用于 Fabric 的 NotebookUtils(前 MSSparkUtils)
Notebook 实用工具 (NotebookUtils) 是一个内置包,可帮助在 Fabric Notebook 中轻松执行常见任务。 可以使用 NotebookUtils 来处理文件系统、获取环境变量、将笔记本链在一起以及处理机密。 NotebookUtils 包在 PySpark (Python) Scala、SparkR 笔记本和 Fabric 管道中可用。
注意
- MsSparkUtils 正式重命名为 NotebookUtils。 现有代码保持向后兼容,不会造成任何中断性变更。 强烈建议升级到 Notebookutils,以确保对新功能的持续支持和访问。 mssparkutils 命名空间将来会停用。
- NotebookUtils 旨在与 Spark 3.4 (Runtime v1.2) 及更高版本配合使用。 所有新功能和更新从今往后都仅受 notebookutils 命名空间支持。
文件系统实用工具
notebookutils.fs 提供用于处理各种文件系统的实用工具,包括 Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen2 和 Azure Blob 存储。 请确保正确配置对 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 和 Azure Blob 存储的访问。
运行以下命令以概要了解可用的方法:
notebookutils.fs.help()
输出
notebookutils.fs provides utilities for working with various FileSystems.
Below is overview about the available methods:
cp(from: String, to: String, recurse: Boolean = false): Boolean -> Copies a file or directory, possibly across FileSystems
fastcp(from: String, to: String, recurse: Boolean = true): Boolean -> [Preview] Copies a file or directory via azcopy, possibly across FileSystems
mv(from: String, to: String, createPath: Boolean = false, overwrite: Boolean = false): Boolean -> Moves a file or directory, possibly across FileSystems
ls(dir: String): Array -> Lists the contents of a directory
mkdirs(dir: String): Boolean -> Creates the given directory if it does not exist, also creating any necessary parent directories
put(file: String, contents: String, overwrite: Boolean = false): Boolean -> Writes the given String out to a file, encoded in UTF-8
head(file: String, maxBytes: int = 1024 * 100): String -> Returns up to the first 'maxBytes' bytes of the given file as a String encoded in UTF-8
append(file: String, content: String, createFileIfNotExists: Boolean): Boolean -> Append the content to a file
rm(dir: String, recurse: Boolean = false): Boolean -> Removes a file or directory
exists(file: String): Boolean -> Check if a file or directory exists
mount(source: String, mountPoint: String, extraConfigs: Map[String, Any]): Boolean -> Mounts the given remote storage directory at the given mount point
unmount(mountPoint: String): Boolean -> Deletes a mount point
mounts(): Array[MountPointInfo] -> Show information about what is mounted
getMountPath(mountPoint: String, scope: String = ""): String -> Gets the local path of the mount point
Use notebookutils.fs.help("methodName") for more info about a method.
NotebookUtils 以与 Spark API 相同的方式处理文件系统。 以 notebookutils.fs.mkdirs() 和 Fabric 湖屋用法为例:
| 使用情况 | HDFS 根目录的相对路径 | ABFS 文件系统的绝对路径 | 驱动程序节点中本地文件系统的绝对路径 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 非默认湖屋 | 不支持 | notebookutils.fs.mkdirs("abfss://<container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.windows.net/<new_dir>") | notebookutils.fs.mkdirs("file:/<new_dir>") |
| 默认湖屋 | “Files”或“Tables”下的目录:notebookutils.fs.mkdirs("Files/<new_dir>") | notebookutils.fs.mkdirs("abfss://<container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.windows.net/<new_dir>") | notebookutils.fs.mkdirs("file:/<new_dir>") |
列出文件
若要列出目录的内容,请使用 notebookutils.fs.ls(“你的目录路径”)。 例如:
notebookutils.fs.ls("Files/tmp") # The relatvie path may work with different base path, details in below
notebookutils.fs.ls("abfss://<container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.windows.net/<path>") # The absolute path, like: ABFS file system
notebookutils.fs.ls("file:/tmp") # The full path of the local file system of driver node
使用相对路径时,notebookutils.fs.ls() API 的行为有所不同,具体取决于笔记本的类型。
Spark 笔记本中:相对路径相对于默认的湖屋 ABFSS 路径。 例如,
notebookutils.fs.ls("Files")指向默认 Lakehouse 中的Files目录。例如:
notebookutils.fs.ls("Files/sample_datasets/public_holidays.parquet")Python 笔记本中:相对路径相对于本地文件系统的工作目录,默认情况下为 /home/trusted-service-user/work。 因此,应使用完整路径而不是相对路径
notebookutils.fs.ls("/lakehouse/default/Files")来访问默认 Lakehouse 中的Files目录。例如:
notebookutils.fs.ls("/lakehouse/default/Files/sample_datasets/public_holidays.parquet")
查看文件属性
此方法会返回文件属性,其中包括文件名、文件路径、文件大小,以及它是目录还是文件。
files = notebookutils.fs.ls('Your directory path')
