你当前正在访问 Microsoft Azure Global Edition 技术文档网站。 如果需要访问由世纪互联运营的 Microsoft Azure 中国技术文档网站,请访问 https://docs.azure.cn。
教程:有关使用 Azure 空间定位点创建新 Android 应用的分步说明
本教程介绍如何使用 Azure 空间定位点创建与 ARCore 功能集成的新 Android 应用。
先决条件
若要完成本教程,请确保做好以下准备:
- 具有 Android Studio 3.4+ 的 Windows 或 macOS 计算机。
- 支持开发人员和 ARCore 功能的 Android 设备。
入门
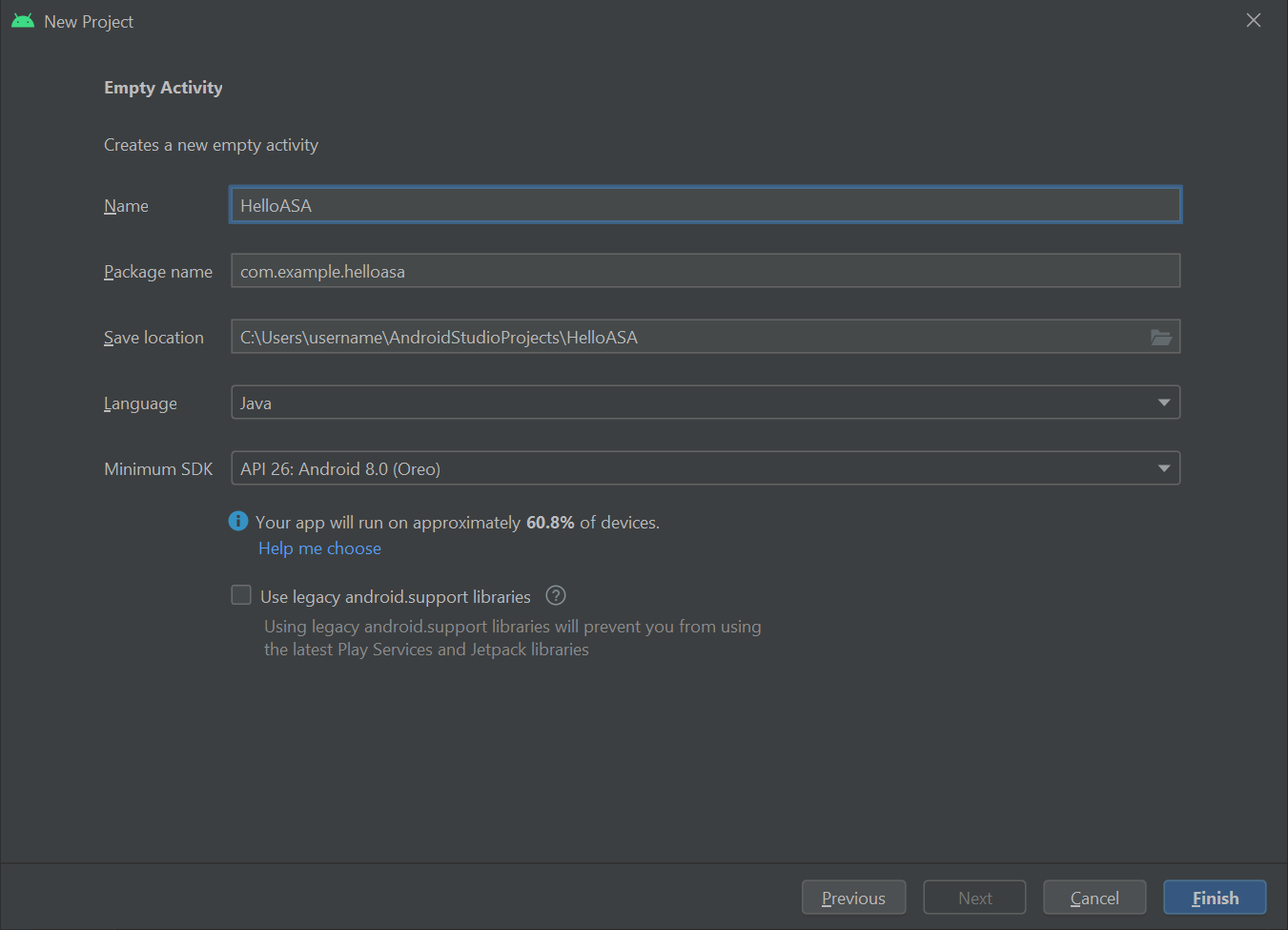
启动 Android Studio。 在“欢迎使用 Android Studio”窗口中,选择“启动新的 Android Studio 项目”。
- 选择“文件”->“新建项目”。
- 在“创建新项目”窗口中的“手机和平板电脑”部分下,选择“空活动”并单击“下一步”。
- 在“新建项目 - 空活动”窗口中,更改以下值:
- 将“名称”、“包名称”和“保存位置”更改为所需值
- 将“语言”设置为
Java - 将“最小 API 级别”设置为
API 26: Android 8.0 (Oreo) - 将其他选项保持不变
- 单击“完成”。
- “组件安装程序”随即运行。 经过某种处理后,Android Studio 将打开 IDE。
体验一下
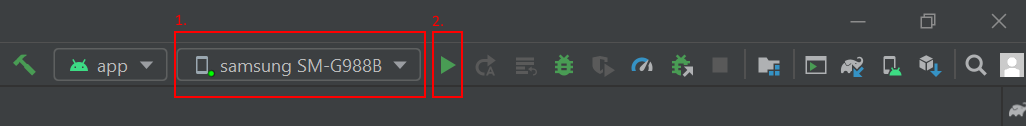
若要测试新应用,请使用 USB 线缆将开发人员启用的设备连接到开发计算机。 在 Android Studio 右上方,选择已连接的设备,然后单击“运行应用”图标。 Android Studio 将在连接的设备上安装并启动该应用。 你现在应该会看到设备上运行的应用中显示“Hello World!”。 单击“运行”->“停止‘应用’”。
集成 ARCore
ARCore 是用于构建增强现实体验的 Google 平台,可让设备在移动时跟踪自身的位置,并建立自身对真实世界的理解。
修改 app\manifests\AndroidManifest.xml,以在根 <manifest> 节点中包含以下条目。 此代码片段的作用如下:
- 允许应用访问设备相机。
- 确保你的应用在 Google Play 商店中仅向支持 ARCore 的设备显示。
- 安装应用后,此代码片段会配置 Google Play 商店以下载并安装 ARCore(如果尚未安装)。
<manifest ...>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<uses-feature android:name="android.hardware.camera.ar" />
<application>
...
