Treemap and sunburst charts in a paginated report in SQL Server Reporting Services (Report Builder)
Applies to:
Microsoft Report Builder (SSRS)
Power BI Report Builder
Report Designer in SQL Server Data Tools
The SQL Server Report Builder treemap and sunburst visualizations are great for visually representing hierarchical data in a paginated report. This article is an overview of how to add a treemap or sunburst chart to a report. The article also includes an AdventureWorks sample query to help you get started.
Treemap chart
A treemap chart divides the chart area into rectangles that represent the different levels and relative sizes of the data hierarchy. The map is similar to branches on a tree that start with a trunk and divide into smaller and smaller branches. Each rectangle is broken into smaller rectangles that represent the next level in the hierarchy. The top-level treemap rectangles are arranged with the largest rectangle in the upper left corner of the chart to the smallest rectangle in the lower right corner. Within a rectangle, the next level of the higher is also arranged with rectangles from the upper left to the lower right.
For example, in the following image of the sample treemap, the Southwest territory is the largest and Germany is the smallest. Within the Southwest, Road Bikes are larger than Mountain Bikes.
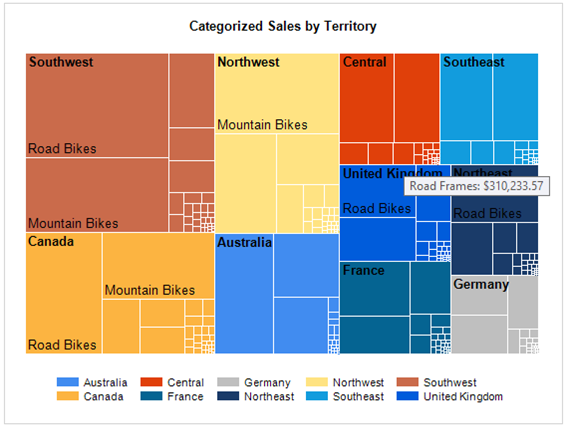
To insert a treemap chart and set up the sample AdventureWorks data
Note
Before you add a chart to your report, create a data source and dataset. For sample data and a sample query, see Sample AdventureWorks data.
Right-click the design surface, then select Insert > Chart. Select the Treemap icon.

Reposition and resize the chart. To use with the sample data, a chart that is 5 inches wide is a good start.
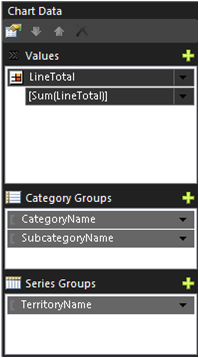
Add the following fields from the sample data:
- Values: LineTotal
- Category Groups (in the following order):
- CategoryName
- SubcategoryName
- Series Groups: TerritoryName
To optimize the page size for the general shape of a treemap, set the legend position to the bottom.
To add tooltips that display the subcategory and the line total, right-click LineTotal, and then select Series Properties.
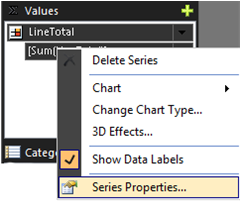
Set the Tooltip property to the following value:
=Fields!SubcategoryName.Value &": " &Format(Sum(Fields!LineTotal.Value),"C")For more information, see Show ToolTips on a series (Report Builder and SSRS).
Change the default chart title to Categorized Sales by Territory.
The number of label values that are displayed are affected by the size of the font, the size of the overall chart area, and the size of specific rectangles. To see more labels, change the Label Font property of LineTotal to 10pt from the default of 8pt.
Sunburst chart
In a sunburst chart, the hierarchy is represented by a series of circles. The highest level of the hierarchy is in the center, and lower levels of the hierarchy are rings displayed outside the center. The lowest level of the hierarchy is the outside ring.
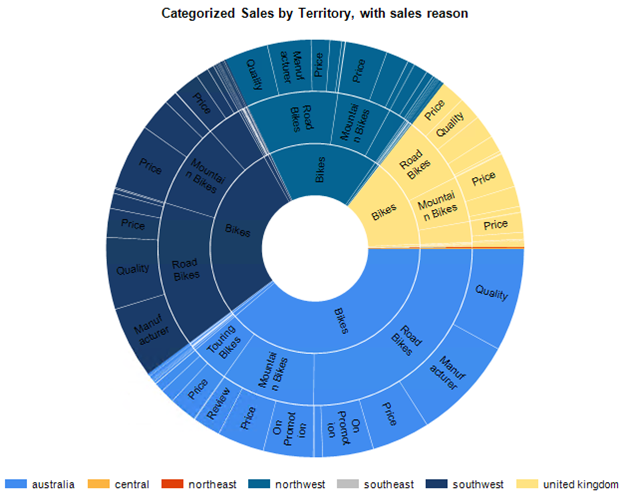
To insert a sunburst chart and set up the sample AdventureWorks data
Note
Before you add a chart to your report, create a data source and dataset. For sample data and a sample query, see Sample AdventureWorks data.
Right-click the design surface, and then select Insert > Chart. Select the Sunburst icon.

