你当前正在访问 Microsoft Azure Global Edition 技术文档网站。 如果需要访问由世纪互联运营的 Microsoft Azure 中国技术文档网站,请访问 https://docs.azure.cn。
快速入门:创建自定义语音助手
在本快速入门中,你将使用语音 SDK 创建连接到你已创建并配置的机器人的自定义语音助手应用程序。 如果需要创建机器人,请参阅相关教程,了解更全面的指南。
满足一些先决条件后,连接自定义语音助手只需几个步骤:
- 通过订阅密钥和区域创建
BotFrameworkConfig对象。 - 使用以上的
BotFrameworkConfig对象创建DialogServiceConnector对象。 - 使用
DialogServiceConnector对象,开始单个言语的侦听过程。 - 检查返回的
ActivityReceivedEventArgs。
备注
适用于 C++、JavaScript、Objective-C、Python 和 Swift 的语音 SDK 支持自定义语音助手,但我们尚未提供有关此内容的指南。
可以在 GitHub 上查看或下载所有语音 SDK C# 示例。
先决条件
在开始之前,请务必:
- 创建语音资源
- 设置开发环境并创建空项目
- 创建连接到 Direct Line Speech 通道的机器人
- 请确保你有权访问麦克风,以便进行音频捕获
注意
请参阅语音助手支持的区域列表,确保你的资源部署在其中一个区域中。
在 Visual Studio 中打开项目
第一步是确保在 Visual Studio 中打开项目。
从一些样本代码入手
添加一些代码作为项目的框架。
在“解决方案资源管理器”中打开
MainPage.xaml。在设计器的 XAML 视图中,将整个内容替换为定义基本用户界面的以下代码片段:
<Page x:Class="helloworld.MainPage" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:local="using:helloworld" xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008" xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006" mc:Ignorable="d" Background="{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}"> <Grid> <StackPanel Orientation="Vertical" HorizontalAlignment="Center" Margin="20,50,0,0" VerticalAlignment="Center" Width="800"> <Button x:Name="EnableMicrophoneButton" Content="Enable Microphone" Margin="0,0,10,0" Click="EnableMicrophone_ButtonClicked" Height="35"/> <Button x:Name="ListenButton" Content="Talk to your bot" Margin="0,10,10,0" Click="ListenButton_ButtonClicked" Height="35"/> <StackPanel x:Name="StatusPanel" Orientation="Vertical" RelativePanel.AlignBottomWithPanel="True" RelativePanel.AlignRightWithPanel="True" RelativePanel.AlignLeftWithPanel="True"> <TextBlock x:Name="StatusLabel" Margin="0,10,10,0" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="Status:" FontSize="20"/> <Border x:Name="StatusBorder" Margin="0,0,0,0"> <ScrollViewer VerticalScrollMode="Auto" VerticalScrollBarVisibility="Auto" MaxHeight="200"> <!-- Use LiveSetting to enable screen readers to announce the status update. --> <TextBlock x:Name="StatusBlock" FontWeight="Bold" AutomationProperties.LiveSetting="Assertive" MaxWidth="{Binding ElementName=Splitter, Path=ActualWidth}" Margin="10,10,10,20" TextWrapping="Wrap" /> </ScrollViewer> </Border> </StackPanel> </StackPanel> <MediaElement x:Name="mediaElement"/> </Grid> </Page>
更新“设计”视图以显示应用程序的用户界面。
- 在“解决方案资源管理器”中,打开代码隐藏源文件
MainPage.xaml.cs。 (其分组在MainPage.xaml下。)将此文件的内容替换为以下内容,其中包括:
Speech和Speech.Dialog命名空间的using语句一个绑定到按钮处理程序的简单实现,用于确保麦克风访问
基本的 UI 帮助程序,用于在应用程序中提供消息和错误
初始化代码路径的登陆点,稍后将填充
用于播放文本转语音的帮助程序(没有流式处理支持)
一个用于启动侦听的空的按钮处理程序,稍后将填充
using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech; using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech.Audio; using Microsoft.CognitiveServices.Speech.Dialog; using System; using System.Diagnostics; using System.IO; using System.Text; using Windows.Foundation; using Windows.Storage.Streams; using Windows.UI.Xaml; using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls; using Windows.UI.Xaml.Media; namespace helloworld { public sealed partial class MainPage : Page { private DialogServiceConnector connector; private enum NotifyType { StatusMessage, ErrorMessage }; public MainPage() { this.InitializeComponent(); } private async void EnableMicrophone_ButtonClicked( object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { bool isMicAvailable = true; try { var mediaCapture = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCapture(); var settings = new Windows.Media.Capture.MediaCaptureInitializationSettings(); settings.StreamingCaptureMode = Windows.Media.Capture.StreamingCaptureMode.Audio; await mediaCapture.InitializeAsync(settings); } catch (Exception) { isMicAvailable = false; } if (!isMicAvailable) { await Windows.System.Launcher.LaunchUriAsync( new Uri("ms-settings:privacy-microphone")); } else { NotifyUser("Microphone was enabled", NotifyType.StatusMessage); } } private void NotifyUser( string strMessage, NotifyType type = NotifyType.StatusMessage) { // If called from the UI thread, then update immediately. // Otherwise, schedule a task on the UI thread to perform the update. if (Dispatcher.HasThreadAccess) { UpdateStatus(strMessage, type); } else { var task = Dispatcher.RunAsync( Windows.UI.Core.CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, () => UpdateStatus(strMessage, type)); } } private void UpdateStatus(string strMessage, NotifyType type) { switch (type) { case NotifyType.StatusMessage: StatusBorder.Background = new SolidColorBrush( Windows.UI.Colors.Green); break; case NotifyType.ErrorMessage: StatusBorder.Background = new SolidColorBrush( Windows.UI.Colors.Red); break; } StatusBlock.Text += string.IsNullOrEmpty(StatusBlock.Text) ? strMessage : "\n" + strMessage; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(StatusBlock.Text)) { StatusBorder.Visibility = Visibility.Visible; StatusPanel.Visibility = Visibility.Visible; } else { StatusBorder.Visibility = Visibility.Collapsed; StatusPanel.Visibility = Visibility.Collapsed; } // Raise an event if necessary to enable a screen reader // to announce the status update. var peer = Windows.UI.Xaml.Automation.Peers.FrameworkElementAutomationPeer.FromElement(StatusBlock); if (peer != null) { peer.RaiseAutomationEvent( Windows.UI.Xaml.Automation.Peers.AutomationEvents.LiveRegionChanged); } } // Waits for and accumulates all audio associated with a given // PullAudioOutputStream and then plays it to the MediaElement. Long spoken // audio will create extra latency and a streaming playback solution // (that plays audio while it continues to be received) should be used -- // see the samples for examples of this. private void SynchronouslyPlayActivityAudio( PullAudioOutputStream activityAudio) { var playbackStreamWithHeader = new MemoryStream(); playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("RIFF"), 0, 4); // ChunkID playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(UInt32.MaxValue), 0, 4); // ChunkSize: max playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("WAVE"), 0, 4); // Format playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("fmt "), 0, 4); // Subchunk1ID playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(16), 0, 4); // Subchunk1Size: PCM playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(1), 0, 2); // AudioFormat: PCM playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(1), 0, 2); // NumChannels: mono playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(16000), 0, 4); // SampleRate: 16kHz playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(32000), 0, 4); // ByteRate playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(2), 0, 2); // BlockAlign playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(16), 0, 2); // BitsPerSample: 16-bit playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("data"), 0, 4); // Subchunk2ID playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(BitConverter.GetBytes(UInt32.MaxValue), 0, 4); // Subchunk2Size byte[] pullBuffer = new byte[2056]; uint lastRead = 0; do { lastRead = activityAudio.Read(pullBuffer); playbackStreamWithHeader.Write(pullBuffer, 0, (int)lastRead); } while (lastRead == pullBuffer.Length); var task = Dispatcher.RunAsync( Windows.UI.Core.CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, () => { mediaElement.SetSource( playbackStreamWithHeader.AsRandomAccessStream(), "audio/wav"); mediaElement.Play(); }); } private void InitializeDialogServiceConnector() { // New code will go here } private async void ListenButton_ButtonClicked( object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) { // New code will go here } } }
