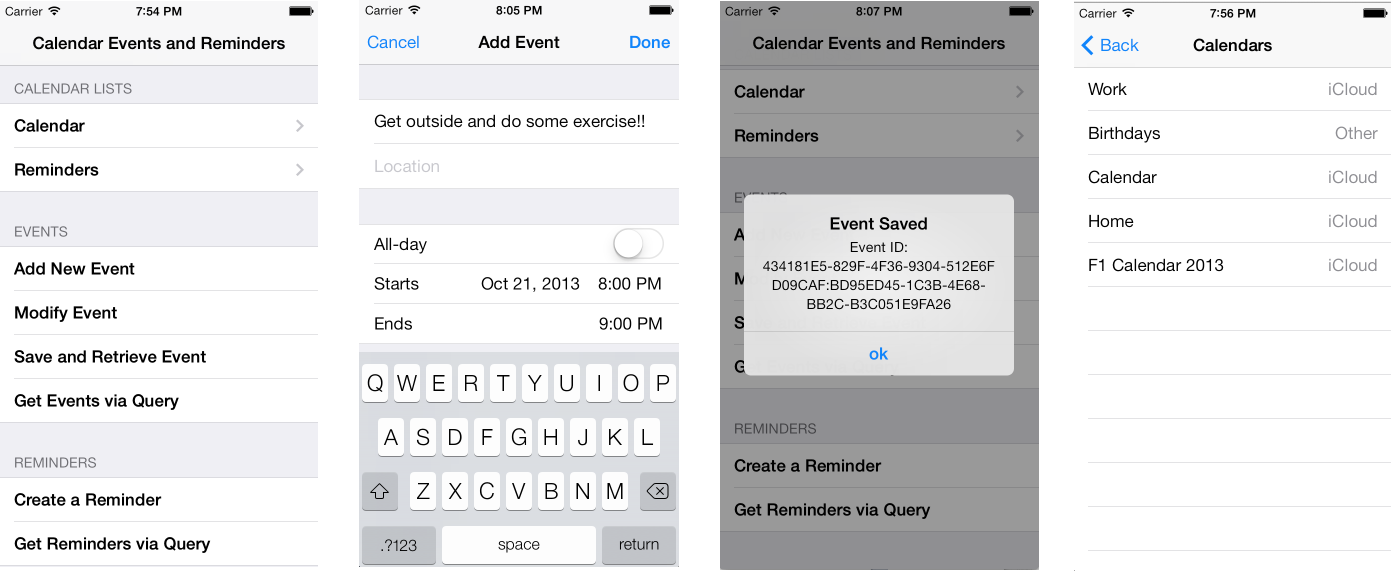
Xamarin.iOS 中的 EventKit
iOS 内置了两个与日历相关的应用程序:日历应用程序和提醒应用程序。 日历应用程序管理日历数据的方式很容易理解,但提醒应用程序相对复杂。 提醒其实可以与日期关联,比如何时到期和何时完成。因此,iOS 将所有日历数据(无论是日历事件还是提醒)存储在一个位置,称为“日历数据库”。
EventKit 框架提供了一种方法来访问日历、日历事件和日历数据库存储的提醒数据。 虽然从 iOS 4 开始就提供了对日历和日历事件的访问权限,但对提醒数据的访问权限是 iOS 6 新提供的。
本指南将介绍:
- EventKit 基础知识–将通过主要类介绍 EventKit 的基本部分,并提供对其用法的理解。 在处理文档的下一部分之前,需要先阅读此部分。
- 常见任务–常见任务部分旨在快速参考如何执行常见操作,例如:枚举日历,创建、保存和检索日历事件和提醒,以及使用内置控制器来创建和修改日历事件。 此部分无需从头到尾阅读,因为它只是特定任务的参考资料。
本指南中的所有任务均在配套示例应用程序中提供:
要求
EventKit 在 iOS 4.0 中引入,但对提醒数据的访问权限是在 iOS 6.0 中引入的。 因此,若要进行常规 EventKit 开发,需要针对至少版本 4.0 和 6.0 的提醒。
此外,提醒应用程序在模拟器上不可用,这意味着提醒数据也将不可用,除非先添加它们。 此外,访问请求仅会在实际设备上向用户显示。 因此,EventKit 开发最好在设备上进行测试。
EventKit 基础知识
使用 EventKit 时,掌握其常见类及其用法至关重要。 所有这些类都可以在 EventKit 和 EventKitUI 中找到(适用于 EKEventEditController)。
EventStore
EventStore 类是 EventKit 中最重要的类,因为它需要在 EventKit 中执行任何操作。 对于所有 EventKit 数据,都可以将其视为持久性存储或数据库引擎。 从 EventStore 可以访问日历应用程序中的日历和日历事件,以及提醒应用程序中的提醒。
由于 EventStore 类似于数据库引擎,因此它应有较长的生存期,这意味着应在应用程序实例的生存期内尽可能少地创建和销毁它。 事实上,建议在应用程序中创建 EventStore 的一个实例后,除非确定不再需要它,否则应将该引用保留至整个应用程序的生命周期结束。 此外,所有调用都应转到单个 EventStore 实例。 因此,建议使用 Singleton 模式来保持单个实例可用。
创建事件存储
以下代码演示了创建 EventStore 类的单个实例并使其在应用程序中静态可用的有效方法:
public class App
{
public static App Current {
get { return current; }
}
private static App current;
public EKEventStore EventStore {
get { return eventStore; }
}
protected EKEventStore eventStore;
static App ()
{
current = new App();
}
protected App ()
{
eventStore = new EKEventStore ( );
}
}
上面的代码使用 Singleton 模式在应用程序加载时实例化 EventStore 的实例。 然后,可以从应用程序中对 EventStore 进行全局访问,如下所示:
App.Current.EventStore;
请注意,此处的所有示例都使用此模式,因此它们通过 App.Current.EventStore 引用 EventStore。
请求访问日历和提醒数据
