SkiaSharp 中的路径和文本
探索路径和文本的交集
在现代图形系统中,文本字体是字符轮廓的集合,通常由二次贝塞尔曲线定义。 因此,许多现代图形系统包含将文本字符转换为图形路径的工具。
你已经看到,你可以用笔触勾勒出文本字符的轮廓,并填充它们。 这样就可以显示具有特定笔触宽度甚至路径效果的字符轮廓,如路径效果文章中所述。 但也可以将字符字符串转换为 SKPath 对象。 这意味着,文本轮廓可用于剪裁,使用按路径和区域进行剪裁中所述的技术。
除了使用路径效果来勾勒字符轮廓之外,还可以创建基于从字符字符串派生的路径的路径效果,甚至可以合并这两种效果:
在上一篇关于路径效果的文章中,你了解了 SKPaint 的 GetFillPath 方法如何获取笔触路径的轮廓。 还可以将此方法与派生自字符轮廓的路径一起使用。
最后,本文演示了路径和文本的另一个交集:SKCanvas 的 DrawTextOnPath 方法让你可以显示文本字符串,以便文本基线遵循曲线路径。
文本到路径转换
SKPaint 的 GetTextPath 方法可将字符字符串转换为 SKPath 对象:
public SKPath GetTextPath (String text, Single x, Single y)
x 和 y 参数指示文本左侧基线的起点。 它们在这里扮演的角色与在 SKCanvas 的 DrawText 方法中一样。 在路径中,文本左侧的基线将具有坐标 (x, y)。
如果只想填充或勾勒结果路径,则 GetTextPath 方法就过于复杂了。 使用普通的 DrawText 方法就可以执行此操作。 GetTextPath 方法对涉及路径的其他任务更有用。
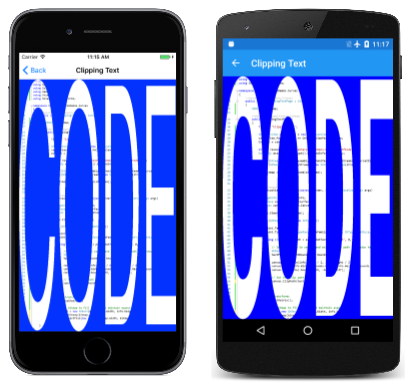
其中一项任务是剪裁。 “剪裁文本”页会基于单词“CODE”的字符轮廓创建一个剪裁路径。此路径会拉伸到页面的大小,以剪裁包含“剪裁文本”源代码的图像的位图:
ClippingTextPage 类构造函数会加载作为嵌入资源存储在解决方案的 Media 文件夹中的位图:
public class ClippingTextPage : ContentPage
{
SKBitmap bitmap;
public ClippingTextPage()
{
Title = "Clipping Text";
SKCanvasView canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
string resourceID = "SkiaSharpFormsDemos.Media.PageOfCode.png";
Assembly assembly = GetType().GetTypeInfo().Assembly;
using (Stream stream = assembly.GetManifestResourceStream(resourceID))
{
bitmap = SKBitmap.Decode(stream);
}
}
...
}
PaintSurface 处理程序首先创建适合文本的 SKPaint 对象。 Typeface 属性和 TextSize 被设置,尽管对于此特定应用程序,TextSize 属性纯粹是任意的。 另请注意,没有 Style 设置。
不需要 TextSize 和 Style 属性设置,因为此 SKPaint 对象仅用于使用文本字符串“CODE”的 GetTextPath 调用。 然后,处理程序会测量生成的 SKPath 对象,并应用三个转换,将其居中并缩放到页面的大小。 然后,可以将路径设置为剪切路径:
public class ClippingTextPage : ContentPage
{
...
