Xamarin.Forms 命令接口
在“模型-视图-视图模型”(即 MVVM)体系结构中,数据绑定是在 ViewModel(通常是派生自 INotifyPropertyChanged 的类)中的属性和视图(通常为 XAML 文件)中的属性之间定义的。 有时,应用程序的需求超越了属性绑定层面,它要求用户启动影响 ViewModel 中某些内容的命令。 这些命令通常通过点击按钮或手指敲击触发信号,往往是以下两个事件的处理程序中的代码隐藏文件中处理它们:Button 的 Clicked 事件或 TapGestureRecognizer 的 Tapped 事件。
命令接口提供了另一种实现命令的方法,这种方法更适合 MVVM 体系结构。 ViewModel 本身可以包含命令,这些命令是针对视图中的特定活动(例如单击 Button)而执行的方法。 在这些命令和 Button 之间定义了数据绑定。
为允许使用 Button 和 ViewModel 之间的绑定数据,Button 定义两个属性:
System.Windows.Input.ICommand类型的CommandObject类型的CommandParameter
若要使用命令接口,请定义将 Button 的 Command 属性作为目标的数据绑定,其中源是 ICommand 类型的 ViewModel 中的属性。 ViewModel 包含与单击按钮时执行的 ICommand 属性关联的代码。 如果多个按钮都绑定到 ViewModel 中的同一个 ICommand 属性,可以将 CommandParameter 设置为任意数据以区分这些按钮。
下列类也定义了 Command 和 CommandParameter 属性:
MenuItem以及派生自MenuItem的ToolbarItemTextCell以及派生自TextCell的ImageCellTapGestureRecognizer
SearchBar 定义一个 ICommand 类型的 SearchCommand 属性和一个 SearchCommandParameter 属性。 ListView 的 RefreshCommand 属性也是 ICommand 类型。
可以在 ViewModel 中以不依赖视图中的特定用户界面对象的方式处理上述所有命令。
ICommand 接口
System.Windows.Input.ICommand 接口不属于 Xamarin.Forms。 而是在 System.Windows.Input 命名空间中定义的,由两个方法和一个事件组成:
public interface ICommand
{
public void Execute (Object parameter);
public bool CanExecute (Object parameter);
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged;
}
若要使用命令接口,ViewModel 需包含 ICommand 类型的属性:
public ICommand MyCommand { private set; get; }
ViewModel 还必须引用实现 ICommand 接口的类。 此类稍后再述。 在视图中,Button 的 Command 属性绑定到该属性:
<Button Text="Execute command"
Command="{Binding MyCommand}" />
用户按下 Button 时,Button 调用绑定到其 Command 属性的 ICommand 对象中的 Execute 方法。 这是命令接口中最简单的一部分。
CanExecute 方法更复杂。 首次在 Button 的 Command 属性上定义绑定时,以及数据绑定以某种方式更改时,Button 调用 ICommand 对象中的 CanExecute 方法。 如果 CanExecute 返回 false,则 Button 将禁用其自身。 这表示特定命令当前不可用或无效。
Button 还在 ICommand 的 CanExecuteChanged 事件上附加处理程序。 该事件是从 ViewModel 内触发的。 触发该事件时,Button 再次调用 CanExecute。 如果 CanExecute 返回 true,Button 启用其自身;如果 CanExecute 返回 false,则禁用其自身。
重要
如果使用命令接口,请勿使用 Button 的 IsEnabled 属性。
命令类
ViewModel 定义 ICommand 类型的属性时,它还必须包含或引用实现 ICommand 接口的类。 该类必须包含或引用 Execute 和 CanExecute 方法,并且每当 CanExecute 方法返回不同的值时均触发 CanExecuteChanged 事件。
可以自己编写这样的类,也可以使用其他人编写的类。 ICommand 是 Microsoft Windows 的一部分,已在 Windows MVVM 应用程序中使用多年。 使用实现 ICommand 的 Windows 类,可以在 Windows 应用程序和 Xamarin.Forms 应用程序之间共享 ViewModel。
如果在 Windows 和 Xamarin.Forms 之间共享 ViewModel 不成问题,则可以使用 Xamarin.Forms 中包含的 Command 或 Command<T> 类来实现 ICommand 接口。 通过这些类,可以在类构造函数中指定 Execute 和 CanExecute 方法的主体。 使用 CommandParameter 属性区分绑定同一 ICommand 属性的多个视图时,请使用 Command<T>不需要区分时,使用更简单的 Command 类。
基本命令
示例程序中的“人员录入”页演示了在 ViewModel 中实现的一些简单命令。
PersonViewModel 定义了分别名为 Name、Age 和 Skills 的三个属性,这三个属性定义一个人。 此类不包含任何 ICommand 属性
public class PersonViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
string name;
double age;
string skills;
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
public string Name
{
set { SetProperty(ref name, value); }
get { return name; }
}
public double Age
{
set { SetProperty(ref age, value); }
get { return age; }
}
public string Skills
{
set { SetProperty(ref skills, value); }
get { return skills; }