for file in files:
print(file.name, file.isDir, file.isFile, file.path, file.size)
创建新目录
此方法会创建给定目录(如果不存在),并创建任何必要的父目录。
notebookutils.fs.mkdirs('new directory name')
notebookutils.fs.mkdirs("Files/<new_dir>") # works with the default lakehouse files using relative path
notebookutils.fs.ls("abfss://<container_name>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.windows.net/<new_dir>") # based on ABFS file system
notebookutils.fs.ls("file:/<new_dir>") # based on local file system of driver node
复制文件
此方法会复制文件或目录,并支持跨文件系统复制活动。
notebookutils.fs.cp('source file or directory', 'destination file or directory', True)# Set the third parameter as True to copy all files and directories recursively
注意
由于 OneLake 快捷方式 的限制,当需要使用 notebookutils.fs.cp() 从 S3/GCS 类型的快捷方式中复制数据时,建议使用挂载路径,而不是使用 abfss 路径。
高性能复制文件
这种方法提供了一种更有效的复制或移动文件的方法,特别是在处理大量数据时。 为了提高 Fabric 的性能,建议将 fastcp 用作传统 cp 方法的替代方法。
注意
notebookutils.fs.fastcp()不支持跨区域复制 OneLake 中的文件。 在本例中,可以改用notebookutils.fs.cp()。- 由于 OneLake 快捷方式的限制,当需要使用
notebookutils.fs.fastcp()从 S3/GCS 类型快捷方式复制数据时,建议使用装载的路径而不是 abfss 路径。
notebookutils.fs.fastcp('source file or directory', 'destination file or directory', True)# Set the third parameter as True to copy all files and directories recursively
预览文件内容
此方法以 UTF-8 编码的字符串形式返回给定文件的第一个“maxBytes”之前的字节。
notebookutils.fs.head('file path', maxBytes to read)
移动文件
此方法会移动文件或目录,并支持跨文件系统移动。
notebookutils.fs.mv('source file or directory', 'destination directory', True) # Set the last parameter as True to firstly create the parent directory if it does not exist
notebookutils.fs.mv('source file or directory', 'destination directory', True, True) # Set the third parameter to True to firstly create the parent directory if it does not exist. Set the last parameter to True to overwrite the updates.
写入文件
此方法将以 UTF-8 编码的给定字符串写入文件。
notebookutils.fs.put("file path", "content to write", True) # Set the last parameter as True to overwrite the file if it existed already
将内容追加到文件
此方法将以 UTF-8 编码的给定字符串追加到文件中。
notebookutils.fs.append("file path", "content to append", True) # Set the last parameter as True to create the file if it does not exist
注意
- 由于缺乏原子性保证,
notebookutils.fs.append()和notebookutils.fs.put()不支持并发写入同一文件。 - 在
for循环中使用notebookutils.fs.appendAPI 写入同一文件时,我们建议在每次重复写入之间添加大约0.5秒到1秒的sleep语句。 此建议是因为notebookutils.fs.appendAPI 的内部flush操作是异步的,因此短延迟有助于确保数据完整性。
删除文件或目录
此方法会删除文件或目录。
notebookutils.fs.rm('file path', True) # Set the last parameter as True to remove all files and directories recursively
装载/卸载目录
在文件装载和卸载中查找有关详细使用情况的更多信息。
笔记本实用工具
使用笔记本实用程序来运行笔记本或退出具有值的笔记本。 运行以下命令以概要了解可用的方法:
notebookutils.notebook.help()
输出:
The notebook module.
exit(value: String): void -> This method lets you exit a notebook with a value.
run(path: String, timeoutSeconds: int, arguments: Map, workspace: String): String -> This method runs a notebook and returns its exit value.
runMultiple(DAG: Any): Map[String, MsNotebookRunResult] -> [Preview] Runs multiple notebooks concurrently with support for dependency relationships.
validateDAG(DAG: Any): Boolean -> [Preview] This method check if the DAG is correctly defined.
[Preview] Below methods are only support Fabric Notebook.
create(name: String, description: String = "", content: String = "", defaultLakehouse: String = "", defaultLakehouseWorkspace: String = "", workspaceId: String = ""): Artifact -> Create a new Notebook.
get(name: String, workspaceId: String = ""): Artifact -> Get a Notebook by name or id.
update(name: String, newName: String, description: String = "", workspaceId: String = ""): Artifact -> Update a Artifact by name.
delete(name: String, workspaceId: String = ""): Boolean -> Delete a Notebook by name.
list(workspaceId: String = "", maxResults: Int = 1000): Array[Artifact] -> List all Notebooks in the workspace.
updateDefinition(name: String, content: String = "", defaultLakehouse: String = "", defaultLakehouseWorkspace: String = "", workspaceId: String = "") -> Update the definition of a Notebook.
Use notebookutils.notebook.help("methodName") for more info about a method.