将以下代码片段添加到
InitializeDialogServiceConnector的方法主体。 此代码会使用你的订阅信息创建DialogServiceConnector。// Create a BotFrameworkConfig by providing a Speech service subscription key // the botConfig.Language property is optional (default en-US) const string speechSubscriptionKey = "YourSpeechSubscriptionKey"; // Your subscription key const string region = "YourServiceRegion"; // Your subscription service region. var botConfig = BotFrameworkConfig.FromSubscription(speechSubscriptionKey, region); botConfig.Language = "en-US"; connector = new DialogServiceConnector(botConfig);注意
请参阅语音助手支持的区域列表,确保你的资源部署在其中一个区域中。
注意
有关配置机器人的信息,请参阅 Direct Line Speech 通道的 Bot Framework 文档。
将字符串
YourSpeechSubscriptionKey和YourServiceRegion分别替换为自己的语音订阅和区域值。将以下代码片段追加到
InitializeDialogServiceConnector的方法主体的末尾。 此代码为DialogServiceConnector依赖的事件设置处理程序,以传达其机器人活动、语音识别结果和其他信息。// ActivityReceived is the main way your bot will communicate with the client // and uses bot framework activities connector.ActivityReceived += (sender, activityReceivedEventArgs) => { NotifyUser( $"Activity received, hasAudio={activityReceivedEventArgs.HasAudio} activity={activityReceivedEventArgs.Activity}"); if (activityReceivedEventArgs.HasAudio) { SynchronouslyPlayActivityAudio(activityReceivedEventArgs.Audio); } }; // Canceled will be signaled when a turn is aborted or experiences an error condition connector.Canceled += (sender, canceledEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Canceled, reason={canceledEventArgs.Reason}"); if (canceledEventArgs.Reason == CancellationReason.Error) { NotifyUser( $"Error: code={canceledEventArgs.ErrorCode}, details={canceledEventArgs.ErrorDetails}"); } }; // Recognizing (not 'Recognized') will provide the intermediate recognized text // while an audio stream is being processed connector.Recognizing += (sender, recognitionEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Recognizing! in-progress text={recognitionEventArgs.Result.Text}"); }; // Recognized (not 'Recognizing') will provide the final recognized text // once audio capture is completed connector.Recognized += (sender, recognitionEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Final speech to text result: '{recognitionEventArgs.Result.Text}'"); }; // SessionStarted will notify when audio begins flowing to the service for a turn connector.SessionStarted += (sender, sessionEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Now Listening! Session started, id={sessionEventArgs.SessionId}"); }; // SessionStopped will notify when a turn is complete and // it's safe to begin listening again connector.SessionStopped += (sender, sessionEventArgs) => { NotifyUser($"Listening complete. Session ended, id={sessionEventArgs.SessionId}"); };将以下代码片段添加到
MainPage类中ListenButton_ButtonClicked方法的正文。 此代码将DialogServiceConnector设置为侦听,因为已建立配置并注册了事件处理程序。if (connector == null) { InitializeDialogServiceConnector(); // Optional step to speed up first interaction: if not called, // connection happens automatically on first use var connectTask = connector.ConnectAsync(); } try { // Start sending audio to your speech-enabled bot var listenTask = connector.ListenOnceAsync(); // You can also send activities to your bot as JSON strings -- // Microsoft.Bot.Schema can simplify this string speakActivity = @"{""type"":""message"",""text"":""Greeting Message"", ""speak"":""Hello there!""}"; await connector.SendActivityAsync(speakActivity); } catch (Exception ex) { NotifyUser($"Exception: {ex.ToString()}", NotifyType.ErrorMessage); }
