收集指标
本文适用范围:✔️ .NET Core 3.1 及更高版本 ✔️ .NET Framework 4.6.1 及更高版本
检测的代码可以记录数值度量值,但通常需要聚合、传输和存储度量值,以创建用于监视的有用指标。 聚合、传输和存储数据的过程称为集合。 本教程演示收集指标的几个示例:
- 使用 OpenTelemetry 和 Prometheus 在 Grafana 中填充指标。
- 使用
dotnet-counters实时查看指标 - 使用基础 .NET MeterListener API 创建自定义集合工具。
有关自定义指标检测和选项的详细信息,请参阅比较指标 API。
先决条件
- .NET Core 3.1 SDK 或更高版本
创建示例应用
必须先生成度量值,然后才能收集指标。 本教程创建具有基本指标检测的应用。 .NET 运行时还内置了各种指标。 有关使用 System.Diagnostics.Metrics.Meter API 创建新指标的详细信息,请参阅检测教程。
dotnet new console -o metric-instr
cd metric-instr
dotnet add package System.Diagnostics.DiagnosticSource
将 Program.cs 的内容替换为以下代码:
using System.Diagnostics.Metrics;
class Program
{
static Meter s_meter = new("HatCo.HatStore", "1.0.0");
static Counter<int> s_hatsSold = s_meter.CreateCounter<int>("hats-sold");
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var rand = Random.Shared;
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit");
while (!Console.KeyAvailable)
{
//// Simulate hat selling transactions.
Thread.Sleep(rand.Next(100, 2500));
s_hatsSold.Add(rand.Next(0, 1000));
}
}
}
前面的代码模拟以随机间隔和随机时间出售帽子的情况。
使用 dotnet-counters 查看指标
dotnet-counters 是一个命令行工具,可按需查看任何 .NET Core 应用的实时指标。 它不需要设置,因此可用于临时调查或验证指标检测是否正常工作。 它与基于 System.Diagnostics.Metrics 的 API 和 EventCounters 配合运作。
如果未安装 dotnet-counters 工具,请运行以下命令:
dotnet tool update -g dotnet-counters
运行示例应用时,启动 dotnet-counters。 以下命令显示了 dotnet-counters 监控来自 HatCo.HatStore 仪表的所有指标的示例。 计量名称是区分大小写的。 示例应用为 metric-instr.exe,请将它替换为示例应用的名称。
dotnet-counters monitor -n metric-instr HatCo.HatStore
显示了类似下面的输出:
Press p to pause, r to resume, q to quit.
Status: Running
[HatCo.HatStore]
hats-sold (Count / 1 sec) 4
可以使用一组不同的指标来运行 dotnet-counters,以查看 .NET 运行时的一些内置检测:
dotnet-counters monitor -n metric-instr
显示了类似下面的输出:
Press p to pause, r to resume, q to quit.
Status: Running
[System.Runtime]
% Time in GC since last GC (%) 0
Allocation Rate (B / 1 sec) 8,168
CPU Usage (%) 0
Exception Count (Count / 1 sec) 0
GC Heap Size (MB) 2
Gen 0 GC Count (Count / 1 sec) 0
Gen 0 Size (B) 2,216,256
Gen 1 GC Count (Count / 1 sec) 0
Gen 1 Size (B) 423,392
Gen 2 GC Count (Count / 1 sec) 0
Gen 2 Size (B) 203,248
LOH Size (B) 933,216
Monitor Lock Contention Count (Count / 1 sec) 0
Number of Active Timers 1
Number of Assemblies Loaded 39
ThreadPool Completed Work Item Count (Count / 1 sec) 0
ThreadPool Queue Length 0
ThreadPool Thread Count 3
Working Set (MB) 30
有关详细信息,请参阅 dotnet-counters。 要详细了解 .NET 中的指标,请参阅内置指标。
使用 OpenTelemetry 和 Prometheus 查看 Grafana 中的指标
概述
- 是一个由云原生计算基金会支持的供应商中立开源项目。
- 标准化云原生软件的遥测数据生成和收集。
- 使用 .NET 指标 API 与 .NET 配合使用。
- 得到 Azure Monitor 和许多 APM 供应商的认可。
