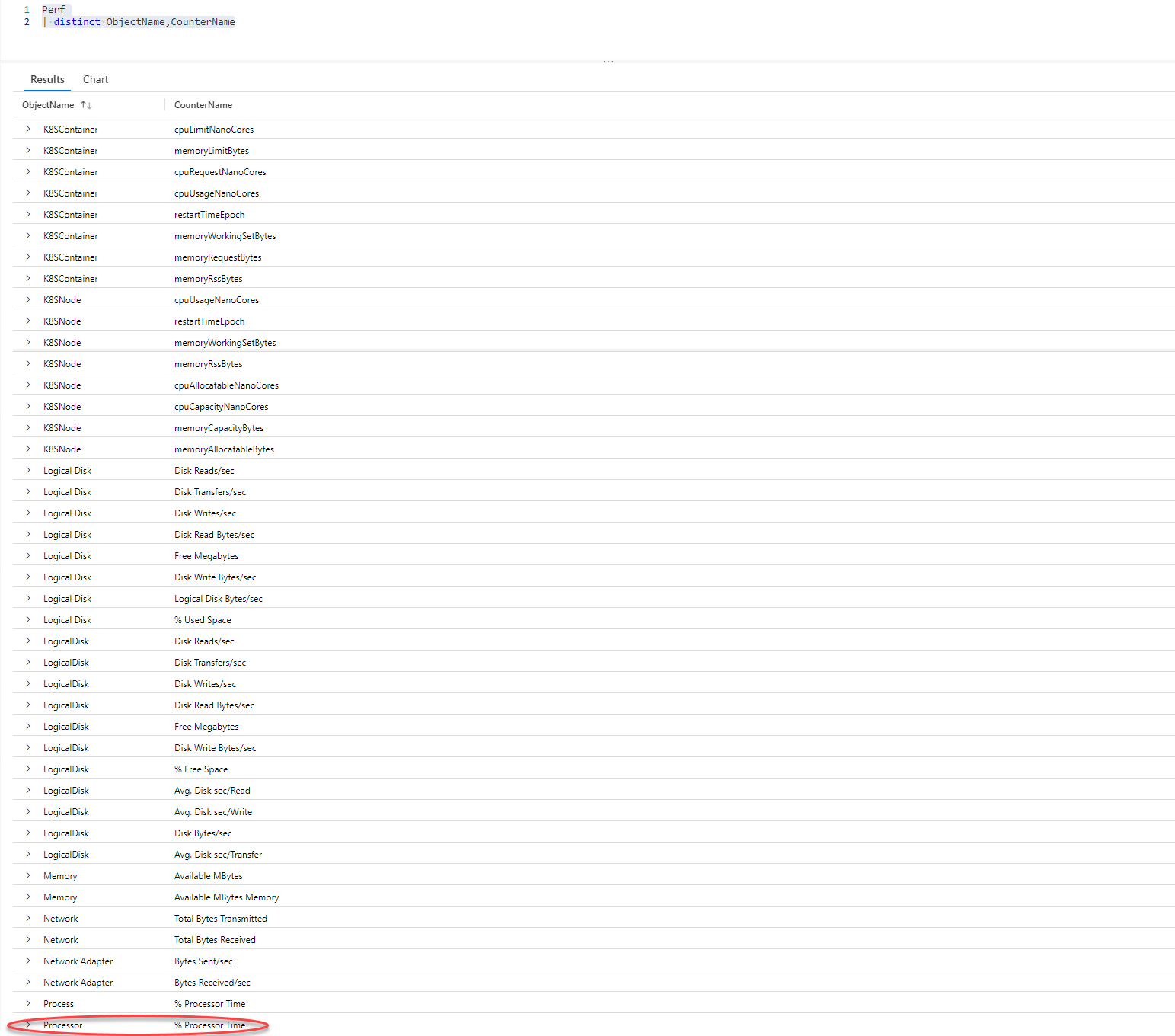
ObjectName 列列出了 Azure Monitor 从受监视计算机收集数据的所有对象的名称。 CounterName 列包含 Azure Monitor 收集的各种性能计数器的名称。 这两个列都保留了大量值,其中许多值多次出现。 为了清楚地查看这些列中的不同值并确定哪些计数器与当前分析相关,让我们运行以下查询:
Perf // The table you’re querying
| distinct ObjectName,CounterName // Lists distinct combinations of ObjectName and CounterName values
此屏幕截图显示了过去 24 小时内 CounterName 列中 ObjectName 和 CounterName 值的不同组合:
通过 % Processor Time 计数器可了解处理器或中央处理器 (CPU) 的利用率。 这就是你需要的信息!
