Project Server CSOM 和 .NET 入门
Project Server 2013 客户端对象模型 (CSOM) 可用于通过 .NET Framework 4 开发 Project Online 和本地解决方案。 本文介绍了如何创建使用 CSOM 创建并发布项目的控制台应用程序。 发布项目之后,应用程序等待 Project Server 队列服务完成发布操作,然后列出已发布的项目。
有关 Project Server CSOM 的一般介绍,请参阅 Project 2013 中面向开发人员的更新。 有关 CSOM 命名空间中的引用主题,请参阅 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client。
在 Visual Studio 中创建 CSOM 项目
可以使用 Visual Studio 2010 或 Visual Studio 2012 开发可使用 Project Server CSOM 的解决方案。 Project Server CSOM 包含三个程序集,用于使用 .Net Framework 4 开发客户端应用程序、Microsoft Silverlight 应用程序和 Windows Phone 8 应用程序。 CSOM 还包括用于开发 Web 应用程序的 JavaScript 文件,如 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client 中所述。
可以将所需的 CSOM 程序集从 Project Server 计算机或从 Project 2013 SDK 下载复制到远程开发计算机。 本主题中所述的 QueueCreateProject 控制台应用程序不是 Silverlight 应用程序,也不是 Windows Phone 8 应用程序,因此需要 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.dll 程序集。 CSOM 独立于基于 WCF 或基于 ASMX 的 Project Server Interface (PSI),因此不必为 PSI 设置服务引用,也不必使用 Microsoft.Office.Project.Server.Library 命名空间。
QueueCreateProject 应用程序将命令行参数用于要创建的项目的名称以及用于队列超时限制。 在过程 1 中,创建基本控制台应用程序、添加一个例程以分析命令行并添加使用消息,前提是命令行中没有错误。
程序 1. 使用 Visual Studio 创建 CSOM 项目
将 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.dll 程序集从
%ProgramFiles%\Common Files\Microsoft Shared\Web Server Extensions\15\ISAPI\文件夹复制到开发计算机。 将程序集复制到要使用的其他 Project Server 和 SharePoint 引用程序集的便捷文件夹,例如C:\Project\Assemblies。将 Microsoft.SharePoint.Client.dll 程序集和 Microsoft.SharePoint.Client.Runtime.dll 程序集从同一源文件夹中复制到开发计算机中。 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.dll 程序集依赖相关 SharePoint 程序集。
在 Visual Studio 中,创建 Windows 控制台应用程序,并将目标框架设置为 .NET Framework 4。 例如,将应用程序命名为 QueueCreateProject。
注意
如果您忘记设置正确的目标,请在 Visual Studio 创建项目之后,在“项目”菜单中打开“QueueCreateProject 属性”。 在“应用程序”选项卡的“目标框架”下拉列表中,选择“.NET Framework 4”。 请勿使用“.NET Framework 4 客户端配置文件”。
在解决方案资源管理器中,设置对以下程序集的引用:
- Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.dll
- Microsoft.SharePoint.Client.dll
- Microsoft.SharePoint.Client.Runtime.dll
在 Program.cs 文件中,编辑
using语句,如下所示。using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client;添加方法以分析用于项目名称和队列超时的秒数的命令行参数,显示使用信息,然后退出应用程序。 将 Program.cs 文件中代码的正文替换为下列代码。
namespace QueueCreateProject { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { if (!ParseCommandLine(args)) { Usage(); ExitApp(); } /* Add calls to methods here to get the project context and create a project. */ ExitApp(); } // Parse the command line. Return true if there are no errors. private static bool ParseCommandLine(string[] args) { bool error = false; int argsLen = args.Length; try { for (int i = 0; i < argsLen; i++) { if (error) break; if (args[i].StartsWith("-") || args[i].StartsWith("/")) args[i] = "*" + args[i].Substring(1).ToLower(); switch (args[i]) { case "*projname": case "*n": if (++i >= argsLen) return false; projName = args[i]; break; case "*timeout": case "*t": if (++i >= argsLen) return false; timeoutSeconds = Convert.ToInt32(args[i]); break; case "*?": default: error = true; break; } } } catch (FormatException) { error = true; } if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(projName)) error = true; return !error; } private static void Usage() { string example = "Usage: QueueCreateProject -projName | -n \"New project name\" [-timeout | -t sec]"; example += "\nExample: QueueCreateProject -n \"My new project\""; example += "\nDefault timeout seconds = " + timeoutSeconds.ToString(); Console.WriteLine(example); } private static void ExitApp() { Console.Write("\nPress any key to exit... "); Console.ReadKey(true); Environment.Exit(0); } } }
获取项目上下文
CSOM 开发要求使用 Project Web App URL 初始化 ProjectContext 对象。 过程 2 中的代码使用 pwaPath 常量。 如果计划对 Project Web App 的多个实例使用该应用程序,可以将 pwaPath 作为一个变量,并添加另一个命令行参数。
程序 2. 获取项目上下文
添加 QueueCreateProject 应用程序将使用的 Program 类常量和变量。 除了 Project Web App URL 之外,应用程序还使用默认企业项目类型 (EPT) 的名称、要创建的项目名称以及以秒为单位的最大队列超时时间。 在本例中,使用 timeoutSeconds 变量可以测试超时的各种值如何影响应用程序。 ProjectContext 对象是用于访问 CSOM 的主要对象。
private const string pwaPath = "https://ServerName /pwa/"; // Change the path to your Project Web App instance. private static string basicEpt = "Enterprise Project"; // Basic enterprise project type. private static string projName = string.Empty; private static int timeoutSeconds = 10; // The maximum wait time for a queue job, in seconds. private static ProjectContext projContext;用以下代码替换
/* Add calls to methods here to get the project context and create a project. */批注。 使用 Project Web App URL 初始化 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.ProjectContext 对象。 CreateTestProject 方法和 ListPublishedProjects 方法如过程 4 和过程 5 中所示。projContext = new ProjectContext(pwaPath); if (CreateTestProject()) ListPublishedProjects(); else Console.WriteLine("\nProject creation failed: {0}", projName);
获取企业项目类型
QueueCreateProject 示例应用程序显式选择企业项目 EPT 以显示应用程序如何才能为项目选择 EPT。 如果项目创建信息未指定 EPT GUID,则应用程序将使用默认 EPT。 GetEptUid 方法由过程 4 中介绍的 CreateTestProject 方法使用。
GetEptUid 方法查询 EnterpriseProjectTypes 集合的 ProjectContext 对象,其中 EPT 名称与指定名称相同。 执行查询后,将 eptUid 变量设置为 eptList 集合中第一个 EnterpriseProjectType 对象的 GUID。 因为 EPT 名称是唯一的,因此只有一个具有指定名称的 EnterpriseProjectType 对象。
过程 3. 为新项目获取 EPT 的 GUID
向 Program 类添加 GetEptUid 方法。
// Get the GUID of the specified enterprise project type. private static Guid GetEptUid(string eptName) { Guid eptUid = Guid.Empty; try { // Get the list of EPTs that have the specified name. // If the EPT name exists, the list will contain only one EPT. var eptList = projContext.LoadQuery( projContext.EnterpriseProjectTypes.Where( ept => ept.Name == eptName)); projContext.ExecuteQuery(); eptUid = eptList.First().Id; } catch (Exception ex) { string msg = string.Format("GetEptUid: eptName = \"{0}\"\n\n{1}", eptName, ex.GetBaseException().ToString()); throw new ArgumentException(msg); } return eptUid; }
查找 EPT GUID 的方法有多种。 GetEptUid 方法中显示的查询效率很高,因为它仅下载一个与 EPT 名称匹配的 EnterpriseProjectType 对象。 下面的备用例程效率不高,因为它将 EPT 的完整列表下载到客户端应用程序并循环访问此列表。
foreach (EnterpriseProjectType ept in projSvr.EnterpriseProjectTypes)
{
if (ept.Name == eptName)
{
eptUid = ept.Id;
break;
}
}
以下例程使用 LINQ 查询和 lambda 表达式来选择 EPT 对象,但仍会下载所有 EnterpriseProjectType 对象。
var eptList = projContext.LoadQuery(projContext.EnterpriseProjectTypes);