生成并运行应用
现在,可以使用语音服务构建应用并测试自定义语音助手。
从菜单栏中,选择“构建”>“构建解决方案”以构建应用程序。 现在,编译代码时应不会提示错误。
选择“调试”>“开始调试”(或按 F5)以启动应用程序。 此时将显示“helloworld”窗口。
选择“启用麦克风”,并在弹出访问权限请求时选择“是”。
选择“对机器人讲话”,然后对着设备的麦克风讲出一个英文短语或句子。 你的语音将传输到 Direct Line Speech 通道并转录为文本,该文本会显示在窗口中。
后续步骤
可以在 GitHub 上查看或下载所有语音 SDK Java 示例。
选择目标环境
先决条件
在开始之前,请务必:
- 创建语音资源
- 设置开发环境并创建空项目
- 创建连接到 Direct Line Speech 通道的机器人
- 请确保你有权访问麦克风,以便进行音频捕获
注意
请参阅语音助手支持的区域列表,确保你的资源部署在其中一个区域中。
创建并配置项目
创建 Eclipse 项目并安装语音 SDK。
此外,若要启用日志记录,请更新 pom.xml 文件以包含以下依赖项:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-simple</artifactId>
<version>1.7.5</version>
</dependency>
添加示例代码
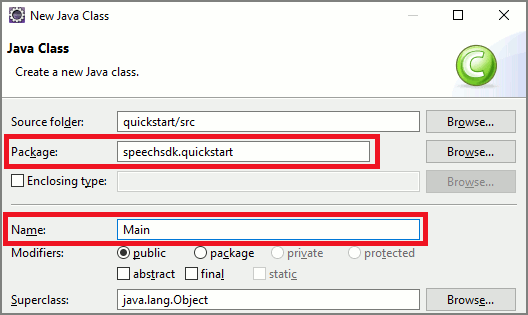
若要向 Java 项目添加新的空类,请选择“文件”>“新建”>“类”。
在“新建 Java 类”窗口中,在“包”字段内输入 speechsdk.quickstart,在“名称”字段内输入 Main。
打开新建的
Main类,将Main.java文件的内容替换为以下起始代码:package speechsdk.quickstart; import com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.audio.AudioConfig; import com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.audio.PullAudioOutputStream; import com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.dialog.BotFrameworkConfig; import com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.dialog.DialogServiceConnector; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import javax.sound.sampled.AudioFormat; import javax.sound.sampled.AudioSystem; import javax.sound.sampled.DataLine; import javax.sound.sampled.SourceDataLine; import java.io.InputStream; public class Main { final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Main.class); public static void main(String[] args) { // New code will go here } private void playAudioStream(PullAudioOutputStream audio) { ActivityAudioStream stream = new ActivityAudioStream(audio); final ActivityAudioStream.ActivityAudioFormat audioFormat = stream.getActivityAudioFormat(); final AudioFormat format = new AudioFormat( AudioFormat.Encoding.PCM_SIGNED, audioFormat.getSamplesPerSecond(), audioFormat.getBitsPerSample(), audioFormat.getChannels(), audioFormat.getFrameSize(), audioFormat.getSamplesPerSecond(), false); try { int bufferSize = format.getFrameSize(); final byte[] data = new byte[bufferSize]; SourceDataLine.Info info = new DataLine.Info(SourceDataLine.class, format); SourceDataLine line = (SourceDataLine) AudioSystem.getLine(info); line.open(format); if (line != null) { line.start(); int nBytesRead = 0; while (nBytesRead != -1) { nBytesRead = stream.read(data); if (nBytesRead != -1) { line.write(data, 0, nBytesRead); } } line.drain(); line.stop(); line.close(); } stream.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }在
main方法中,首先配置DialogServiceConfig并使用它来创建DialogServiceConnector实例。 此实例会连接到 Direct Line Speech 通道以便与机器人交互。AudioConfig实例还用于指定音频输入的源。 在此示例中,对AudioConfig.fromDefaultMicrophoneInput()使用了默认麦克风。注意
请参阅语音助手支持的区域列表,确保你的资源部署在其中一个区域中。
final String subscriptionKey = "YourSubscriptionKey"; // Your subscription key final String region = "YourServiceRegion"; // Your speech subscription service region final BotFrameworkConfig botConfig = BotFrameworkConfig.fromSubscription(subscriptionKey, region); // Configure audio input from a microphone. final AudioConfig audioConfig = AudioConfig.fromDefaultMicrophoneInput(); // Create a DialogServiceConnector instance. final DialogServiceConnector connector = new DialogServiceConnector(botConfig, audioConfig);连接器