<meta-data android:name="com.google.ar.core" android:value="required" />
...
</application>
</manifest>
修改 Gradle Scripts\build.gradle (Module: app) 以包含以下条目。 此代码将确保应用面向 ARCore 版本 1.25。 完成此项更改后,Gradle 可能会发出一条通知,询问是否要同步:请单击“立即同步”。
dependencies {
...
implementation 'com.google.ar:core:1.25.0'
...
}
集成 Sceneform
使用 Sceneform 能够轻松地在增强现实应用中渲染逼真的 3D 场景,且无需学习 OpenGL。
修改 Gradle Scripts\build.gradle (Module: app) 以包含以下条目。 此代码允许应用使用 Java 8 中的语言构造,而 Sceneform 要求使用此类构造。 它还将确保应用面向 Sceneform 版本 1.15。 完成此项更改后,Gradle 可能会发出一条通知,询问是否要同步:请单击“立即同步”。
android {
...
compileOptions {
sourceCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
targetCompatibility JavaVersion.VERSION_1_8
}
}
dependencies {
...
implementation 'com.google.ar.sceneform.ux:sceneform-ux:1.15.0'
...
}
打开 app\res\layout\activity_main.xml,将现有的 Hello Wolrd <TextView ... /> 元素替换为以下 ArFragment。 此代码导致相机源显示在屏幕上,使 ARCore 能够跟踪设备在移动时所处的位置。
<fragment android:name="com.google.ar.sceneform.ux.ArFragment"
android:id="@+id/ux_fragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
注意
若要查看主活动的原始 xml,请单击 Android Studio 右上方的“代码”或“拆分”按钮。
将应用重新部署到设备,以再次对其进行验证。 这一次,系统应会请求提供相机权限。 在批准后,你应该会看到屏幕上渲染相机源。
将对象放入真实世界
让我们使用该应用创建并放置一个对象。 首先,将以下 import 语句添加到 app\java\<PackageName>\MainActivity:
import com.google.ar.core.HitResult;
import com.google.ar.core.Plane;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.AnchorNode;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.math.Vector3;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.rendering.Color;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.rendering.MaterialFactory;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.rendering.Renderable;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.rendering.ShapeFactory;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.ux.ArFragment;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
然后,将以下成员变量添加到 MainActivity 类:
private boolean tapExecuted = false;
private final Object syncTaps = new Object();
private ArFragment arFragment;
private AnchorNode anchorNode;
private Renderable nodeRenderable = null;
private float recommendedSessionProgress = 0f;
接下来,将以下代码添加到 app\java\<PackageName>\MainActivity onCreate() 方法中。 此代码将挂接名为 handleTap() 的侦听器,当用户点击设备上的屏幕时,该侦听器可以检测到此动作。 如果恰好是在 ARCore 跟踪功能已识别到的表面上进行点击,则会运行该侦听器。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
this.arFragment = (ArFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.ux_fragment);
this.arFragment.setOnTapArPlaneListener(this::handleTap);
}
最后,添加以下 handleTap() 方法,用于将所有元素关联到一起。 此方法将创建一个球体,并将其放在点击位置。 该球体最初为黑色,因为 this.recommendedSessionProgress 目前设置为零。 稍后将调整此值。
protected void handleTap(HitResult hitResult, Plane plane, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
if (this.tapExecuted) {
return;
}
this.tapExecuted = true;
}
this.anchorNode = new AnchorNode();
this.anchorNode.setAnchor(hitResult.createAnchor());
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress))
.thenAccept(material -> {
this.nodeRenderable = ShapeFactory.makeSphere(0.1f, new Vector3(0.0f, 0.15f, 0.0f), material);
this.anchorNode.setRenderable(nodeRenderable);
this.anchorNode.setParent(arFragment.getArSceneView().getScene());
});
}
将应用重新部署到设备,以再次对其进行验证。 此时,可以四处移动设备,让 ARCore 开始识别环境。 然后点击屏幕,以创建黑色球体并将其放在所选的表面上。
附加本地 Azure 空间定位点
修改 Gradle Scripts\build.gradle (Module: app) 以包含以下条目。 此示例代码片段面向 Azure 空间定位点 SDK 版本 2.10.2。 请注意,SDK 版本 2.7.0 是目前支持的最低版本,引用任何较新版本的 Azure 空间定位点也应能正常运行。 建议使用最新版本的 Azure 空间定位点 SDK。 你可在此处找到 SDK 的版本说明。
dependencies {
...
implementation 'com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors:spatialanchors_jni:[2.10.2]'
implementation 'com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors:spatialanchors_java:[2.10.2]'
...
}
如果面向 Azure 空间定位点 SDK 2.10.0 或更高版本,请在你项目的 settings.gradle 文件的 repositories 部分中包含以下条目。 这其中包括了 Maven 包源的 URL,该 URL 托管了适用于 SDK 2.10.0 或更高版本的 Azure 空间定位点 Android 包:
dependencyResolutionManagement {
...
repositories {
...
maven {
url 'https://pkgs.dev.azure.com/aipmr/MixedReality-Unity-Packages/_packaging/Maven-packages/maven/v1'
}
...
