Run R and Python Remotely in SQL Server from Jupyter Notebooks or any IDE
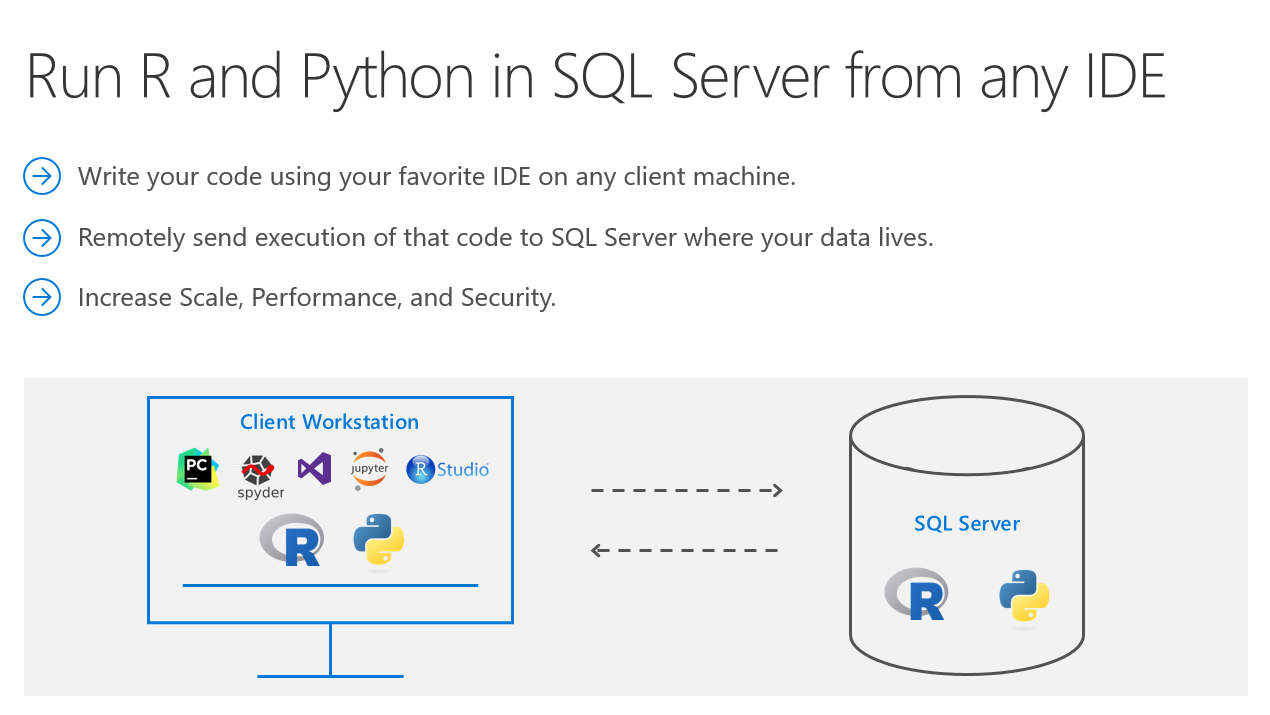
Did you know that you can execute R and Python code remotely in SQL Server from any IDE? This eliminates the need to move data around. Instead of transferring large and sensitive data over the network or losing accuracy with sample csv files, you can have your R/Python code execute within your database. You can work in Jupyter Notebooks, RStudio, PyCharm, VSCode, Visual Studio, wherever you want, and then send function execution to SQL Server bringing intelligence to where your data lives.
This tutorial will show you an example of how you can send your python code from Juptyter notebooks to execute within SQL Server. The same principles apply to R and any other IDE as well. If you prefer to learn through videos, this tutorial is also published on YouTube here:
Environment Setup
In order for R or Python to execute within SQL, you need the Machine Learning Services feature installed and configured. See this how-to guide: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/mlserver/2018/05/18/getting-started-with-machine-learning-services-in-sql-server/
In order to send Python execution to SQL, you need to use Microsoft's RevoscalePy package.
- To get revoscalepy, download and install Microsoft's Python Client. Documentation Page or Direct Download Link (for Windows).
- After downloading, open powershell as an administrator and navigate to the download folder.
- Start the installation with this command (feel free to customize the install folder):
- .\Install-PyForMLS.ps1 -InstallFolder "C:\Program Files\MicrosoftPythonClient"
- Be patient while the installation can take a little while. Once installed navigate to the new path you installed in.
- Let's make an empty folder and open Jupyter Notebooks:
- mkdir JupyterNotebooks; cd JupyterNotebooks; ..\Scripts\jupyter-notebook
- Create a new notebook with Python 3 interpreter:
- To test if everything is setup, import revoscalepy in the first cell and execute.
- If there are no error messages you are ready to move forward.
Database Setup
For the rest of the tutorial you can also clone this Jupyter Notebook if you don't want to copy paste all of the code: https://aka.ms/RemoteExecJupyter
This database setup is a one time step to ensure you have the same data for this tutorial. You won't need to perform any of these steps to use your own data.