在允许通过 EventStore 访问任何数据之前,应用程序必须首先请求访问日历事件数据或提醒数据,具体取决于所需的数据。 为便于执行此操作,EventStore 公开一种称为 RequestAccess 的方法,在调用该方法时会向用户显示警报视图,告知用户应用程序请求访问日历数据或提醒数据,具体取决于传递给它的 EKEntityType。 由于它会引发警报视图,因此调用是异步的,并将调用作为 NSAction (或 Lambda)传递给它的完成处理程序,这将接收两个参数;一个决定是否授予访问权限的布尔值,以及一个 NSError,如果其不为 null,则该布尔值将包含请求中的任何错误信息。 例如,以下编码将请求访问日历事件数据,并在未授予请求时显示警报视图。
App.Current.EventStore.RequestAccess (EKEntityType.Event,
(bool granted, NSError e) => {
if (granted)
//do something here
else
new UIAlertView ( "Access Denied",
"User Denied Access to Calendar Data", null,
"ok", null).Show ();
} );
授予请求后,只要应用程序安装在设备上,它就会被记住,并且不会向用户弹出警报。 但是,仅会授予对资源类型的访问权限,即授予日历事件或提醒。 如果应用程序需要同时访问两者,则应请求此两者。
由于记住了权限,因此每次发出请求相对更便宜,因此最好在执行操作之前始终请求访问权限。
此外,由于完成处理程序是在单独的(非 UI)线程上调用的,因此完成处理程序中的任何更新都应通过 InvokeOnMainThread 进行调用,否则将引发异常,而如果未捕获,应用程序将崩溃。
EKEntityType
EKEntityType 是描述 EventKit 项或数据的类型的枚举。 它具有两个值:Event 和提醒。 它用于多种方法,包括 EventStore.RequestAccess 用于告知 EventKit 应访问或检索哪种类型的数据。
EKCalendar
EKCalendar 表示包含一组日历事件的日历。 日历可以存储在很多不同的位置,例如本地、iCloud、第三方提供商位置(例如 Exchange Server 或 Google等)。很多时候,EKCalendar 用于告知 EventKit 应查找事件的位置或保存事件的位置。
EKEventEditController
EKEventEditController 可在 EventKitUI 命名空间中找到,它是可用于编辑或创建日历事件的内置控制器。 与内置相机控制器一样,EKEventEditController 会在显示 UI 和处理保存方面为你承担繁重的工作。
EKEvent
EKEvent 表示日历事件。 EKEvent 和 EKReminder 都继承自 EKCalendarItem,并具有 Title、Notes 等字段。
EKReminder
EKReminder 表示提醒项。
EKSpan
EKSpan 是一个枚举,用于描述修改可递归的事件时的事件范围,并具有两个值:ThisEvent 和 FutureEvents。 ThisEvent 意味着任何更改都只会发生于所引用的序列中的特定事件,而 FutureEvents 则将影响该事件和所有将来的重复事件。
任务
为方便使用,已将 EventKit 用法分解为常见任务,如以下部分所述。
枚举日历
若要枚举用户在设备上配置的日历,请在 EventStore 上调用 GetCalendars,并传递要接收的日历类型(提醒或事件):
EKCalendar[] calendars =
App.Current.EventStore.GetCalendars ( EKEntityType.Event );
使用内置控制器添加或修改事件
如果要创建或编辑与使用日历应用程序时向用户显示的相同 UI 的事件,EKEventEditViewController 会执行大量工作:
若要使用它,需要将其声明为类级变量,以便在方法中声明时不会进行垃圾回收:
public class HomeController : DialogViewController
{
protected CreateEventEditViewDelegate eventControllerDelegate;
...
