Walkthrough: Creating a Query to Link Two Tables
This walkthrough demonstrates how to create a query that links two tables.
About This Walkthrough
This walkthrough illustrates the following tasks:
Creating a query that links the Customer table and the Sales Line table.
Running the query to view the data that this query describes.
Prerequisites
To complete this walkthrough, you will need:
Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2018 with a developer license.
CRONUS International Ltd. demonstration database.
Story
Viktor is a Microsoft Certified Partner working for CRONUS International Ltd. He has been asked to create a query that will get the quantity of items in every sales order for each customer. Viktor knows how to do this in SQL, but he wants to use a Dynamics NAV query.
The SQL query for the dataset that Viktor wants is the following:
SELECT C.Name, C.No_, SL.Amount FROM [CRONUS International Ltd_$Customer] AS C, [CRONUS International Ltd_$Sales Line] AS SL WHERE C.No_ = SL.[Sell-to Customer No_]
Creating a Query That Links Two Tables
Viktor wants to create a dataset that contains the quantity of items and the customer name for every sales order. The customer name is stored in the Customer table. Sales order quantities are stored in the Sales Line table. To create this dataset, Viktor will use Query Designer to create a query and do the following:
Include data items and columns for the Customer and Sales Lines tables and their fields.
A data item defines a table to retrieve data from. Viktor will add one data item for the Customer table and another data item for the Sales Line table. A column specifies a field from a table to be displayed in the resulting dataset. Viktor will add columns for the No. and Name fields from the Customer table, and a column for the Quantity field from the Sales Line table.
Link the Customer table and Sales Line table.
To generate a dataset from the Customer table and Sales Line table, Viktor must link the two tables. A link specifies a condition between two fields of the tables that must be met for a record to be included in the dataset. To link the two tables, Viktor must first identify a field that is common in both tables. He determines that the No. field in the Customer table is the same as the Sell-to Customer No. field in the Sales Line table. For a record to be included in the resulting dataset, the value of the No. field in the Customer table must equal the Sell-to Customer No. field in the Sales Line table.
To create this dataset in a Dynamics NAV query, Viktor creates a query in Object Designer.
To create a query that includes columns from the Customer table and the Sales Line table
In the development environment, on the Tools menu, choose Object Designer.
In Object Designer, choose Query, and then choose the New button.
In Query Designer, add five rows as described in the following table. Choose the drop-down arrow to select tables and fields from the drop-down list box.
Line No. Type Data Source Name Line 1 DataItem Customer C Line 2 Column No. <No> Line 3 Column Name <Name> Line 4 DataItem Sales Line SL Line 5 Column Quantity <Quantity>
Tip
The Name column in Query Designer is equivalent to using the AS keyword in an SQL statement. It defines an alias for the data item. Type a value in this column when you want to replace the default value with an alias.
To link the Customer table and the Sales Line table
In Query Designer, select the SL data item.
Important
When you create a link between two data items, you set up the link on the lower of the two data items in Query Designer.
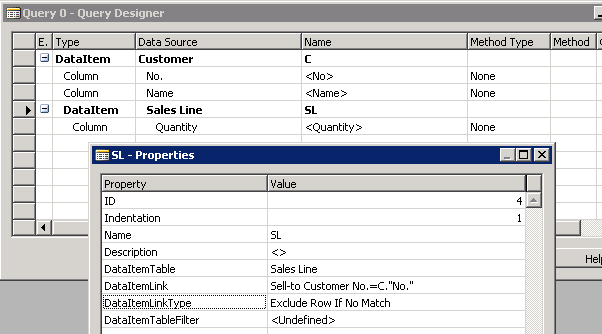
On the View menu, choose Properties. The SL - Properties window opens
In the Value field of the DataItemLink property, choose the AssistEdit button.
The DataItem Link window opens. You use this window to create a reference link between the Sell-to Customer No. field of the Sales Line table and the No. field of the Customer table.
In the DataItem Link window, in the Field column, choose the up arrow.
Note
DataItem Link is like a WHERE clause in an SQL statement.
In the Sales Line – Field List window, select Sell-to Customer No., and then choose the OK button.
In the Reference DataItem column, choose the up arrow.
The DataItem List – Table window opens. You use this window to create a link to the Customer table.
In the DataItem List window. select the C data item row, and then choose the OK button.
In the Reference Field column, choose the up arrow.
In the Customer – Field List window, select No., and then choose the OK button.
Choose the OK button to close the DataItem Link window.
In the SL Properties window, in the Value field of the DataItemLinkType property, choose Exclude If No Match from the drop-down list.
Note
Exclude If No Match only includes rows where the linked fields from both data items are equal.
The following figure shows Query Designer and Properties window.
Saving and Running the Query
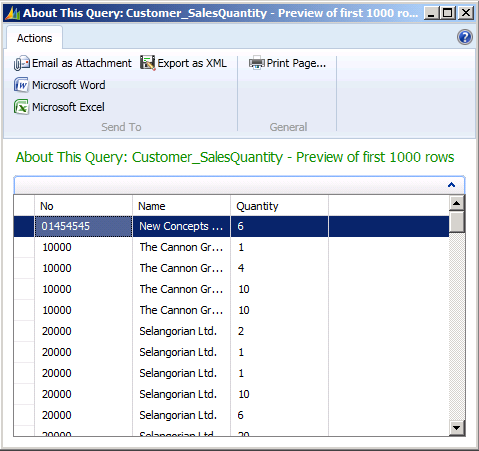
Viktor wants to verify that the query describes the dataset that he wants. He saves the query, and then runs it from Object Designer. The call to run the query runs on Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server and opens a view of the dataset in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Windows client.
To save and run a query
On the File menu, choose Save.
In the Save As window, in the ID field, enter 50001. In the Name field, enter Customer_SalesQuantity. Verify that the Compiled check box is selected, and then choose the OK button.
Note
If 50001 is already being used by another query, you will get an error when you try to save the query. If so, use another ID.
In Object Designer, select query 50001, and then choose the Run button. When you run a query, you can view the data in the dataset.
Next Steps
Viktor’s next steps are to create more complex queries. For more information, see Walkthrough: Creating a Query That Uses a Totaling Method and Sorting and Walkthrough: Creating a Query to Link Three Tables.