}
}
右键单击 app\java\<PackageName>->“新建”->“Java 类”。 将“名称”设置为 MyFirstApp,并设置“类”。 将创建名为 MyFirstApp.java 的文件。 将以下 import 语句添加到该文件:
import com.microsoft.CloudServices;
将 android.app.Application 定义为其超类。
public class MyFirstApp extends android.app.Application {...
然后,在新的 MyFirstApp 类中添加以下代码,以确保使用应用程序的上下文初始化 Azure 空间定位点。
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
CloudServices.initialize(this);
}
现在修改 app\manifests\AndroidManifest.xml,以在根 <application> 节点中包含以下条目。 此代码将创建的 Application 类挂接到应用中。
<application
android:name=".MyFirstApp"
...
</application>
返回到 app\java\<PackageName>\MainActivity,在其中添加以下 import 语句:
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.util.Log;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.ArSceneView;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.Scene;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.CloudSpatialAnchor;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.CloudSpatialAnchorSession;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.SessionLogLevel;
然后,将以下成员变量添加到 MainActivity 类:
private float recommendedSessionProgress = 0f;
private ArSceneView sceneView;
private CloudSpatialAnchorSession cloudSession;
private boolean sessionInitialized = false;
接下来,在 mainActivity 类中添加以下 initializeSession() 方法。 调用该方法后,它会确保在启动应用期间创建并正确初始化 Azure 空间定位点会话。 此代码通过提前返回来确保通过 cloudSession.setSession 调用传递到 ASA 会话的 sceneview 会话不为空。
private void initializeSession() {
if (sceneView.getSession() == null) {
//Early return if the ARCore Session is still being set up
return;
}
if (this.cloudSession != null) {
this.cloudSession.close();
}
this.cloudSession = new CloudSpatialAnchorSession();
this.cloudSession.setSession(sceneView.getSession());
this.cloudSession.setLogLevel(SessionLogLevel.Information);
this.cloudSession.addOnLogDebugListener(args -> Log.d("ASAInfo", args.getMessage()));
this.cloudSession.addErrorListener(args -> Log.e("ASAError", String.format("%s: %s", args.getErrorCode().name(), args.getErrorMessage())));
sessionInitialized = true;
}
由于 initializeSession() 在 sceneView 会话尚未设置时(即,如果 sceneView.getSession() 为 null)可以进行提前返回,因此我们会添加 onUpdate 调用,以确保在创建 sceneView 会话后初始化 ASA 会话。
private void scene_OnUpdate(FrameTime frameTime) {
if (!sessionInitialized) {
//retry if initializeSession did an early return due to ARCore Session not yet available (i.e. sceneView.getSession() == null)
initializeSession();
}
}
现在,将 initializeSession() 和 scene_OnUpdate(...) 方法挂接到 onCreate() 方法。 另外,请确保将相机源中的帧发送到 Azure 空间定位点 SDK 进行处理。
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
this.arFragment = (ArFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.ux_fragment);
this.arFragment.setOnTapArPlaneListener(this::handleTap);
this.sceneView = arFragment.getArSceneView();
Scene scene = sceneView.getScene();
scene.addOnUpdateListener(frameTime -> {
if (this.cloudSession != null) {
this.cloudSession.processFrame(sceneView.getArFrame());
}
});
scene.addOnUpdateListener(this::scene_OnUpdate);
initializeSession();
}
最后,将以下代码添加到 handleTap() 方法中。 此代码将本地 Azure 空间定位点附加到要放入真实世界的黑色球体。
protected void handleTap(HitResult hitResult, Plane plane, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
if (this.tapExecuted) {
return;
}
this.tapExecuted = true;
}
this.anchorNode = new AnchorNode();
this.anchorNode.setAnchor(hitResult.createAnchor());
CloudSpatialAnchor cloudAnchor = new CloudSpatialAnchor();
cloudAnchor.setLocalAnchor(this.anchorNode.getAnchor());
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress))
