练习 - 使用 Numpy 执行线性回归
散点图便于直观呈现数据,而现在假设你想要在散点图上叠加趋势线,显示数据随时间变化而呈现的趋势。 计算此类趋势线的一种方法是线性回归。 在本练习中,你将使用 NumPy 执行线性回归,使用 Matplotlib 根据数据绘制趋势线。
将光标放在笔记本底部的空白单元格中。 将单元格类型更改为 Markdown 并输入文本“执行线性回归”。
添加 Code 单元格并将以下代码粘贴到其中。 花点儿时间阅读注释(以 # 符号开头的数行文字),了解代码的作用。
# Creates a linear regression from the data points m,b = np.polyfit(yearsBase, meanBase, 1) # This is a simple y = mx + b line function def f(x): return m*x + b # This generates the same scatter plot as before, but adds a line plot using the function above plt.scatter(yearsBase, meanBase) plt.plot(yearsBase, f(yearsBase)) plt.title('scatter plot of mean temp difference vs year') plt.xlabel('years', fontsize=12) plt.ylabel('mean temp difference', fontsize=12) plt.show() # Prints text to the screen showing the computed values of m and b print(' y = {0} * x + {1}'.format(m, b)) plt.show()现在运行单元格以显示带回归线的散点图。
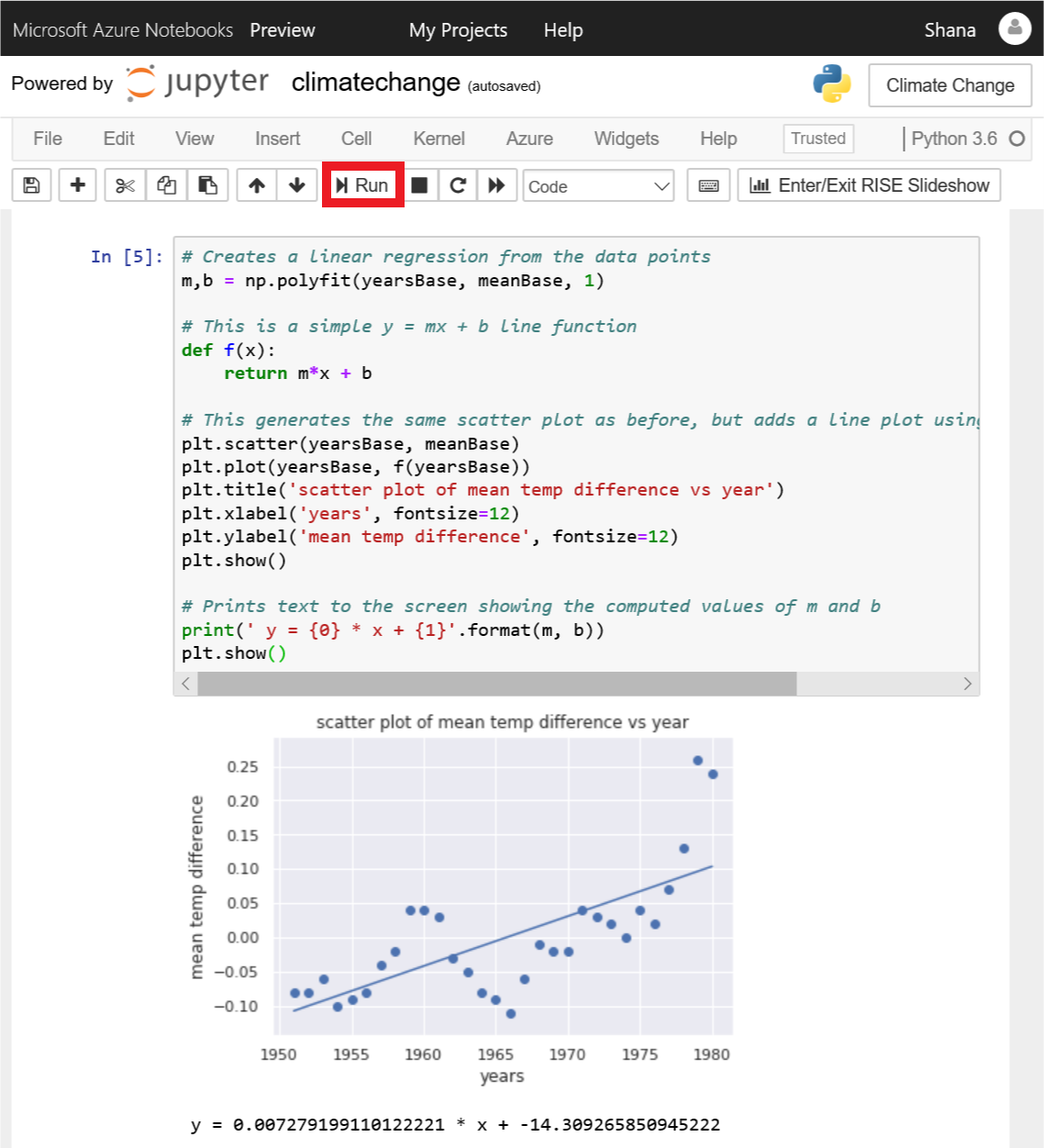
带回归线的散点图
从回归线可以看到 30 年平均温度和 5 年平均温度之间随着时间不断增加。 生成回归线所需的大部分计算工作都是由 NumPy 的 polyfit 函数完成的,该函数计算等式 y = mx + b 中 m 和 b 的值。