}
然后,若要启动它:对其进行实例化,为它提供对 EventStore 的引用,连接 EKEventEditViewDelegate 委托,然后使用 PresentViewController 显示它:
EventKitUI.EKEventEditViewController eventController =
new EventKitUI.EKEventEditViewController ();
// set the controller's event store - it needs to know where/how to save the event
eventController.EventStore = App.Current.EventStore;
// wire up a delegate to handle events from the controller
eventControllerDelegate = new CreateEventEditViewDelegate ( eventController );
eventController.EditViewDelegate = eventControllerDelegate;
// show the event controller
PresentViewController ( eventController, true, null );
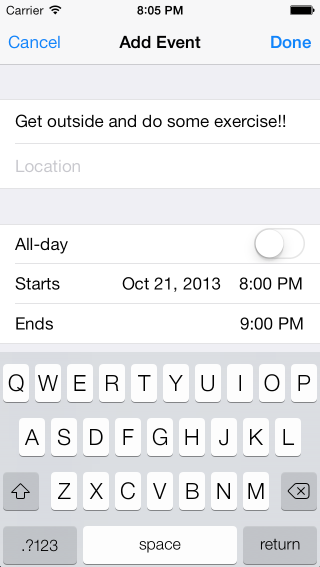
(可选)如果要预填充事件,则可以创建全新的事件(如下所示),也可以检索已保存的事件:
EKEvent newEvent = EKEvent.FromStore ( App.Current.EventStore );
// set the alarm for 10 minutes from now
newEvent.AddAlarm ( EKAlarm.FromDate ( DateTime.Now.AddMinutes ( 10 ) ) );
// make the event start 20 minutes from now and last 30 minutes
newEvent.StartDate = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes ( 20 );
newEvent.EndDate = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes ( 50 );
newEvent.Title = "Get outside and exercise!";
newEvent.Notes = "This is your reminder to go and exercise for 30 minutes.”;
如果要预填充 UI,请确保在控制器上设置事件属性:
eventController.Event = newEvent;
若要使用现有事件,请参阅后面的“按 ID 检索事件”部分。
委托应重写 Completed 方法,当用户完成对话框时由控制器进行调用:
protected class CreateEventEditViewDelegate : EventKitUI.EKEventEditViewDelegate
{
// we need to keep a reference to the controller so we can dismiss it
protected EventKitUI.EKEventEditViewController eventController;
public CreateEventEditViewDelegate (EventKitUI.EKEventEditViewController eventController)
{
// save our controller reference
this.eventController = eventController;
}
// completed is called when a user eith
public override void Completed (EventKitUI.EKEventEditViewController controller, EKEventEditViewAction action)
{
eventController.DismissViewController (true, null);
}
}
}
(可选)在委托中,可以在 Completed 方法中检查操作,以修改事件并重新保存,或者执行其他操作(如果已取消,等等):
public override void Completed (EventKitUI.EKEventEditViewController controller, EKEventEditViewAction action)
{
eventController.DismissViewController (true, null);
switch ( action ) {
case EKEventEditViewAction.Canceled:
break;
case EKEventEditViewAction.Deleted:
break;
case EKEventEditViewAction.Saved:
// if you wanted to modify the event you could do so here,
// and then save:
//App.Current.EventStore.SaveEvent ( controller.Event, )
break;
}
}
以编程方式创建事件
若要在代码中创建事件,请在 EKEvent 类上使用 FromStore 工厂方法,并在其中设置任何数据:
EKEvent newEvent = EKEvent.FromStore ( App.Current.EventStore );
// set the alarm for 10 minutes from now
newEvent.AddAlarm ( EKAlarm.FromDate ( DateTime.Now.AddMinutes ( 10 ) ) );
// make the event start 20 minutes from now and last 30 minutes
newEvent.StartDate = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes ( 20 );
newEvent.EndDate = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes ( 50 );