让我们来评估如何使用此数据,以及哪些 KQL 操作可以帮助提取和转换数据:
| 列 | 说明 | 分析目标 | 相关的 KQL 操作 |
|---|---|---|---|
TimeGenerated |
指示虚拟机何时生成每个日志。 | 定义分析的时间范围。 | where TimeGenerated > ago(1d) 有关详细信息,请参阅 ago()、where 运算符和数值运算符。 |
Computer |
从中收集事件的计算机。 | 将 CPU 使用率与特定计算机相关联。 | summarize... by Computer 有关详细信息,请参阅 summarize 运算符。 |
ObjectName |
保留为其在表中保留性能数据的所有对象的名称。 | 监视处理器的性能。 | where ObjectName == "Processor" 有关详细信息,请参阅 == (equals) 运算符。 |
CounterName |
保留表中所有性能计数器的名称。 | 监视 % Processor Time 性能计数器。 |
where CounterName == "% Processor Time" 有关详细信息,请参阅 where 运算符和 == (equals) 运算符。 |
InstanceName |
列出受监视对象的受监视实例。 | 监视所有处理器核心。 | where InstanceName == "_Total" 有关详细信息,请参阅 where 运算符和 == (equals) 运算符。 |
CounterValue |
为计数器收集的测量值。 | 检索 % Processor Time 性能计数器的性能测量值。 |
summarize min(CounterValue), avg(CounterValue), max(CounterValue), percentiles(CounterValue, 90,99) 有关详细信息,请参阅 summarize 运算符,以及 min()、max()、avg() 和 percentiles() 聚合函数。 |
3. 编写查询
编写一个查询,总结过去一天所有计算机的平均、最小和最大 CPU 使用率。
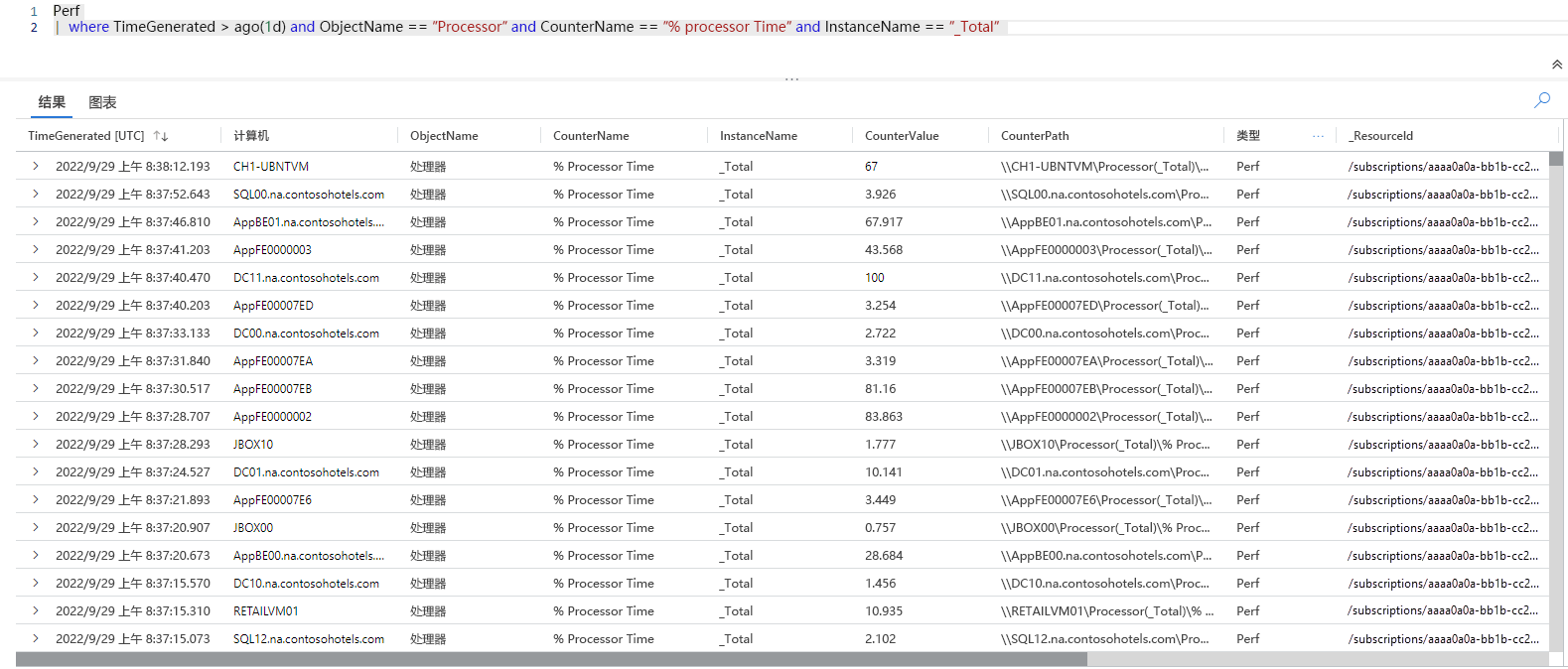