projContext.ExecuteQuery();
eptUid = eptList.First(ept => ept.Name == eptName).Id;
设置创建信息并发布项目
CreateTestProject 方法创建一个 ProjectCreationInformation 对象并指定创建项目所需的信息。 项目 GUID 和名称是必需的;开始日期、项目描述和 EPT GUID 是可选的。
设置新的项目属性后,Projects.Add 方法会将项目添加到 Projects 集合中。 若要保存并发布项目,您必须调用 Projects.Update 方法向 Project Server 队列发送一条消息并创建项目。
过程 4. 查看新项目属性、创建项目并发布项目
将 CreateTestProject 方法添加到 Program 类。 下列代码创建并发布项目,但不会等待队列作业完成。
// Create a project. private static bool CreateTestProject() { bool projCreated = false; try { Console.Write("\nCreating project: {0} ...", projName); ProjectCreationInformation newProj = new ProjectCreationInformation(); newProj.Id = Guid.NewGuid(); newProj.Name = projName; newProj.Description = "Test creating a project with CSOM"; newProj.Start = DateTime.Today.Date; // Setting the EPT GUID is optional. If no EPT is specified, Project Server // uses the default EPT. newProj.EnterpriseProjectTypeId = GetEptUid(basicEpt); PublishedProject newPublishedProj = projContext.Projects.Add(newProj); QueueJob qJob = projContext.Projects.Update(); /* Add code here to wait for the queue. */ } catch(Exception ex) { Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red; Console.WriteLine("\nError: {0}", ex.Message); Console.ResetColor(); } return projCreated; }用以下代码替换
/* Add code here to wait for the queue. */批注以等待队列作业。 该例程等待指定的 timeoutSeconds 秒数最大值,如果队列作业在超时之前完成,则继续。 有关可能的队列作业状态,请参阅 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.JobState。为 QueueJob 对象调用 Load 方法和 ExecuteQuery 方法是可选的。 如果 QueueJob 对象在您调用 WaitForQueue 方法时未进行初始化,则 Project Server 将初始化它。
// Calling Load and ExecuteQuery for the queue job is optional. // projContext.Load(qJob); // projContext.ExecuteQuery(); JobState jobState = projContext.WaitForQueue(qJob, timeoutSeconds); if (jobState == JobState.Success) { projCreated = true; } else { Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow; Console.WriteLine("\nThere is a problem in the queue. Timeout is {0} seconds.", timeoutSeconds); Console.WriteLine("\tQueue JobState: {0}", jobState.ToString()); Console.ResetColor(); } Console.WriteLine();
列出已发布的项目
ListPublishedProjects 方法用于获取 Project Web App 中发布的所有项目集合。 如果在过程 4 中创建项目的队列作业未成功完成或超时,新项目将不会包含在 Projects 集合中。
过程 5. 列出已发布项目
向 Program 类添加 ListPublishedProjects 方法。
// List the published projects. private static void ListPublishedProjects() { // Get the list of projects on the server. projContext.Load(projContext.Projects); projContext.ExecuteQuery(); Console.WriteLine("\nProject ID : Project name : Created date"); foreach (PublishedProject pubProj in projContext.Projects) { Console.WriteLine("\n\t{0} :\n\t{1} : {2}", pubProj.Id.ToString(), pubProj.Name, pubProj.CreatedDate.ToString()); } }为 Project Web App URL 设置正确的值,编译 QueueCreateProject 应用程序,然后按过程 6 中的步骤测试应用程序。
测试 QueueCreateProject 应用程序
在 Project Web App 的测试实例上首次运行 QueueCreateProject 应用程序时,尤其是如果 Project Server 安装在虚拟机上,则应用程序可能需要比默认的 10 秒队列超时时间更长的时间运行。
过程 6. 测试 QueueCreateProject 应用程序
打开 QueueCreateProject 属性 窗口,选择 调试 选项卡,然后在 开始选项 部分添加以下命令行参数:
-n "Test proj 1" -t 20运行应用程序(例如,按 F5)。 如果超时值足够长,应用程序将显示下列输出(如果其他已发布项目存在于 Project Web App 实例中,还将显示这些项目):
