Xamarin.Android Web View
WebView
allows you to create your own window for viewing web pages (or even
develop a complete browser). In this tutorial, you'll create a simple
Activity
that can view and navigate web pages.
Create a new project named HelloWebView.
Open Resources/Layout/Main.axml and insert the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<WebView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/webview"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
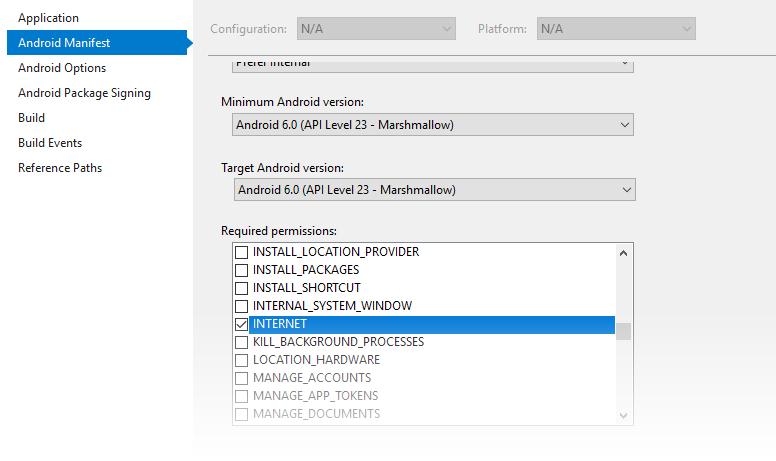
Because this application will access the Internet, you must add the
appropriate permissions to the Android manifest file. Open your
project's properties to specify which permissions your application
requires to operate. Enable the INTERNET permission as shown
below:
Now open MainActivity.cs and add a using directive for Webkit:
using Android.Webkit;
At the top of the MainActivity class, declare a
WebView object:
WebView web_view;
When the WebView is asked to load a URL, it will by default
delegate the request to the default browser. To have the WebView
load the URL (rather than the default browser), you must subclass
Android.Webkit.WebViewClient and override the
ShouldOverriderUrlLoading method. An instance of this custom
WebViewClient is provided to the WebView. To do this, add the
following nested HelloWebViewClient class inside MainActivity:
public class HelloWebViewClient : WebViewClient
{
public override bool ShouldOverrideUrlLoading (WebView view, string url)
{
view.LoadUrl(url);
return false;
}
}
When ShouldOverrideUrlLoading returns false, it signals to Android
that the current WebView instance handled the request and that no
further action is necessary.
If you are targeting API level 24 or later, use the overload of
ShouldOverrideUrlLoading that takes an IWebResourceRequest for
the second argument instead of a string:
public class HelloWebViewClient : WebViewClient
{
// For API level 24 and later
public override bool ShouldOverrideUrlLoading (WebView view, IWebResourceRequest request)
{
view.LoadUrl(request.Url.ToString());
return false;
}
}
Next, use the following code for the
OnCreate())
method:
protected override void OnCreate (Bundle bundle)
{
base.OnCreate (bundle);
// Set our view from the "main" layout resource
SetContentView (Resource.Layout.Main);
web_view = FindViewById<WebView> (Resource.Id.webview);
web_view.Settings.JavaScriptEnabled = true;
web_view.SetWebViewClient(new HelloWebViewClient());
web_view.LoadUrl ("https://www.xamarin.com/university");
}
This initializes the member
WebView with the one from
the
Activity layout and enables
JavaScript for the
WebView with
JavaScriptEnabled
= true (see the
Call C# from JavaScript
recipe for information about how to call C# functions from
JavaScript). Finally, an initial web page is loaded with
LoadUrl(String).
