RDP not working for my cloud service
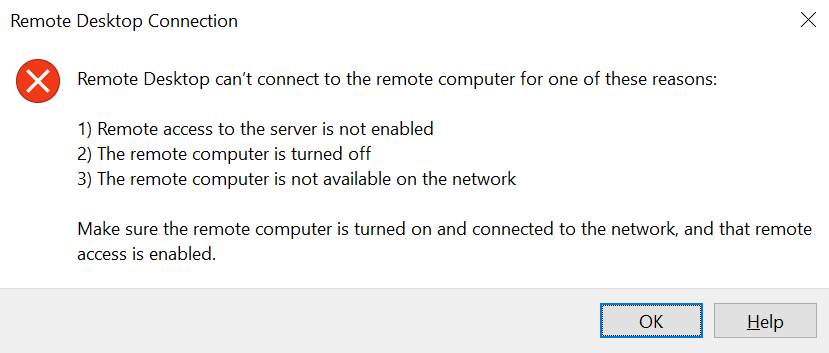
Today I am going to discuss one of the most common scenario faced by the Azure customers who are using classic cloud service resource - RDP not working throwing the below error !!
Sometimes you will not be able to download the RDP file itself and will get this error - "Failed to download the file. Error details: error 400 Bad Request".
You may get the above errors for multiple reasons:
- RDP user account or Encryption certificate got expired.
- TCP Port 3389 for RDP is blocked.
- RDP extension got disabled.
Sometimes while troubleshooting the RDP issues with my customers I have found that resetting the RDP user account expiration date or renewing the encryption certificate doesn't work. In those cases I always follow the below steps which resolves all the RDP issues with 100% certainty. ;-)
- Create a self-signed certificate in .pfx format.
- Upload the self-signed certificate in cloud service certificate store from the Azure Portal.
- Delete all the existing RDP extensions if present.
- Re-enable Remote Desktop for the roles by using the self-signed certificate which you created in the step 1.
I have automated all the above four steps using a PowerShell script so that it makes our life much easier. :-) .... Run the below PowerShell script in admin or elevated mode, however please make sure you have Azure PowerShell Service Management module installed in your system before running it.
$SubscriptionId = "your-subscription-id" # Subscription Id
$CloudServiceName = "mycloudservice" # Cloud Service name
$CertPassword = "CertPassword" # Password for the self-signed certificate
$CertExportFilePath = "C:\my-cert-file.pfx" # Local file path where self-signed certificate will be exported
$RdpUserName = "RemoteUserName" # RDP user name
$RdpUserPassw0rd = "RdpPassword" # RDP user password
$Slot = "Production" # Cloud Service slot
$RdpAccountExpiry = $(Get-Date).AddDays(365) # RDP user account expiration DateTime
# Creating self-signed certificate
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Creating self-signed certificate." -ForegroundColor Magenta
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName ($CloudServiceName + ".cloudapp.net") -CertStoreLocation "cert:\LocalMachine\My" -KeyLength 2048 -KeySpec "KeyExchange"
$SecureCertPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String $CertPassword -Force -AsPlainText
Export-PfxCertificate -Cert $cert -FilePath $CertExportFilePath -Password $SecureCertPassword
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Self-signed certificate created successfully at" $CertExportFilePath -ForegroundColor Magenta
# Login to your Azure account
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Logging into your Azure account." -ForegroundColor Magenta
Add-AzureAccount
Select-AzureSubscription -SubscriptionId $SubscriptionId
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Logged in successfully." -ForegroundColor Magenta