1. Create a database
Modify the connection string for your server and use pyodbc to create a new database.
import pyodbc # creating a new db to load Iris sample in new_db_name = "MLRemoteExec" connection_string = "Driver=SQL Server;Server=localhost\MSSQLSERVER2017;Database={0};Trusted_Connection=Yes;" # you can also swap Trusted_Connection for UID={your username};PWD={your password} cnxn = pyodbc.connect(connection_string.format("master"), autocommit=True) cnxn.cursor().execute("IF EXISTS(SELECT * FROM sys.databases WHERE [name] = '{0}') DROP DATABASE {0}".format(new_db_name)) cnxn.cursor().execute("CREATE DATABASE " + new_db_name) cnxn.close() print("Database created")
2. Import Iris sample from SkLearn
from sklearn import datasets import pandas as pd # SkLearn has the Iris sample dataset built in to the package iris = datasets.load_iris() df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
3. Use RecoscalePy APIs to create a table and load the Iris data
(You can also do this with pyodbc, sqlalchemy or other packages)
from revoscalepy import RxSqlServerData, rx_data_step # Example of using RX APIs to load data into SQL table. You can also do this with pyodbc table_ref = RxSqlServerData(connection_string=connection_string.format(new_db_name), table="Iris") rx_data_step(input_data = df, output_file = table_ref, overwrite = True) print("New Table Created: Iris") print("Sklearn Iris sample loaded into Iris table")
Define Function to Send to SQL Server
Write any python code you want to execute in SQL. In this example we are creating a scatter matrix on the iris dataset and only returning the bytestream of the .png back to Jupyter Notebooks to render on our client.
def send_this_func_to_sql(): from revoscalepy import RxSqlServerData, rx_import from pandas.tools.plotting import scatter_matrix import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import io # remember the scope of the variables in this func are within our SQL Server Python Runtime connection_string = "Driver=SQL Server;Server=localhost\MSSQLSERVER2017;Database=MLRemoteExec;Trusted_Connection=Yes;" # specify a query and load into pandas dataframe df sql_query = RxSqlServerData(connection_string=connection_string, sql_query = "select * from Iris") df = rx_import(sql_query) scatter_matrix(df) # return bytestream of image created by scatter_matrix buf = io.BytesIO() plt.savefig(buf, format="png") buf.seek(0) return buf.getvalue()
Send execution to SQL
Now that we are set up, check out how easy this really is. Import revoscalepy, Create a sql compute context, and then send the execution of any function seamlessly to SQL Server with RxExec. No raw data had to be transferred from SQL to the Jupyter Notebook. All computation happened within the database and only the image file was returned to be displayed.
from IPython import display import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from revoscalepy import RxInSqlServer, rx_exec # create a remote compute context with connection to SQL Server sql_compute_context = RxInSqlServer(connection_string=connection_string.format(new_db_name)) # use rx_exec to send the function execution to SQL Server image = rx_exec(send_this_func_to_sql, compute_context=sql_compute_context)[0] # only an image was returned to my jupyter client. All data remained secure and was manipulated in my db. display.Image(data=image)
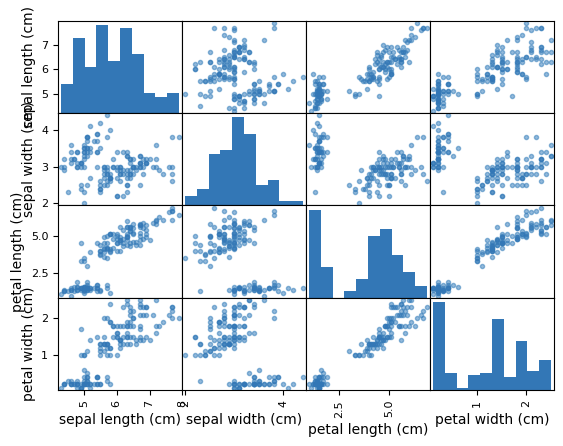
While this example is trivial with the Iris dataset, imagine the capabilities that you have now unlocked. You can use any of the latest open source R/Python packages to build Deep Learning and AI applications on large amounts of data in SQL Server. We also offer leading edge, high-performance algorithms in Microsoft's RevoScaleR and RevoScalePy APIs. Using these with the latest innovations in the open source world allows you to bring unparalleled selection, performance, and scale to your applications.
Learn More
Check out SQL Machine Learning Services Documentation to learn how you can also easily deploy your R/Python code with SQL stored procedures making them accessible in your ETL processes or to any application. Train and store machine learning models in your database bringing intelligence to where your data lives.
Basic R and Python Execution in SQL Server: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/mlserver/2018/05/24/basics-of-r-and-python-execution-in-sql-server/
Set up Machine Learning Services in SQL Server: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/mlserver/2018/05/18/getting-started-with-machine-learning-services-in-sql-server/
End-to-end tutorial solutions on Github: https://microsoft.github.io/sql-ml-tutorials/
Other YouTube Tutorials:
- How to Install SQL Server Machine Learning Services: https://aka.ms/InstallMLServices
- How to Enable SQL Server Machine Learning Services: https://aka.ms/EnableMLServices
- Basics of R and Python Execution in SQL: https://aka.ms/ExecuteMLServices