本教程使用 OSS Prometheus 和 Grafana 项目展示了可用于 OpenTelemetry 指标的集成之一。 指标数据流:
.NET 指标 API 记录示例应用中的度量值。
在应用中运行的 OpenTelemetry 库将聚合这些度量值。
Prometheus 导出程序库通过 HTTP 指标终结点提供聚合数据。 “导出程序”指的是 OpenTelemetry 调用库来将遥测数据传输到供应商特定的后端。
Prometheus 服务器:
- 轮询指标终结点
- 读取数据
- 将数据存储在数据库中以实现长期持久存储。 Prometheus 将读取和存储数据称为抓取终结点。
- 可以在其他计算机上运行
Grafana 服务器:
- 查询 Prometheus 中存储的数据并将其显示在基于 Web 的监控仪表板上。
- 可以在其他计算机上运行。
将示例应用配置为使用 OpenTelemetry 的 Prometheus 导出程序
向示例应用添加对 OpenTelemetry Prometheus 导出程序的引用:
dotnet add package OpenTelemetry.Exporter.Prometheus.HttpListener --prerelease
注意
本教程使用编写本文时 OpenTelemetry 的 Prometheus 支持的预发布版本。
使用 OpenTelemetry 配置更新 Program.cs:
using OpenTelemetry;
using OpenTelemetry.Metrics;
using System.Diagnostics.Metrics;
class Program
{
static Meter s_meter = new("HatCo.HatStore", "1.0.0");
static Counter<int> s_hatsSold = s_meter.CreateCounter<int>(
name: "hats-sold",
unit: "Hats",
description: "The number of hats sold in our store");
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using MeterProvider meterProvider = Sdk.CreateMeterProviderBuilder()
.AddMeter("HatCo.HatStore")
.AddPrometheusHttpListener(options => options.UriPrefixes = new string[] { "http://localhost:9184/" })
.Build();
var rand = Random.Shared;
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit");
while (!Console.KeyAvailable)
{
//// Simulate hat selling transactions.
Thread.Sleep(rand.Next(100, 2500));
s_hatsSold.Add(rand.Next(0,1000));
}
}
}
在上述代码中:
AddMeter("HatCo.HatStore")将 OpenTelemetry 配置为传输应用中定义的计量收集的所有指标。AddPrometheusHttpListener将 OpenTelemetry 配置为:- 在端口
9184上公开 Prometheus 的指标终结点 - 使用 HttpListener。
- 在端口
有关 OpenTelemetry 配置选项的详细信息,请参阅 OpenTelemetry 文档。 OpenTelemetry 文档显示了 ASP.NET 应用的托管选项。
运行应用并使其保持运行状态,以便可以收集度量值:
dotnet run
设置和配置 Prometheus
按照 Prometheus 起始步骤设置 Prometheus 服务器并确认其正常工作。
修改 prometheus.yml 配置文件,以便 Prometheus 抓取示例应用公开的指标终结点。 在 scrape_configs 部分中添加以下突出显示的文本:
# my global config
global:
scrape_interval: 15s # Set the scrape interval to every 15 seconds. Default is every 1 minute.
evaluation_interval: 15s # Evaluate rules every 15 seconds. The default is every 1 minute.
# scrape_timeout is set to the global default (10s).
# Alertmanager configuration
alerting:
alertmanagers:
- static_configs:
- targets:
# - alertmanager:9093
# Load rules once and periodically evaluate them according to the global 'evaluation_interval'.
rule_files:
# - "first_rules.yml"
# - "second_rules.yml"
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape:
# Here it's Prometheus itself.
scrape_configs:
# The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config.
- job_name: "prometheus"