}
public override string ToString()
{
return Name + ", age " + Age;
}
bool SetProperty<T>(ref T storage, T value, [CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
if (Object.Equals(storage, value))
return false;
storage = value;
OnPropertyChanged(propertyName);
return true;
}
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
下面所示的 PersonCollectionViewModel 创建 PersonViewModel 类型的新对象,并允许用户填写数据。 为此,类定义两个属性:bool 类型的 IsEditing 和 PersonViewModel 类型的 PersonEdit。 此外,该类还定义了 ICommand 类型的三个属性和 IList<PersonViewModel> 类型的一个名为 Persons 的属性:
public class PersonCollectionViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
PersonViewModel personEdit;
bool isEditing;
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
···
public bool IsEditing
{
private set { SetProperty(ref isEditing, value); }
get { return isEditing; }
}
public PersonViewModel PersonEdit
{
set { SetProperty(ref personEdit, value); }
get { return personEdit; }
}
public ICommand NewCommand { private set; get; }
public ICommand SubmitCommand { private set; get; }
public ICommand CancelCommand { private set; get; }
public IList<PersonViewModel> Persons { get; } = new ObservableCollection<PersonViewModel>();
bool SetProperty<T>(ref T storage, T value, [CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
if (Object.Equals(storage, value))
return false;
storage = value;
OnPropertyChanged(propertyName);
return true;
}
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
这个简短的列表不包括类的构造函数,该构造函数是定义 ICommand 类型的三个属性的位置,稍后再作演示。 请注意,对 ICommand 类型的三个属性以及 Persons 属性的更改不会触发 PropertyChanged 事件。 这些属性都是在类首次创建时设置的,此后不会更改。
在检查 PersonCollectionViewModel 类的构造函数之前,看一看“人员录入”程序的 XAML 文件。 此文件包含 Grid,其 BindingContext 属性设置为 PersonCollectionViewModel。 Grid 包含:一个 Button(其文本为“New”,Command 属性绑定到 ViewModel 中的 NewCommand 属性)、一个输入窗体(其属性绑定到 IsEditing 属性以及 PersonViewModel 的属性)以及另外两个绑定到 ViewModel 的 SubmitCommand 和 CancelCommand 属性的按钮。 最后 ListView 显示已录入的人员的集合:
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:DataBindingDemos"
x:Class="DataBindingDemos.PersonEntryPage"
Title="Person Entry">
<Grid Margin="10">
<Grid.BindingContext>
<local:PersonCollectionViewModel />
</Grid.BindingContext>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<!-- New Button -->
<Button Text="New"
Grid.Row="0"
Command="{Binding NewCommand}"
HorizontalOptions="Start" />
<!-- Entry Form -->
<Grid Grid.Row="1"
IsEnabled="{Binding IsEditing}">
<Grid BindingContext="{Binding PersonEdit}">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" />
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Label Text="Name: " Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" />
<Entry Text="{Binding Name}"
Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="1" />
<Label Text="Age: " Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" />
<StackLayout Orientation="Horizontal"
Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1">
<Stepper Value="{Binding Age}"
Maximum="100" />
<Label Text="{Binding Age, StringFormat='{0} years old'}"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