Creating project: Test proj 1 ... Project ID : Project name : Created date b34d7009-753f-4abb-9191-f4b15a82aac3 : Test proj 1 : 9/22/2011 11:27:57 AM Press any key to exit...使用下列命令行参数运行另一个测试,以便使用默认的 10 秒队列超时值:
-n "Test proj 1"由于测试项目 1 已存在,应用程序显示以下输出。
Creating project: Test proj 1 ... Error: PJClientCallableException: ProjectNameAlreadyExists ProjectNameAlreadyExists projName = Test proj 1 Project creation failed: Test proj 1 Press any key to exit...使用下列命令行参数运行另一个测试,以便使用默认的 10 秒队列超时值:
-n "Test proj 2"QueueCreateProject 应用程序创建和发布名为“测试项目 2”的项目。
使用下列命令行参数运行另一个测试,将超时值设置得过短,使队列作业无法完成:
-n "Test proj 3" -t 1由于队列超时太短,因此未创建项目。 应用程序将显示下列输出。
Creating project: Test proj 3 ... There is a problem in the queue. Timeout is 1 seconds. Queue JobState: Unknown Project creation failed: Test proj 3 Press any key to exit...修改代码,使应用程序就不会等待队列作业。 例如,注释掉等待队列的代码(行除外
projCreated = true),如下所示。//JobState jobState = projContext.WaitForQueue(qJob, timeoutSeconds); //if (jobState == JobState.Success) //{ projCreated = true; //} //else //{ // Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow; // Console.WriteLine("\nThere is a problem in the queue. Timeout is {0} seconds.", // timeoutSeconds); // Console.WriteLine("\tQueue JobState: {0}", jobState.ToString()); // Console.ResetColor(); //}重新编译应用程序并使用下列命令行参数运行另一个测试:
-n "Test proj 4"由于已注释 WaitForQueue 例程,因此应用程序不会使用默认超时值。 即使应用程序不等待队列,如果 Project Server 中的发布操作足够快,则也可能显示 Test proj 4。
Creating project: Test proj 4 ... Project ID : Project name : Created date cdd54103-082f-425c-b075-9ff52ac7d4e6 : Test proj 2 : 9/25/2011 4:28:55 PM b34d7009-753f-4abb-9191-f4b15a82aac3 : Test proj 1 : 9/22/2011 11:27:57 AM 5c0c73f2-f5dd-499b-8bd8-ebb74bf8c122 : Test proj 4 : 9/25/2011 4:39:21 PM Press any key to exit...
刷新 Project Web App 中的“项目中心”页 (https://ServerName/ProjectServerName/Projects.aspx),显示已发布的项目。 下图显示已发布的测试项目。
在 Project Web App 中查看已发布的项目
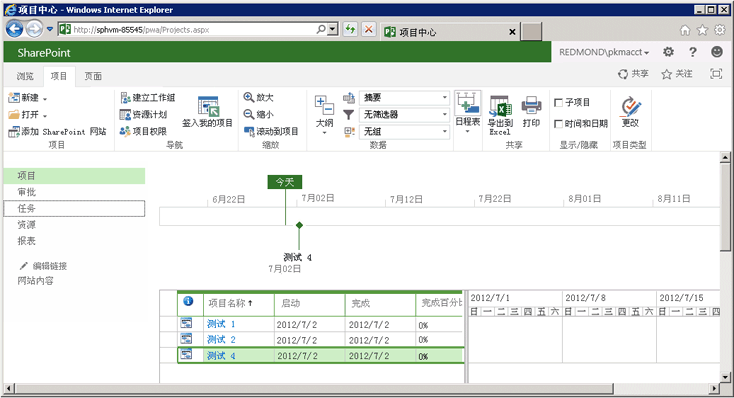
QueueCreateProject 示例应用程序显示以下典型示例:如何通过 ProjectCreationInformation 类使用 CSOM 创建项目实体、如何将项目添加到已发布集合、如何使用 WaitForQueue 方法等待队列作业,以及如何枚举已发布项目的集合。
完整的代码示例
下面是 QueueCreateProject 示例应用程序的完整代码。 Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client.ProjectCreationInformation 类引用还包含本主题中的代码。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.ProjectServer.Client;
namespace QueueCreateProject
{
class Program
{
private const string pwaPath = "https://ServerName /pwa/"; // Change the path to your Project Web App instance.
private static string basicEpt = "Enterprise Project"; // Basic enterprise project type.
private static string projName = string.Empty;
private static int timeoutSeconds = 10; // The maximum wait time for a queue job, in seconds.
private static ProjectContext projContext;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
if (!ParseCommandLine(args))
{
Usage();
ExitApp();
}
projContext = new ProjectContext(pwaPath);
if (CreateTestProject())
ListPublishedProjects();
else
Console.WriteLine("\nProject creation failed: {0}", projName);
ExitApp();
}
// Create a project.