# metrics_path defaults to '/metrics'
# scheme defaults to 'http'.
static_configs:
- targets: ["localhost:9090"]
- job_name: 'OpenTelemetryTest'
scrape_interval: 1s # poll very quickly for a more responsive demo
static_configs:
- targets: ['localhost:9184']
启动 Prometheus
重新加载配置或重启 Prometheus 服务器。
确认 OpenTelemetryTest 在 Prometheus Web 门户的“状态”>“目标”页中处于 UP 状态。
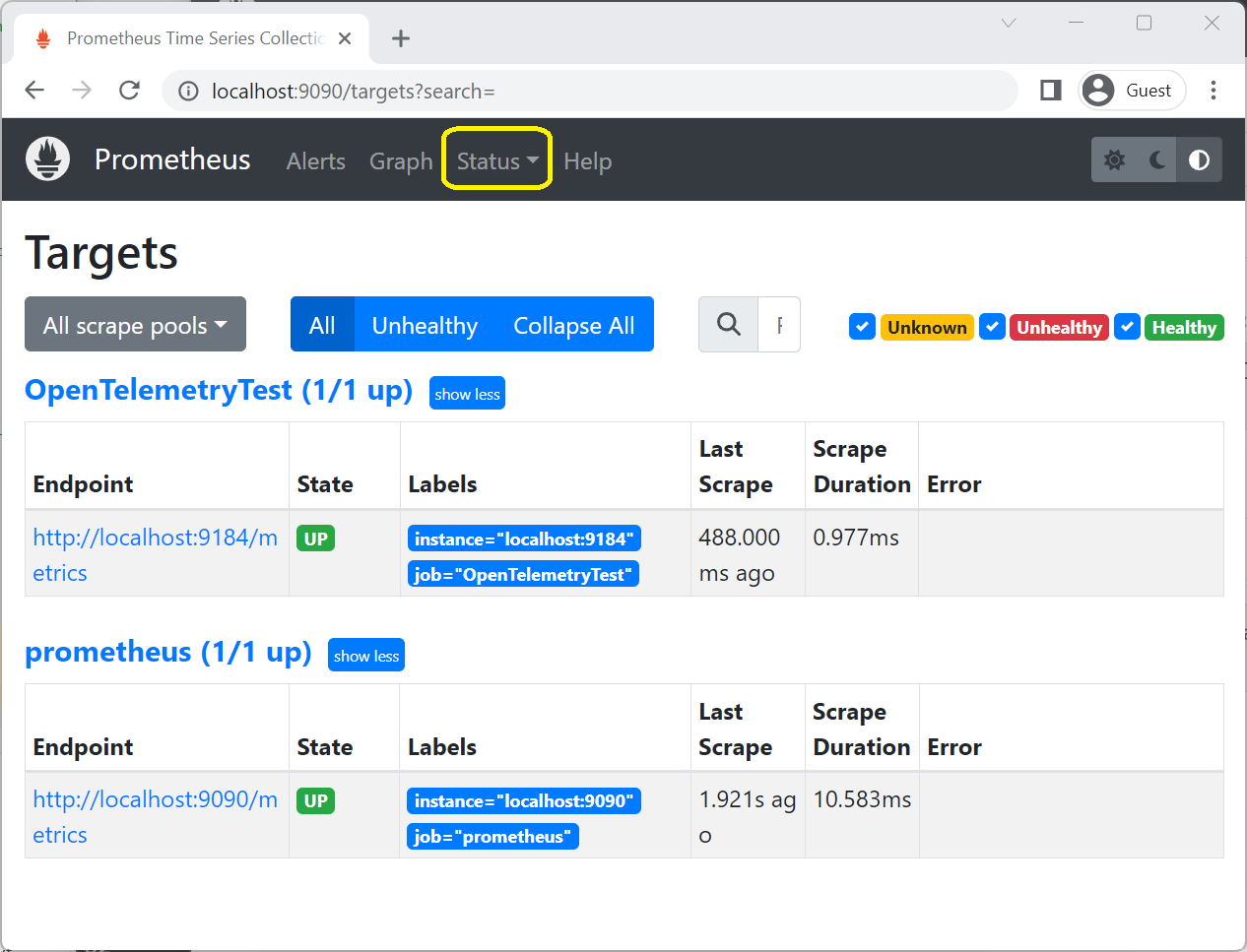
在 Prometheus 门户网站“图表”页面,在表达式文本框中输入
hats并在图表选项卡中选择hats_sold_Hats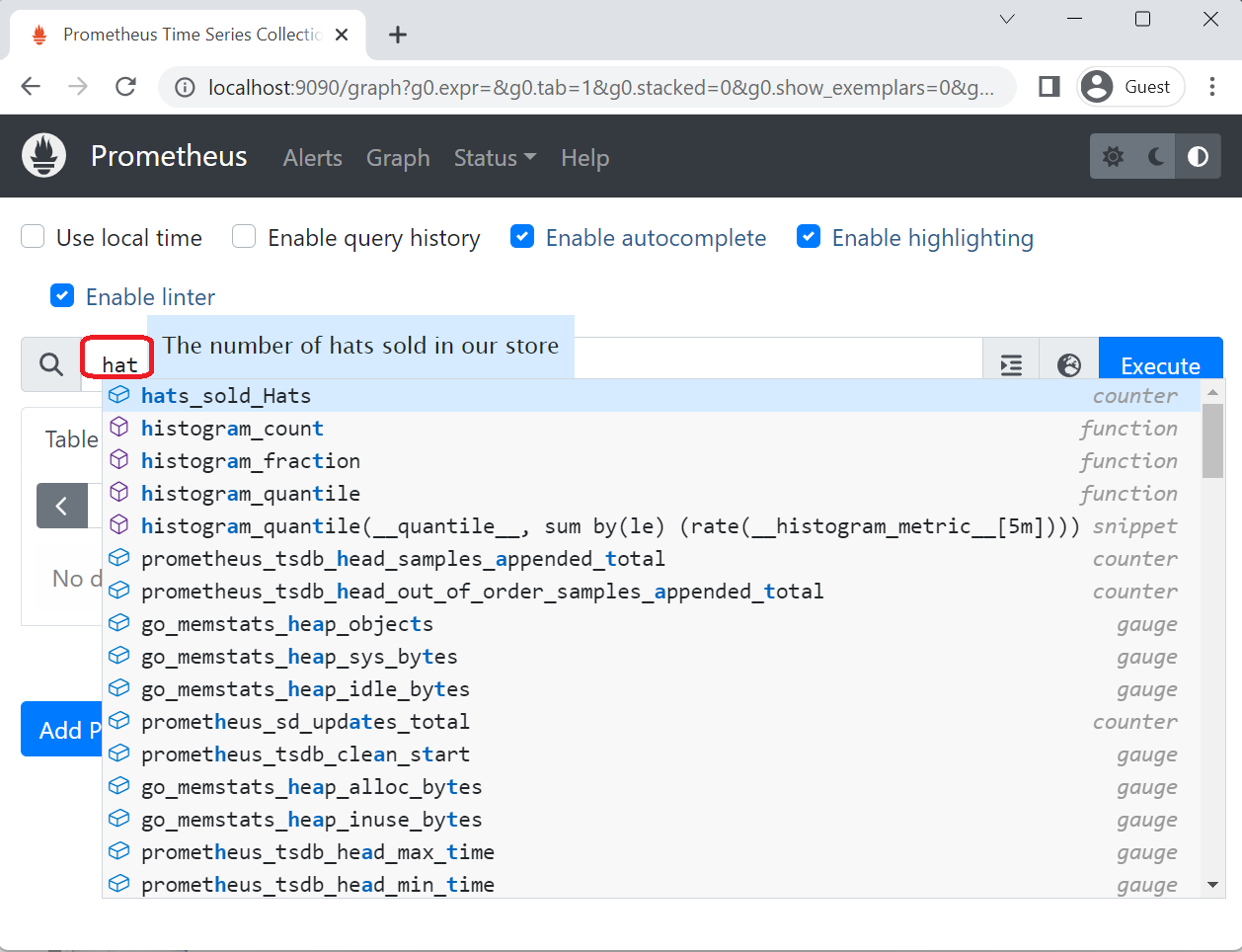 ,Prometheus 将显示示例应用程序发出的“hats-sold”计数器的值不断增加。