# Uploading self-signed certificate to the cloud service certificate store
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Uploading self-signed certificate to the cloud service certificate store." -ForegroundColor Magenta
Add-AzureCertificate -serviceName $CloudServiceName -certToDeploy $CertExportFilePath –password $CertPassword
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Self-signed certificate uploaded successfully." -ForegroundColor Magenta
# Delete all the existing RDP extensions for a given cloud service slot
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Deleting all the existing RDP extensions for" $Slot "slot." -ForegroundColor Magenta
Remove-AzureServiceRemoteDesktopExtension -ServiceName $CloudServiceName -UninstallConfiguration -Slot $Slot
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Successfully deleted all the existing RDP extensions for" $Slot "slot." -ForegroundColor Magenta
# Enabling remote desktop extension on specified role(s) or all roles on a cloud service slot
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Enabling remote desktop extension on all the roles." -ForegroundColor Magenta
$SecureRdpPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String $RdpUserPassw0rd -Force -AsPlainText
$Credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential $RdpUserName,$SecureRdpPassword
Set-AzureServiceRemoteDesktopExtension -ServiceName $CloudServiceName -Credential $Credential -CertificateThumbprint $cert.Thumbprint -Expiration $RdpAccountExpiry -Slot $Slot
Write-Host (Get-Date).ToString() " : Remote desktop extension applied successfully." -ForegroundColor Magenta
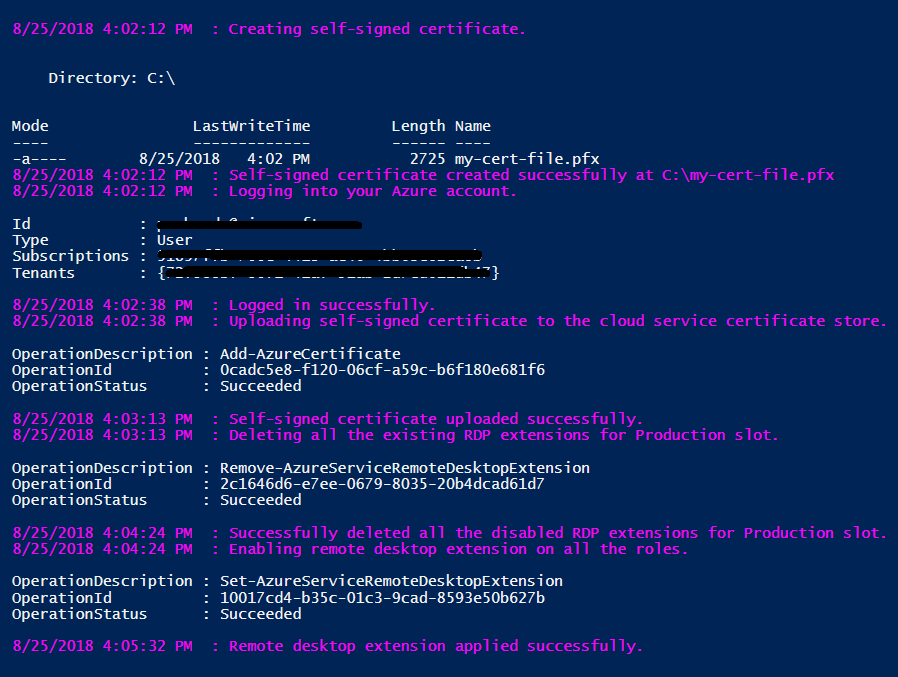
Output of the script will be something like below:
Even after running the above script if you are not able to RDP, then definitely it's a networking issue. Few possible reasons:
- May be the network from where you are trying to RDP is blocking the traffic.
- There could be some ACL rules configured in your cloud service.
- Firewall rules configured using startup tasks.
- If your cloud service is sitting behind an NSG, you may need to create rules that allow traffic on ports 3389 and 20000. The RemoteForwarder and RemoteAccess agents require that port 20000* is open, which may be blocked if you have an NSG.
Most of time I have seen that customer's corporate network blocks the RDP traffic due to security reasons. So the first thing you should check if you are able to reach to RDP ports 3389 and 20000 (if applicable as mentioned above) using PsPing or PortQry or Telnet. You can refer my blog where I have discussed how to troubleshoot RDP issues using various tools like PsPing and Network monitor. If you are not getting any response, try to RDP from a different network, may be home network or mobile hotspot, etc.
I hope you this blog will help you resolve all the RDP issues related to Azure Cloud Service.
Happy Learning !