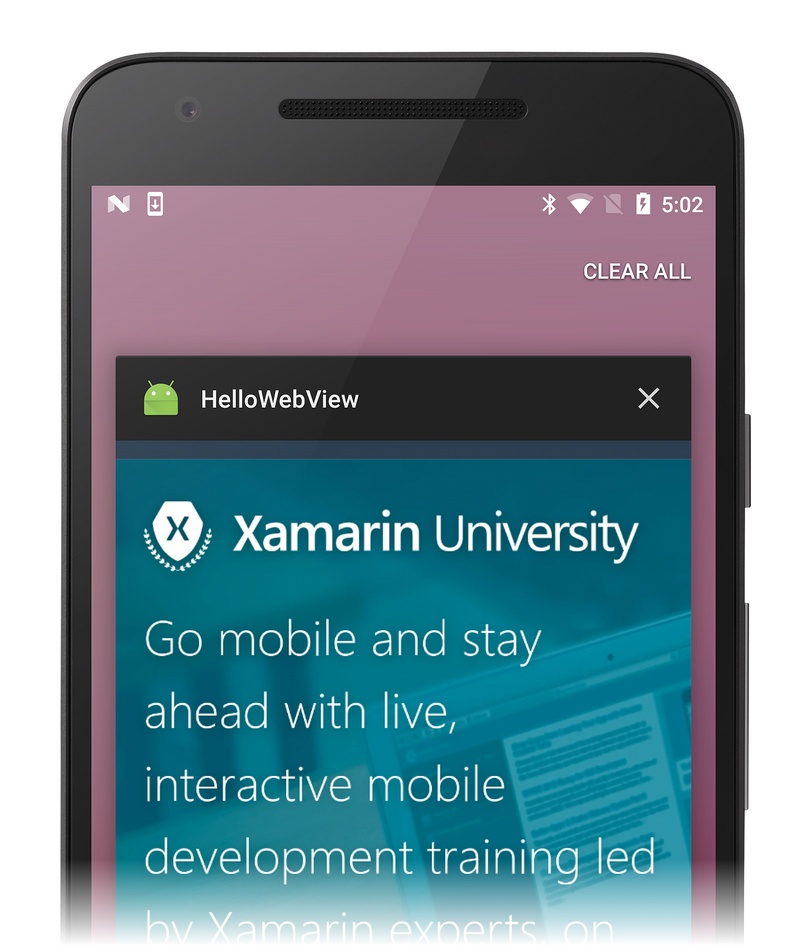
Build and run the app. You should see a simple web page viewer app as the one seen in the following screenshot:
To handle the BACK button key press, add the following using statement:
using Android.Views;
Next, add the following method inside the HelloWebView Activity:
public override bool OnKeyDown (Android.Views.Keycode keyCode, Android.Views.KeyEvent e)
{
if (keyCode == Keycode.Back && web_view.CanGoBack ())
{
web_view.GoBack ();
return true;
}
return base.OnKeyDown (keyCode, e);
}
This
OnKeyDown(int, KeyEvent)
callback method will be called whenever a button is pressed while
the Activity is running. The condition inside uses the
KeyEvent to check whether
the key pressed is the BACK button and whether the
WebView is actually capable
of navigating back (if it has a history). If both are true, then
the
GoBack() method is
called, which will navigate back one step in the
WebView history. Returning
true indicates that the event has been handled. If this condition
is not met, then the event is sent back to the system.
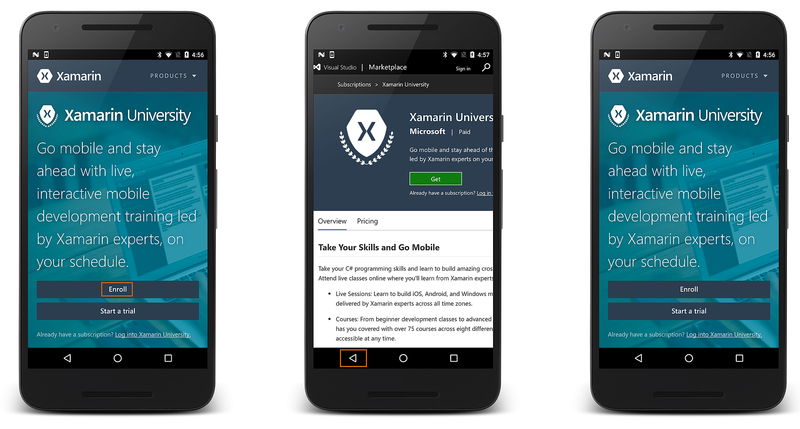
Run the application again. You should now be able to follow links and navigate back through the page history:
Portions of this page are modifications based on work created and shared by the Android Open Source Project and used according to terms described in the Creative Commons 2.5 Attribution License.