</StackLayout>
<Label Text="Skills: " Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0" />
<Entry Text="{Binding Skills}"
Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1" />
</Grid>
</Grid>
<!-- Submit and Cancel Buttons -->
<Grid Grid.Row="2">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Button Text="Submit"
Grid.Column="0"
Command="{Binding SubmitCommand}"
VerticalOptions="CenterAndExpand" />
<Button Text="Cancel"
Grid.Column="1"
Command="{Binding CancelCommand}"
VerticalOptions="CenterAndExpand" />
</Grid>
<!-- List of Persons -->
<ListView Grid.Row="3"
ItemsSource="{Binding Persons}" />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
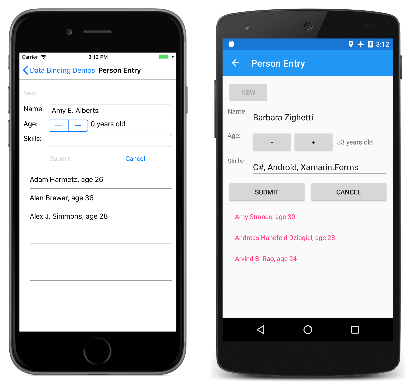
它的工作原理如下:用户首先按“新建”按钮。 这将启用输入窗体,但禁用“新建”按钮。 然后用户输入姓名、年龄和技能。 在编辑过程中,用户随时都可以按下“取消”按钮重新开始。 只有在输入了姓名和有效年龄后,才启用“提交”按钮。 按“提交”按钮可将人员转移到 ListView 显示的集合中。 按“取消”或“提交”按钮后,会清除输入窗体中的内容并再次启用“新建”按钮。
左侧的 iOS 屏幕显示输入有效年龄之前的布局。 Android 屏幕显示设置年龄之后启用的“提交”按钮:
该程序没有任何功能可供编辑现有条目,并且在离开该页面时不会保存这些条目。
“新建”、“提交”和“取消”按钮的所有逻辑都通过定义 NewCommand、SubmitCommand 和 CancelCommand 属性在 PersonCollectionViewModel 中处理。 PersonCollectionViewModel 的构造函数将这三个属性设置为 Command 类型的对象。
通过 Command 类的构造函数,你可以传递与 Execute 和 CanExecute 方法对应的 Action 和 Func<bool> 类型的参数。 在 Command 构造函数中将这些操作和函数定义为 lambda 函数是最简单的。 下面是 NewCommand 属性的 Command 对象的定义:
public class PersonCollectionViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public PersonCollectionViewModel()
{
NewCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
PersonEdit = new PersonViewModel();
PersonEdit.PropertyChanged += OnPersonEditPropertyChanged;
IsEditing = true;
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: () =>
{
return !IsEditing;
});
···
}
void OnPersonEditPropertyChanged(object sender, PropertyChangedEventArgs args)
{
(SubmitCommand as Command).ChangeCanExecute();
}
void RefreshCanExecutes()
{
(NewCommand as Command).ChangeCanExecute();
(SubmitCommand as Command).ChangeCanExecute();
(CancelCommand as Command).ChangeCanExecute();
}
···
}
用户单击“新建”按钮时,执行传递给 Command 构造函数的 execute 函数。 这将创建一个新的 PersonViewModel 对象,为该对象的 PropertyChanged 事件设置一个处理程序,将 IsEditing 设置为 true,并调用在构造函数之后定义的 RefreshCanExecutes 方法。
除了实现 ICommand 接口外,Command 类还定义了名为 ChangeCanExecute 的方法。 每当发生任何可能更改 CanExecute 方法返回值的事情时,ViewModel 都应该为 ICommand 属性调用 ChangeCanExecute。 调用 ChangeCanExecute 将导致 Command 类触发 CanExecuteChanged 方法。 Button 已为该事件附加了一个处理程序,并通过再次调用 CanExecute 进行响应,然后根据该方法的返回值启用自身。
当 NewCommand 的 execute 方法调用 RefreshCanExecutes 时,NewCommand 属性得到对 ChangeCanExecute 的调用,Button 调用 canExecute 方法,该方法现在返回 false,因为 IsEditing 的属性现在是 true。
新 PersonViewModel 对象的 PropertyChanged 处理程序调用 SubmitCommand 的 ChangeCanExecute 方法。 以下是该命令属性的实现方式:
public class PersonCollectionViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public PersonCollectionViewModel()
{
···
SubmitCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
Persons.Add(PersonEdit);
PersonEdit.PropertyChanged -= OnPersonEditPropertyChanged;
PersonEdit = null;
IsEditing = false;
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: () =>