检索过去一天生成的所有日志,这些日志报告了
% Processor Time性能计数器:Perf // The table you’re querying | where TimeGenerated > ago(1d) and ObjectName == "Processor" and CounterName == "% Processor Time" and InstanceName == "_Total" // Filters for entries generated in the past day related to total processor time measurements该查询检索过去一天中与总处理器时间度量相关的所有日志。
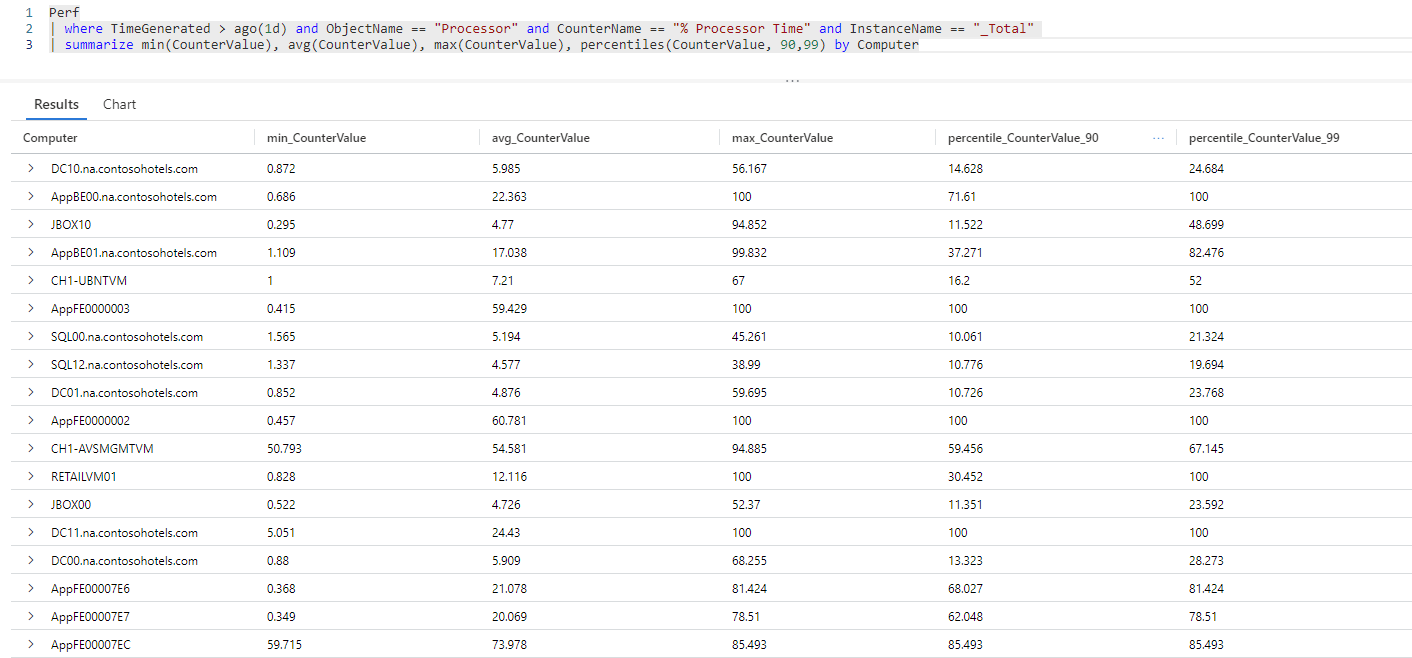
找出最小、最大和平均计数器值,并计算每台计算机的第 90 和第 99 个百分位数计数器值:
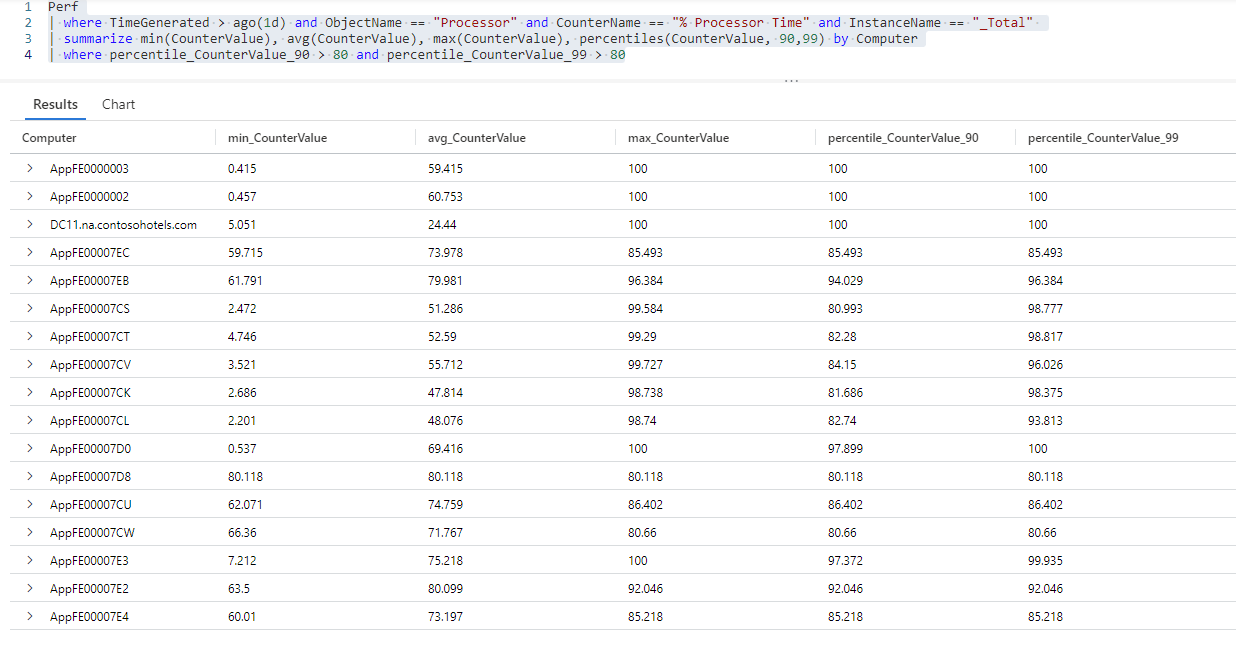
Perf // The table you’re querying | where TimeGenerated > ago(1d) and ObjectName == "Processor" and CounterName == "% Processor Time" and InstanceName == "_Total" // Filters for entries generated in the past day related to total processor time measurements | summarize min(CounterValue), avg(CounterValue), max(CounterValue), percentiles(CounterValue, 90,99) by Computer // Presents the minimum, maximum, average, 90th and 99th percentile counter values for each computer此查询的结果集显示 Log Analytics 工作区中有数据的每台计算机的最小值、最大值、平均值、第 90 和第 99 个百分位
% Processor Time计数器值。在第 90 和第 99 个百分位范围内筛选
% Processor Time计数器值高于 80 的条目的查询结果:Perf // The table you’re querying | where TimeGenerated > ago(1d) and ObjectName == "Processor" and CounterName == "% Processor Time" and InstanceName == "_Total" // Filters for entries generated in the past day related to total processor time measurements | summarize min(CounterValue), avg(CounterValue), max(CounterValue), percentiles(CounterValue, 90,99) by Computer // Presents the minimum, maximum, average, 90th and 99th percentile counter values for each computer | where percentile_CounterValue_90 > 80 and percentile_CounterValue_99 > 80 // Filters previous query results for instances where the 90th and 99th percentile counters are higher than 80此查询的结果集包含前 10% 和 15%
% Processor Time值超过 80 的所有计算机。
挑战:将 Heartbeat 表中的操作系统信息添加到查询结果中
通过使用 join 运算符将来自不同表的信息与查询结果相关联,通常可以更好地了解查询结果。 有关详细信息,请参阅 join 运算符。
能否使用 join 运算符添加有关每台计算机上运行的操作系统的信息,这些信息可在 Heartbeat 表中找到,就像我们在第一个练习中看到的那样?