,Prometheus 将显示示例应用程序发出的“hats-sold”计数器的值不断增加。
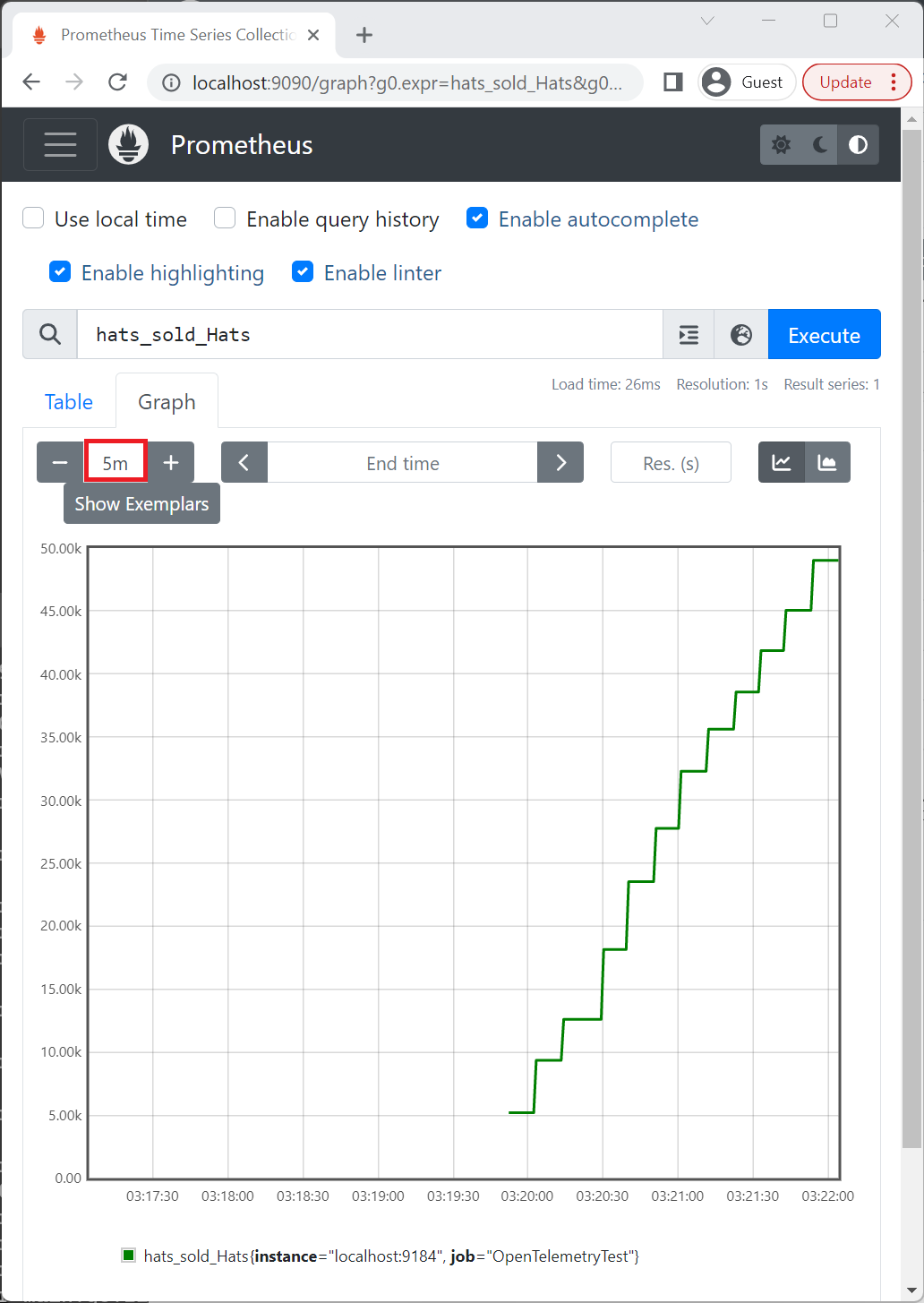
在上图中,图形时间设置为 5m,即 5 分钟。
如果 Prometheus 服务器长时间未抓取示例应用,可能需要等待数据累积。
在 Grafana 仪表板上显示指标
按照标准说明安装 Grafana,并将其连接到 Prometheus 数据源。
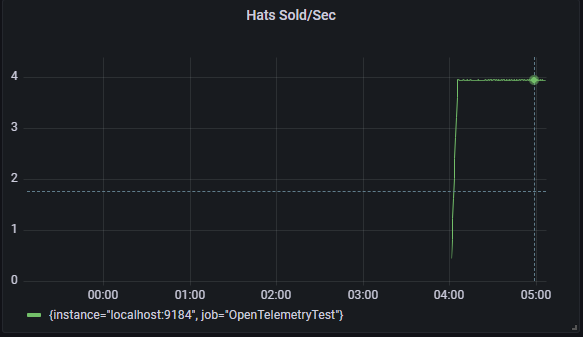
创建 Grafana 仪表板:单击 Grafana Web 门户左侧工具栏上的 + 图标,然后选择“仪表板”。 在出现的仪表板编辑器中,在标题输入框中输入 Hats Sold/Sec,并在 PromQL 表达式字段中输入 rate(hats_sold[5m]):
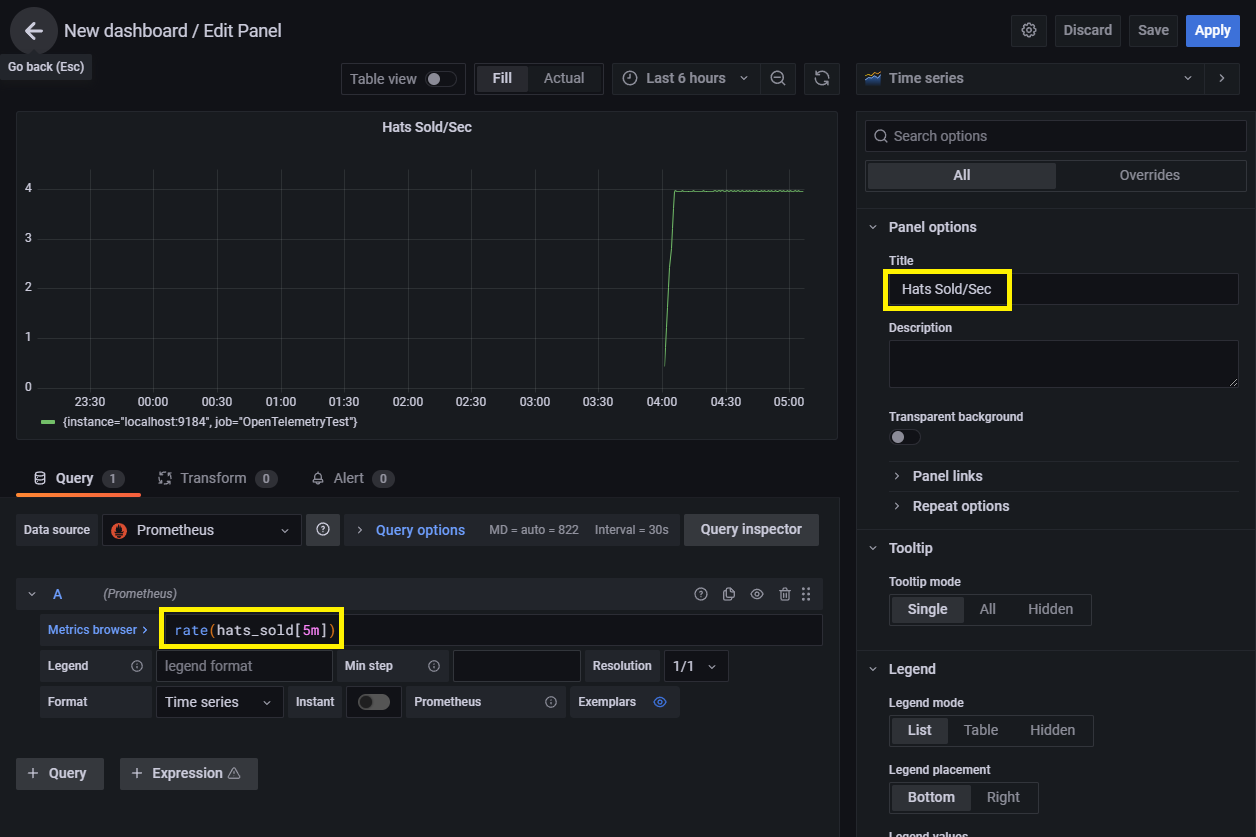
单击“应用”保存并查看新仪表板。
 ]
]
使用 .NET MeterListener API 创建自定义集合工具
.NET MeterListener API 允许创建自定义进程内逻辑,以观察 System.Diagnostics.Metrics.Meter 所记录的度量值。 有关创建与旧版 EventCounters 检测兼容的自定义逻辑的指导,请参阅 EventCounters。
修改 Program.cs 的代码以使用 MeterListener:
using System.Diagnostics.Metrics;
class Program
{
static Meter s_meter = new("HatCo.HatStore", "1.0.0");
static Counter<int> s_hatsSold = s_meter.CreateCounter<int>(
name: "hats-sold",
unit: "Hats",
description: "The number of hats sold in our store");
static void Main(string[] args)
{
using MeterListener meterListener = new();
meterListener.InstrumentPublished = (instrument, listener) =>
{
if (instrument.Meter.Name is "HatCo.HatStore")
{
listener.EnableMeasurementEvents(instrument);
}
};
meterListener.SetMeasurementEventCallback<int>(OnMeasurementRecorded);
// Start the meterListener, enabling InstrumentPublished callbacks.
meterListener.Start();
var rand = Random.Shared;
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit");
while (!Console.KeyAvailable)
{
//// Simulate hat selling transactions.
