创建业务逻辑层 (C#)
本教程介绍如何将业务规则集中到业务逻辑层 (BLL) 中,该层充当表示层与 DAL 之间的数据交换的中介。
简介
在第一个教程中创建的数据访问层 (DAL) 将数据访问逻辑与表示逻辑完全分开。 但是,尽管 DAL 将数据访问详细信息与表示层完全分离,但它不强制实施任何可能适用的业务规则。 例如,对于我们的应用程序,我们可能希望禁止CategoryID在字段设置为 1 时Discontinued修改表的 Products 或 SupplierID 字段,或者我们可能希望强制执行资历规则,从而禁止员工由继其后雇用的人员管理的情况。 另一种常见方案是,授权可能只有具有特定角色的用户才能删除产品或更改 UnitPrice 值。
本教程介绍如何将这些业务规则集中到业务逻辑层 (BLL) 中,该层充当表示层与 DAL 之间的数据交换的中介。 在实际应用程序中,BLL 应作为单独的类库项目实现;但是,对于这些教程,我们将在文件夹中将 BLL 作为一系列类 App_Code 实现,以简化项目结构。 图 1 说明了表示层、BLL 和 DAL 之间的体系结构关系。
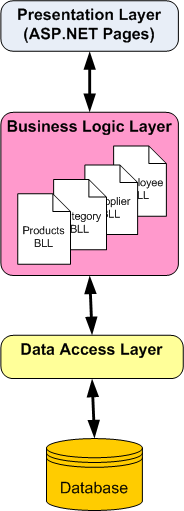
图 1:BLL 将表示层与数据访问层分开并实施业务规则
步骤 1:创建 BLL 类
我们的 BLL 将由四个类组成,DAL 中的每个 TableAdapter 各有一个;其中每个 BLL 类都有用于从 DAL 中相应的 TableAdapter 检索、插入、更新和删除的方法,并应用相应的业务规则。
为了更清晰地分隔与 DAL 和 BLL 相关的类,让我们在 App_Code 文件夹中创建两个子文件夹: DAL 和 BLL。 只需右键单击App_Code解决方案资源管理器中的文件夹,然后选择“新建文件夹”。 创建这两个文件夹后,将第一个教程中创建的类型化数据集移动到 DAL 子文件夹中。
接下来,在 子文件夹中创建四个 BLL BLL 类文件。 为此,请 BLL 右键单击子文件夹,选择“添加新项”,然后选择“类”模板。 将四个类命名为 ProductsBLL、 CategoriesBLL、 SuppliersBLL和 EmployeesBLL。
图 2:向文件夹添加四个新类App_Code
接下来,让我们向每个类添加方法,以包装第一个教程中为 TableAdapters 定义的方法。 目前,这些方法将直接调用 DAL;稍后我们将返回以添加任何所需的业务逻辑。
注意
如果使用的是 Visual Studio Standard Edition 或更高版本 (即不使用 Visual Web Developer) ,则可以选择使用类Designer以可视方式设计类。 有关 Visual Studio 中这项新功能的详细信息,请参阅类Designer博客。
对于 类, ProductsBLL 总共需要添加七种方法:
GetProducts()返回所有产品GetProductByProductID(productID)返回具有指定产品 ID 的产品GetProductsByCategoryID(categoryID)返回指定类别中的所有产品GetProductsBySupplier(supplierID)从指定供应商返回所有产品AddProduct(productName, supplierID, categoryID, quantityPerUnit, unitPrice, unitsInStock, unitsOnOrder, reorderLevel, discontinued)使用传入的值将新产品插入数据库;返回ProductID新插入的记录的值UpdateProduct(productName, supplierID, categoryID, quantityPerUnit, unitPrice, unitsInStock, unitsOnOrder, reorderLevel, discontinued, productID)使用传入值更新数据库中的现有产品;true如果只更新了一行,则返回 ,false否则返回DeleteProduct(productID)从数据库中删除指定的产品
ProductsBLL.cs
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Configuration;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Security;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls.WebParts;
using System.Web.UI.HtmlControls;
using NorthwindTableAdapters;
[System.ComponentModel.DataObject]
public class ProductsBLL
{
private ProductsTableAdapter _productsAdapter = null;
protected ProductsTableAdapter Adapter
{
get {
if (_productsAdapter == null)
_productsAdapter = new ProductsTableAdapter();
return _productsAdapter;
}
}
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Select, true)]
public Northwind.ProductsDataTable GetProducts()
{
return Adapter.GetProducts();
}
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Select, false)]
public Northwind.ProductsDataTable GetProductByProductID(int productID)
