教程:在 ML.NET 中使用预先训练的 TensorFlow 模型分析电影评论的情绪
本教程介绍如何使用预先训练的 TensorFlow 模型对网站评论中的情绪进行分类。 二进制情绪分类器是使用 Visual Studio 开发的 C# 控制台应用程序。
本教程中使用的 TensorFlow 模型是使用 IMDB 数据库中的电影评论训练的。 完成应用程序开发后,你将能够提供电影评论文本,应用程序将告诉你评论是否有正面或负面情绪。
在本教程中,您将学习如何:
- 加载预先训练的 TensorFlow 模型
- 将网站注释文本转换为适合模型的功能
- 使用模型进行预测
可以在 dotnet/samples 存储库中找到本教程的源代码。
先决条件
- 安装了“.NET 桌面开发”工作负荷的 Visual Studio 2022。
安装
创建应用程序
创建名为“TextClassificationTF”的 C# 控制台应用程序。 单击下一步 按钮。
选择 .NET 8 作为要使用的框架。 单击“创建”按钮。
在项目中创建名为 Data 的目录以保存数据集文件。
安装 Microsoft.ML NuGet 包:
注意
此示例使用提到的 NuGet 包的最新稳定版本,除非另有说明。
在“解决方案资源管理器”中,右键单击项目,然后选择“管理 NuGet 包”。 选择“nuget.org”作为包源,然后选择“浏览”选项卡。搜索 Microsoft.ML,选择所需的包,然后选择 安装。 同意所选包的许可条款,继续执行安装。 对 Microsoft.ML.TensorFlow、Microsoft.ML.SampleUtils 和 SciSharp.TensorFlow.Redist重复这些步骤。
将 TensorFlow 模型添加到项目
注意
本教程的模型来自 dotnet/machinelearning-testdata GitHub 存储库。 该模型采用 TensorFlow SavedModel 格式。
下载 sentiment_model zip 文件,然后解压缩。
zip 文件包含:
saved_model.pb:TensorFlow 模型本身。 该模型接受一个固定长度(大小为 600)的整数数组,这些数组代表 IMDB 影评字符串中的文本,输出两个概率,总和为 1:即输入影评具有正面情感的概率和具有负面情感的概率。imdb_word_index.csv:从单个单词到整数值的映射。 该映射用于生成 TensorFlow 模型的输入特征。
将最内部
sentiment_model目录的内容复制到 TextClassificationTF 项目sentiment_model目录中。 此目录包含本教程所需的模型和其他支持文件,如下图所示: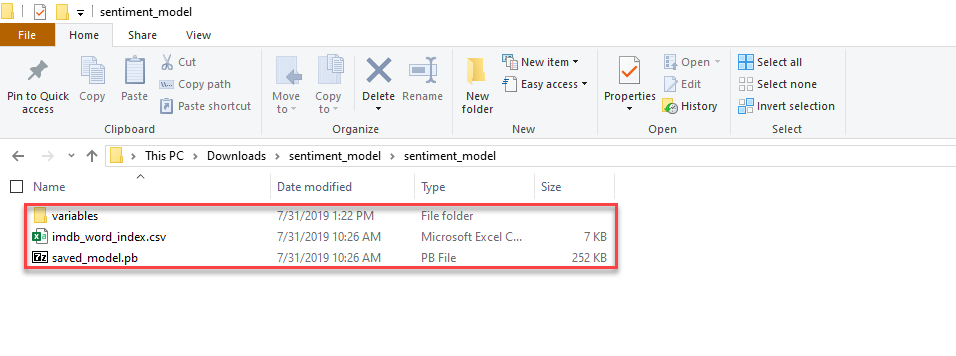
在解决方案资源管理器中,右键单击
sentiment_model目录和子目录中的每个文件,然后选择 属性。 在“高级”下,将“复制到输出目录”的值更改为“如果较新则复制”。
添加 using 指令和全局变量
将以下附加
using指令添加到 Program.cs 文件的顶部:using Microsoft.ML; using Microsoft.ML.Data; using Microsoft.ML.Transforms;在
using指令后面创建全局变量,以保存保存的模型文件路径。string _modelPath = Path.Combine(Environment.CurrentDirectory, "sentiment_model");_modelPath是已训练模型的文件路径。
为数据建模
电影评论是自由格式的文本。 应用程序将文本转换为模型在多个离散阶段中预期的输入格式。
第一个是将文本拆分为单独的单词,并使用提供的映射文件将每个单词映射到整数编码。 此转换的结果是一个可变长度整数数组,其长度对应于句子中的单词数。
| 财产 | 值 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| ReviewText | 这部电影真好 | 字符串 |
| VariableLengthFeatures | 14,22,9,66,78,... | int[] |
然后将可变长度特征数组的大小调整为固定长度 600。 这是 TensorFlow 模型期望的长度。
| 财产 | 值 | 类型 |
|---|---|---|
| ReviewText | 这部电影真好 | 字符串 |
| VariableLengthFeatures | 14,22,9,66,78,... | int[] |
| 功能 | 14,22,9,66,78,... | int[600] |
在 Program.cs 文件底部为输入数据创建一个类:
/// <summary> /// Class to hold original sentiment data. /// </summary> public class MovieReview { public string? ReviewText { get; set; } }输入数据类
MovieReview具有用于用户评论 (ReviewText) 的string。为
MovieReview类后面的可变长度特征创建类:/// <summary> /// Class to hold the variable length feature vector. Used to define the /// column names used as input to the custom mapping action. /// </summary> public class VariableLength { /// <summary> /// This is a variable length vector designated by VectorType attribute. /// Variable length vectors are produced by applying operations such as 'TokenizeWords' on strings /// resulting in vectors of tokens of variable lengths. /// </summary> [VectorType] public int[]? VariableLengthFeatures { get; set; } }VariableLengthFeatures属性具有 VectorType 属性,将其指定为向量。 所有向量元素都必须是同一类型。 在包含大量列的数据集中,将多个列加载为单个向量可减少应用数据转换时传递的数据数。此类在