DialogServiceConnector依赖于多个事件来传达其机器人活动、语音识别结果和其他信息。 接下来请添加这些事件侦听器。// Recognizing will provide the intermediate recognized text while an audio stream is being processed. connector.recognizing.addEventListener((o, speechRecognitionResultEventArgs) -> { log.info("Recognizing speech event text: {}", speechRecognitionResultEventArgs.getResult().getText()); }); // Recognized will provide the final recognized text once audio capture is completed. connector.recognized.addEventListener((o, speechRecognitionResultEventArgs) -> { log.info("Recognized speech event reason text: {}", speechRecognitionResultEventArgs.getResult().getText()); }); // SessionStarted will notify when audio begins flowing to the service for a turn. connector.sessionStarted.addEventListener((o, sessionEventArgs) -> { log.info("Session Started event id: {} ", sessionEventArgs.getSessionId()); }); // SessionStopped will notify when a turn is complete and it's safe to begin listening again. connector.sessionStopped.addEventListener((o, sessionEventArgs) -> { log.info("Session stopped event id: {}", sessionEventArgs.getSessionId()); }); // Canceled will be signaled when a turn is aborted or experiences an error condition. connector.canceled.addEventListener((o, canceledEventArgs) -> { log.info("Canceled event details: {}", canceledEventArgs.getErrorDetails()); connector.disconnectAsync(); }); // ActivityReceived is the main way your bot will communicate with the client and uses Bot Framework activities. connector.activityReceived.addEventListener((o, activityEventArgs) -> { final String act = activityEventArgs.getActivity().serialize(); log.info("Received activity {} audio", activityEventArgs.hasAudio() ? "with" : "without"); if (activityEventArgs.hasAudio()) { playAudioStream(activityEventArgs.getAudio()); } });调用
connectAsync()方法将DialogServiceConnector连接到 Direct Line Speech。 若要测试机器人,可以调用listenOnceAsync方法以从麦克风发送音频输入。 此外,还可以使用sendActivityAsync方法以序列化字符串的形式发送自定义活动。 这些自定义活动可以提供机器人在聊天中使用的其他数据。connector.connectAsync(); // Start listening. System.out.println("Say something ..."); connector.listenOnceAsync(); // connector.sendActivityAsync(...)保存对
Main文件的更改。为支持响应播放,请添加一个额外的类,该类用于将从 getAudio() API 返回的 PullAudioOutputStream 对象转换为一个 java InputStream 以方便处理。 此
ActivityAudioStream是一个专用类,用于处理来自 Direct Line Speech 通道的音频响应。 它提供访问器来提取处理播放所需的音频格式信息。 为此,请选择“文件”>“新建”>“类”。在“新建 Java 类”窗口中,在“包”字段中输入 speechsdk.quickstart,在“名称”字段中输入 ActivityAudioStream。
打开新建的
ActivityAudioStream类,将其内容替换为以下代码:package com.speechsdk.quickstart; import com.microsoft.cognitiveservices.speech.audio.PullAudioOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; public final class ActivityAudioStream extends InputStream { /** * The number of samples played per second (16 kHz). */ public static final long SAMPLE_RATE = 16000; /** * The number of bits in each sample of a sound that has this format (16 bits). */ public static final int BITS_PER_SECOND = 16; /** * The number of audio channels in this format (1 for mono). */ public static final int CHANNELS = 1; /** * The number of bytes in each frame of a sound that has this format (2). */ public static final int FRAME_SIZE = 2; /** * Reads up to a specified maximum number of bytes of data from the audio * stream, putting them into the given byte array. * * @param b the buffer into which the data is read * @param off the offset, from the beginning of array <code>b</code>, at which * the data will be written * @param len the maximum number of bytes to read * @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or -1 if there * is no more data because the end of the stream has been reached */ @Override public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) { byte[] tempBuffer = new byte[len]; int n = (int) this.pullStreamImpl.read(tempBuffer); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (off + i > b.length) { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(b.length); } b[off + i] = tempBuffer[i]; } if (n == 0) { return -1; } return n; } /** * Reads the next byte of data from the activity audio stream if available. * * @return the next byte of data, or -1 if the end of the stream is