注意
笔记本实用工具不适用于 Apache Spark 作业定义 (SJD)。
引用笔记本
此方法会引用笔记本并返回其退出值。 可以在笔记本中以交互方式或在管道中运行嵌套函数调用。 所引用的笔记本将在其调用此函数的笔记本的 Spark 池上运行。
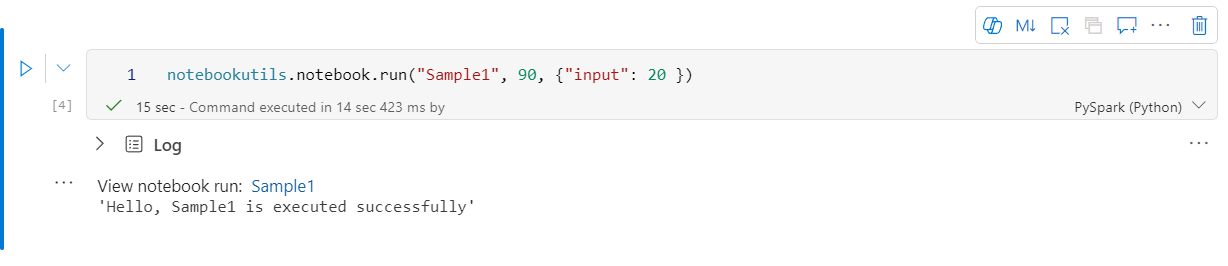
notebookutils.notebook.run("notebook name", <timeoutSeconds>, <parameterMap>, <workspaceId>)
例如:
notebookutils.notebook.run("Sample1", 90, {"input": 20 })
Fabric 笔记本还支持通过指定工作区 ID 跨多个工作区引用笔记本。
notebookutils.notebook.run("Sample1", 90, {"input": 20 }, "fe0a6e2a-a909-4aa3-a698-0a651de790aa")
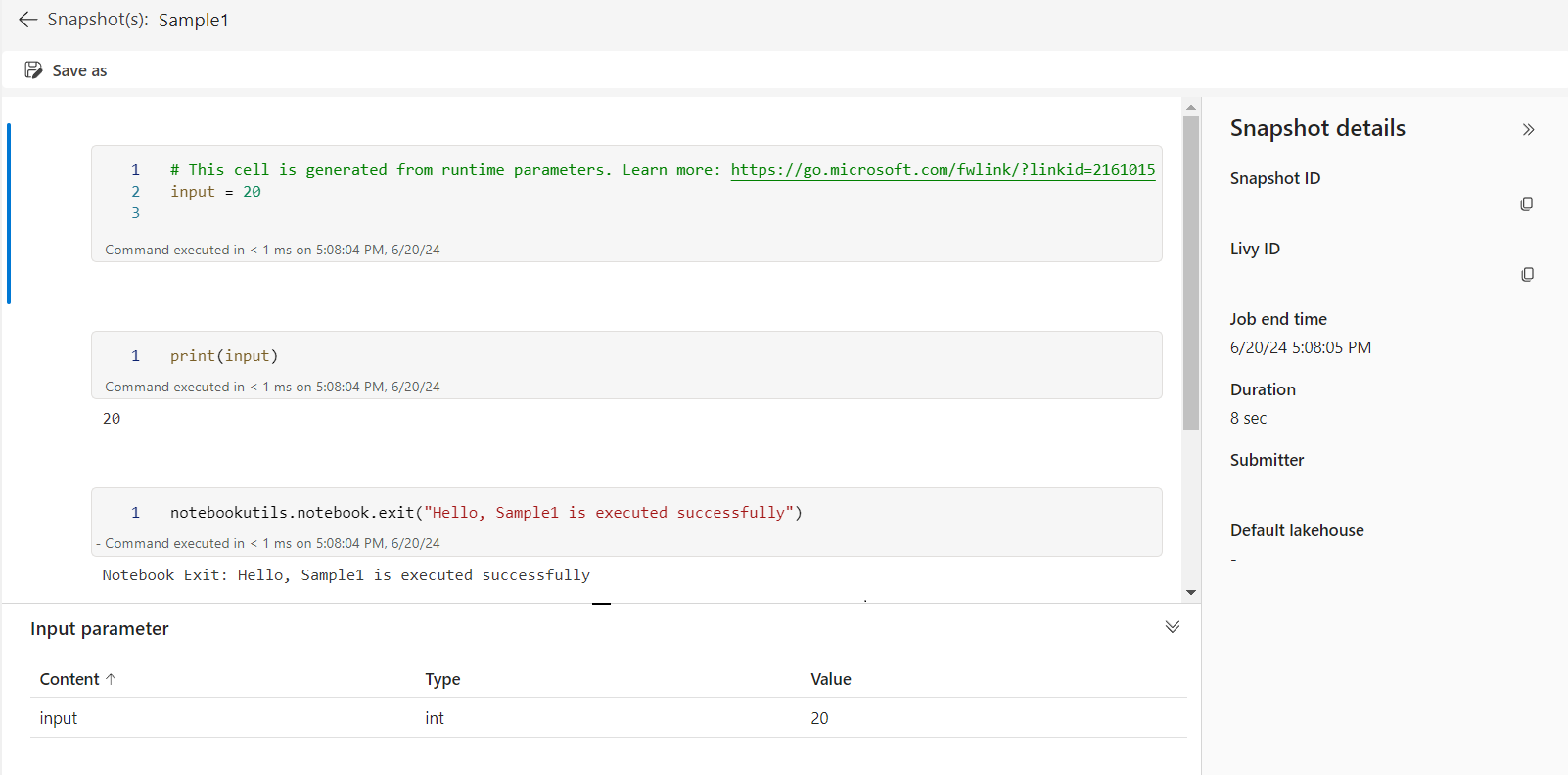
可以在单元格输出中打开引用运行的快照链接。 快照会捕获代码运行结果,并允许你轻松调试引用运行。
注意
- 运行时版本 1.2 及更高版本支持跨工作区引用笔记本。
- 如果使用笔记本资源下的文件,请在引用的笔记本中使用
notebookutils.nbResPath,以确保它指向与交互式运行相同的文件夹。
并行引用运行多个笔记本
重要
此功能目前为预览版。
notebookutils.notebook.runMultiple() 方法让你可以并行运行多个笔记本,或使用预定义的拓扑结构。 API 在 Spark 会话中使用多线程实现机制,这意味着参考笔记本运行共享计算资源。
通过 notebookutils.notebook.runMultiple(),您可以:
同时执行多个笔记本,而无需等待每个笔记本完成。
使用简单的 JSON 格式为笔记本指定依赖项和执行顺序。
优化 Spark 计算资源的使用,并降低 Fabric 项目的成本。
在输出中查看每个笔记本运行记录的快照,并方便地调试/监视笔记本任务。
获取每个执行活动的退出值,并在下游任务中使用它们。
还可以尝试运行 notebookutils.notebook.help("runMultiple") 来查找示例和详细用法。
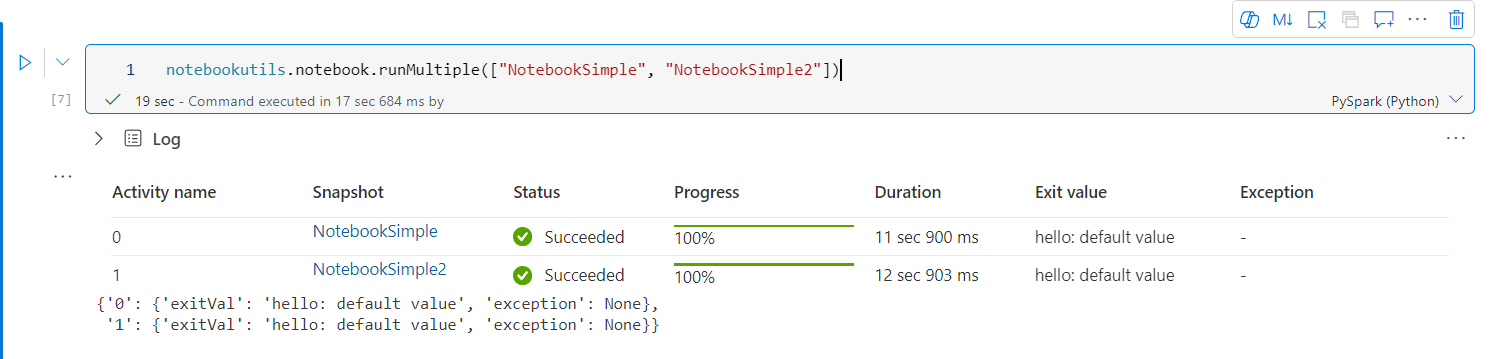
下面是使用此方法并行运行一组笔记本的简单示例:
notebookutils.notebook.runMultiple(["NotebookSimple", "NotebookSimple2"])
根笔记本中的执行结果如下所示:
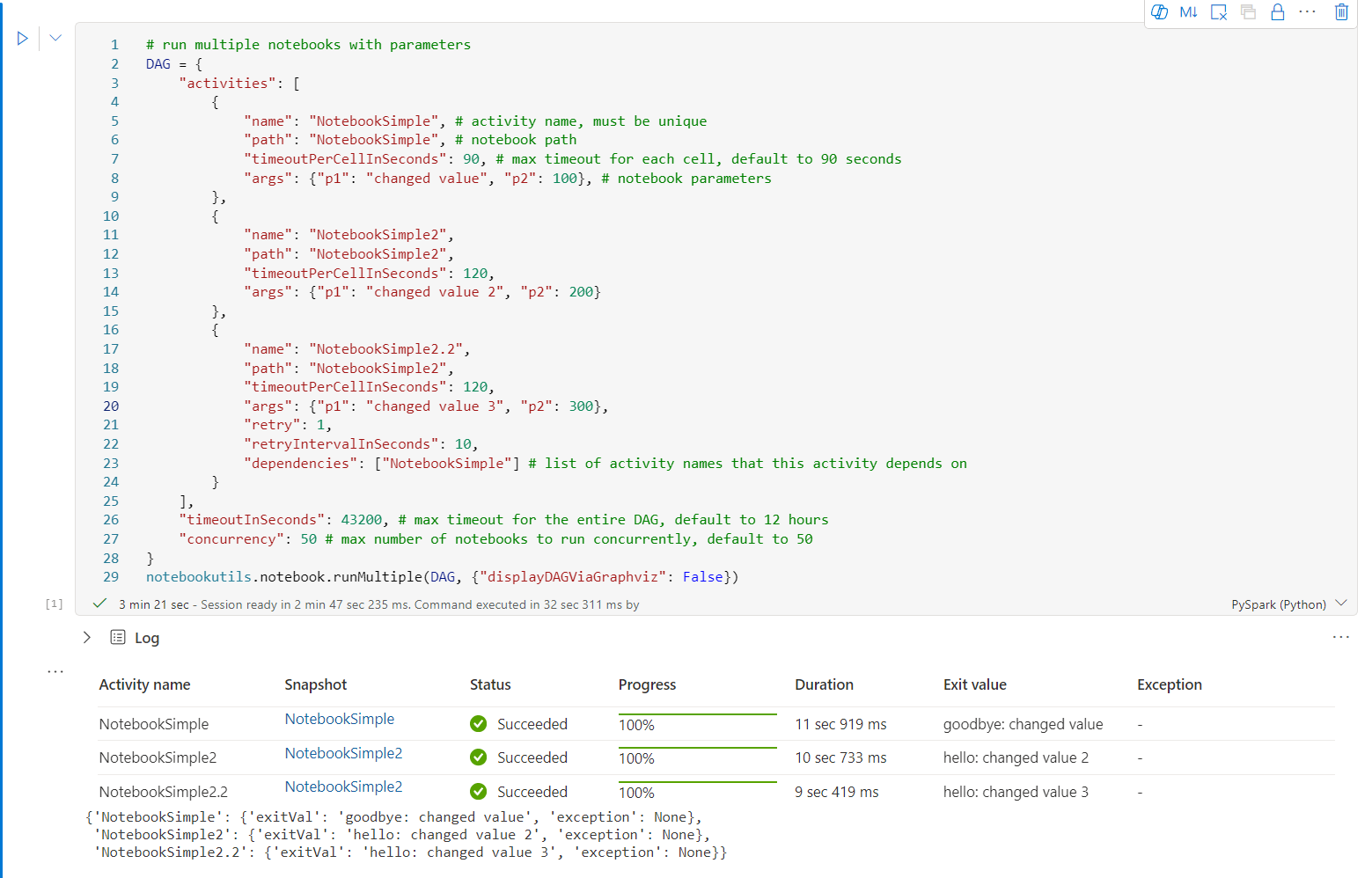
下面是使用 notebookutils.notebook.runMultiple()运行具有拓扑结构的笔记本的示例。 使用此方法通过代码体验轻松编排笔记本。
# run multiple notebooks with parameters
DAG = {