.thenAccept(material -> {
this.nodeRenderable = ShapeFactory.makeSphere(0.1f, new Vector3(0.0f, 0.15f, 0.0f), material);
this.anchorNode.setRenderable(nodeRenderable);
this.anchorNode.setParent(arFragment.getArSceneView().getScene());
});
}
再次重新部署应用。 四处移动设备,点击屏幕,然后放置黑色球体。 不过,代码这一次会创建本地 Azure 空间定位点并将其附加到球体。
在继续进一步的操作之前,需要创建 Azure 空间定位点帐户以获取帐户标识符、密钥和域(如果尚未创建)。 遵循以下部分获取这些信息。
创建空间定位点资源
转到 Azure 门户。
在左窗格中,选择“创建资源”。
使用搜索框以搜索“空间定位点”。
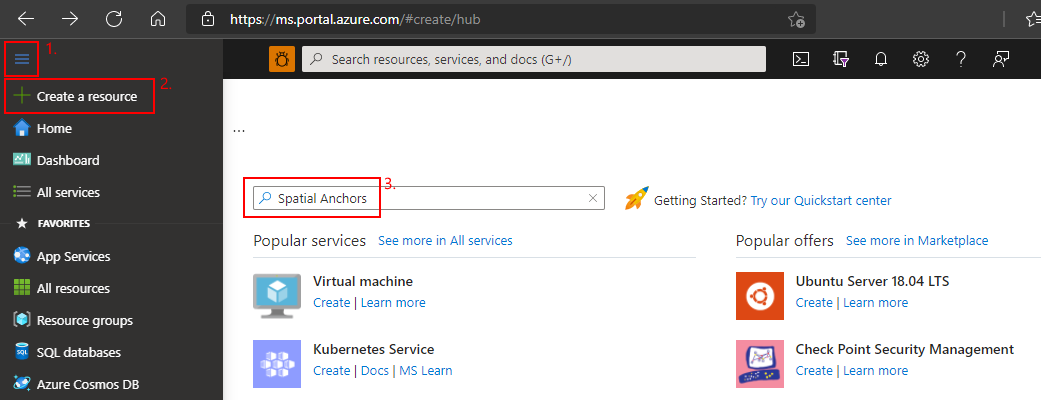
选择“空间定位点”,然后选择“创建” 。
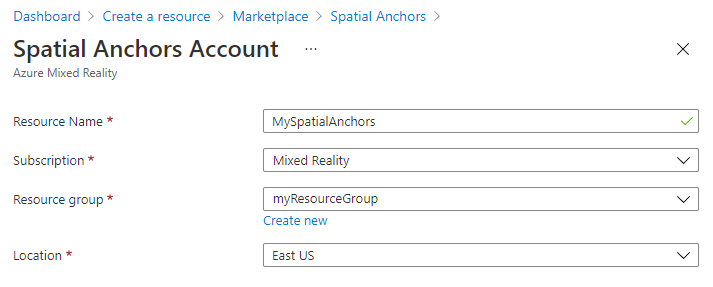
在“空间定位点帐户”窗格中,执行以下操作:
使用常规字母数字字符输入唯一的资源名称。
选择想要将资源附加到的订阅。
选择“新建”可创建资源组。 将其命名为 myResourceGroup,然后选择“确定” 。
资源组是在其中部署和管理 Azure 资源(例如 Web 应用、数据库和存储帐户)的逻辑容器。 例如,可以选择在使用完之后通过一个简单的步骤删除整个资源组。
选择可在其中放置资源的位置(区域)。
选择“创建”开始创建资源。
创建资源后,Azure 门户显示部署已完成。
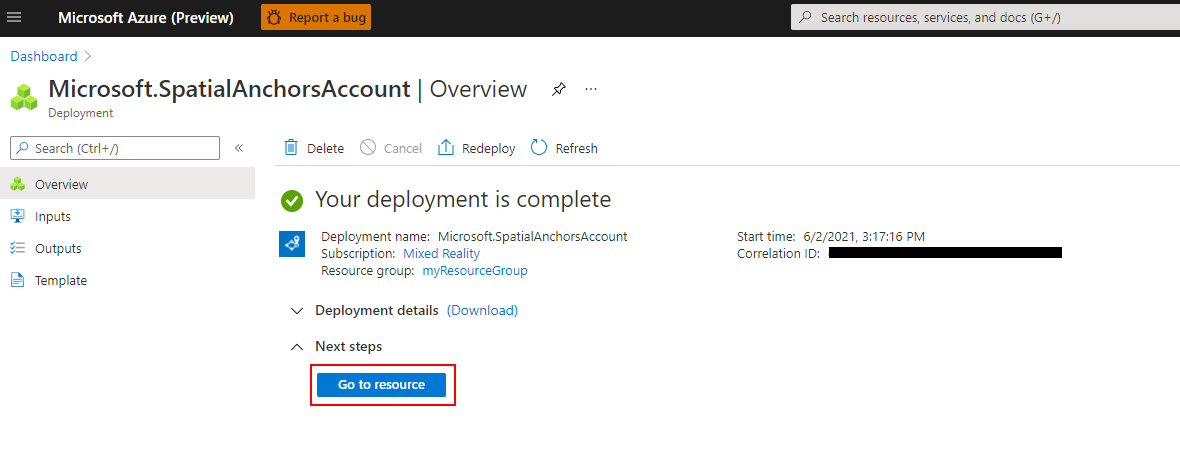
选择“转到资源”。 你现在可以查看资源属性。
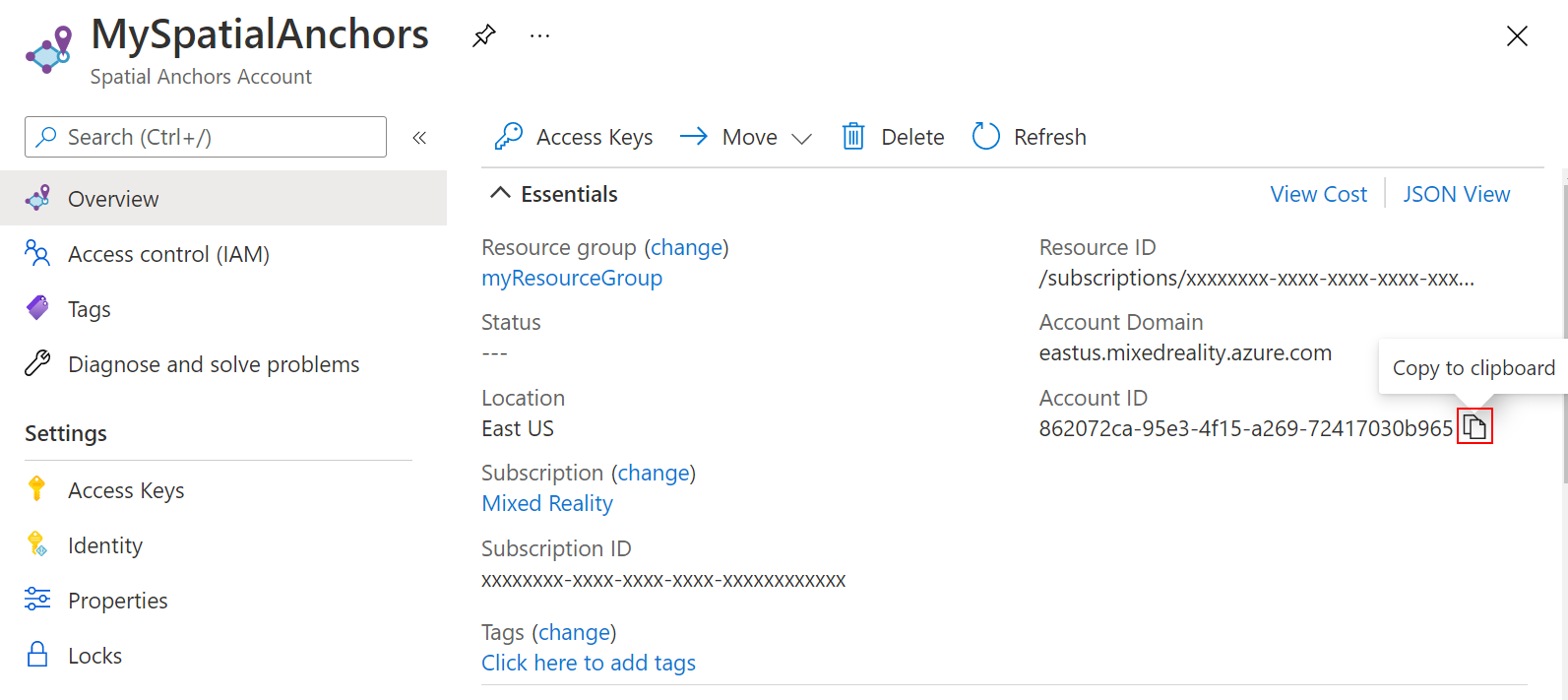
将资源的“帐户 ID”值复制到文本编辑器中,供稍后使用。
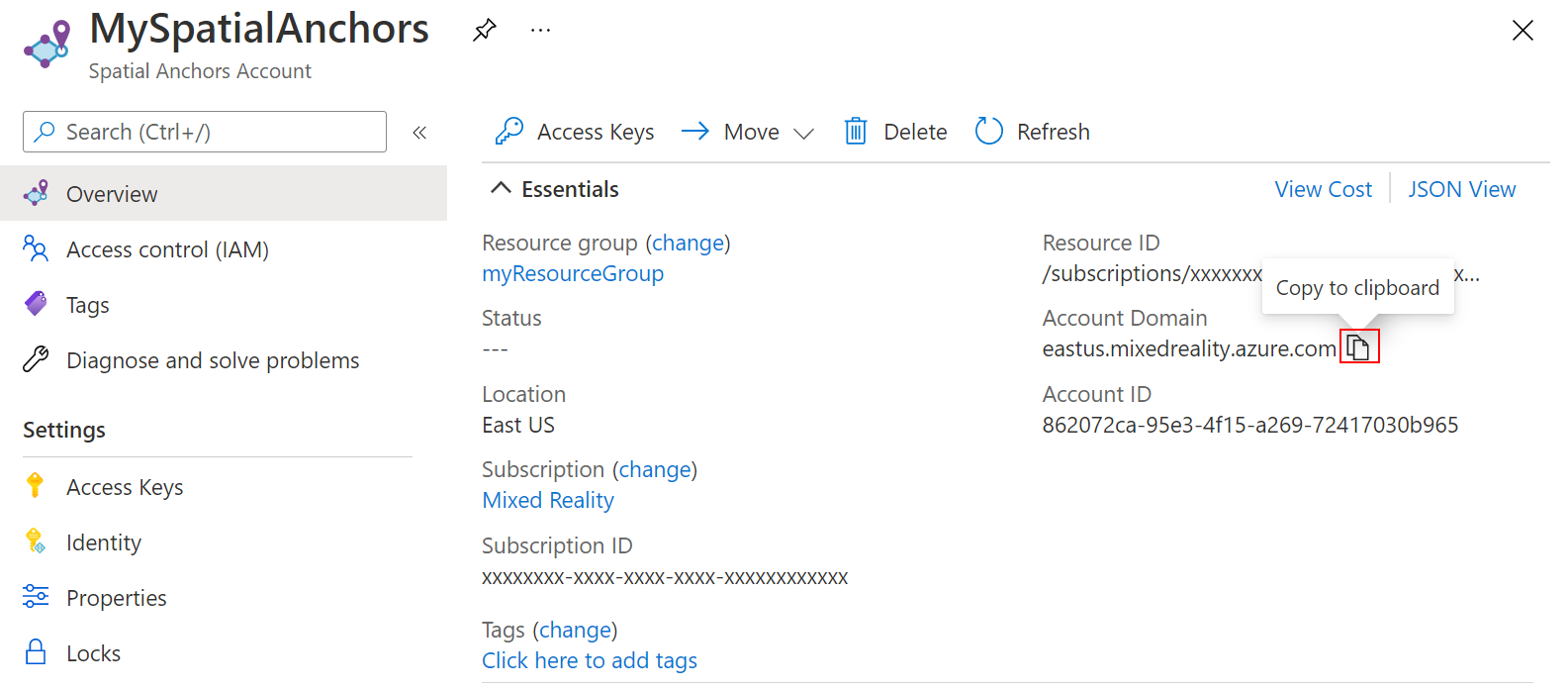
另外,将资源的“帐户域”值复制到文本编辑器中,供稍后使用。
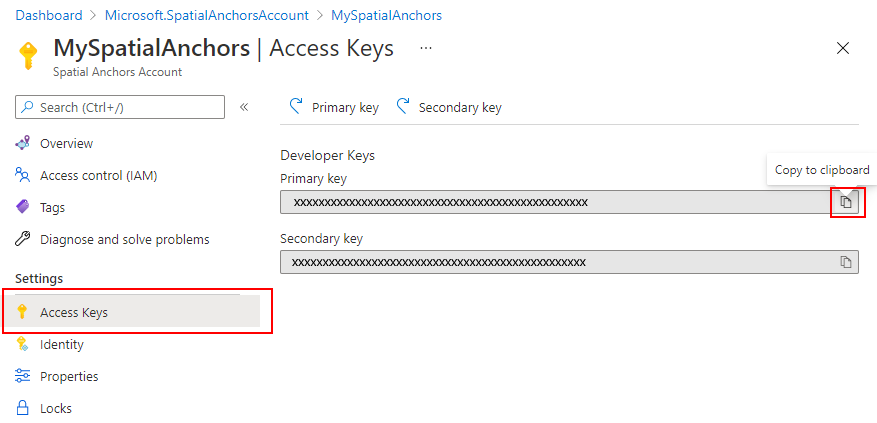
在“设置”下,选择“访问密钥” 。 将“帐户密钥”的“主密钥”值复制到文本编辑器中,供稍后使用 。
将本地定位点上传到云中
创建 Azure 空间定位点帐户标识符、密钥和域后,可以返回到 app\java\<PackageName>\MainActivity 并在其中添加以下 import 语句:
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.SessionLogLevel;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
然后,将以下成员变量添加到 MainActivity 类:
private boolean sessionInitialized = false;
private String anchorId = null;
private boolean scanningForUpload = false;
private final Object syncSessionProgress = new Object();
private ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
现在,将以下代码添加到 initializeSession() 方法中。 首先,此代码允许应用监视 Azure 空间定位点 SDK 从相机源收集帧的进度。 在收集期间,球体颜色将从最初的黑色开始变为灰色。 收集到足够的帧,可将定位点提交到云中之后,球体将变为白色。 其次,此代码将提供所需的凭据来与云后端通信。 可在以下位置将应用配置为使用你的帐户标识符、密钥和域。 在设置空间定位点资源时,将它们复制到文本编辑器中。
private void initializeSession() {
if (sceneView.getSession() == null) {
//Early return if the ARCore Session is still being set up
return;
}
if (this.cloudSession != null) {
this.cloudSession.close();
}
this.cloudSession = new CloudSpatialAnchorSession();
this.cloudSession.setSession(sceneView.getSession());
this.cloudSession.setLogLevel(SessionLogLevel.Information);
this.cloudSession.addOnLogDebugListener(args -> Log.d("ASAInfo", args.getMessage()));
this.cloudSession.addErrorListener(args -> Log.e("ASAError", String.format("%s: %s", args.getErrorCode().name(), args.getErrorMessage())));
sessionInitialized = true;
this.cloudSession.addSessionUpdatedListener(args -> {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
this.recommendedSessionProgress = args.getStatus().getRecommendedForCreateProgress();
Log.i("ASAInfo", String.format("Session progress: %f", this.recommendedSessionProgress));
if (!this.scanningForUpload) {
return;
}
}
runOnUiThread(() -> {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress))
.thenAccept(material -> {
this.nodeRenderable.setMaterial(material);
});
}
});
});
this.cloudSession.getConfiguration().setAccountId(/* Copy your account Identifier in here */);
this.cloudSession.getConfiguration().setAccountKey(/* Copy your account Key in here */);
this.cloudSession.getConfiguration().setAccountDomain(/* Copy your account Domain in here */);
this.cloudSession.start();
}
接下来,在 mainActivity 类中添加以下 uploadCloudAnchorAsync() 方法。 调用此方法后,它会以异步方式等到从设备中收集了足够的帧为止。 收集到足够的帧后,此方法会立即将球体颜色切换为黄色,然后开始将本地 Azure 空间定位点上传到云中。 上传完成后,该代码会返回定位标识符。
private CompletableFuture<String> uploadCloudAnchorAsync(CloudSpatialAnchor anchor) {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