ResizeFeatures操作中使用。 它的属性名称(本例中只有一个)用于指示 DataView 中的哪些列可用作自定义映射操作的输入。在
VariableLength类之后,为固定长度特征创建类:/// <summary> /// Class to hold the fixed length feature vector. Used to define the /// column names used as output from the custom mapping action, /// </summary> public class FixedLength { /// <summary> /// This is a fixed length vector designated by VectorType attribute. /// </summary> [VectorType(Config.FeatureLength)] public int[]? Features { get; set; } }此类在
ResizeFeatures操作中使用。 它的属性名称(本例中只有一个)用于指示 DataView 中的哪些列可用作自定义映射操作的输出。请注意,属性
Features的名称由 TensorFlow 模型确定。 不能更改此属性名称。在
FixedLength类之后,为预测功能创建一个类:/// <summary> /// Class to contain the output values from the transformation. /// </summary> public class MovieReviewSentimentPrediction { [VectorType(2)] public float[]? Prediction { get; set; } }MovieReviewSentimentPrediction是模型训练后使用的预测类。MovieReviewSentimentPrediction具有单个float数组(Prediction)和VectorType属性。创建另一个类来保存配置值,例如特征向量长度:
static class Config { public const int FeatureLength = 600; }
创建 MLContext、查找字典以及用于调整特征大小的操作
MLContext 类 是所有 ML.NET 操作的起点。 初始化 mlContext 创建一个新的 ML.NET 环境,可在模型创建工作流对象之间共享。 从概念上讲,它类似于实体框架中的 DBContext。
将
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!")行替换为以下代码来声明和初始化 mlContext 变量:MLContext mlContext = new MLContext();使用
LoadFromTextFile方法从文件加载映射数据,创建一个字典,以将单词编码为整数,如下表所示:Word Index 孩子 362 want 181 wrong 355 影响 302 feeling 547 添加下面的代码,创建查找映射:
var lookupMap = mlContext.Data.LoadFromTextFile(Path.Combine(_modelPath, "imdb_word_index.csv"), columns: new[] { new TextLoader.Column("Words", DataKind.String, 0), new TextLoader.Column("Ids", DataKind.Int32, 1), }, separatorChar: ',' );添加一个
Action,将可变长度字整数数组的大小调整为固定大小的整数数组,并添加下一行代码:Action<VariableLength, FixedLength> ResizeFeaturesAction = (s, f) => { var features = s.VariableLengthFeatures; Array.Resize(ref features, Config.FeatureLength); f.Features = features; };
加载预先训练的 TensorFlow 模型
添加代码以加载 TensorFlow 模型:
TensorFlowModel tensorFlowModel = mlContext.Model.LoadTensorFlowModel(_modelPath);加载模型后,可以提取其输入和输出架构。 这些模式仅供兴趣和学习之用。 对于最终应用程序,不需要此代码才能运行:
DataViewSchema schema = tensorFlowModel.GetModelSchema(); Console.WriteLine(" =============== TensorFlow Model Schema =============== "); var featuresType = (VectorDataViewType)schema["Features"].Type; Console.WriteLine($"Name: Features, Type: {featuresType.ItemType.RawType}, Size: ({featuresType.Dimensions[0]})"); var predictionType = (VectorDataViewType)schema["Prediction/Softmax"].Type; Console.WriteLine($"Name: Prediction/Softmax, Type: {predictionType.ItemType.RawType}, Size: ({predictionType.Dimensions[0]})");输入架构是整数编码单词的固定长度数组。 输出架构是一个浮点数数组,指示评审的情绪是负面的还是积极的。 这些值总和为 1,因为正的概率是情绪为负的概率的补充。
创建 ML.NET 管道
创建管道并使用 TokenizeIntoWords 转换将输入文本拆分为单词,从而将文本拆分为单词以作为下一行代码:
IEstimator<ITransformer> pipeline = // Split the text into individual words mlContext.Transforms.Text.TokenizeIntoWords("TokenizedWords", "ReviewText")TokenizeIntoWords 转换使用空格将文本/字符串分析为单词。 它创建一个新列,并根据用户定义的分隔符将每个输入字符串拆分为子字符串的向量。
使用你在上面声明的查找表将单词映射到其整数编码:
// Map each word to an integer value. The array of integer makes up the input features. .Append(mlContext.Transforms.Conversion.MapValue("VariableLengthFeatures", lookupMap, lookupMap.Schema["Words"], lookupMap.Schema["Ids"], "TokenizedWords"))将可变长度整数编码调整为模型所需的固定长度编码:
// Resize variable length vector to fixed length vector. .Append(mlContext.Transforms.CustomMapping(ResizeFeaturesAction, "Resize"))使用加载的 TensorFlow 模型对输入进行分类:
// Passes the data to TensorFlow for scoring .Append(tensorFlowModel.ScoreTensorFlowModel("Prediction/Softmax", "Features"))TensorFlow 模型输出称为
Prediction/Softmax。 请注意,名称Prediction/Softmax由 TensorFlow 模型确定。 无法更改此名称。为输出预测创建新列:
// Retrieves the 'Prediction' from TensorFlow and copies to a column .Append(mlContext.Transforms.CopyColumns("Prediction", "Prediction/Softmax"));需要将
Prediction/Softmax列复制到一个新列中,该新列的名称可用作 C# 类的属性:Prediction。 C# 属性名称中不允许/字符。
从管道创建 ML.NET 模型
添加代码以从管道创建模型:
// Create an executable model from the estimator pipeline IDataView dataView = mlContext.Data.LoadFromEnumerable(new List<MovieReview>()); ITransformer model = pipeline.Fit(dataView);通过调用
Fit方法,从管道中的估算器链创建 ML.NET 模型。 在这种情况下,你无法拟合任何数据来创建模型,因为 TensorFlow 模型以前已经训练过。 提供空数据视图对象以满足Fit方法的要求。
使用模型进行预测
在
MovieReview类上方添加PredictSentiment方法:void PredictSentiment(MLContext mlContext, ITransformer model) { }添加以下代码以创建
PredictionEngine作为PredictSentiment()方法中的第一行:var engine = mlContext.Model.CreatePredictionEngine<MovieReview, MovieReviewSentimentPrediction>(model);PredictionEngine 是一种方便的 API,可用于对单个数据实例执行预测。
PredictionEngine不是线程安全的。 可以在单线程或原型环境中使用。 为了提高生产环境中的性能和线程安全性,请使用PredictionEnginePool服务,该服务可创建PredictionEngine对象的ObjectPool,以便在应用程序中使用。 请参阅本指南,了解如何在 ASP.NET Core Web API中使用 。 注意
PredictionEnginePool服务扩展目前为预览版。通过创建
MovieReview实例,添加注释以在Predict()方法中测试定型模型的预测:var review = new MovieReview() { ReviewText = "this film is really good" };通过在
PredictSentiment()方法中添加下一行代码,将测试注释数据传递给Prediction Engine:var sentimentPrediction = engine.Predict(review);Predict() 函数对单行数据进行预测:
财产 值 类型 预测 [0.5459937, 0.454006255] float[] 使用以下代码显示情绪预测:
Console.WriteLine($"Number of classes: {sentimentPrediction.Prediction?.Length}"); Console.WriteLine($"Is sentiment/review positive? {(sentimentPrediction.Prediction?[1] > 0.5 ? "Yes." : "No.")}");在调用
Fit()方法后添加对PredictSentiment的调用:PredictSentiment(mlContext, model);
结果
生成并运行应用程序。
结果应如下所示。 在处理过程中,将显示消息。 你可能会看到警告或处理消息。 为了清楚起见,这些消息已从以下结果中删除。
Number of classes: 2
Is sentiment/review positive ? Yes
祝贺! 现在,你已通过在 ML.NET 中重用预先训练的 TensorFlow 模型,成功构建了一个机器学习模型,用于对消息情绪进行分类和预测。
可以在 dotnet/samples 存储库中找到本教程的源代码。
在本教程中,你将学习如何:
- 加载预先训练的 TensorFlow 模型
- 将网站注释文本转换为适合模型的功能
- 使用模型进行预测