Thread.Sleep(rand.Next(100, 2500));
s_hatsSold.Add(rand.Next(0, 1000));
}
}
static void OnMeasurementRecorded<T>(
Instrument instrument,
T measurement,
ReadOnlySpan<KeyValuePair<string, object?>> tags,
object? state)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{instrument.Name} recorded measurement {measurement}");
}
}
以下输出显示了应用的输出,并针对每个度量值使用自定义回调:
> dotnet run
Press any key to exit
hats-sold recorded measurement 978
hats-sold recorded measurement 775
hats-sold recorded measurement 666
hats-sold recorded measurement 66
hats-sold recorded measurement 914
hats-sold recorded measurement 912
...
说明示例代码
本部分中的代码片段来自前面的示例。
在以下突出显示的代码中,将创建一个 MeterListener 实例来接收度量值。 当 meterListener 超出范围时,using 关键字会导致调用 Dispose。
using MeterListener meterListener = new();
meterListener.InstrumentPublished = (instrument, listener) =>
{
if (instrument.Meter.Name is "HatCo.HatStore")
{
listener.EnableMeasurementEvents(instrument);
}
};
以下突出显示的代码配置侦听器从中接收度量值的检测。 InstrumentPublished 是一个委托,在应用中创建新检测时将调用该委托。
using MeterListener meterListener = new();
meterListener.InstrumentPublished = (instrument, listener) =>
{
if (instrument.Meter.Name is "HatCo.HatStore")
{
listener.EnableMeasurementEvents(instrument);
}
};
委托可以检查检测以确定是否订阅。 例如,委托可以检查名称、仪表或任何其他公共属性。 EnableMeasurementEvents 允许从指定检测接收度量值。 通过另一种方法获取检测引用的代码:
- 但一般不这样操作。
- 可以随时通过该引用来调用
EnableMeasurementEvents()。
通过调用 SetMeasurementEventCallback 来配置在从检测接收到度量值时调用的委托:
meterListener.SetMeasurementEventCallback<int>(OnMeasurementRecorded);
// Start the meterListener, enabling InstrumentPublished callbacks.
meterListener.Start();
var rand = Random.Shared;
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit");
while (!Console.KeyAvailable)
{
//// Simulate hat selling transactions.
Thread.Sleep(rand.Next(100, 2500));
s_hatsSold.Add(rand.Next(0, 1000));
}
}
static void OnMeasurementRecorded<T>(
Instrument instrument,
T measurement,
ReadOnlySpan<KeyValuePair<string, object?>> tags,
object? state)
{
Console.WriteLine($"{instrument.Name} recorded measurement {measurement}");
}
泛型参数控制回调接收的度量数据类型。 例如,Counter<int> 生成 int 度量值,Counter<double> 生成 double 值度量。 可以使用 byte、short、int、long、float、double 和 decimal 类型创建检测。 建议为每种数据类型注册回调,除非你了解特定于场景的知识,知道并非所有数据类型都是必需的。 使用不同的泛型参数重复调用 SetMeasurementEventCallback 可能看起来有点异常。 API 的设计方式使 MeterListener 能以较低的性能开销接收度量值,通常只有几纳秒。
调用 MeterListener.EnableMeasurementEvents 时,可以将 state 对象作为其中一个参数提供。 对象 state 是任意的。 如果在该调用中提供状态对象,则它将随该检测一起存储,并作为回调中的 state 参数返回。 这是为了方便起见,也是为了优化性能。 侦听器通常需要:
- 为每个在内存中存储测量值的检测创建一个对象。
- 有代码对这些度量值执行计算。
或者,创建一个从检测映射到存储对象的 Dictionary,并在每次测量时查找它。 使用 Dictionary 比从 state 访问它要慢得多。
meterListener.Start();
前面的代码启动了启用回调的 MeterListener。 流程中每个预先存在的检测都会调用 InstrumentPublished 委托。 新创建的检测对象也会触发 InstrumentPublished 调用。
using MeterListener meterListener = new MeterListener();
应用完成侦听后,释放侦听器会停止回调流,并释放对侦听器对象的任何内部引用。 声明 meterListener 时使用的 using 关键字会导致在变量超出范围时调用 Dispose。 请注意,Dispose 只保证它不会发起新的回调。 因为回调发生在不同的线程上,因此在对 Dispose 的调用返回后,可能仍有正在进行中的回调。
要保证回调中的某个代码区域当前未执行且将来也不会执行,必须添加线程同步。 Dispose 默认情况下不包括同步,因为:
- 同步会增加每个测量回调的性能开销。
MeterListener设计为具有高性能意识的 API。