this.scanningForUpload = true;
}
return CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
float currentSessionProgress;
do {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
currentSessionProgress = this.recommendedSessionProgress;
}
if (currentSessionProgress < 1.0) {
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
while (currentSessionProgress < 1.0);
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
this.scanningForUpload = false;
}
runOnUiThread(() -> {
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(android.graphics.Color.YELLOW))
.thenAccept(yellowMaterial -> {
this.nodeRenderable.setMaterial(yellowMaterial);
});
});
this.cloudSession.createAnchorAsync(anchor).get();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
Log.e("ASAError", e.toString());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, executorService).thenApply(ignore -> anchor.getIdentifier());
}
最后,让我们将所有元素挂接到一起。 在 handleTap() 方法中添加以下代码。 创建球体后,此代码将立即调用 uploadCloudAnchorAsync() 方法。 该方法返回后,以下代码将对球体执行一次最终更新,将其颜色更改为蓝色。
protected void handleTap(HitResult hitResult, Plane plane, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
if (this.tapExecuted) {
return;
}
this.tapExecuted = true;
}
this.anchorNode = new AnchorNode();
this.anchorNode.setAnchor(hitResult.createAnchor());
CloudSpatialAnchor cloudAnchor = new CloudSpatialAnchor();
cloudAnchor.setLocalAnchor(this.anchorNode.getAnchor());
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress))
.thenAccept(material -> {
this.nodeRenderable = ShapeFactory.makeSphere(0.1f, new Vector3(0.0f, 0.15f, 0.0f), material);
this.anchorNode.setRenderable(nodeRenderable);
this.anchorNode.setParent(arFragment.getArSceneView().getScene());
});
uploadCloudAnchorAsync(cloudAnchor)
.thenAccept(id -> {
this.anchorId = id;
Log.i("ASAInfo", String.format("Cloud Anchor created: %s", this.anchorId));
runOnUiThread(() -> {
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(android.graphics.Color.BLUE))
.thenAccept(blueMaterial -> {
this.nodeRenderable.setMaterial(blueMaterial);
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
this.tapExecuted = false;
}
});
});
});
}
再次重新部署应用。 四处移动设备,点击屏幕,然后放置球体。 不过,这一次,在收集相机帧的过程中,球体颜色将从黑色更改为白色。 收集到足够的帧后,球体将变为黄色,并且云上传操作将会开始。 请确保你的手机已连接到 Internet。 上传完成后,球体将变为蓝色。 (可选)可以在 Android Studio 中监视 Logcat 窗口以查看应用发送的日志消息。 记录的消息示例包括帧捕获期间的会话进度,以及上传完成后由云返回的定位点标识符。
注意
如果未看到 recommendedSessionProgress 值(在调试日志中称为 Session progress),请确保在放置的球体周围移动和旋转手机。
查找云空间定位点
将定位点上传到云后,可以再次尝试查找该定位点。 首先,将以下 import 语句添加到代码中。
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.AnchorLocateCriteria;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.LocateAnchorStatus;
然后,将以下代码添加到 handleTap() 方法中。 此代码将会:
- 从屏幕中删除现有的蓝色球体。
- 再次初始化 Azure 空间定位点会话。 此操作确保要查找的定位点来自云,而不是创建的本地定位点。
- 针对上传到云的定位点发出查询。
protected void handleTap(HitResult hitResult, Plane plane, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
if (this.tapExecuted) {
return;
}
this.tapExecuted = true;
}
if (this.anchorId != null) {
this.anchorNode.getAnchor().detach();
this.anchorNode.setParent(null);
this.anchorNode = null;
initializeSession();
AnchorLocateCriteria criteria = new AnchorLocateCriteria();
criteria.setIdentifiers(new String[]{this.anchorId});
cloudSession.createWatcher(criteria);
return;
}
this.anchorNode = new AnchorNode();
this.anchorNode.setAnchor(hitResult.createAnchor());
CloudSpatialAnchor cloudAnchor = new CloudSpatialAnchor();
cloudAnchor.setLocalAnchor(this.anchorNode.getAnchor());
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress))