newEvent.Title = "Get outside and do some exercise!";
newEvent.Notes = "This is your motivational event to go and do 30 minutes of exercise. Super important. Do this.";
必须设置要保存事件的日历,但如果没有首选项,则可以使用默认值:
newEvent.Calendar = App.Current.EventStore.DefaultCalendarForNewEvents;
若要保存事件,请对 EventStore 调用 SaveEvent 方法:
NSError e;
App.Current.EventStore.SaveEvent ( newEvent, EKSpan.ThisEvent, out e );
保存后,EventIdentifier 属性将使用唯一标识符进行更新,稍后即可使用该标识符检索事件:
Console.WriteLine ("Event Saved, ID: " + newEvent.CalendarItemIdentifier);
EventIdentifier 是字符串格式的 GUID。
以编程方式创建提醒
在代码中创建提醒的方法与创建日历事件大致相同:
EKReminder reminder = EKReminder.Create ( App.Current.EventStore );
reminder.Title = "Do something awesome!";
reminder.Calendar = App.Current.EventStore.DefaultCalendarForNewReminders;
若要保存,请对 EventStore 调用 SaveReminder 方法:
NSError e;
App.Current.EventStore.SaveReminder ( reminder, true, out e );
按 ID 检索事件
若要按 ID 检索事件,请使用 EventStore 上的 EventFromIdentifier 方法,并向其传递从事件中提取的 EventIdentifier:
EKEvent mySavedEvent = App.Current.EventStore.EventFromIdentifier ( newEvent.EventIdentifier );
对于事件,还有两个其他标识符属性,但 EventIdentifier 是唯一适用于此属性的标识符属性。
按 ID 检索提醒
若要检索提醒,请使用 EventStore上的 GetCalendarItem 方法,并将其传递给 CalendarItemIdentifier:
EKCalendarItem myReminder = App.Current.EventStore.GetCalendarItem ( reminder.CalendarItemIdentifier );
由于 GetCalendarItem 会返回 EKCalendarItem,因此如果需要访问提醒数据或使用实例作为 EKReminder,则必须将其强制转换为 EKReminder。
请勿对日历事件使用 GetCalendarItem,就像在撰写时一样,它不会工作。
删除事件
若要删除日历事件,请在 EventStore 上调用 RemoveEvent 并传递对事件的引用,以及相应的 EKSpan:
NSError e;
App.Current.EventStore.RemoveEvent ( mySavedEvent, EKSpan.ThisEvent, true, out e);
但是,在删除事件后,事件引用将为 null。
删除提醒
若要删除提醒,请对 EventStore 调用 RemoveReminder 并传递对提醒的引用:
NSError e;
App.Current.EventStore.RemoveReminder ( myReminder as EKReminder, true, out e);
请注意,在上面的代码中,有一个强制转换是 EKReminder,因为使用 GetCalendarItem 对它进行了检索
搜索事件
若要搜索日历事件,则必须通过 EventStore 上的 PredicateForEvents 方法创建 NSPredicate 对象。 NSPredicate 是 iOS 用于查找匹配项的查询数据对象:
DateTime startDate = DateTime.Now.AddDays ( -7 );
DateTime endDate = DateTime.Now;
// the third parameter is calendars we want to look in, to use all calendars, we pass null
NSPredicate query = App.Current.EventStore.PredicateForEvents ( startDate, endDate, null );
创建 NSPredicate 后,对 EventStore 使用 EventsMatching 方法:
// execute the query
EKCalendarItem[] events = App.Current.EventStore.EventsMatching ( query );
请注意,查询是同步的(阻塞),可能需要很长时间,具体取决于查询,因此可能需要启动新的线程或任务来执行此操作。
搜索提醒
搜索提醒类似于事件;它需要谓词,但调用已是异步的,因此你不必担心会阻止线程:
// create our NSPredicate which we'll use for the query
NSPredicate query = App.Current.EventStore.PredicateForReminders ( null );
// execute the query
App.Current.EventStore.FetchReminders (
query, ( EKReminder[] items ) => {
// do someting with the items
} );
总结
本文档概述了 EventKit 框架的重要部分和一些最常见的任务。 但是,EventKit 框架非常大且功能强大,并且包括尚未在此处引入的功能,例如:批处理更新、配置警报、配置事件定期、注册和侦听日历数据库上的更改、设置 GeoFences 等。 有关详细信息,请参阅 Apple 的“日历和提醒编程指南”。