Reposition and resize the chart. To use with the sample data, a chart that is 5 inches wide is a good start.
Add the following fields from the sample data:
- Values: LineTotal
- Category Groups (in the following order):
- CategoryName
- SubcategoryName
- SalesReasonName
- Series Groups: TerritoryName

To optimize the page size for the general shape of a sunburst chart, set the legend position to the bottom.
Change the default chart title to Categorized Sales by Territory, with sales reason.
To add the values of the category groups to the sunburst as labels, set the label properties Visible=true and UseValueAsLabel=false.
The label values that are displayed are affected by the size of the font, the size of the overall chart area, and the size of specific rectangles. To see more labels, change the Label Font property of LineTotal to 10pt from the default of 8pt.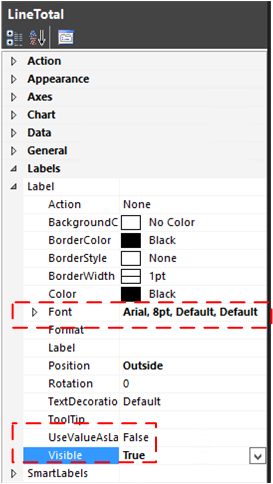
If you want a different range of colors, change the chart Palette property.
Sample AdventureWorks data
This section includes a sample query and the basic steps for creating a data source and dataset in Report Builder. If your report already contains a data source and dataset, you can skip this section.
The query returns AdventureWorks sales order detail data with sales territory, product category, product subcategory, and sales reason data.
Get the data.
The code samples in this article use the
AdventureWorks2022orAdventureWorksDW2022sample database, which you can download from the Microsoft SQL Server Samples and Community Projects home page.Create a data source.
Under Report Data, right-click Data Sources, and then select Add data source.
Select Use a connection embedded in my report.
For connection type, select Microsoft SQL Server.
Enter the connection string to your server and database. For example:
Data Source=[server name];Initial Catalog=AdventureWorks2022To verify the connection, select the Test Connection button, and then select OK.
For more information about creating a data source, see Add and verify a data connection (Report Builder and SSRS).
Create a dataset.
Under Report Data, right-click Datasets, and then select Add dataset.
Select Use a dataset embedded in my report.
Select the data source that you created.
Select the Text query type, and then copy and paste the following query into the Query text box:
SELECT Sales.SalesOrderHeader.SalesOrderID, Sales.SalesOrderHeader.OrderDate, Sales.SalesOrderDetail.SalesOrderDetailID, Sales.SalesOrderDetail.ProductID, Sales.SalesOrderDetail.LineTotal, Sales.SalesOrderDetail.UnitPrice, Sales.SalesOrderDetail.OrderQty, Production.Product.Name, Production.Product.ProductNumber, Sales.SalesTerritory.TerritoryID, lower(Sales.SalesTerritory.Name) AS TerritoryName, Production.ProductSubcategory.Name AS SubcategoryName, Production.ProductCategory.Name AS CategoryName, Sales.SalesReason.SalesReasonID, Sales.SalesReason.Name AS SalesReasonName FROM Sales.SalesOrderDetail INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderHeader ON Sales.SalesOrderDetail.SalesOrderID = Sales.SalesOrderHeader.SalesOrderID INNER JOIN Production.Product ON Sales.SalesOrderDetail.ProductID = Production.Product.ProductID INNER JOIN Sales.SalesTerritory ON Sales.SalesOrderHeader.TerritoryID = Sales.SalesTerritory.TerritoryID AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.TerritoryID = Sales.SalesTerritory.TerritoryID AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.TerritoryID = Sales.SalesTerritory.TerritoryID INNER JOIN Production.ProductSubcategory ON Production.Product.ProductSubcategoryID = Production.ProductSubcategory.ProductSubcategoryID AND Production.Product.ProductSubcategoryID = Production.ProductSubcategory.ProductSubcategoryID AND Production.Product.ProductSubcategoryID = Production.ProductSubcategory.ProductSubcategoryID INNER JOIN Production.ProductCategory ON Production.ProductSubcategory.ProductCategoryID = Production.ProductCategory.ProductCategoryID AND Production.ProductSubcategory.ProductCategoryID = Production.ProductCategory.ProductCategoryID AND Production.ProductSubcategory.ProductCategoryID = Production.ProductCategory.ProductCategoryID INNER JOIN Sales.SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason ON Sales.SalesOrderHeader.SalesOrderID = Sales.SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason.SalesOrderID AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.SalesOrderID = Sales.SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason.SalesOrderID AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.SalesOrderID = Sales.SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason.SalesOrderID AND Sales.SalesOrderHeader.SalesOrderID = Sales.SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason.SalesOrderID INNER JOIN Sales.SalesReason ON Sales.SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason.SalesReasonID = Sales.SalesReason.SalesReasonID AND Sales.SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason.SalesReasonID = Sales.SalesReason.SalesReasonID AND Sales.SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason.SalesReasonID = Sales.SalesReason.SalesReasonID AND Sales.SalesOrderHeaderSalesReason.SalesReasonID = Sales.SalesReason.SalesReasonIDSelect OK.
For more information about creating a dataset, see Create a shared dataset or embedded dataset (Report Builder and SSRS).