.thenAccept(material -> {
this.nodeRenderable = ShapeFactory.makeSphere(0.1f, new Vector3(0.0f, 0.15f, 0.0f), material);
this.anchorNode.setRenderable(nodeRenderable);
this.anchorNode.setParent(arFragment.getArSceneView().getScene());
});
uploadCloudAnchorAsync(cloudAnchor)
.thenAccept(id -> {
this.anchorId = id;
Log.i("ASAInfo", String.format("Cloud Anchor created: %s", this.anchorId));
runOnUiThread(() -> {
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(android.graphics.Color.BLUE))
.thenAccept(blueMaterial -> {
this.nodeRenderable.setMaterial(blueMaterial);
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
this.tapExecuted = false;
}
});
});
});
}
现在,让我们挂接在找到要查询的定位点之后所要调用的代码。 在 initializeSession() 方法中添加以下代码。 找到云空间定位点后,此代码片段将创建并放置一个绿色球体。 它还支持再次点击屏幕,以便可以再次重复整个方案:创建另一个本地定位点,将其上传,然后再次找到它。
private void initializeSession() {
if (sceneView.getSession() == null) {
//Early return if the ARCore Session is still being set up
return;
}
if (this.cloudSession != null) {
this.cloudSession.close();
}
this.cloudSession = new CloudSpatialAnchorSession();
this.cloudSession.setSession(sceneView.getSession());
this.cloudSession.setLogLevel(SessionLogLevel.Information);
this.cloudSession.addOnLogDebugListener(args -> Log.d("ASAInfo", args.getMessage()));
this.cloudSession.addErrorListener(args -> Log.e("ASAError", String.format("%s: %s", args.getErrorCode().name(), args.getErrorMessage())));
sessionInitialized = true;
this.cloudSession.addSessionUpdatedListener(args -> {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
this.recommendedSessionProgress = args.getStatus().getRecommendedForCreateProgress();
Log.i("ASAInfo", String.format("Session progress: %f", this.recommendedSessionProgress));
if (!this.scanningForUpload) {
return;
}
}
runOnUiThread(() -> {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress))
.thenAccept(material -> {
this.nodeRenderable.setMaterial(material);
});
}
});
});
this.cloudSession.addAnchorLocatedListener(args -> {
if (args.getStatus() == LocateAnchorStatus.Located) {
runOnUiThread(() -> {
this.anchorNode = new AnchorNode();
this.anchorNode.setAnchor(args.getAnchor().getLocalAnchor());
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(android.graphics.Color.GREEN))
.thenAccept(greenMaterial -> {
this.nodeRenderable = ShapeFactory.makeSphere(0.1f, new Vector3(0.0f, 0.15f, 0.0f), greenMaterial);
this.anchorNode.setRenderable(nodeRenderable);
this.anchorNode.setParent(arFragment.getArSceneView().getScene());
this.anchorId = null;
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
this.tapExecuted = false;
}
});
});
}
});
this.cloudSession.getConfiguration().setAccountId(/* Copy your account Identifier in here */);
this.cloudSession.getConfiguration().setAccountKey(/* Copy your account Key in here */);
this.cloudSession.getConfiguration().setAccountDomain(/* Copy your account Domain in here */);
this.cloudSession.start();
}
就这么简单! 最后一次重新部署应用,以从头到尾体验整个方案。 四处移动设备,并放置黑色球体。 然后,不断移动设备以捕获相机帧,直到球体变为黄色。 本地定位点将会上传,球体将变为蓝色。 最后,再次点击屏幕以删除本地定位点,然后查询该定位点在云中的对应定位点。 继续移动设备,直到找到云空间定位点。 绿色球体应会显示在正确的位置;可以再次清除并重复整个方案。
将所有内容放在一起
下面是将所有不同的元素放在一起后,完整的 MainActivity 类文件看起来的样子。 可以将它用做参考与自己的文件进行比较,看是否有任何差异。
package com.example.myfirstapp;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import com.google.ar.core.HitResult;