"activities": [
{
"name": "NotebookSimple", # activity name, must be unique
"path": "NotebookSimple", # notebook path
"timeoutPerCellInSeconds": 90, # max timeout for each cell, default to 90 seconds
"args": {"p1": "changed value", "p2": 100}, # notebook parameters
},
{
"name": "NotebookSimple2",
"path": "NotebookSimple2",
"timeoutPerCellInSeconds": 120,
"args": {"p1": "changed value 2", "p2": 200}
},
{
"name": "NotebookSimple2.2",
"path": "NotebookSimple2",
"timeoutPerCellInSeconds": 120,
"args": {"p1": "changed value 3", "p2": 300},
"retry": 1,
"retryIntervalInSeconds": 10,
"dependencies": ["NotebookSimple"] # list of activity names that this activity depends on
}
],
"timeoutInSeconds": 43200, # max timeout for the entire DAG, default to 12 hours
"concurrency": 50 # max number of notebooks to run concurrently, default to 50
}
notebookutils.notebook.runMultiple(DAG, {"displayDAGViaGraphviz": False})
根笔记本中的执行结果如下所示:
我们还提供了一种方法来检查 DAG 是否被正确定义。
notebookutils.notebook.validateDAG(DAG)
注意
- 多个笔记本运行的并行度受限于 Spark 会话的总可用计算资源。
- 笔记本活动或并发笔记本的上限为 50。 超出此限制可能会因计算资源使用过度而导致稳定性和性能问题。 如果出现相关问题,请考虑将笔记本拆分为多个
runMultiple调用,或者通过调整 DAG 参数中的“并发”字段来减少并发。 - 整个 DAG 的默认超时为 12 小时,子笔记本中每个单元格的默认超时时间为 90 秒。 可以通过在 DAG 参数中设置 timeoutInSeconds 和 timeoutPerCellInSeconds 字段来更改超时。
退出笔记本
此方法会退出具有值的笔记本。 可以在笔记本中以交互方式或在管道中运行嵌套函数调用。
在笔记本中以交互方式调用 exit() 函数时,Fabric 笔记将引发异常、跳过后续运行单元格,并使 Spark 会话保持活动状态。