{
return PersonEdit != null &&
PersonEdit.Name != null &&
PersonEdit.Name.Length > 1 &&
PersonEdit.Age > 0;
});
···
}
···
}
每当编辑的 PersonViewModel 对象中的属性发生更改时,都会调用 SubmitCommand 的 canExecute 函数。 仅当 Name 属性的长度至少为一个字符且 Age 大于 0 时,它返回 true。 此时,“提交”按钮将变为启用状态。
“提交”的 execute 函数从 PersonViewModel 中删除属性已更改的处理程序,将对象添加到 Persons 集合中,并使所有内容回到初始状态。
“取消”按钮的 execute 函数执行“提交”按钮所执行的所有操作,但不将对象添加到集合中:
public class PersonCollectionViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public PersonCollectionViewModel()
{
···
CancelCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
PersonEdit.PropertyChanged -= OnPersonEditPropertyChanged;
PersonEdit = null;
IsEditing = false;
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: () =>
{
return IsEditing;
});
}
···
}
canExecute 方法在编辑 PersonViewModel 时随时返回 true。
这些技术可以适用于更复杂的场景:可以将 PersonCollectionViewModel 中的属性绑定到 ListView 的 SelectedItem 属性以编辑现有项,还可以添加“删除”按钮以删除这些项。
不必将 execute 和 canExecute 方法定义为 lambda 函数。 在 ViewModel 中可以将它们作为常规的专用方法写入,并在 Command 构造函数中引用它们。 但是,这种方式往往会导致许多方法在 ViewModel 中只得到一次引用。
使用命令参数
有时,一个或多个按钮(或其他用户界面对象)在 ViewModel 中共享相同的 ICommand 属性是很方便的。 在这种情况下,使用 CommandParameter 属性来区分按钮。
可以继续为这些共享 ICommand 属性使用 Command 类。 该类定义构造函数,该构造函数接受参数为 Object 类型的 execute 和 canExecute 方法。 这就是将 CommandParameter 传递给这些方法的方式。
但是,在使用 CommandParameter 时,最容易使用泛型 Command<T> 类来指定对象设置为 CommandParameter 的类型。 指定的 execute 和 canExecute 方法具有该类型的参数。
“十进制键盘”页通过展示如何实现用于输入十进制数字的键盘,对这种技术作出了说明。 Grid 的 BindingContext 是 DecimalKeypadViewModel。 此 ViewModel 的 Entry 属性绑定到 Label 的 Text 属性。 所有 Button 对象都绑定到 ViewModel 中的各种命令:ClearCommand、BackspaceCommand 和 DigitCommand:
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:DataBindingDemos"
x:Class="DataBindingDemos.DecimalKeypadPage"
Title="Decimal Keyboard">
<Grid WidthRequest="240"
HeightRequest="480"
ColumnSpacing="2"
RowSpacing="2"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Center">
<Grid.BindingContext>
<local:DecimalKeypadViewModel />
</Grid.BindingContext>
<Grid.Resources>
<ResourceDictionary>
<Style TargetType="Button">
<Setter Property="FontSize" Value="32" />
<Setter Property="BorderWidth" Value="1" />
<Setter Property="BorderColor" Value="Black" />
</Style>
</ResourceDictionary>
</Grid.Resources>
<Label Text="{Binding Entry}"
Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="3"
FontSize="32"
LineBreakMode="HeadTruncation"
VerticalTextAlignment="Center"
HorizontalTextAlignment="End" />
<Button Text="CLEAR"
Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"
Command="{Binding ClearCommand}" />
<Button Text="⇦"
Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding BackspaceCommand}" />
<Button Text="7"
Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="7" />
<Button Text="8"
Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="8" />
<Button Text="9"
Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="9" />
<Button Text="4"
Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="0"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="4" />
<Button Text="5"
Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="1"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="5" />
<Button Text="6"
Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="6" />
<Button Text="1"
Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="0"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="1" />
<Button Text="2"
Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="1"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="2" />
<Button Text="3"
Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="3" />
<Button Text="0"
Grid.Row="5" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="0" />
<Button Text="·"
Grid.Row="5" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="." />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
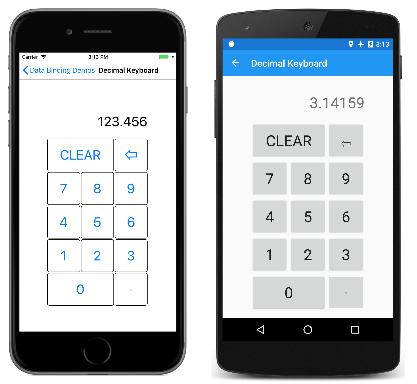
表示 10 位数和小数点的共计 11 个按钮共享与 DigitCommand 的绑定。 CommandParameter 区分这些按钮。 设置为 CommandParameter 的值通常与按钮显示的文本相同,但小数点除外,为了清晰起见,它在按钮中间显示一个点。
下面是正在执行操作的程序:
注意,所有屏幕截图中的小数点按钮均为禁用状态,因为输入的数字中已包含一个小数点。
DecimalKeypadViewModel 定义 string 类型的 Entry 属性(这是触发 PropertyChanged 事件的唯一属性)和 ICommand 类型的三个属性:
public class DecimalKeypadViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
string entry = "0";
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
···
public string Entry
{
private set
{
if (entry != value)
{
entry = value;
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs("Entry"));
}
}
get
{
return entry;
}
}
public ICommand ClearCommand { private set; get; }
public ICommand BackspaceCommand { private set; get; }
public ICommand DigitCommand { private set; get; }
}
始终启用与 ClearCommand 对应的按钮,并将条目设置为“0”:
public class DecimalKeypadViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public DecimalKeypadViewModel()
{
ClearCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
Entry = "0";
RefreshCanExecutes();
});
···
}
void RefreshCanExecutes()
{
((Command)BackspaceCommand).ChangeCanExecute();
((Command)DigitCommand).ChangeCanExecute();
}
···
}
由于始终启用按钮,因此不必在 Command 构造函数中指定 canExecute 参数。
输入数字和退格的逻辑有点复杂,因为如果没有输入数字,那么 Entry 属性就是字符串“0”。 即使用户键入更多的零,Entry 仍然只包含一个零。 如果用户键入任何其他数字,该数字将替换零。 但是如果用户在其他数字之前键入小数点,那么 Entry 就是字符串“0.”。
退格按钮仅在输入的长度大于 1 或 Entry 不等于字符串“0”时启用:
public class DecimalKeypadViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public DecimalKeypadViewModel()
{
···
BackspaceCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
Entry = Entry.Substring(0, Entry.Length - 1);
if (Entry == "")
{
Entry = "0";
}
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: () =>
{
return Entry.Length > 1 || Entry != "0";
});
···
}
···
}
退格按钮的 execute 函数的逻辑确保 Entry 至少是字符串“0”。
DigitCommand 属性绑定到 11 个按钮,每个按钮用 CommandParameter 属性标识自己。 可以将 DigitCommand 设置为常规 Command 类的实例,但使用 Command<T> 泛型类更容易。 当使用 XAML 命令接口时,CommandParameter 属性通常是字符串,这是泛型参数的类型。 然后,execute 和 canExecute 函数具有 string 类型的参数:
public class DecimalKeypadViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public DecimalKeypadViewModel()
{
···
DigitCommand = new Command<string>(
execute: (string arg) =>
{
Entry += arg;
if (Entry.StartsWith("0") && !Entry.StartsWith("0."))