{
return Adapter.GetProductByProductID(productID);
}
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Select, false)]
public Northwind.ProductsDataTable GetProductsByCategoryID(int categoryID)
{
return Adapter.GetProductsByCategoryID(categoryID);
}
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Select, false)]
public Northwind.ProductsDataTable GetProductsBySupplierID(int supplierID)
{
return Adapter.GetProductsBySupplierID(supplierID);
}
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Insert, true)]
public bool AddProduct(string productName, int? supplierID, int? categoryID,
string quantityPerUnit, decimal? unitPrice, short? unitsInStock,
short? unitsOnOrder, short? reorderLevel, bool discontinued)
{
// Create a new ProductRow instance
Northwind.ProductsDataTable products = new Northwind.ProductsDataTable();
Northwind.ProductsRow product = products.NewProductsRow();
product.ProductName = productName;
if (supplierID == null) product.SetSupplierIDNull();
else product.SupplierID = supplierID.Value;
if (categoryID == null) product.SetCategoryIDNull();
else product.CategoryID = categoryID.Value;
if (quantityPerUnit == null) product.SetQuantityPerUnitNull();
else product.QuantityPerUnit = quantityPerUnit;
if (unitPrice == null) product.SetUnitPriceNull();
else product.UnitPrice = unitPrice.Value;
if (unitsInStock == null) product.SetUnitsInStockNull();
else product.UnitsInStock = unitsInStock.Value;
if (unitsOnOrder == null) product.SetUnitsOnOrderNull();
else product.UnitsOnOrder = unitsOnOrder.Value;
if (reorderLevel == null) product.SetReorderLevelNull();
else product.ReorderLevel = reorderLevel.Value;
product.Discontinued = discontinued;
// Add the new product
products.AddProductsRow(product);
int rowsAffected = Adapter.Update(products);
// Return true if precisely one row was inserted,
// otherwise false
return rowsAffected == 1;
}
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Update, true)]
public bool UpdateProduct(string productName, int? supplierID, int? categoryID,
string quantityPerUnit, decimal? unitPrice, short? unitsInStock,
short? unitsOnOrder, short? reorderLevel, bool discontinued, int productID)
{
Northwind.ProductsDataTable products = Adapter.GetProductByProductID(productID);
if (products.Count == 0)
// no matching record found, return false
return false;
Northwind.ProductsRow product = products[0];
product.ProductName = productName;
if (supplierID == null) product.SetSupplierIDNull();
else product.SupplierID = supplierID.Value;
if (categoryID == null) product.SetCategoryIDNull();
else product.CategoryID = categoryID.Value;