解决方案:
从
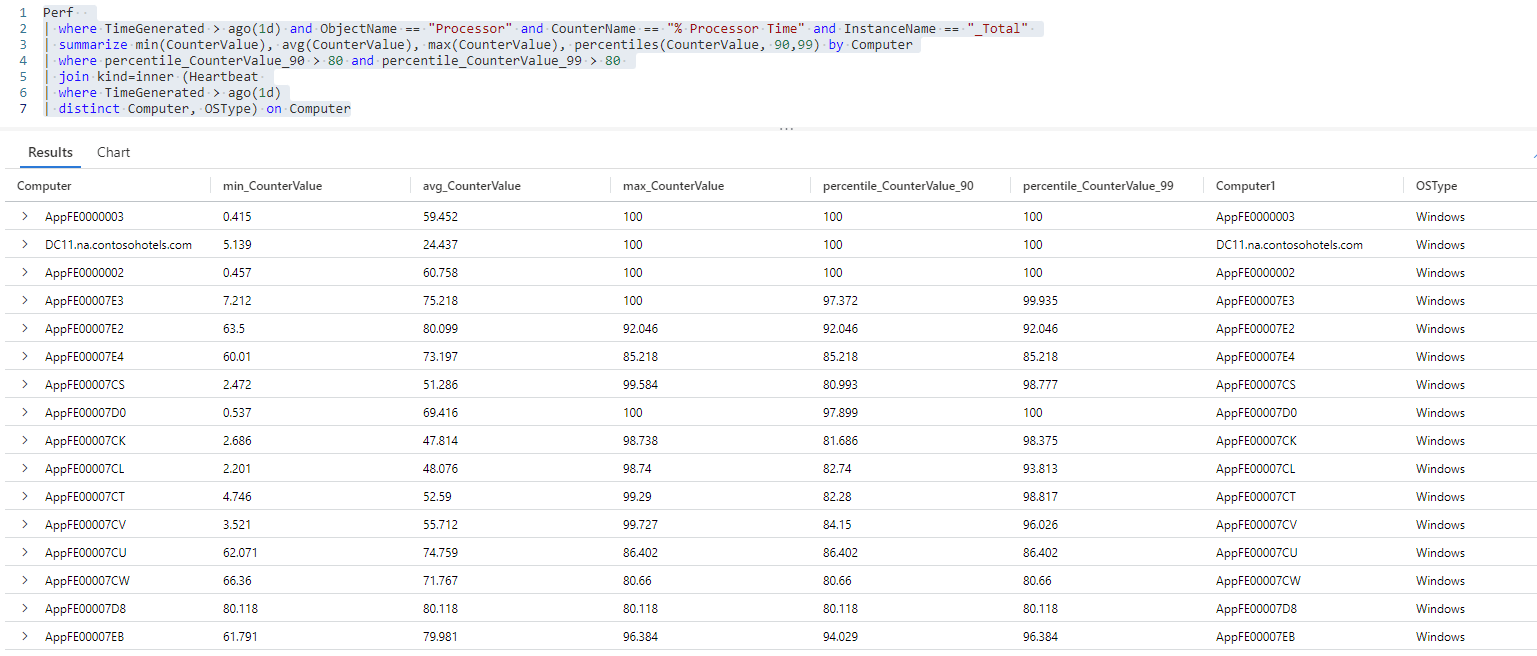
Heartbeat表中添加有关查询结果中每台计算机上运行的操作系统的信息:Perf // The table you’re querying | where TimeGenerated > ago(1d) and ObjectName == "Processor" and CounterName == "% Processor Time" and InstanceName == "_Total" // Filters for entries generated in the past day related to total processor time measurements | summarize min(CounterValue), avg(CounterValue), max(CounterValue), percentiles(CounterValue, 90,99) by Computer // Presents the minimum, maximum, average, 90th and 99th percentile counter values for each computer | where percentile_CounterValue_90 > 80 and percentile_CounterValue_99 > 80 // Filters previous query results for instances where the 90th and 99th percentile counters are higher than 50 | join kind=inner (Heartbeat // Introduces data from the "Heartbeat" table to the previous query results | where TimeGenerated > ago(1d) // Time range for the data added from the "Heartbeat" table | distinct Computer, OSType) on Computer // Adds distinct combinations of computer and operating system此查询迭代会将
Heartbeat表中的Computer和OSType列添加到先前的查询结果中。Computer列现在会在查询结果中出现两次 - 一次来自对Perf表的查询,一次来自对Heartbeat表的查询。Heartbeat表中的Computer列已重命名为Computer1,但两个表包含相同的数据。 同时拥有这两个列可以将两个表的结果关联起来,但是现在可以筛选掉重复的列。从查询结果中删除