import com.google.ar.core.Plane;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.AnchorNode;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.ArSceneView;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.FrameTime;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.Scene;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.math.Vector3;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.rendering.Color;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.rendering.MaterialFactory;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.rendering.Renderable;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.rendering.ShapeFactory;
import com.google.ar.sceneform.ux.ArFragment;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.AnchorLocateCriteria;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.CloudSpatialAnchor;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.CloudSpatialAnchorSession;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.LocateAnchorStatus;
import com.microsoft.azure.spatialanchors.SessionLogLevel;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private boolean tapExecuted = false;
private final Object syncTaps = new Object();
private ArFragment arFragment;
private AnchorNode anchorNode;
private Renderable nodeRenderable = null;
private float recommendedSessionProgress = 0f;
private ArSceneView sceneView;
private CloudSpatialAnchorSession cloudSession;
private boolean sessionInitialized = false;
private String anchorId = null;
private boolean scanningForUpload = false;
private final Object syncSessionProgress = new Object();
private ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
this.arFragment = (ArFragment) getSupportFragmentManager().findFragmentById(R.id.ux_fragment);
this.arFragment.setOnTapArPlaneListener(this::handleTap);
this.sceneView = arFragment.getArSceneView();
Scene scene = sceneView.getScene();
scene.addOnUpdateListener(frameTime -> {
if (this.cloudSession != null) {
this.cloudSession.processFrame(sceneView.getArFrame());
}
});
scene.addOnUpdateListener(this::scene_OnUpdate);
initializeSession();
}
// <scene_OnUpdate>
private void scene_OnUpdate(FrameTime frameTime) {
if (!sessionInitialized) {
//retry if initializeSession did an early return due to ARCore Session not yet available (i.e. sceneView.getSession() == null)
initializeSession();
}
}
// </scene_OnUpdate>
// <initializeSession>
private void initializeSession() {
if (sceneView.getSession() == null) {
//Early return if the ARCore Session is still being set up
return;
}
if (this.cloudSession != null) {
this.cloudSession.close();
}
this.cloudSession = new CloudSpatialAnchorSession();
this.cloudSession.setSession(sceneView.getSession());
this.cloudSession.setLogLevel(SessionLogLevel.Information);
this.cloudSession.addOnLogDebugListener(args -> Log.d("ASAInfo", args.getMessage()));
this.cloudSession.addErrorListener(args -> Log.e("ASAError", String.format("%s: %s", args.getErrorCode().name(), args.getErrorMessage())));
sessionInitialized = true;
this.cloudSession.addSessionUpdatedListener(args -> {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
this.recommendedSessionProgress = args.getStatus().getRecommendedForCreateProgress();
Log.i("ASAInfo", String.format("Session progress: %f", this.recommendedSessionProgress));
if (!this.scanningForUpload) {
return;
}
}
runOnUiThread(() -> {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress))
.thenAccept(material -> {
this.nodeRenderable.setMaterial(material);
});
}
});
});
this.cloudSession.addAnchorLocatedListener(args -> {
if (args.getStatus() == LocateAnchorStatus.Located) {
runOnUiThread(() -> {
this.anchorNode = new AnchorNode();