reached * @see #read(byte[], int, int) * @see #read(byte[]) * @see #available * <p> */ @Override public int read() { byte[] data = new byte[1]; int temp = read(data); if (temp <= 0) { // we have a weird situation if read(byte[]) returns 0! return -1; } return data[0] & 0xFF; } /** * Reads up to a specified maximum number of bytes of data from the activity audio stream, * putting them into the given byte array. * * @param b the buffer into which the data is read * @return the total number of bytes read into the buffer, or -1 if there * is no more data because the end of the stream has been reached */ @Override public int read(byte[] b) { int n = (int) pullStreamImpl.read(b); if (n == 0) { return -1; } return n; } /** * Skips over and discards a specified number of bytes from this * audio input stream. * * @param n the requested number of bytes to be skipped * @return the actual number of bytes skipped * @throws IOException if an input or output error occurs * @see #read * @see #available */ @Override public long skip(long n) { if (n <= 0) { return 0; } if (n <= Integer.MAX_VALUE) { byte[] tempBuffer = new byte[(int) n]; return read(tempBuffer); } long count = 0; for (long i = n; i > 0; i -= Integer.MAX_VALUE) { int size = (int) Math.min(Integer.MAX_VALUE, i); byte[] tempBuffer = new byte[size]; count += read(tempBuffer); } return count; } /** * Closes this audio input stream and releases any system resources associated * with the stream. */ @Override public void close() { this.pullStreamImpl.close(); } /** * Fetch the audio format for the ActivityAudioStream. The ActivityAudioFormat defines the sample rate, bits per sample, and the # channels. * * @return instance of the ActivityAudioFormat associated with the stream */ public ActivityAudioStream.ActivityAudioFormat getActivityAudioFormat() { return activityAudioFormat; } /** * Returns the maximum number of bytes that can be read (or skipped over) from this * audio input stream without blocking. * * @return the number of bytes that can be read from this audio input stream without blocking. * As this implementation does not buffer, this will be defaulted to 0 */ @Override public int available() { return 0; } public ActivityAudioStream(final PullAudioOutputStream stream) { pullStreamImpl = stream; this.activityAudioFormat = new ActivityAudioStream.ActivityAudioFormat(SAMPLE_RATE, BITS_PER_SECOND, CHANNELS, FRAME_SIZE, AudioEncoding.PCM_SIGNED); } private PullAudioOutputStream pullStreamImpl; private ActivityAudioFormat activityAudioFormat; /** * ActivityAudioFormat is an internal format which contains metadata regarding the type of arrangement of * audio bits in this activity audio stream. */ static class ActivityAudioFormat { private long samplesPerSecond; private int bitsPerSample; private int channels; private int frameSize; private AudioEncoding encoding; public ActivityAudioFormat(long samplesPerSecond, int bitsPerSample, int channels, int frameSize, AudioEncoding encoding) { this.samplesPerSecond = samplesPerSecond; this.bitsPerSample = bitsPerSample; this.channels = channels; this.encoding = encoding; this.frameSize = frameSize; } /** * Fetch the number of samples played per second for the associated audio stream format. * * @return the number of samples played per second */ public long getSamplesPerSecond() { return samplesPerSecond; } /** * Fetch the number of bits in each sample of a sound that has this audio stream format. * * @return the number of bits per sample */ public int getBitsPerSample() { return bitsPerSample; } /** * Fetch the number of audio channels used by this audio stream format. * * @return the number of channels */ public int getChannels() { return channels; } /** * Fetch the default number of bytes in a frame required by this audio stream format. * * @return the number of bytes */ public int getFrameSize() { return frameSize; } /** * Fetch the audio encoding type associated with this audio stream format. * * @return the encoding associated */ public AudioEncoding getEncoding() { return encoding; } } /** * Enum defining the types of audio encoding supported by this stream. */ public enum AudioEncoding { PCM_SIGNED("PCM_SIGNED"); String value; AudioEncoding(String value) { this.value = value; } } }保存对