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear(SKColors.Blue);
using (SKPaint paint = new SKPaint())
{
paint.Typeface = SKTypeface.FromFamilyName(null, SKTypefaceStyle.Bold);
paint.TextSize = 10;
using (SKPath textPath = paint.GetTextPath("CODE", 0, 0))
{
// Set transform to center and enlarge clip path to window height
SKRect bounds;
textPath.GetTightBounds(out bounds);
canvas.Translate(info.Width / 2, info.Height / 2);
canvas.Scale(info.Width / bounds.Width, info.Height / bounds.Height);
canvas.Translate(-bounds.MidX, -bounds.MidY);
// Set the clip path
canvas.ClipPath(textPath);
}
}
// Reset transforms
canvas.ResetMatrix();
// Display bitmap to fill window but maintain aspect ratio
SKRect rect = new SKRect(0, 0, info.Width, info.Height);
canvas.DrawBitmap(bitmap,
rect.AspectFill(new SKSize(bitmap.Width, bitmap.Height)));
}
}
设置了剪切路径后,可以显示位图,它将被剪切为字符轮廓。 请注意,使用 SKRect 的 AspectFill 方法来计算矩形以填充页面,同时保留纵横比。
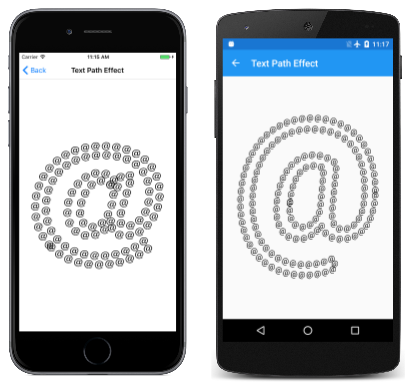
“文本路径效果”页将单个与字符转换为一个路径以创建 1D 路径效果。 然后,具有此路径效果的画图对象用于勾勒该相同字符的较大版本的轮廓:
TextPathEffectPath 类中的大部分工作发生在字段和构造函数中。 定义为字段的两个 SKPaint 对象用于两个不同的目的:第一个(名为 textPathPaint)用于将 TextSize 为 50 的与字符转换为 1D 路径效果的路径。 第二个 (textPaint) 用于显示具有该路径效果的更大版本的与字符。 因此,第二个画图对象的 Style 设置为 Stroke,但 StrokeWidth 属性未设置,因为在使用 1D 路径效果时不需要该属性:
public class TextPathEffectPage : ContentPage
{
const string character = "@";
const float littleSize = 50;
SKPathEffect pathEffect;
SKPaint textPathPaint = new SKPaint
{
TextSize = littleSize
};
SKPaint textPaint = new SKPaint
{
Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke,
Color = SKColors.Black
};
public TextPathEffectPage()
{
Title = "Text Path Effect";
SKCanvasView canvasView = new SKCanvasView();
canvasView.PaintSurface += OnCanvasViewPaintSurface;
Content = canvasView;
// Get the bounds of textPathPaint
SKRect textPathPaintBounds = new SKRect();
textPathPaint.MeasureText(character, ref textPathPaintBounds);
// Create textPath centered around (0, 0)
SKPath textPath = textPathPaint.GetTextPath(character,
-textPathPaintBounds.MidX,
-textPathPaintBounds.MidY);
// Create the path effect
pathEffect = SKPathEffect.Create1DPath(textPath, littleSize, 0,
SKPath1DPathEffectStyle.Translate);
}
...
}
构造函数首先使用 textPathPaint 对象来测量 TextSize 为 50 的与字符。 然后,该矩形的中心坐标的负数将传递给 GetTextPath 方法以将文本转换为路径。 生成的路径在字符的中心具有 (0, 0) 点,非常适合 1D 路径效果。
你可能会认为在构造函数末尾创建的 SKPathEffect 对象可以设置为 textPaint 的 PathEffect 属性,而不是另存为字段。 但事实证明,这样效果不好,因为它扭曲了 PaintSurface 处理程序中 MeasureText 调用的结果:
public class TextPathEffectPage : ContentPage
{
...
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
// Set textPaint TextSize based on screen size
textPaint.TextSize = Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height);
// Do not measure the text with PathEffect set!