this.anchorNode.setAnchor(args.getAnchor().getLocalAnchor());
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(android.graphics.Color.GREEN))
.thenAccept(greenMaterial -> {
this.nodeRenderable = ShapeFactory.makeSphere(0.1f, new Vector3(0.0f, 0.15f, 0.0f), greenMaterial);
this.anchorNode.setRenderable(nodeRenderable);
this.anchorNode.setParent(arFragment.getArSceneView().getScene());
this.anchorId = null;
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
this.tapExecuted = false;
}
});
});
}
});
this.cloudSession.getConfiguration().setAccountId(/* Copy your account Identifier in here */);
this.cloudSession.getConfiguration().setAccountKey(/* Copy your account Key in here */);
this.cloudSession.getConfiguration().setAccountDomain(/* Copy your account Domain in here */);
this.cloudSession.start();
}
// </initializeSession>
// <handleTap>
protected void handleTap(HitResult hitResult, Plane plane, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
if (this.tapExecuted) {
return;
}
this.tapExecuted = true;
}
if (this.anchorId != null) {
this.anchorNode.getAnchor().detach();
this.anchorNode.setParent(null);
this.anchorNode = null;
initializeSession();
AnchorLocateCriteria criteria = new AnchorLocateCriteria();
criteria.setIdentifiers(new String[]{this.anchorId});
cloudSession.createWatcher(criteria);
return;
}
this.anchorNode = new AnchorNode();
this.anchorNode.setAnchor(hitResult.createAnchor());
CloudSpatialAnchor cloudAnchor = new CloudSpatialAnchor();
cloudAnchor.setLocalAnchor(this.anchorNode.getAnchor());
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress,
this.recommendedSessionProgress))
.thenAccept(material -> {
this.nodeRenderable = ShapeFactory.makeSphere(0.1f, new Vector3(0.0f, 0.15f, 0.0f), material);
this.anchorNode.setRenderable(nodeRenderable);
this.anchorNode.setParent(arFragment.getArSceneView().getScene());
});
uploadCloudAnchorAsync(cloudAnchor)
.thenAccept(id -> {
this.anchorId = id;
Log.i("ASAInfo", String.format("Cloud Anchor created: %s", this.anchorId));
runOnUiThread(() -> {
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(android.graphics.Color.BLUE))
.thenAccept(blueMaterial -> {
this.nodeRenderable.setMaterial(blueMaterial);
synchronized (this.syncTaps) {
this.tapExecuted = false;
}
});
});
});
}
// </handleTap>
// <uploadCloudAnchorAsync>
private CompletableFuture<String> uploadCloudAnchorAsync(CloudSpatialAnchor anchor) {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
this.scanningForUpload = true;
}
return CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
float currentSessionProgress;
do {
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
currentSessionProgress = this.recommendedSessionProgress;
}
if (currentSessionProgress < 1.0) {
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
while (currentSessionProgress < 1.0);
synchronized (this.syncSessionProgress) {
this.scanningForUpload = false;
}
runOnUiThread(() -> {
MaterialFactory.makeOpaqueWithColor(this, new Color(android.graphics.Color.YELLOW))
.thenAccept(yellowMaterial -> {
this.nodeRenderable.setMaterial(yellowMaterial);
});
});
this.cloudSession.createAnchorAsync(anchor).get();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
Log.e("ASAError", e.toString());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, executorService).thenApply(ignore -> anchor.getIdentifier());
}
// </uploadCloudAnchorAsync>
}
后续步骤
本教程介绍了如何使用 Azure 空间定位点创建与 ARCore 功能集成的新 Android 应用。 若要了解有关 Azure 空间定位点库的详细信息,请继续阅读我们有关如何创建并找到定位点的教程。