在调用 exit() 函数的管道中协调笔记本时,笔记本活动会返回一个退出值。这会完成管道运行并停止 Spark 会话。
在所引用的笔记本中调用 exit() 函数时,Fabric Spark 将在其中停止进一步的执行,并继续运行调用 run() 函数的主笔记本中的下一个单元格。 例如:Notebook1 有三个单元格,调用第二个单元格中的 exit() 函数。 Notebook2 有五个单元格,调用第三个单元格中的 run(notebook1) 函数。 运行 Notebook2 时,如果命中 exit() 函数,Notebook1 将在第二个单元格停止。 Notebook2 会继续运行其第四和第五个单元格。
notebookutils.notebook.exit("value string")
注意
exit() 函数覆盖当前单元格输出。 为了避免丢失其他代码语句的输出,请调用单独的单元格中的 notebookutils.notebook.exit()。
例如:
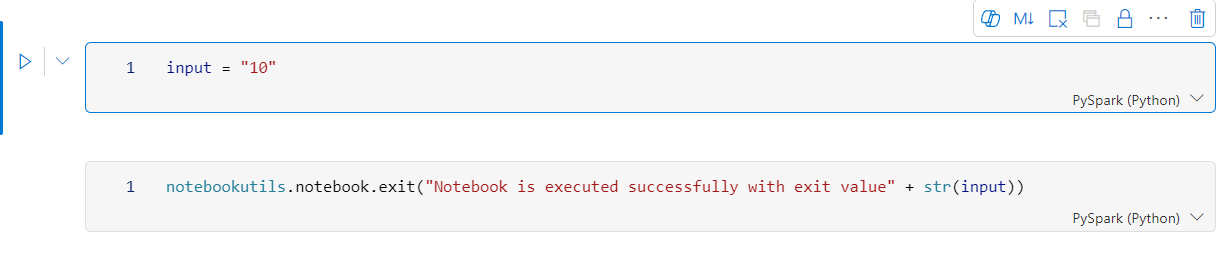
示例1 笔记本有以下两个单元格:
单元格 1 定义 input 参数,默认值设为 10。
单元格 2 退出笔记本,input 作为退出值。
可以使用默认值在另一笔记本中运行 Sample1:
exitVal = notebookutils.notebook.run("Sample1")
print (exitVal)
输出:
Notebook is executed successfully with exit value 10
可以在另一笔记本中运行 Sample1,并将 input 值设为 20 :
exitVal = notebookutils.notebook.run("Sample1", 90, {"input": 20 })
print (exitVal)
输出:
Notebook is executed successfully with exit value 20
管理笔记本项目
notebookutils.notebook 提供了用于以编程方式管理笔记本项的专用实用工具。 这些 API 可帮助轻松创建、获取、更新和删除笔记本项。
若要有效利用这些方法,请考虑以下使用情况示例:
创建笔记本
with open("/path/to/notebook.ipynb", "r") as f:
content = f.read()
artifact = notebookutils.notebook.create("artifact_name", "description", "content", "default_lakehouse_name", "default_lakehouse_workspace_id", "optional_workspace_id")
获取笔记本的内容
artifact = notebookutils.notebook.get("artifact_name", "optional_workspace_id")
更新笔记本