if (quantityPerUnit == null) product.SetQuantityPerUnitNull();
else product.QuantityPerUnit = quantityPerUnit;
if (unitPrice == null) product.SetUnitPriceNull();
else product.UnitPrice = unitPrice.Value;
if (unitsInStock == null) product.SetUnitsInStockNull();
else product.UnitsInStock = unitsInStock.Value;
if (unitsOnOrder == null) product.SetUnitsOnOrderNull();
else product.UnitsOnOrder = unitsOnOrder.Value;
if (reorderLevel == null) product.SetReorderLevelNull();
else product.ReorderLevel = reorderLevel.Value;
product.Discontinued = discontinued;
// Update the product record
int rowsAffected = Adapter.Update(product);
// Return true if precisely one row was updated,
// otherwise false
return rowsAffected == 1;
}
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Delete, true)]
public bool DeleteProduct(int productID)
{
int rowsAffected = Adapter.Delete(productID);
// Return true if precisely one row was deleted,
// otherwise false
return rowsAffected == 1;
}
}
仅返回数据 GetProducts、 GetProductByProductID、 GetProductsByCategoryID和 GetProductBySuppliersID 的方法非常简单,因为它们只是调用 DAL。 虽然在某些情况下,可能需要在此级别实现业务规则, (例如基于当前登录的用户或用户所属角色) 的授权规则,但我们只是将这些方法保留原样。 对于这些方法,BLL 仅充当代理,表示层通过该代理从数据访问层访问基础数据。
AddProduct和 UpdateProduct 方法都采用各个产品字段的值作为参数,并分别添加新产品或更新现有产品。 由于表的许多 Product 列可以接受 NULL (CategoryID、 SupplierID和 UnitPrice的值(仅举几例) ),因此,映射到此类列的 AddProduct 和 UpdateProduct 的输入参数使用 可以为 null 的类型。 可为 Null 的类型是 .NET 2.0 的新增功能,它提供一种技术来指示值类型是否应 null改为 。 在 C# 中,可以通过在类型 ((如 int? x;) )后面添加 ? ,将值类型标记为可为 null 的类型。 有关详细信息,请参阅 C# 编程指南中的可以为 Null 的类型部分。
这三种方法都返回一个布尔值,该值指示是否插入、更新或删除了行,因为该操作不会导致受影响的行。 例如,如果页面开发人员为不存在的产品调用 DeleteProduct 传入 ProductID 的 ,则 DELETE 向数据库发出的 语句将不起作用,因此该方法 DeleteProduct 将返回 false。
请注意,在添加新产品或更新现有产品时,我们会将新产品或修改的产品的字段值作为标量列表,而不是接受 ProductsRow 实例。 之所以选择此方法, ProductsRow 是因为 类派生自 ADO.NET DataRow 类,该类没有默认的无参数构造函数。 若要创建新 ProductsRow 实例,必须首先创建一个 ProductsDataTable 实例,然后调用其 NewProductRow() 方法 (AddProduct) 。 当我们转向使用 ObjectDataSource 插入和更新产品时,这种缺点会抬头。 简而言之,ObjectDataSource 将尝试创建输入参数的实例。 如果 BLL 方法需要实例 ProductsRow ,ObjectDataSource 将尝试创建一个实例,但由于缺少默认无参数构造函数而失败。 有关此问题的详细信息,请参阅以下两篇 ASP.NET 论坛文章: 使用 Strongly-Typed 数据集更新 ObjectDataSources 和 ObjectDataSource 和 Strongly-Typed DataSet 的问题。
接下来,在 和 UpdateProduct中AddProduct,代码将创建 一个 ProductsRow 实例,并使用刚刚传入的值填充该实例。 向 DataRow 的 DataColumns 分配值时,可能会进行各种字段级验证检查。 因此,手动将传入的值放回 DataRow 有助于确保传递给 BLL 方法的数据的有效性。 遗憾的是,Visual Studio 生成的强类型 DataRow 类不使用可为 null 的类型。 相反,为了指示 DataRow 中的特定 DataColumn 应与 NULL 数据库值相对应,必须使用 SetColumnNameNull() 方法。
在 中 UpdateProduct ,我们首先在产品中加载以使用 GetProductByProductID(productID)进行更新。 虽然这似乎是对数据库的不必要的访问,但在探索乐观并发的未来教程中,此额外行程将被证明是值得的。 乐观并发是一种技术,可确保同时处理相同数据的两个用户不会意外覆盖彼此的更改。 抓取整个记录还可以更轻松地在 BLL 中创建仅修改 DataRow 列子集的更新方法。 当我们浏览 类时, SuppliersBLL 我们将看到这样一个示例。