ActivityAudioStream文件的更改。
生成并运行应用
选择 F11,或选择“运行”>“调试”。
控制台会显示消息“请讲话”。此时,请讲出机器人理解的英语短语或句子。 你的语音将通过 Direct Line Speech 通道传送到机器人,机器人将识别并处理你的语言, 然后返回活动形式的响应。 如果机器人返回了语音作为响应,则会使用 AudioPlayer 类播放音频。
后续步骤
可以在 GitHub 上查看或下载所有语音 SDK Go 示例。
先决条件
准备工作:
- 创建语音资源
- 设置开发环境并创建空项目
- 创建连接到 Direct Line Speech 通道的机器人
- 请确保你有权访问麦克风,以便进行音频捕获
注意
请参阅语音助手支持的区域列表,确保你的资源部署在其中一个区域中。
设置你的环境
通过添加以下行,使用最新的 SDK 版本更新 go.mod 文件
require (
github.com/Microsoft/cognitive-services-speech-sdk-go v1.15.0
)
从一些样本代码入手
将源文件(例如 quickstart.go)的内容替换为以下内容,其中包括:
- “主要”包定义
- 从语音 SDK 导入所需的模块
- 用于存储机器人信息的变量,本快速入门的后面部分会替换该信息
- 使用麦克风进行音频输入的简单实现
- 在语音交互期间发生的各种事件的事件处理程序
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"github.com/Microsoft/cognitive-services-speech-sdk-go/audio"
"github.com/Microsoft/cognitive-services-speech-sdk-go/dialog"
"github.com/Microsoft/cognitive-services-speech-sdk-go/speech"
)
func main() {
subscription := "YOUR_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY"
region := "YOUR_BOT_REGION"
audioConfig, err := audio.NewAudioConfigFromDefaultMicrophoneInput()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Got an error: ", err)
return
}
defer audioConfig.Close()
config, err := dialog.NewBotFrameworkConfigFromSubscription(subscription, region)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Got an error: ", err)
return
}
defer config.Close()
connector, err := dialog.NewDialogServiceConnectorFromConfig(config, audioConfig)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Got an error: ", err)
return
}
defer connector.Close()
activityReceivedHandler := func(event dialog.ActivityReceivedEventArgs) {
defer event.Close()
fmt.Println("Received an activity.")
}
connector.ActivityReceived(activityReceivedHandler)
recognizedHandle := func(event speech.SpeechRecognitionEventArgs) {
defer event.Close()
fmt.Println("Recognized ", event.Result.Text)
}
connector.Recognized(recognizedHandle)
recognizingHandler := func(event speech.SpeechRecognitionEventArgs) {
defer event.Close()
fmt.Println("Recognizing ", event.Result.Text)
}
connector.Recognizing(recognizingHandler)
connector.ListenOnceAsync()
<-time.After(10 * time.Second)
}
用语音资源中的实际值替换 YOUR_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY 值和 YOUR_BOT_REGION 值。
导航到 Azure 门户,然后打开语音资源
在左侧的“密钥和终结点”下,有两个可用的订阅密钥
- 使用其中的任一密钥来替换
YOUR_SUBSCRIPTION_KEY值
- 使用其中的任一密钥来替换
在左侧的“概览”下,记下该区域并将其映射到区域标识符
- 使用区域标识符来替换
YOUR_BOT_REGION值,例如:使用"westus"来替换“美国西部”
注意
请参阅语音助手支持的区域列表,确保你的资源部署在其中一个区域中。
注意
有关配置机器人的信息,请参阅 Direct Line Speech 通道的 Bot Framework 文档。
- 使用区域标识符来替换
代码说明
需要语音订阅密钥和区域才能创建语音配置对象。 实例化语音识别器对象需要配置对象。
识别器实例公开了多种用于识别语音的方法。 在此示例中持续识别语音。 此功能告知语音服务,你要发送许多需识别的短语,并在程序终止时停止识别语音。 生成结果后,代码会将它们写入控制台。
生成并运行
现在,可以使用语音服务生成项目并测试自定义语音助手。
- 生成项目,例如 "go build"
- 运行模块并对着设备的麦克风讲出一个短语或句子。 你的语音将传输到 Direct Line Speech 通道并转录为文本,该文本会显示为输出。
注意
语音 SDK 默认识别 en-us 语言。若要了解如何选择源语言,请参阅如何识别语音。
后续步骤
其他语言和平台支持
如果已单击此选项卡,则可能看不到采用你偏好的编程语言的快速入门。 别担心,我们在 GitHub 上提供了其他快速入门材料和代码示例。 使用表格查找适用于编程语言和平台/OS 组合的相应示例。
| 语言 | 代码示例 |
|---|---|
| C# | .NET Framework、.NET Core、UWP、Unity |
| C++ | Windows、Linux、macOS |
| Java | Android、JRE |
| JavaScript | Browser、Node.js |
| Objective-C | iOS、macOS |
| Python | Windows、Linux 和 macOS |
| Swift | iOS、macOS |