命名实参和可选实参(C# 编程指南)
通过命名实参,你可以为形参指定实参,方法是将实参与该形参的名称匹配,而不是与形参在形参列表中的位置匹配。 通过可选参数,你可以为某些形参省略实参。 这两种技术都可与方法、索引器、构造函数和委托一起使用。
使用命名参数和可选参数时,将按实参出现在实参列表(而不是形参列表)中的顺序计算这些实参。
通过命名形参和可选形参,你可以为所选形参提供实参。 此功能极大地方便了对 COM 接口(例如 Microsoft Office 自动化 API)的调用。
命名参数
有了命名实参,你将不再需要将实参的顺序与所调用方法的形参列表中的形参顺序相匹配。 每个形参的实参都可按形参名称进行指定。 例如,打印订单详细信息(如卖家名称、订单号和产品名称)的函数可以通过按位置发送参数来调用,该函数定义的顺序。
PrintOrderDetails("Gift Shop", 31, "Red Mug");
如果不记得形参的顺序,但却知道其名称,则可以按任意顺序发送实参。
PrintOrderDetails(orderNum: 31, productName: "Red Mug", sellerName: "Gift Shop");
PrintOrderDetails(productName: "Red Mug", sellerName: "Gift Shop", orderNum: 31);
命名实参还可以标识每个实参所表示的含义,从而改进代码的可读性。 在下面的示例方法中,sellerName 不得为 NULL 或空白符。 由于 sellerName 和 productName 都是字符串类型,所以使用命名实参而不是按位置发送实参是有意义的,可以区分这两种类型并减少代码阅读者的困惑。
当命名实参与位置实参一起使用时,只要
没有后接任何位置实参或
PrintOrderDetails("Gift Shop", 31, productName: "Red Mug");它们用在正确位置。 在以下示例中,形参
orderNum位于正确的位置,但未显式命名。PrintOrderDetails(sellerName: "Gift Shop", 31, productName: "Red Mug");
遵循任何无序命名参数的位置参数无效。
// This generates CS1738: Named argument specifications must appear after all fixed arguments have been specified.
PrintOrderDetails(productName: "Red Mug", 31, "Gift Shop");
示例
以下代码执行本节以及某些其他节中的示例。
class NamedExample
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// The method can be called in the normal way, by using positional arguments.
PrintOrderDetails("Gift Shop", 31, "Red Mug");
// Named arguments can be supplied for the parameters in any order.
PrintOrderDetails(orderNum: 31, productName: "Red Mug", sellerName: "Gift Shop");
PrintOrderDetails(productName: "Red Mug", sellerName: "Gift Shop", orderNum: 31);
// Named arguments mixed with positional arguments are valid
// as long as they are used in their correct position.
PrintOrderDetails("Gift Shop", 31, productName: "Red Mug");
PrintOrderDetails(sellerName: "Gift Shop", 31, productName: "Red Mug");
PrintOrderDetails("Gift Shop", orderNum: 31, "Red Mug");
// However, mixed arguments are invalid if used out-of-order.
// The following statements will cause a compiler error.
// PrintOrderDetails(productName: "Red Mug", 31, "Gift Shop");
// PrintOrderDetails(31, sellerName: "Gift Shop", "Red Mug");
// PrintOrderDetails(31, "Red Mug", sellerName: "Gift Shop");
}
static void PrintOrderDetails(string sellerName, int orderNum, string productName)
{
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(sellerName))
{
throw new ArgumentException(message: "Seller name cannot be null or empty.", paramName: nameof(sellerName));
}
Console.WriteLine($"Seller: {sellerName}, Order #: {orderNum}, Product: {productName}");
}
}
可选自变量
方法、构造函数、索引器或委托的定义可以指定其形参为必需还是可选。 任何调用都必须为所有必需的形参提供实参,但可以为可选的形参省略实参。 可为空的引用类型(T?)允许参数显式化为null,但本质上并不会使参数成为可选的。
每个可选形参都有一个默认值作为其定义的一部分。 如果没有为该形参发送实参,则使用默认值。 默认值必须是以下类型的表达式之一:
- 常量表达式;
new ValType()形式的表达式,其中ValType是值类型,例如 enum 或 struct;- default(ValType) 形式的表达式,其中
ValType是值类型。
可选参数定义于参数列表的末尾和必需参数之后。 调用方必须为所有必需的参数和它指定的参数前面的任何可选参数提供参数。 参数列表中的逗号分隔间隙不受支持。例如,在以下代码中,实例方法 ExampleMethod 使用一个必需参数和两个可选参数定义。
public void ExampleMethod(int required, string optionalstr = "default string",
int optionalint = 10)
下面对 ExampleMethod 的调用会导致编译器错误,原因是为第三个形参而不是为第二个形参提供了实参。
// anExample.ExampleMethod(3, ,4);
但是,如果知道第三个形参的名称,则可以使用命名实参来完成此任务。
anExample.ExampleMethod(3, optionalint: 4);
IntelliSense 使用括号表示可选形参,如下图所示:
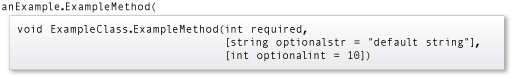
注意
此外,还可通过使用 .NET OptionalAttribute 类声明可选参数。 OptionalAttribute 形参不需要默认值。 但是,如果需要默认值,请查看 DefaultParameterValueAttribute 类。
示例
在以下示例中,ExampleClass 的构造函数具有一个可选形参。 实例方法 ExampleMethod 具有一个必选形参(required)和两个可选形参(optionalstr 和 optionalint)。 Main 中的代码演示了可用于调用构造函数和方法的不同方式。
namespace OptionalNamespace
{
class OptionalExample
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Instance anExample does not send an argument for the constructor's
// optional parameter.