SKRect textBounds = new SKRect();
textPaint.MeasureText(character, ref textBounds);
// Coordinates to center text on screen
float xText = info.Width / 2 - textBounds.MidX;
float yText = info.Height / 2 - textBounds.MidY;
// Set the PathEffect property and display text
textPaint.PathEffect = pathEffect;
canvas.DrawText(character, xText, yText, textPaint);
}
}
MeasureText 调用用于在页面中使字符居中。 为避免问题,PathEffect 属性在测量文本后,显示文本前设置为画图对象。
字符轮廓概览
通常,SKPaint 的 GetFillPath 方法通过应用画图属性将一个路径转换为另一个路径,最主要的是笔触宽度和路径效果。 在没有路径效果的情况下使用时,GetFillPath 可有效地创建一条能勾勒出另一条路径的路径。 这在“路径效果”一文中的“点击以勾勒路径”页中进行了演示。
还可以对从 GetTextPath 返回的路径调用 GetFillPath,但起初可能不太确定它会是什么样子。
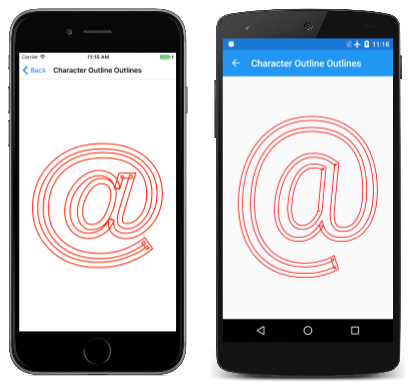
“字符轮廓概览”页演示了该技术。 所有相关代码都位于 CharacterOutlineOutlinesPage 类的 PaintSurface 处理程序中。
构造函数首先基于页面的大小创建一个名为 textPaint 的 SKPaint 对象,带有 TextSize 属性。 通过 GetTextPath 方法将它转换为路径。 GetTextPath 的坐标参数有效地将该路径在屏幕上居中:
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
using (SKPaint textPaint = new SKPaint())
{
// Set Style for the character outlines
textPaint.Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke;
// Set TextSize based on screen size
textPaint.TextSize = Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height);
// Measure the text
SKRect textBounds = new SKRect();
textPaint.MeasureText("@", ref textBounds);
// Coordinates to center text on screen
float xText = info.Width / 2 - textBounds.MidX;
float yText = info.Height / 2 - textBounds.MidY;
// Get the path for the character outlines
using (SKPath textPath = textPaint.GetTextPath("@", xText, yText))
{
// Create a new path for the outlines of the path
using (SKPath outlinePath = new SKPath())
{
// Convert the path to the outlines of the stroked path
textPaint.StrokeWidth = 25;
textPaint.GetFillPath(textPath, outlinePath);
// Stroke that new path
using (SKPaint outlinePaint = new SKPaint())
{
outlinePaint.Style = SKPaintStyle.Stroke;
outlinePaint.StrokeWidth = 5;
outlinePaint.Color = SKColors.Red;
canvas.DrawPath(outlinePath, outlinePaint);
}
}
}
}
}
然后,PaintSurface 处理程序会创建名为 outlinePath 的新路径。 这将成为对 GetFillPath 的调用中的目标路径。 StrokeWidth 属性 25 会使得 outlinePath 勾勒 25 像素宽的路径,描边文本字符。 然后,此路径以红色显示,笔触宽度为 5:
仔细查看,你将看到路径轮廓形成尖角处有重叠。 这些是此过程的正常工件。
沿路径的文本
文本通常显示在水平基线上。 文本可以旋转以垂直或对角线运行,但基线仍然是直线。
但是,有时你会希望文本沿曲线运行。 这是 SKCanvas 的 DrawTextOnPath 方法的目的:
public Void DrawTextOnPath (String text, SKPath path, Single hOffset, Single vOffset, SKPaint paint)
在第一个参数中指定的文本沿指定为第二个参数的路径运行。 可以使用 hOffset 参数从路径的开头处以偏移量开始文本。 通常,路径构成文本的基线:文本升线在路径的一侧,文本降线在另一侧。 但是,可以使用 vOffset 参数从路径偏移文本基线。
此方法没有提供有关如何设置 SKPaint 的 TextSize 属性的指导,此方法会使文本大小完美地适配从路径的开头运行到末尾。 有时,你可以自行弄清楚该文本大小。 其他时候则需要使用路径测量函数,这在下一篇文章路径信息和枚举中有介绍。
圆形文本程序可将文本环绕一个圆圈。 可以轻松确定圆的周长,因此可以轻松调整文本的大小以适应。 CircularTextPage 类的 PaintSurface 处理程序会根据页面的大小计算圆的半径。 该圆会变成 circularPath:
public class CircularTextPage : ContentPage
{
const string text = "xt in a circle that shapes the te";
...
void OnCanvasViewPaintSurface(object sender, SKPaintSurfaceEventArgs args)
{
SKImageInfo info = args.Info;
SKSurface surface = args.Surface;
SKCanvas canvas = surface.Canvas;
canvas.Clear();
using (SKPath circularPath = new SKPath())
{
float radius = 0.35f * Math.Min(info.Width, info.Height);
circularPath.AddCircle(info.Width / 2, info.Height / 2, radius);
using (SKPaint textPaint = new SKPaint())
{
textPaint.TextSize = 100;
float textWidth = textPaint.MeasureText(text);
textPaint.TextSize *= 2 * 3.14f * radius / textWidth;
canvas.DrawTextOnPath(text, circularPath, 0, 0, textPaint);
}
}
}
}
然后会调整 textPaint 的 TextSize 属性,使文本宽度与圆的周长匹配:
文本本身的选择也有点像圆圈:“circle”一词既是句子的主语,也是一个介词短语的宾语。