{
Entry = Entry.Substring(1);
}
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: (string arg) =>
{
return !(arg == "." && Entry.Contains("."));
});
}
···
}
execute 方法将字符串参数追加到 Entry 属性。 但是,如果结果以零(但不是零和小数点)开头,则必须使用 Substring 函数删除初始零。
canExecute 方法仅在参数为小数点(指示按下小数点)且 Entry 已经包含小数点时才返回 false。
所有 execute 方法都调用 RefreshCanExecutes,然后它再为 DigitCommand 和 ClearCommand 调用 ChangeCanExecute。 这确保根据当前输入的数字的序列启用或禁用小数点和退格按钮。
导航菜单的异步命令
命令便于实现导航菜单。 以下是部分“MainPage.xaml”:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ContentPage xmlns="http://xamarin.com/schemas/2014/forms"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:DataBindingDemos"
x:Class="DataBindingDemos.MainPage"
Title="Data Binding Demos"
Padding="10">
<TableView Intent="Menu">
<TableRoot>
<TableSection Title="Basic Bindings">
<TextCell Text="Basic Code Binding"
Detail="Define a data-binding in code"
Command="{Binding NavigateCommand}"
CommandParameter="{x:Type local:BasicCodeBindingPage}" />
<TextCell Text="Basic XAML Binding"
Detail="Define a data-binding in XAML"
Command="{Binding NavigateCommand}"
CommandParameter="{x:Type local:BasicXamlBindingPage}" />
<TextCell Text="Alternative Code Binding"
Detail="Define a data-binding in code without a BindingContext"
Command="{Binding NavigateCommand}"
CommandParameter="{x:Type local:AlternativeCodeBindingPage}" />
···
</TableSection>
</TableRoot>
</TableView>
</ContentPage>
通过 XAML 使用命令时,CommandParameter 属性通常设置为字符串。 但本例使用的是 XAML 标记扩展,因此 CommandParameter 的类型为 System.Type。
每个 Command 属性都绑定到一个名为 NavigateCommand 的属性。 该属性是在代码隐藏文件“MainPage.xaml.cs”中定义的:
public partial class MainPage : ContentPage
{
public MainPage()
{
InitializeComponent();
NavigateCommand = new Command<Type>(
async (Type pageType) =>
{
Page page = (Page)Activator.CreateInstance(pageType);
await Navigation.PushAsync(page);
});
BindingContext = this;
}
public ICommand NavigateCommand { private set; get; }
}
构造函数将 NavigateCommand 属性设置为 execute 方法,该方法将 System.Type 参数实例化,然后导航到它。 因为 PushAsync 调用需要一个 await 操作符,所以必须将 execute 方法标记为异步。 这是通过参数列表前面的 async 关键字完成的。
构造函数还将页面的 BindingContext 设置为其自身,以便绑定在该类中引用 NavigateCommand。
此构造函数中代码的顺序会产生一定影响:InitializeComponent 调用导致 XAML 得到解析,但此时无法解析与名为 NavigateCommand 的属性的绑定,因为 BindingContext 设置为 null。 如果于设置 NavigateCommand 之前在构造函数中设置了 BindingContext,则可在设置 BindingContext 时解析绑定,但此时 NavigateCommand 仍然是 null。 在 BindingContext 之后设置 NavigateCommand 不会对绑定产生影响,因为更改 NavigateCommand 不会触发 PropertyChanged 事件,绑定不知道 NavigateCommand 现在是有效的。
在调用 InitializeComponent 之前设置 NavigateCommand 和 BindingContext(按照任何顺序)均有效,因为在 XAML 解析器遇到绑定定义时设置了绑定的两个组件。
数据绑定有时很棘手,但正如本系列文章中所述,它们功能强大且用途广泛,并且它们从用户界面分离底层逻辑,非常有助于组织代码。