ExampleClass anExample = new ExampleClass();
anExample.ExampleMethod(1, "One", 1);
anExample.ExampleMethod(2, "Two");
anExample.ExampleMethod(3);
// Instance anotherExample sends an argument for the constructor's
// optional parameter.
ExampleClass anotherExample = new ExampleClass("Provided name");
anotherExample.ExampleMethod(1, "One", 1);
anotherExample.ExampleMethod(2, "Two");
anotherExample.ExampleMethod(3);
// The following statements produce compiler errors.
// An argument must be supplied for the first parameter, and it
// must be an integer.
//anExample.ExampleMethod("One", 1);
//anExample.ExampleMethod();
// You cannot leave a gap in the provided arguments.
//anExample.ExampleMethod(3, ,4);
//anExample.ExampleMethod(3, 4);
// You can use a named parameter to make the previous
// statement work.
anExample.ExampleMethod(3, optionalint: 4);
}
}
class ExampleClass
{
private string _name;
// Because the parameter for the constructor, name, has a default
// value assigned to it, it is optional.
public ExampleClass(string name = "Default name")
{
_name = name;
}
// The first parameter, required, has no default value assigned
// to it. Therefore, it is not optional. Both optionalstr and
// optionalint have default values assigned to them. They are optional.
public void ExampleMethod(int required, string optionalstr = "default string",
int optionalint = 10)
{
Console.WriteLine(
$"{_name}: {required}, {optionalstr}, and {optionalint}.");
}
}
// The output from this example is the following:
// Default name: 1, One, and 1.
// Default name: 2, Two, and 10.
// Default name: 3, default string, and 10.
// Provided name: 1, One, and 1.
// Provided name: 2, Two, and 10.
// Provided name: 3, default string, and 10.
// Default name: 3, default string, and 4.
}
前面的代码演示了以下几种情况:正确和错误地使用了可选参数。 必须为所有必需参数提供参数。 可选参数中的间隙必须用命名参数填充。
调用方信息属性
调用方信息属性(例如 CallerFilePathAttribute、CallerLineNumberAttribute、CallerMemberNameAttribute 和 CallerArgumentExpressionAttribute)用于获取方法调用方的相关信息。 在调试或需要记录有关方法调用的信息时,这些属性特别有用。
这些属性是具有编译器提供的默认值的可选参数。 调用方不应为这些参数显式提供值。
COM 接口
命名实参和可选实参,以及对动态对象的支持大大提高了与 COM API(例如 Office Automation API)的互操作性。
例如,Microsoft Office Excel 的 AutoFormat 接口中的 Range 方法有七个可选形参。 这些形参如下图所示:

但是,可以通过使用命名实参和可选实参来大大简化对 AutoFormat 的调用。 如果不希望更改形参的默认值,则可以通过使用命名实参和可选实参来省略可选形参的实参。 在下面的调用中,仅为 7 个形参中的其中一个指定了值。
var excelApp = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.Application();
excelApp.Workbooks.Add();
excelApp.Visible = true;
var myFormat =
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel.XlRangeAutoFormat.xlRangeAutoFormatAccounting1;
excelApp.Range["A1", "B4"].AutoFormat( Format: myFormat );
有关详细信息和示例,请参阅如何在 Office 编程中使用命名参数和可选参数和如何使用 C# 功能访问 Office 互操作性对象。
重载决策
使用命名实参和可选实参将在以下方面对重载决策产生影响:
- 如果方法、索引器或构造函数的每个参数是可选的,或按名称或位置对应于调用语句中的单个自变量,且该自变量可转换为参数的类型,则方法、索引器或构造函数为执行的候选项。
- 如果找到多个候选项,则会将用于首选转换的重载决策规则应用于显式指定的自变量。 将忽略可选形参已省略的实参。
- 如果两个候选项不相上下,则会将没有可选形参的候选项作为首选项,对于这些可选形参,已在调用中为其省略了实参。 重载决策通常首选具有较少形参的候选项。
C# 语言规范
有关详细信息,请参阅 C# 语言规范。 该语言规范是 C# 语法和用法的权威资料。