updated_artifact = notebookutils.notebook.update("old_name", "new_name", "optional_description", "optional_workspace_id")
updated_artifact_definition = notebookutils.notebook.updateDefinition("artifact_name", "content", "default_lakehouse_name", "default_Lakehouse_Workspace_name", "optional_workspace_id")
删除笔记本
is_deleted = notebookutils.notebook.delete("artifact_name", "optional_workspace_id")
在工作区中列出笔记本
artifacts_list = notebookutils.notebook.list("optional_workspace_id")
凭据实用工具
可以使用凭据实用工具获取访问令牌,并管理 Azure Key Vault 中的机密。
运行以下命令以概要了解可用的方法:
notebookutils.credentials.help()
输出:
Help on module notebookutils.credentials in notebookutils:
NAME
notebookutils.credentials - Utility for credentials operations in Fabric
FUNCTIONS
getSecret(akvName, secret) -> str
Gets a secret from the given Azure Key Vault.
:param akvName: The name of the Azure Key Vault.
:param secret: The name of the secret.
:return: The secret value.
getToken(audience) -> str
Gets a token for the given audience.
:param audience: The audience for the token.
:return: The token.
help(method_name=None)
Provides help for the notebookutils.credentials module or the specified method.
Examples:
notebookutils.credentials.help()
notebookutils.credentials.help("getToken")
:param method_name: The name of the method to get help with.
DATA
creds = <notebookutils.notebookutils.handlers.CredsHandler.CredsHandler...