最后,请注意, ProductsBLL 类应用了 DataObject 属性 , [System.ComponentModel.DataObject] (位于靠近文件顶部的类语句的语法) 并且方法具有 DataObjectMethodAttribute 属性。 特性 DataObject 将类标记为适合绑定到 ObjectDataSource 控件的对象,而 DataObjectMethodAttribute 指示方法的用途。 正如我们在以后的教程中看到的,ASP.NET 2.0 的 ObjectDataSource 使从类以声明方式访问数据变得容易。 为了帮助筛选要绑定到 ObjectDataSource 向导中的可能类的列表,默认情况下,向导的下拉列表中仅显示标记为 DataObjects 的类。 在没有这些属性的情况下, ProductsBLL 类同样工作,但添加它们可以更轻松地在 ObjectDataSource 的向导中使用。
添加其他类
类 ProductsBLL 完成后,我们仍需要添加类,以便处理类别、供应商和员工。 请花点时间使用上述示例中的概念创建以下类和方法:
CategoriesBLL.cs
GetCategories()GetCategoryByCategoryID(categoryID)
SuppliersBLL.cs
GetSuppliers()GetSupplierBySupplierID(supplierID)GetSuppliersByCountry(country)UpdateSupplierAddress(supplierID, address, city, country)
EmployeesBLL.cs
GetEmployees()GetEmployeeByEmployeeID(employeeID)GetEmployeesByManager(managerID)
需要注意的一种方法是 SuppliersBLL 类的 UpdateSupplierAddress 方法。 此方法提供一个接口,用于仅更新供应商的地址信息。 在内部,此方法使用 GetSupplierBySupplierID) 读取SupplierDataRow指定 supplierID (的 对象,设置其与地址相关的属性,然后向下调用 的 SupplierDataTableUpdate 方法。 方法 UpdateSupplierAddress 如下:
[System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodAttribute
(System.ComponentModel.DataObjectMethodType.Update, true)]
public bool UpdateSupplierAddress
(int supplierID, string address, string city, string country)
{
Northwind.SuppliersDataTable suppliers =
Adapter.GetSupplierBySupplierID(supplierID);
if (suppliers.Count == 0)
// no matching record found, return false
return false;
else
{
Northwind.SuppliersRow supplier = suppliers[0];
if (address == null) supplier.SetAddressNull();
else supplier.Address = address;
if (city == null) supplier.SetCityNull();
else supplier.City = city;
if (country == null) supplier.SetCountryNull();
else supplier.Country = country;
// Update the supplier Address-related information
int rowsAffected = Adapter.Update(supplier);
// Return true if precisely one row was updated,
// otherwise false
return rowsAffected == 1;
}
}
有关 BLL 类的完整实现,请参阅本文的下载。
步骤 2:通过 BLL 类访问类型化数据集
在第一个教程中,我们看到了以编程方式直接使用类型化数据集的示例,但添加 BLL 类后,表示层应改为针对 BLL 工作。 在第 AllProducts.aspx 一个教程的示例中, ProductsTableAdapter 用于将产品列表绑定到 GridView,如以下代码所示:
ProductsTableAdapter productsAdapter = new ProductsTableAdapter();
GridView1.DataSource = productsAdapter.GetProducts();
GridView1.DataBind();
若要使用新的 BLL 类,只需将 第一行代码替换为 ProductsTableAdapter 对象 ProductBLL 即可:
ProductsBLL productLogic = new ProductsBLL();
GridView1.DataSource = productLogic.GetProducts();
GridView1.DataBind();
还可以以声明方式访问 BLL 类, (类型化数据集也可以使用 ObjectDataSource) 。 我们将在以下教程中更详细地讨论 ObjectDataSource。
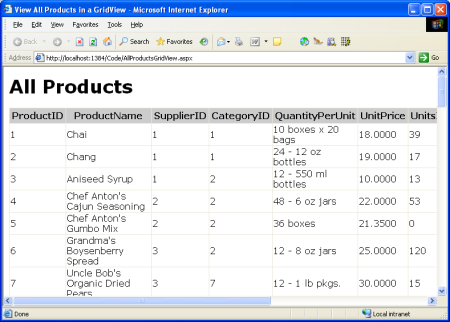
