在 ASP.NET Web API 中发送 HTML 表单数据:表单 url 编码的数据
第 1 部分:表单 urlencoded 数据
本文介绍如何将表单 url 编码的数据发布到 Web API 控制器。
注意
HTML 表单概述
HTML 表单使用 GET 或 POST 将数据发送到服务器。 form 元素的 method 属性提供 HTTP 方法:
<form action="api/values" method="post">
默认方法是 GET。 如果表单使用 GET,则会在 URI 中将表单数据编码为查询字符串。 如果表单使用 POST,则表单数据将放置在请求正文中。 对于 POSTed 数据, enctype 属性指定请求正文的格式:
| enctype | 说明 |
|---|---|
| application/x-www-form-urlencoded | 表单数据编码为名称/值对,类似于 URI 查询字符串。 这是 POST 的默认格式。 |
| multipart/form-data | 表单数据编码为多部分 MIME 消息。 如果要将文件上传到服务器,请使用此格式。 |
本文的第 1 部分介绍 x-www-form-urlencoded 格式。 第 2 部分 介绍多部分 MIME。
发送复杂类型
通常,将发送一个复杂类型,该类型由从多个窗体控件获取的值组成。 请考虑以下表示状态更新的模型:
namespace FormEncode.Models
{
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
public class Update
{
[Required]
[MaxLength(140)]
public string Status { get; set; }
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
}
}
下面是通过 POST 接受 Update 对象的 Web API 控制器。
namespace FormEncode.Controllers
{
using FormEncode.Models;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Http;
public class UpdatesController : ApiController
{
static readonly Dictionary<Guid, Update> updates = new Dictionary<Guid, Update>();
[HttpPost]
[ActionName("Complex")]
public HttpResponseMessage PostComplex(Update update)
{
if (ModelState.IsValid && update != null)
{
// Convert any HTML markup in the status text.
update.Status = HttpUtility.HtmlEncode(update.Status);
// Assign a new ID.
var id = Guid.NewGuid();
updates[id] = update;
// Create a 201 response.
var response = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Created)
{
Content = new StringContent(update.Status)
};
response.Headers.Location =
new Uri(Url.Link("DefaultApi", new { action = "status", id = id }));
return response;
}
else
{
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
}
[HttpGet]
public Update Status(Guid id)
{
Update update;
if (updates.TryGetValue(id, out update))
{
return update;
}
else
{
throw new HttpResponseException(HttpStatusCode.NotFound);
}
}
}
}
注意
此控制器使用 基于操作的路由,因此路由模板为“api/{controller}/{action}/{id}”。 客户端会将数据发布到“/api/updates/complex”。
现在,让我们编写一个 HTML 表单,供用户提交状态更新。
<h1>Complex Type</h1>
<form id="form1" method="post" action="api/updates/complex"
enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded">
<div>
<label for="status">Status</label>
</div>
<div>
<input name="status" type="text" />
</div>
<div>
<label for="date">Date</label>
</div>
<div>
<input name="date" type="text" />
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</div>
</form>
请注意,窗体上的 操作 属性是控制器操作的 URI。 下面是在 中输入了一些值的窗体:
当用户单击“提交”时,浏览器会发送类似于以下内容的 HTTP 请求:
POST http://localhost:38899/api/updates/complex HTTP/1.1
Accept: text/html, application/xhtml+xml, */*
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; WOW64; Trident/5.0)
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 47
status=Shopping+at+the+mall.&date=6%2F15%2F2012
请注意,请求正文包含格式为名称/值对的表单数据。 Web API 会自动将名称/值对转换为 类的 Update 实例。
通过 AJAX 发送表单数据
当用户提交表单时,浏览器会离开当前页并呈现响应消息的正文。 当响应为 HTML 页面时,这没关系。 但是,使用 Web API 时,响应正文通常为空或包含结构化数据,例如 JSON。 在这种情况下,使用 AJAX 请求发送表单数据更有意义,以便页面可以处理响应。
以下代码演示如何使用 jQuery 发布表单数据。
<script type="text/javascript">
$("#form1").submit(function () {
var jqxhr = $.post('api/updates/complex', $('#form1').serialize())
.success(function () {
var loc = jqxhr.getResponseHeader('Location');
var a = $('<a/>', { href: loc, text: loc });
$('#message').html(a);
})
.error(function () {
$('#message').html("Error posting the update.");
});
return false;
});
</script>
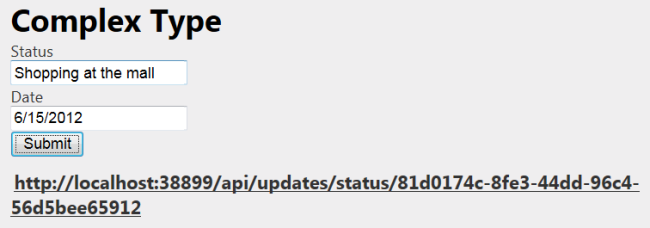
jQuery submit 函数将表单操作替换为新函数。 这会替代“提交”按钮的默认行为。 serialize 函数将表单数据序列化为名称/值对。 若要将表单数据发送到服务器,请调用 $.post()。
请求完成后, .success() 或 .error() 处理程序向用户显示相应的消息。
发送简单类型
在前面的部分中,我们发送了一个复杂类型,该类型 Web API 反序列化为模型类的实例。 还可以发送简单类型,例如字符串。
注意
在发送简单类型之前,请考虑改为将值包装在复杂类型中。 这为你提供了服务器端模型验证的优势,并在需要时更轻松地扩展模型。
发送简单类型的基本步骤是相同的,但有两个细微的差异。 首先,在控制器中,必须使用 FromBody 属性修饰参数名称。
[HttpPost]
[ActionName("Simple")]
public HttpResponseMessage PostSimple([FromBody] string value)
{
if (value != null)
{
Update update = new Update()
{
Status = HttpUtility.HtmlEncode(value),
Date = DateTime.UtcNow
};
var id = Guid.NewGuid();
updates[id] = update;
var response = new HttpResponseMessage(HttpStatusCode.Created)
{
Content = new StringContent(update.Status)
};
response.Headers.Location =
new Uri(Url.Link("DefaultApi", new { action = "status", id = id }));
return response;
}
else
{
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.BadRequest);
}
默认情况下,Web API 会尝试从请求 URI 获取简单类型。 FromBody 属性告知 Web API 从请求正文中读取值。
注意
Web API 最多读取一次响应正文,因此一个操作的一个参数只能来自请求正文。 如果需要从请求正文获取多个值,请定义一个复杂类型。
其次,客户端需要使用以下格式发送值:
=value
具体而言,对于简单类型,名称/值对的名称部分必须为空。 并非所有浏览器都支持 HTML 表单的此格式,但可以在脚本中创建此格式,如下所示:
$.post('api/updates/simple', { "": $('#status1').val() });
下面是一个示例窗体:
<h1>Simple Type</h1>
<form id="form2">
<div>
<label for="status">Status</label>
</div>
<div>
<input id="status1" type="text" />
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</div>
</form>
下面是用于提交表单值的脚本。 与上一个脚本的唯一区别是传递到 post 函数的参数。
$('#form2').submit(function () {
var jqxhr = $.post('api/updates/simple', { "": $('#status1').val() })
.success(function () {
var loc = jqxhr.getResponseHeader('Location');
var a = $('<a/>', { href: loc, text: loc });
$('#message').html(a);
})
.error(function () {
$('#message').html("Error posting the update.");
});
return false;
});
可以使用同一方法发送简单类型的数组:
$.post('api/updates/postlist', { "": ["update one", "update two", "update three"] });