FILE
/home/trusted-service-user/cluster-env/trident_env/lib/python3.10/site-packages/notebookutils/credentials.py
获取令牌
getToken 为给定受众和名称返回 Microsoft Entra 令牌(可选)。 以下列表显示了当前可用的受众密钥:
- 存储受众资源: "storage"
- Power BI 资源: "pbi"
- 创建 Azure 密钥保管库资源: "keyvault"
- Synapse RTA KQL DB 资源: "kusto"
运行以下命令以获取这些令牌:
notebookutils.credentials.getToken('audience Key')
使用用户凭据获取机密
getSecret 将会使用用户凭据返回给定 Azure Key Vault 端点和机密名称的 Azure Key Vault 机密。
notebookutils.credentials.getSecret('https://<name>.vault.azure.net/', 'secret name')
文件装载和卸载
Fabric 支持以下 Microsoft Spark 实用工具包中的装载方案。 可以使用 mount、unmount、getMountPath() 和 mounts() API 将远程存储 (ADLS Gen2) 附加到所有工作节点(驱动程序节点和工作器节点)。 存储装入点就位后,使用本地文件 API 访问数据,如同数据存储在本地文件系统中一样。
如何装载 ADLS Gen2 帐户
以下示例演示如何装载 Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2。 装载 Blob 存储的方式是类似的。
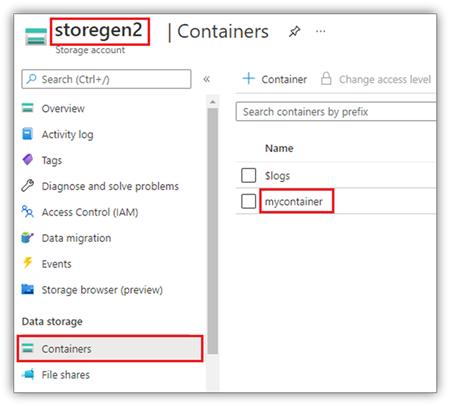
本示例假定你有一个名为 storegen2 的 Data Lake Storage Gen2 帐户,并且该帐户有一个名为 mycontainer 的容器,你希望将其装载到笔记本 Spark 会话中的 /test。
若要装载名为 mycontainer 的容器,notebookutils 首先需要检查你是否具有访问该容器的权限。 目前,Fabric 支持两种用于触发器装载操作的身份验证方法:accountKey 和 sastoken。
通过共享访问签名令牌或帐户密钥进行装载
NotebookUtils 支持将帐户密钥或共享访问签名 (SAS) 令牌作为参数显式传递以挂载目标。
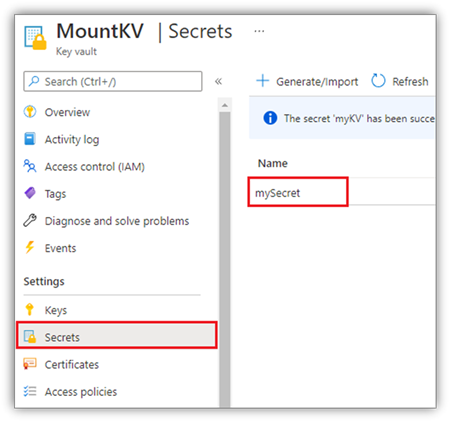
出于安全原因,建议将帐户密钥或 SAS 令牌存储在 Azure Key Vault 中(如以下屏幕截图所示)。 可以使用 notebookutils.credentials.getSecret API 来检索它们。 有关 Azure Key Vault 的详细信息,请参阅关于 Azure Key Vault 托管存储帐户密钥。
accountKey 方法的示例代码:
# get access token for keyvault resource
# you can also use full audience here like https://vault.azure.net
accountKey = notebookutils.credentials.getSecret("<vaultURI>", "<secretName>")
notebookutils.fs.mount(
"abfss://mycontainer@<accountname>.dfs.core.windows.net",
"/test",
{"accountKey":accountKey}
)
sastoken 的示例代码:
# get access token for keyvault resource
# you can also use full audience here like https://vault.azure.net
sasToken = notebookutils.credentials.getSecret("<vaultURI>", "<secretName>")
notebookutils.fs.mount(
"abfss://mycontainer@<accountname>.dfs.core.windows.net",
"/test",
{"sasToken":sasToken}
)
装载参数:
- fileCacheTimeout:默认情况下,Blob 在本地临时文件夹中缓存 120 秒。 在此期间,blobfuse 不会检查文件是否是最新的。 可以设置参数以更改默认超时时间。 当多个客户端同时修改文件时,为了避免本地和远程文件之间的不一致,我们建议缩短缓存时间,甚至将其更改为 0,并且始终从服务器获取最新文件。
- 超时:默认情况下,装载操作超时为 120 秒。 可以设置参数以更改默认超时时间。 当执行程序过多或装载超时时,建议增加值。
可以使用如下所示的这些参数:
notebookutils.fs.mount(
"abfss://mycontainer@<accountname>.dfs.core.windows.net",
"/test",
{"fileCacheTimeout": 120, "timeout": 120}
)
注意
出于安全考虑,建议避免将凭据直接嵌入代码中。 为了进一步保护您的凭据,笔记本输出中显示的任何机密都会被隐藏。 有关详细信息,请查看机密编修。
如何装载湖屋
将湖屋装载到 /<mount_name> 的示例代码:
notebookutils.fs.mount(
"abfss://<workspace_name>@onelake.dfs.fabric.microsoft.com/<lakehouse_name>.Lakehouse",
"/<mount_name>"
)
使用 notebookutils fs API 访问装入点下的文件
装载操作的主要目的是让客户能够使用本地文件系统 API 访问远程存储帐户中存储的数据。 也可以使用 notebookutils fs API 以装载路径作为参数来访问数据。 此路径格式稍有不同。
假设已使用装载 API 将 Data Lake Storage Gen2 容器 mycontainer 装载到 /test。 当你使用本地文件系统 API 访问数据时,路径格式如下所示:
/synfs/notebook/{sessionId}/test/{filename}
如果要使用 notebookutils fs API 访问数据,建议使用 getMountPath() 获取准确路径:
path = notebookutils.fs.getMountPath("/test")
列出目录:
notebookutils.fs.ls(f"file://{notebookutils.fs.getMountPath('/test')}")读取文件内容:
notebookutils.fs.head(f"file://{notebookutils.fs.getMountPath('/test')}/myFile.txt")创建目录:
notebookutils.fs.mkdirs(f"file://{notebookutils.fs.getMountPath('/test')}/newdir")
通过本地路径访问装载点下的文件
可以使用标准文件系统在装载点中轻松读取和写入文件。 下面是 Python 示例:
#File read
with open(notebookutils.fs.getMountPath('/test2') + "/myFile.txt", "r") as f:
print(f.read())
#File write