图 3:产品列表显示在 GridView 中 (单击以查看全尺寸图像)
步骤 3:向 DataRow 类添加 Field-Level 验证
字段级验证是插入或更新时与业务对象的属性值相关的检查。 产品的一些字段级验证规则包括:
- 该
ProductName字段的长度必须为 40 个字符或更少 - 该
QuantityPerUnit字段的长度必须为 20 个字符或更少 ProductID、ProductName和Discontinued字段是必需的,但所有其他字段都是可选的UnitPrice、UnitsInStock、UnitsOnOrder和ReorderLevel字段必须大于或等于零
这些规则可以而且应该在数据库级别表示。 和 字段的ProductName字符限制分别由表中这些列Products的数据类型捕获 (nvarchar(40) 和 nvarchar(20)) 。QuantityPerUnit 如果数据库表列允许 NULL ,则字段是否为必填字段和可选字段的表示方式。 存在四个检查约束,这些约束确保只有大于或等于零的值才能将其转换为 UnitPrice、UnitsInStock、 UnitsOnOrder或 ReorderLevel 列。
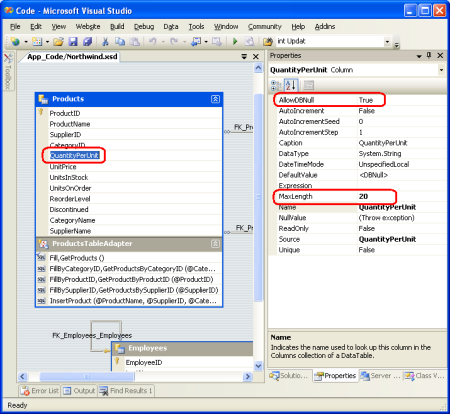
除了在数据库中强制实施这些规则外,还应在数据集级别强制执行这些规则。 事实上,已为每个 DataTable 的 DataColumns 集捕获字段长度以及值是必需值还是可选值。 若要查看自动提供的现有字段级验证,请转到 DataSet Designer,从其中一个数据表中选择一个字段,然后转到属性窗口。 如图 4 所示, 中的 QuantityPerUnitProductsDataTable DataColumn 的最大长度为 20 个字符,并且允许 NULL 值。 如果尝试将 ProductsDataRow的 QuantityPerUnit 属性设置为长度超过 20 个字符 ArgumentException 的字符串值,则会引发 。
图 4:DataColumn 提供基本 Field-Level 验证 (单击以查看全尺寸图像)
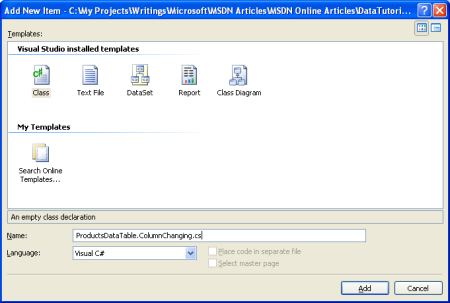
遗憾的是,无法通过属性窗口指定边界检查,例如UnitPrice值必须大于或等于零。 为了提供这种类型的字段级验证,我们需要为 DataTable 的 ColumnChanging 事件创建事件处理程序。 如 前一教程中所述,可以通过使用分部类扩展由类型化数据集创建的 DataSet、DataTables 和 DataRow 对象。 使用此技术,我们可以为 ProductsDataTable 类创建ColumnChanging事件处理程序。 首先在 App_Code 名为 ProductsDataTable.ColumnChanging.cs的文件夹中创建类。
图 5:向文件夹添加新类 App_Code (单击以查看全尺寸图像)
接下来,为 ColumnChanging 事件创建事件处理程序,确保 UnitsOnOrderReorderLevelUnitPriceUnitsInStock (NULL) 列值大于或等于零。 如果任何此类列在范围外,则 ArgumentException引发 。
ProductsDataTable.ColumnChanging.cs
public partial class Northwind
{
public partial class ProductsDataTable
{
public override void BeginInit()
{
this.ColumnChanging += ValidateColumn;
}
void ValidateColumn(object sender,
DataColumnChangeEventArgs e)
{
if(e.Column.Equals(this.UnitPriceColumn))
{
if(!Convert.IsDBNull(e.ProposedValue) &&
(decimal)e.ProposedValue < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentException(
"UnitPrice cannot be less than zero", "UnitPrice");
}
}
else if (e.Column.Equals(this.UnitsInStockColumn) ||
e.Column.Equals(this.UnitsOnOrderColumn) ||
e.Column.Equals(this.ReorderLevelColumn))
{
if (!Convert.IsDBNull(e.ProposedValue) &&
(short)e.ProposedValue < 0)
{
throw new ArgumentException(string.Format(
"{0} cannot be less than zero", e.Column.ColumnName),
e.Column.ColumnName);
}
}
}
}
}
步骤 4:将自定义业务规则添加到 BLL 的类
除了字段级验证之外,还可能存在涉及不同实体或概念的高级自定义业务规则,这些实体或概念无法在单列级别表达,例如:
- 如果产品已停产,
UnitPrice则无法更新 - 员工的居住国家/地区必须与经理的居住国相同
- 如果某个产品是供应商提供的唯一产品,则不能将其停产
BLL 类应包含检查,以确保遵守应用程序的业务规则。 这些检查可以直接添加到它们所应用的方法中。
假设我们的业务规则规定,如果某个产品是给定供应商提供的唯一产品,则不能将其标记为已停产。 也就是说,如果产品 X 是我们从供应商 Y 处购买的唯一产品,则我们无法将 X 标记为已停产;但是,如果供应商 Y 向我们提供了三种产品 A、 B 和 C,那么我们可以将所有这些产品标记为已停产。 一个奇怪的业务规则,但业务规则和常识并不总是一致的!