private static bool CreateTestProject()
{
bool projCreated = false;
try
{
Console.Write("\nCreating project: {0} ...", projName);
ProjectCreationInformation newProj = new ProjectCreationInformation();
newProj.Id = Guid.NewGuid();
newProj.Name = projName;
newProj.Description = "Test creating a project with CSOM";
newProj.Start = DateTime.Today.Date;
// Setting the EPT GUID is optional. If no EPT is specified, Project Server uses
// the default EPT.
newProj.EnterpriseProjectTypeId = GetEptUid(basicEpt);
PublishedProject newPublishedProj = projContext.Projects.Add(newProj);
QueueJob qJob = projContext.Projects.Update();
// Calling Load and ExecuteQuery for the queue job is optional. If qJob is
// not initialized when you call WaitForQueue, Project Server initializes it.
// projContext.Load(qJob);
// projContext.ExecuteQuery();
JobState jobState = projContext.WaitForQueue(qJob, timeoutSeconds);
if (jobState == JobState.Success)
{
projCreated = true;
}
else
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow;
Console.WriteLine("\nThere is a problem in the queue. Timeout is {0} seconds.",
timeoutSeconds);
Console.WriteLine("\tQueue JobState: {0}", jobState.ToString());
Console.ResetColor();
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Red;
Console.WriteLine("\nError: {0}", ex.Message);
Console.ResetColor();
}
return projCreated;
}
// Get the GUID of the specified enterprise project type.
private static Guid GetEptUid(string eptName)
{
Guid eptUid = Guid.Empty;
try
{
// Get the list of EPTs that have the specified name.
// If the EPT name exists, the list will contain only one EPT.
var eptList = projContext.LoadQuery(
projContext.EnterpriseProjectTypes.Where(
ept => ept.Name == eptName));
projContext.ExecuteQuery();
eptUid = eptList.First().Id;
// Alternate routines to find the EPT GUID. Both (a) and (b) download the entire list of EPTs.
// (a) Using a foreach block:
//foreach (EnterpriseProjectType ept in projSvr.EnterpriseProjectTypes)
//{
// if (ept.Name == eptName)
// {
// eptUid = ept.Id;
// break;
// }
//}
// (b) Querying for the EPT list, and then using a lambda expression to select the EPT:
//var eptList = projContext.LoadQuery(projContext.EnterpriseProjectTypes);
//projContext.ExecuteQuery();
//eptUid = eptList.First(ept => ept.Name == eptName).Id;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
string msg = string.Format("GetEptUid: eptName = \"{0}\"\n\n{1}",
eptName, ex.GetBaseException().ToString());
throw new ArgumentException(msg);
}
return eptUid;
}
// List the published projects.
private static void ListPublishedProjects()
{
// Get the list of projects on the server.
projContext.Load(projContext.Projects);
projContext.ExecuteQuery();
Console.WriteLine("\nProject ID : Project name : Created date");
foreach (PublishedProject pubProj in projContext.Projects)
{
Console.WriteLine("\n\t{0} :\n\t{1} : {2}", pubProj.Id.ToString(), pubProj.Name,
pubProj.CreatedDate.ToString());
}
}
// Parse the command line. Return true if there are no errors.
private static bool ParseCommandLine(string[] args)
{
bool error = false;
int argsLen = args.Length;
try
{
for (int i = 0; i < argsLen; i++)
{
if (error) break;
if (args[i].StartsWith("-") || args[i].StartsWith("/"))
args[i] = "*" + args[i].Substring(1).ToLower();
switch (args[i])
{
case "*projname":
case "*n":
if (++i >= argsLen) return false;
projName = args[i];
break;
case "*timeout":
case "*t":
if (++i >= argsLen) return false;
timeoutSeconds = Convert.ToInt32(args[i]);
break;
case "*?":
default:
error = true;
break;
}
}
}
catch (FormatException)
{
error = true;
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(projName)) error = true;
return !error;
}
private static void Usage()
{
string example = "Usage: QueueCreateProject -projName | -n \"New project name\" [-timeout | -t sec]";
example += "\nExample: QueueCreateProject -n \"My new project\"";
example += "\nDefault timeout seconds = " + timeoutSeconds.ToString();
Console.WriteLine(example);
}
private static void ExitApp()
{
Console.Write("\nPress any key to exit... ");
Console.ReadKey(true);
Environment.Exit(0);
}
}
}