with open(notebookutils.fs.getMountPath('/test2') + "/myFile.txt", "w") as f:
print(f.write("dummy data"))
如何检查现有装入点
可以使用 notebookutils.fs.mounts() API 来检查所有现有装入点信息:
notebookutils.fs.mounts()
如何卸载装入点
使用以下代码可卸载装入点(在此示例中为 /test):
notebookutils.fs.unmount("/test")
已知限制
当前装载是作业级别的配置,建议使用 mounts API 来检查装入点是否存在或不可用。
卸载机制不是自动应用的。 应用程序运行完成后,若要卸载装入点并释放磁盘空间,需要在代码中显式调用卸载 API。 否则,应用程序运行完成后,装入点仍会存在于节点中。
不支持装载 ADLS Gen1 存储帐户。
Lakehouse 实用工具
notebookutils.lakehouse 提供专为管理 Lakehouse 项目而定制的实用工具。 这些实用工具使你能够轻松创建、获取、更新和删除 Lakehouse 项目。
方法概述
下面是 notebookutils.lakehouse提供的可用方法的概述:
# Create a new Lakehouse artifact
create(name: String, description: String = "", definition: ItemDefinition = null, workspaceId: String = ""): Artifact
# Retrieve a Lakehouse artifact
get(name: String, workspaceId: String = ""): Artifact
# Get a Lakehouse artifact with properties
getWithProperties(name: String, workspaceId: String = ""): Artifact
# Update an existing Lakehouse artifact
update(name: String, newName: String, description: String = "", workspaceId: String = ""): Artifact
# Delete a Lakehouse artifact
delete(name: String, workspaceId: String = ""): Boolean
# List all Lakehouse artifacts
list(workspaceId: String = "", maxResults: Int = 1000): Array[Artifact]
# List all tables in a Lakehouse artifact
listTables(lakehouse: String, workspaceId: String = "", maxResults: Int = 1000): Array[Table]
# Starts a load table operation in a Lakehouse artifact
loadTable(loadOption: collection.Map[String, Any], table: String, lakehouse: String, workspaceId: String = ""): Array[Table]
用法示例
若要有效利用这些方法,请考虑以下使用情况示例:
创建湖屋
artifact = notebookutils.lakehouse.create("artifact_name", "Description of the artifact", "optional_workspace_id")
获取湖屋
artifact = notebookutils.lakehouse.get("artifact_name", "optional_workspace_id")
artifact = notebookutils.lakehouse.getWithProperties("artifact_name", "optional_workspace_id")
更新湖屋
updated_artifact = notebookutils.lakehouse.update("old_name", "new_name", "Updated description", "optional_workspace_id")
删除湖屋
is_deleted = notebookutils.lakehouse.delete("artifact_name", "optional_workspace_id")
列出工作区中的湖屋
artifacts_list = notebookutils.lakehouse.list("optional_workspace_id")
列出湖屋中的所有表
artifacts_tables_list = notebookutils.lakehouse.listTables("artifact_name", "optional_workspace_id")
在湖屋中启动加载表操作
notebookutils.lakehouse.loadTable(
{
"relativePath": "Files/myFile.csv",
"pathType": "File",
"mode": "Overwrite",
"recursive": False,
"formatOptions": {
"format": "Csv",
"header": True,
"delimiter": ","
}
}, "table_name", "artifact_name", "optional_workspace_id")
其他信息
有关每个方法及其参数的更详细信息,请使用 notebookutils.lakehouse.help("methodName") 函数。
运行时实用工具
显示会话上下文信息
借助 notebookutils.runtime.context,可以获取当前实时会话的上下文信息,包括笔记本名称、默认 Lakehouse、工作区信息、是否是管道运行等。
notebookutils.runtime.context
会话管理
停止交互式会话
有时通过在代码中调用 API 来停止交互式会话更方便,而不是手动单击停止按钮。 对于此类情况,我们提供 API notebookutils.session.stop() 来支持通过代码停止交互式会话,它可用于 Scala 和 PySpark。
notebookutils.session.stop()
notebookutils.session.stop() API 在后台异步停止当前交互式会话。 它还会停止 Spark 会话并释放会话占用的资源,因此它们可用于同一池中的其他会话。
重启 Python 解释器
notebookutils.session 实用工具提供了重启 Python 解释器的方法。
notebookutils.session.restartPython()
注意
- 在笔记本引用运行案例中,
restartPython()仅重启所引用的当前笔记本的 Python 解释器。 - 在极少数情况下,由于 Spark 反射机制,命令可能会失败,添加重试可以缓解问题。
已知问题
使用 1.2 以上的运行时版本并运行
notebookutils.help()时,列出的 fabricClient、PBIClient API 目前不支持,将在后续版本中提供。 此外,Scala 笔记本目前不支持凭据 API。Python 笔记本在使用 notebookutils.session 实用工具进行会话管理时,不支持 停止和 重启Python API。