为了在 方法中 UpdateProducts 强制执行此业务规则,我们首先检查 是否 Discontinued 设置为 true ,如果是,我们将调用 GetProductsBySupplierID 以确定从此产品的供应商购买的产品数量。 如果只从此供应商购买了一个 ApplicationException产品,则会引发 。
public bool UpdateProduct(string productName, int? supplierID, int? categoryID,
string quantityPerUnit, decimal? unitPrice, short? unitsInStock,
short? unitsOnOrder, short? reorderLevel, bool discontinued, int productID)
{
Northwind.ProductsDataTable products = Adapter.GetProductByProductID(productID);
if (products.Count == 0)
// no matching record found, return false
return false;
Northwind.ProductsRow product = products[0];
// Business rule check - cannot discontinue
// a product that is supplied by only
// one supplier
if (discontinued)
{
// Get the products we buy from this supplier
Northwind.ProductsDataTable productsBySupplier =
Adapter.GetProductsBySupplierID(product.SupplierID);
if (productsBySupplier.Count == 1)
// this is the only product we buy from this supplier
throw new ApplicationException(
"You cannot mark a product as discontinued if it is the only
product purchased from a supplier");
}
product.ProductName = productName;
if (supplierID == null) product.SetSupplierIDNull();
else product.SupplierID = supplierID.Value;
if (categoryID == null) product.SetCategoryIDNull();
else product.CategoryID = categoryID.Value;
if (quantityPerUnit == null) product.SetQuantityPerUnitNull();
else product.QuantityPerUnit = quantityPerUnit;
if (unitPrice == null) product.SetUnitPriceNull();
else product.UnitPrice = unitPrice.Value;
if (unitsInStock == null) product.SetUnitsInStockNull();
else product.UnitsInStock = unitsInStock.Value;
if (unitsOnOrder == null) product.SetUnitsOnOrderNull();
else product.UnitsOnOrder = unitsOnOrder.Value;
if (reorderLevel == null) product.SetReorderLevelNull();
else product.ReorderLevel = reorderLevel.Value;
product.Discontinued = discontinued;
// Update the product record
int rowsAffected = Adapter.Update(product);
// Return true if precisely one row was updated,
// otherwise false
return rowsAffected == 1;
}
响应演示层中的验证错误
从表示层调用 BLL 时,我们可以决定是尝试处理可能引发的任何异常,还是让它们冒泡到 ASP.NET (这会引发 HttpApplication的事件 Error) 。 若要在以编程方式使用 BLL 时处理异常,可以使用 尝试...catch 块,如以下示例所示:
ProductsBLL productLogic = new ProductsBLL();
// Update information for ProductID 1
try
{
// This will fail since we are attempting to use a
// UnitPrice value less than 0.
productLogic.UpdateProduct(
"Scott s Tea", 1, 1, null, -14m, 10, null, null, false, 1);
}
catch (ArgumentException ae)
{
Response.Write("There was a problem: " + ae.Message);
}
正如我们在以后的教程中看到的,在使用数据 Web 控件插入、更新或删除数据时,处理从 BLL 冒升的异常可以直接在事件处理程序中进行处理,而不必在块中 try...catch 包装代码。
总结
架构良好的应用程序设计成不同的层,每个层封装一个特定角色。 在本系列文章的第一个教程中,我们使用类型化数据集创建了数据访问层;在本教程中,我们在应用程序的 App_Code 文件夹中构建了一个业务逻辑层作为一系列类,这些类调用了 DAL。 BLL 为应用程序实现字段级和业务级逻辑。 除了创建单独的 BLL 之外,如在本教程中所做的那样,另一种选择是通过使用分部类扩展 TableAdapters 的方法。 但是,使用此方法不允许我们替代现有方法,也不能像本文中采用的方法那样干净地分离 DAL 和 BLL。
完成 DAL 和 BLL 后,我们就可以开始演示层了。 在下一教程中,我们将简要介绍数据访问主题,并定义一致的页面布局以在整个教程中使用。
编程愉快!
关于作者
Scott Mitchell 是七本 ASP/ASP.NET 书籍的作者, 4GuysFromRolla.com 的创始人,自 1998 年以来一直从事 Microsoft Web 技术工作。 Scott 担任独立顾问、培训师和作家。 他的最新书是 山姆斯在24小时内 ASP.NET 2.0自学。 可以在 上联系 mitchell@4GuysFromRolla.com他, 也可以通过他的博客联系到他,该博客可在 http://ScottOnWriting.NET中找到。
特别感谢
本教程系列由许多有用的审阅者查看。 本教程的主要审阅者是 Liz Shulok、Dennis Patterson、Carlos Santos 和 Hilton Giesenow。 有兴趣查看我即将发布的 MSDN 文章? 如果是,请在 处放置一行 mitchell@4GuysFromRolla.com。