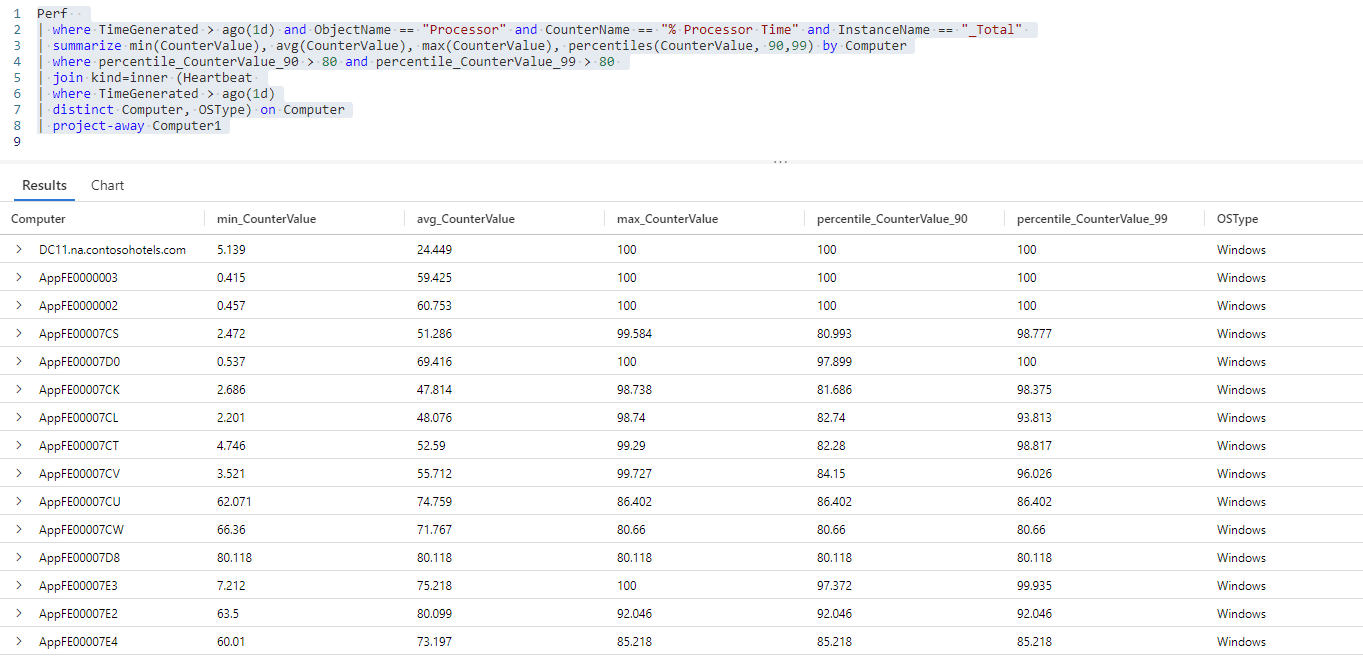
Computer1列:Perf // The table you’re querying | where TimeGenerated > ago(1d) and ObjectName == "Processor" and CounterName == "% Processor Time" and InstanceName == "_Total" // Filters for entries generated in the past day related to total processor time measurements | summarize min(CounterValue), avg(CounterValue), max(CounterValue), percentiles(CounterValue, 90,99) by Computer // Presents the minimum, maximum, average, 90th and 99th percentile counter values for each computer | where percentile_CounterValue_90 > 80 and percentile_CounterValue_99 > 80 // Filters previous query results for instances where the 90th and 99th percentile counters are higher than 50 | join kind=inner (Heartbeat // Introduces data from the "Heartbeat" table to the previous query results | where TimeGenerated > ago(1d) // Time range for the data added from the "Heartbeat" table | distinct Computer, OSType) on Computer // Adds distinct combinations of computer and operating system | project-away Computer1 // Removes the "Computer1" column from the query results此查询的结果集列出了所有达到其全部 CPU 容量的计算机以及每台计算机上运行的操作系统,这将有助于进一步分析。